Micro-wet treatment process for foundry waste sand
A technology for casting waste sand and wet treatment, which is applied to the cleaning/processing machinery, manufacturing tools, casting molding equipment, etc. of casting mold materials, and can solve the problems of high acid consumption of regenerated sand, cracks on the surface of regenerated sand, mixed mold There are few issues such as research on the regeneration technology of foundry waste sand, so as to achieve the effect of improving utilization rate and high regeneration efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
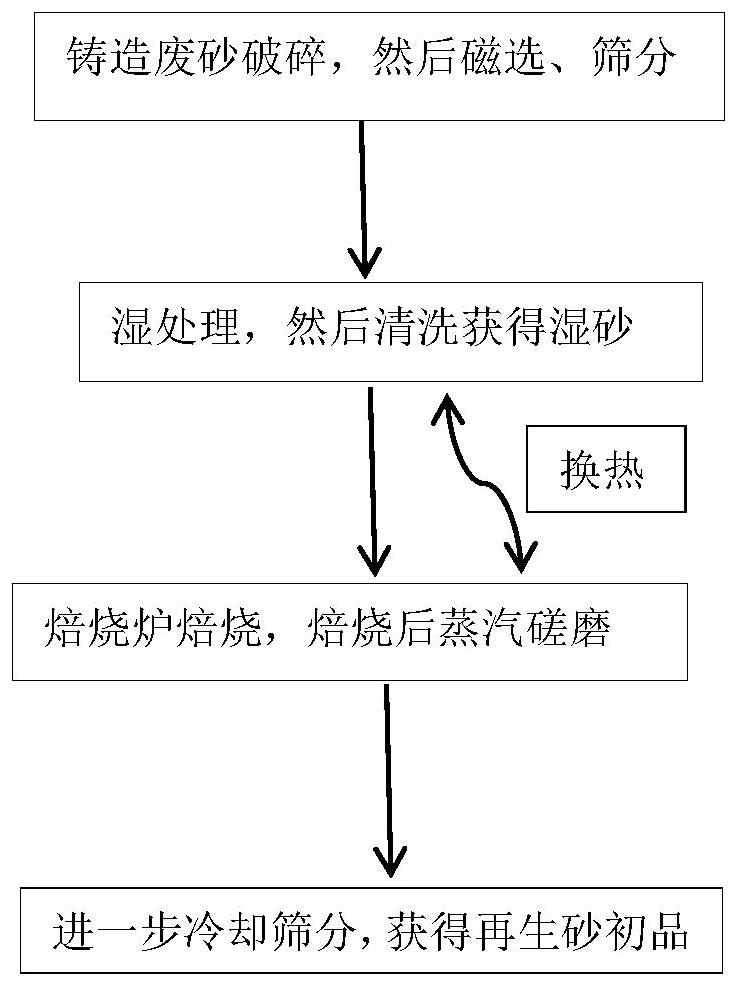
[0064] A micro-wet treatment process for foundry waste sand, comprising the following steps:
[0065] S1. Crushing the foundry waste sand, then magnetic separation and screening;
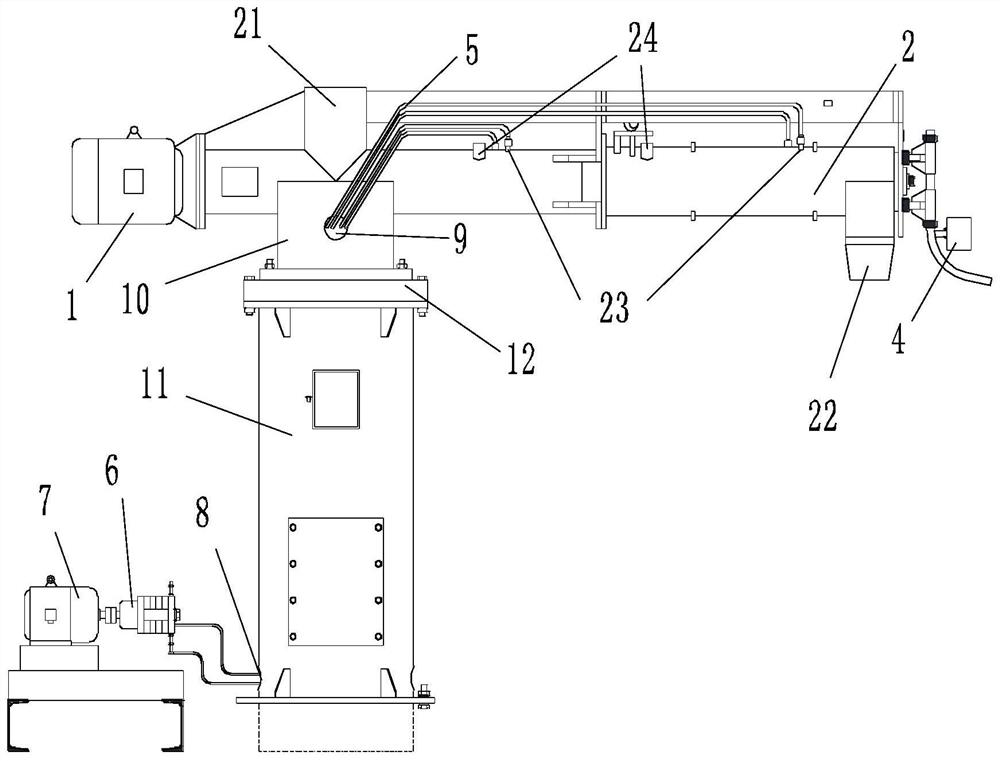
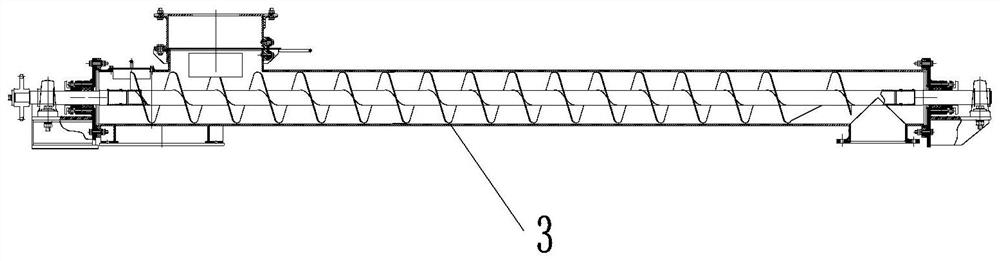
[0066] S2. Wet treatment is carried out on the screened waste sand by a swing-arm mixer, and the solution adopted in the wet treatment is a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and 10% sulfuric acid, and the mass ratio of hydrofluoric acid and 10% sulfuric acid is 2: 1; Then wash to obtain wet sand, and dry the wet sand after heat exchange;
[0067] S3. enter the roasting furnace for roasting, the roasting temperature is 800 ℃, and the time is 20min; after the roasting is finished, enter the heat exchange grinding equipment for steam grinding, and exchange heat with the wet sand in S2 at the same time;
[0068] S4. Cooling and screening the waste sand after heat exchange to obtain the first product of regenerated sand.
Embodiment 2
[0070] A micro-wet treatment process for foundry waste sand, comprising the following steps:
