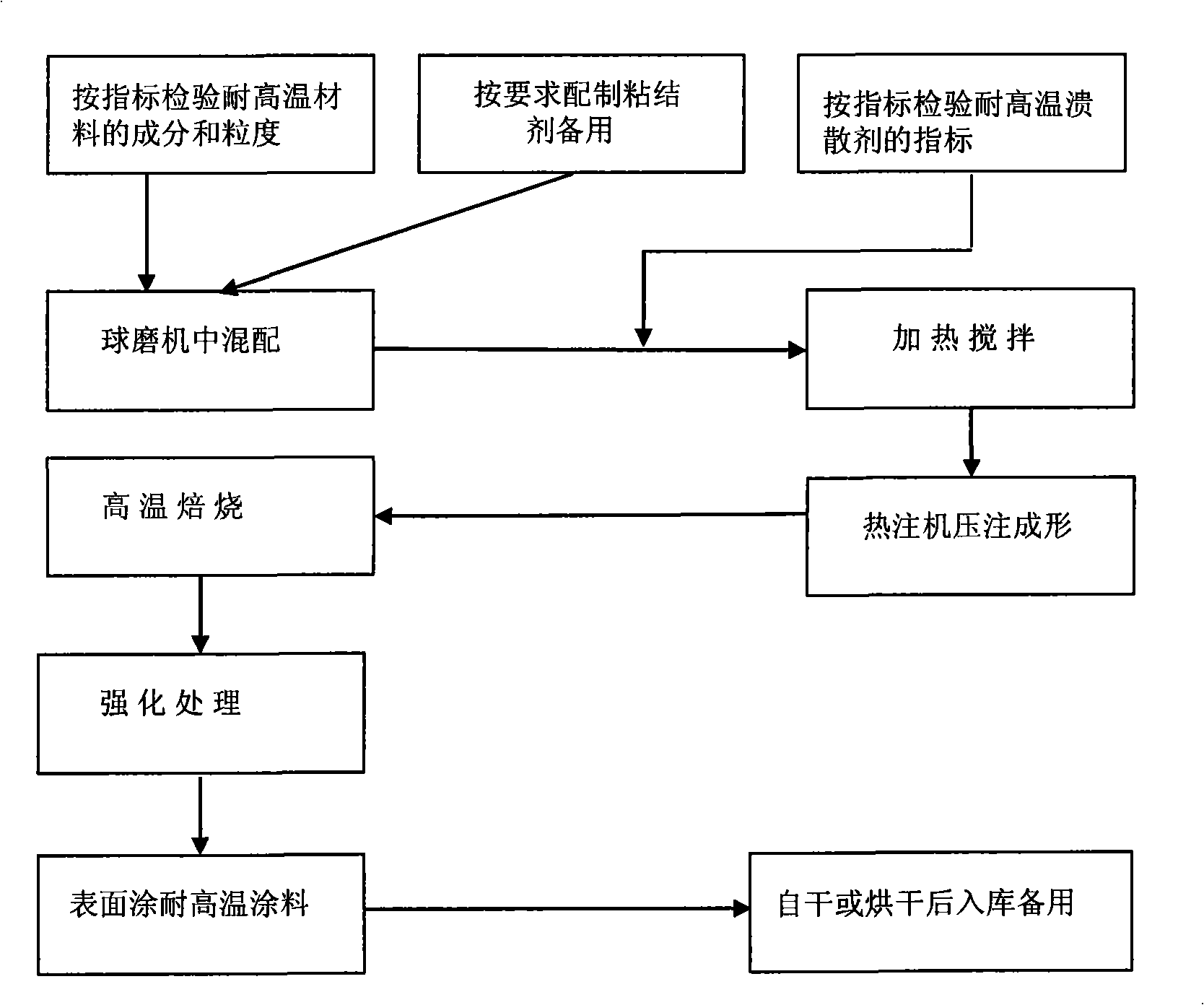
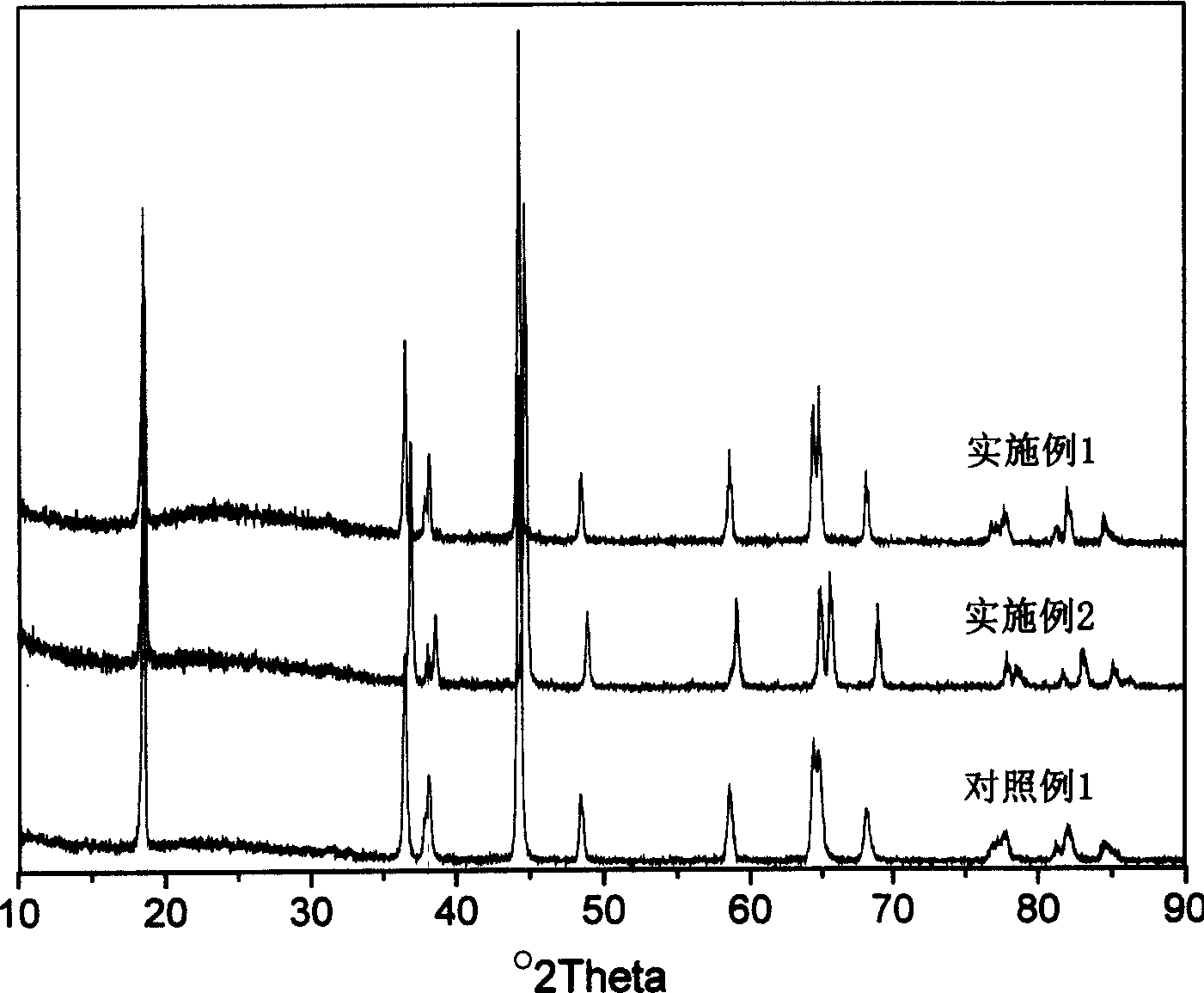
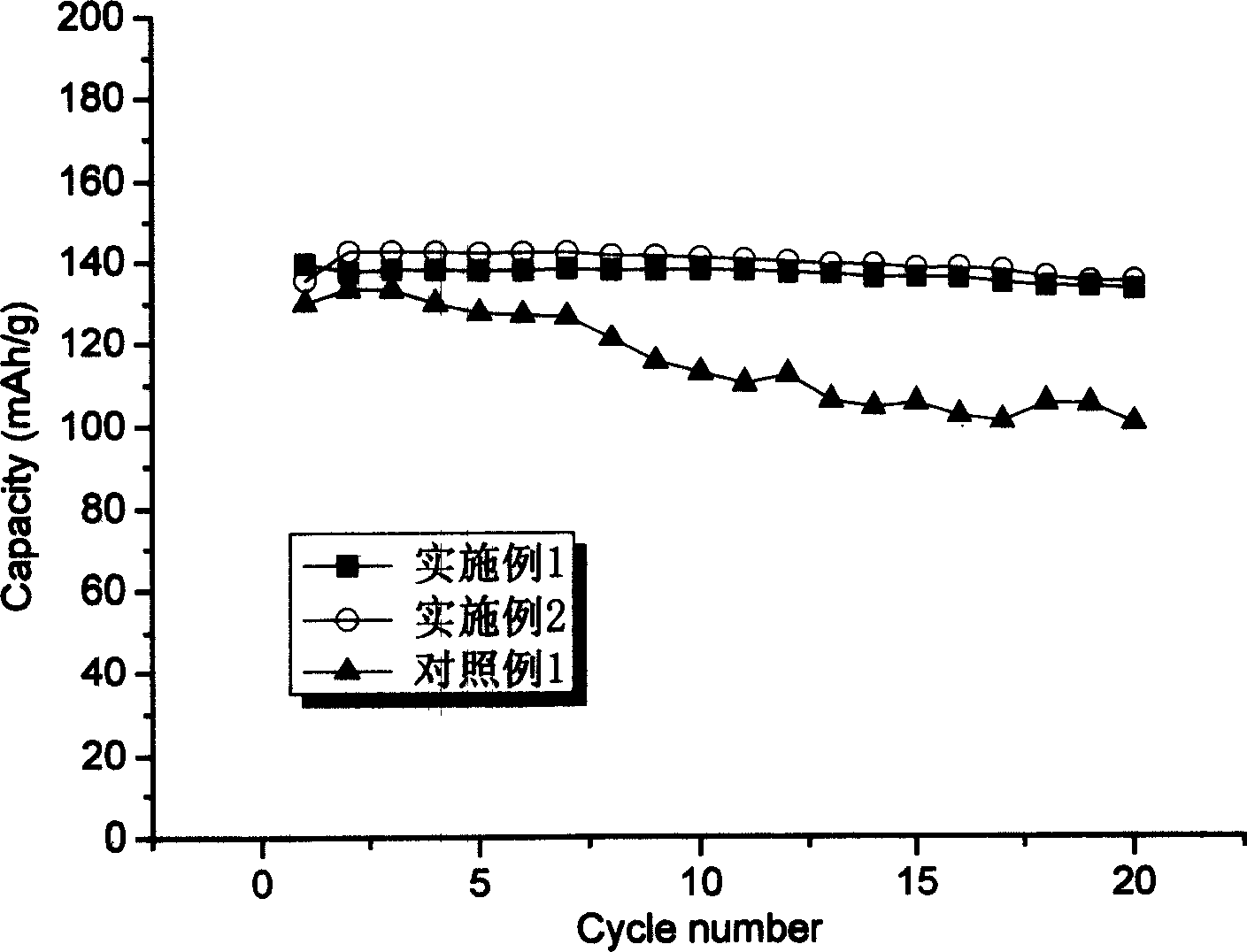
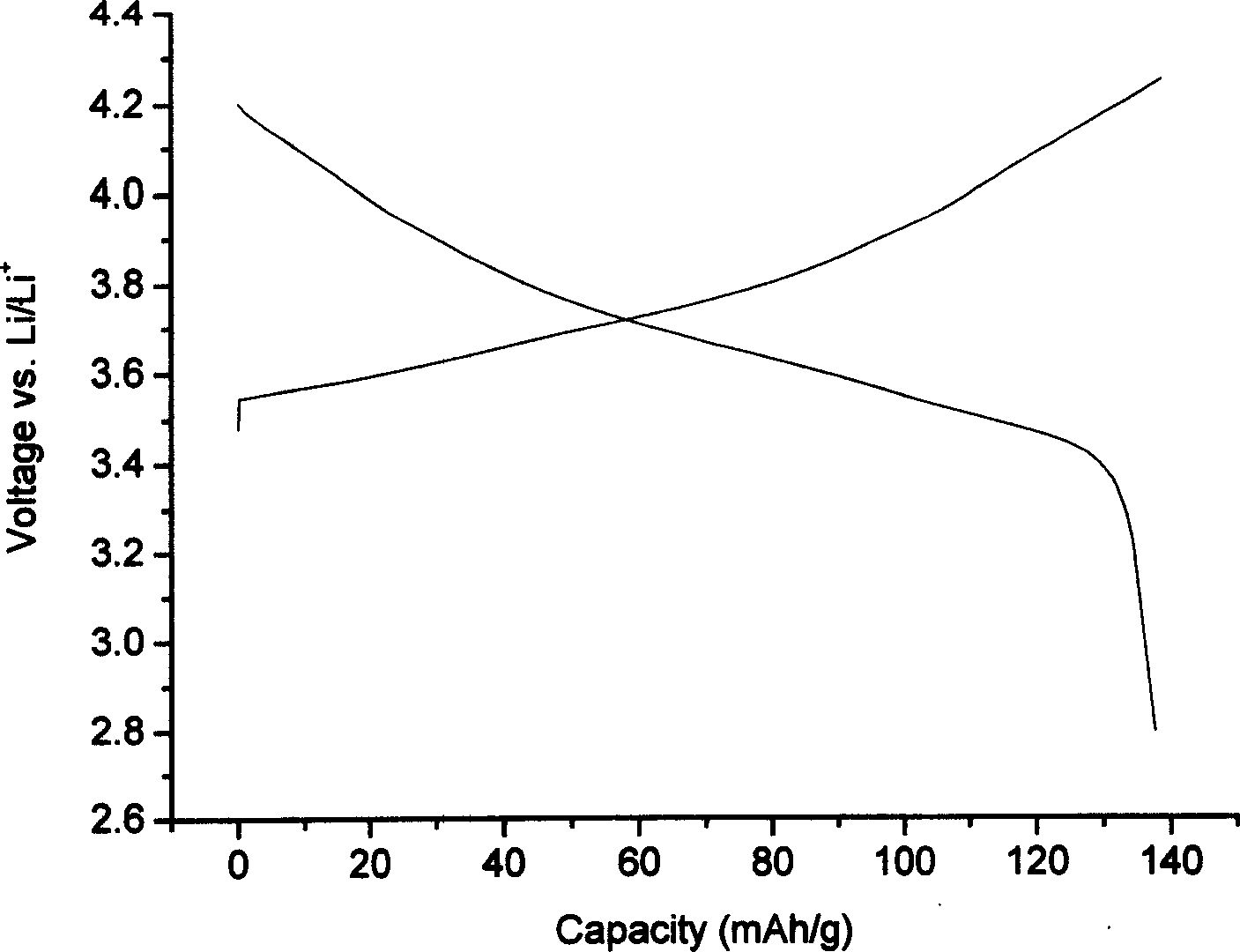
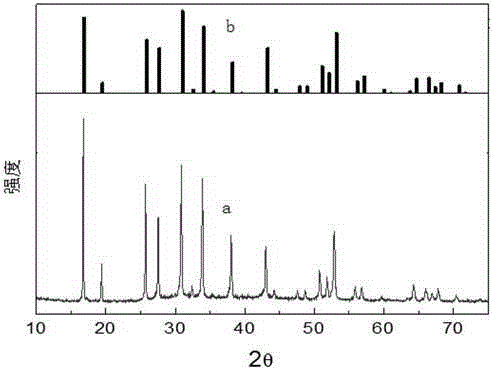
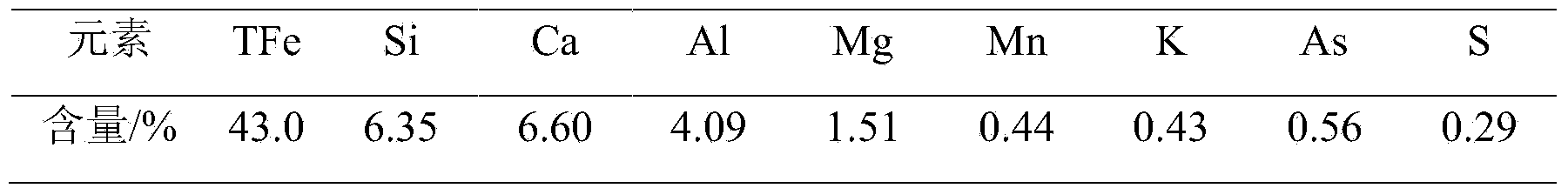Patents
Literature
150results about How to "Shorten roasting time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ceramic core for silica sol precision casting and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveCN101537473AShorten roasting timeLow firing temperatureFoundry mouldsMould handling/dressing devicesTemperature resistanceChoice making
The invention discloses a ceramic core for silica sol precision casting and a manufacturing process thereof. Main body components of the ceramic core comprise refined quartz powder and a proper amount of collapsing agent, and the surface of the ceramic core is coated with high-temperature resistant paint with a thickness of 0.1 to 0.2 millimeter; and at the same reasonable manufacturing processes such as mixing, core making and roasting are adopted. In the ceramic core for casting, the unique material mixing and manufacturing processes are adopted, and the reasonable use of the refined quartz powder and the collapsing agent improves the collapsibility of the ceramic core after casting considerably, the high-quality high-temperature resistant material in ingredients enables the core to resist the erosion of high-temperature molten metals, and the high-temperature resistant paint on the surface of the ceramic core not only improves the high temperature resistance during casting, but also increases the cooling speed of the molten metal.