[0071] S1. Crushing the foundry waste sand, then magnetic separation and screening;
[0072] S2. Wet treatment is carried out on the screened waste sand by a swing-arm mixer, and the solution adopted in the wet treatment is a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and 10% sulfuric acid, and the mass ratio of hydrofluoric acid and 10% sulfuric acid is 1: 1; Then wash to obtain wet sand, and dry the wet sand after heat exchange;
[0073] S3. enter the roasting furnace for roasting, the roasting temperature is 900 ℃, and the time is 10min; after the roasting is finished, enter the heat exchange grinding equipment for steam grinding, and simultaneously exchange heat with the wet sand in S2;
[0074] S4. Cooling and screening the waste sand after heat exchange to obtain the first product of regenerated sand.
Embodiment 3
[0076] A micro-wet treatment process for foundry waste sand, comprising the following steps:
[0077] S1. Crushing the foundry waste sand, then magnetic separation and screening;
[0078] S2. Wet treatment is carried out on the screened waste sand by a swing-arm mixer, and the solution adopted in the wet treatment is a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and 10% sulfuric acid, and the mass ratio of hydrofluoric acid and 10% sulfuric acid is 1: 2; Then wash to obtain wet sand, and the wet sand is dried after heat exchange;
[0079] S3. enter the roasting furnace for roasting, the roasting temperature is 850 ℃, and the time is 15min; after the roasting is finished, enter the heat exchange grinding equipment for steam grinding, and simultaneously exchange heat with the wet sand in S2;
[0080] S4. Cooling and screening the waste sand after heat exchange to obtain the first product of regenerated sand.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com