Owner:上海市机械制造工艺研究所有限公司
Shell powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102311137ALow firing temperatureReduce the number of roastingCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium oxides/hydroxidesCooking & bakingCalcite
The invention relates to shell powder and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides the high-quality shell powder and solves the technical problems of reducing the baking temperature, shortening time and reducing energy consumption. The preparation method of theshell powder comprises the following steps of: washing ruditapes philippin (known as ruditapes philippinarum in the southern part of China, clam in Liaoning province, China, and surf clam in Shandong province, China), clams, oysters, scallop and conchs, drying, pulverizing, adding an auxiliary agent, mixing, baking, grinding, and sifting to prepare powder; determining that the powder has the main component of CaCO3 and a small amount of CaO by using an infrared spectrograph, a powder X-ray spectrograph and a specific surface measurement device; placing in the air; and then converting CaO to [Ca(OH)2]. The shell powder belongs to calcite type crystal, can be used as a natural material and for replacing a chemical product and has broad application prospect.
Owner:BEHAN NEW ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY CONSTR MATERIALS CO LTD JILIN PROVINCE
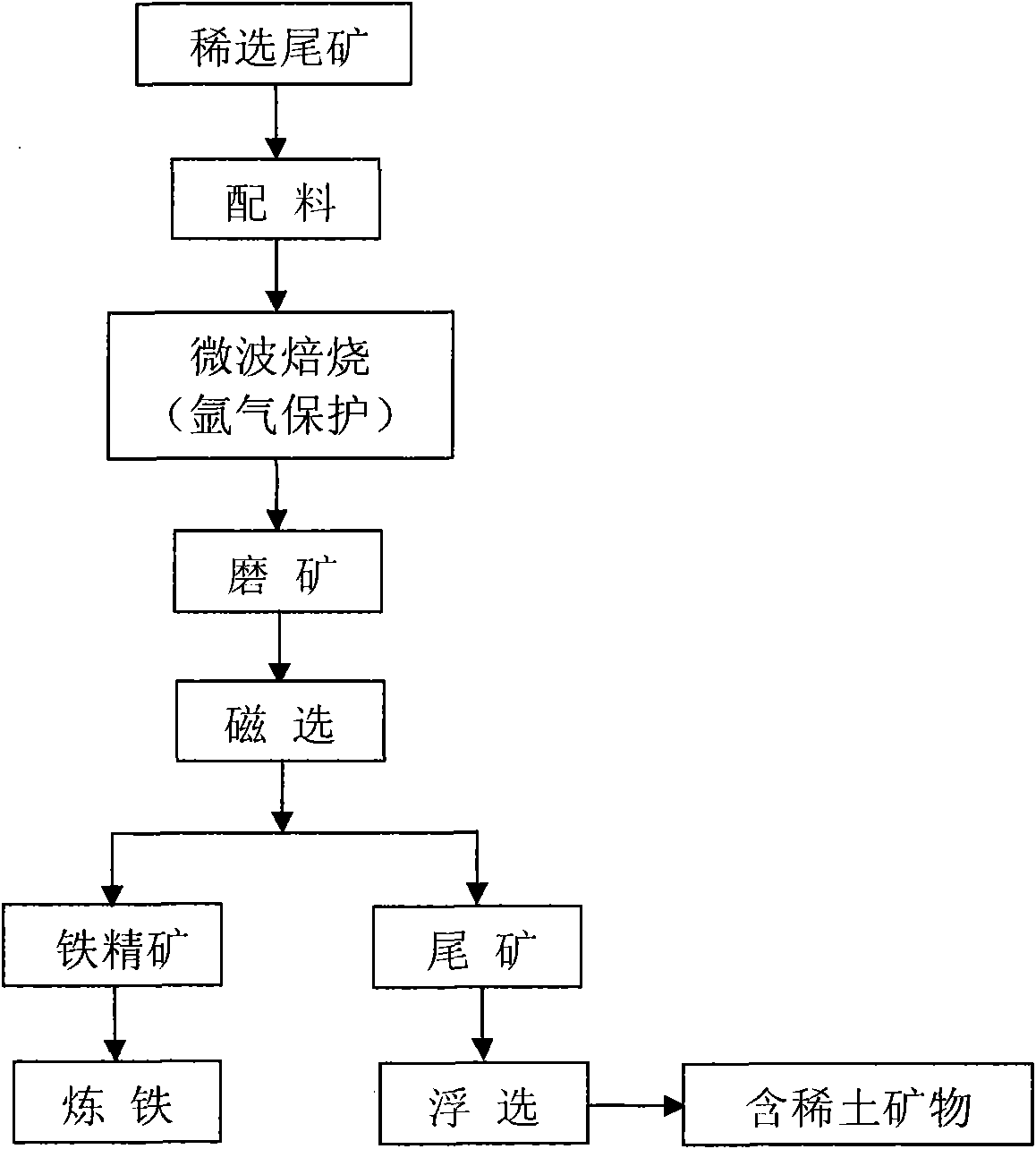
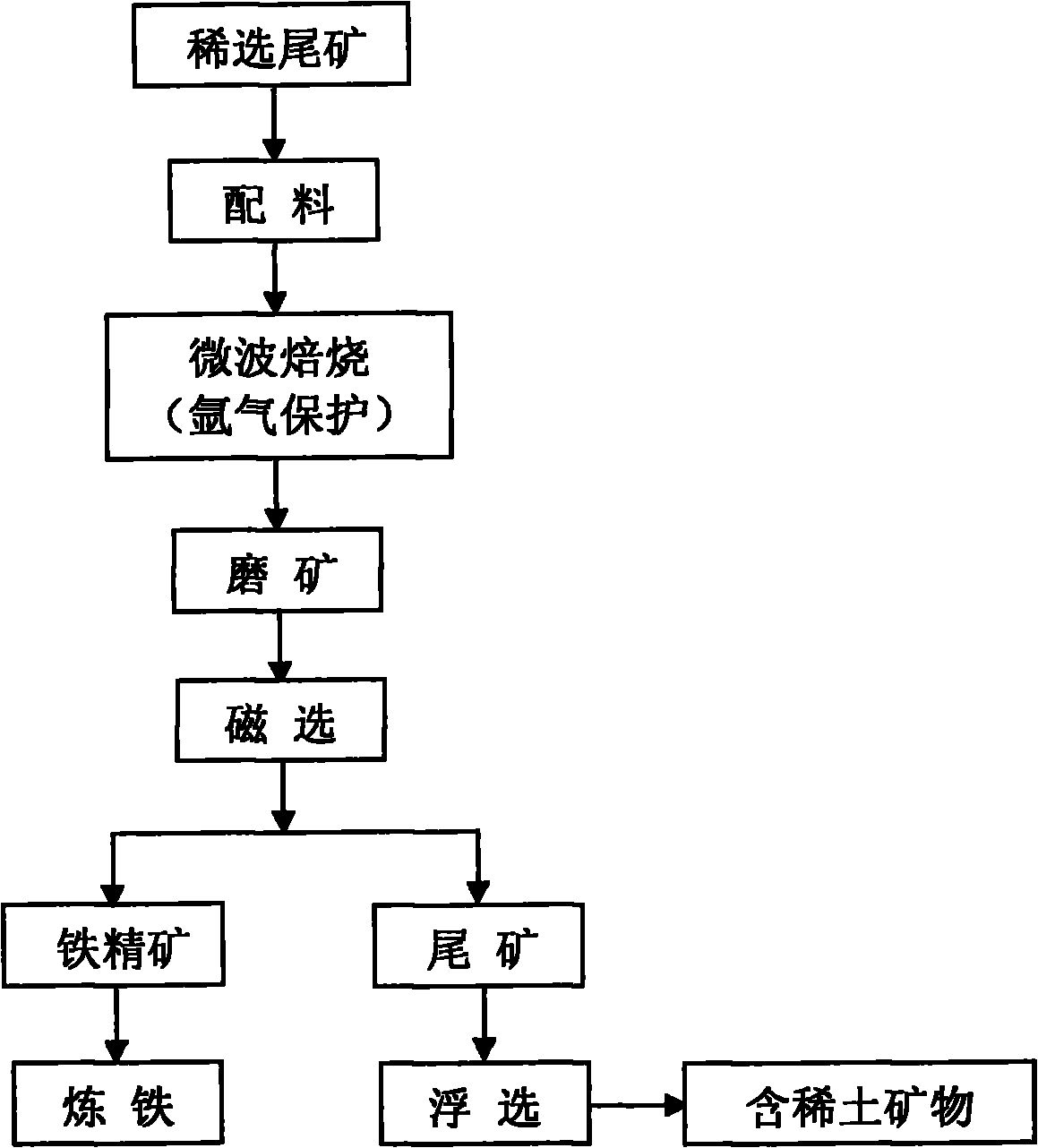
Method for extracting rare earth from rare earth tailings
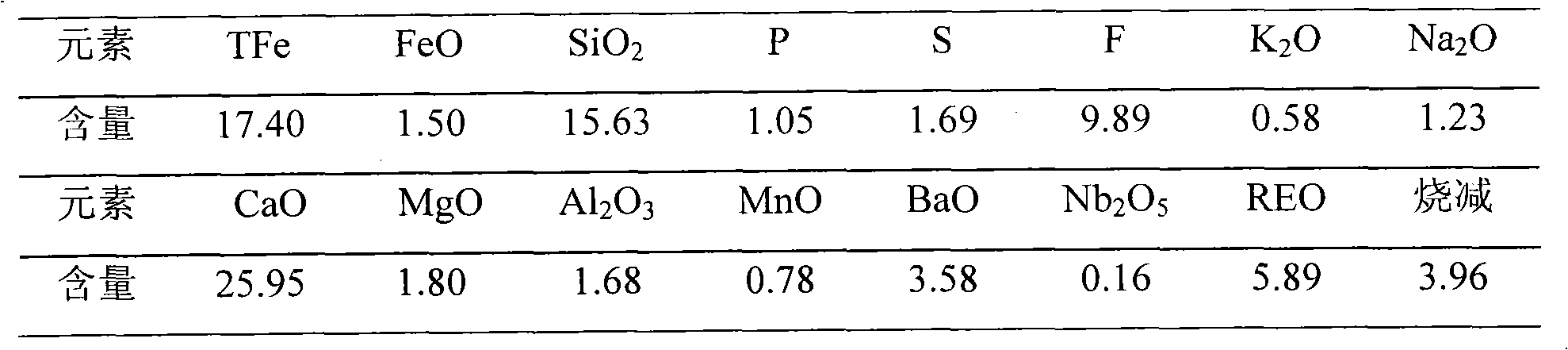
The invention relates to a method for extracting rare earth from rare earth tailings, and belongs to the technical field of mineral extraction metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing the rare earth tailings and a carbon-containing reducing agent uniformly in a certain ratio, and roasting the mixture for 8 to 20 minutes in a microwave roasting oven; (2) performing magnetic separation on the roasted product in a weak magnetic separation tube to separate magnetic iron minerals so that the rare earth minerals are enriched in the tailings; and (3) treating the rare-earth-containing magnetic separation tailings by using a flotation method so as to realize effective extraction of the rare earth. The method has the advantages of short roasting time, low consumption of the reducing agent, energy and a flotation agent, and good flotation effect, can be used for realizing selective reduction of the iron minerals in the reducing process and eliminating environmental pollution caused by the tailings, and is economic and environmentally friendly. The iron mineral impurities such as S, P and the like obtained by the magnetic separation are fewer, the grade of the iron mineral is more than 60 percent, the iron mineral can be used for making iron, the rare earth oxide content of the mineral obtained by primary flotation is 34.12 percent, and the grade of the mineral can reach over 50 percent by concentration.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
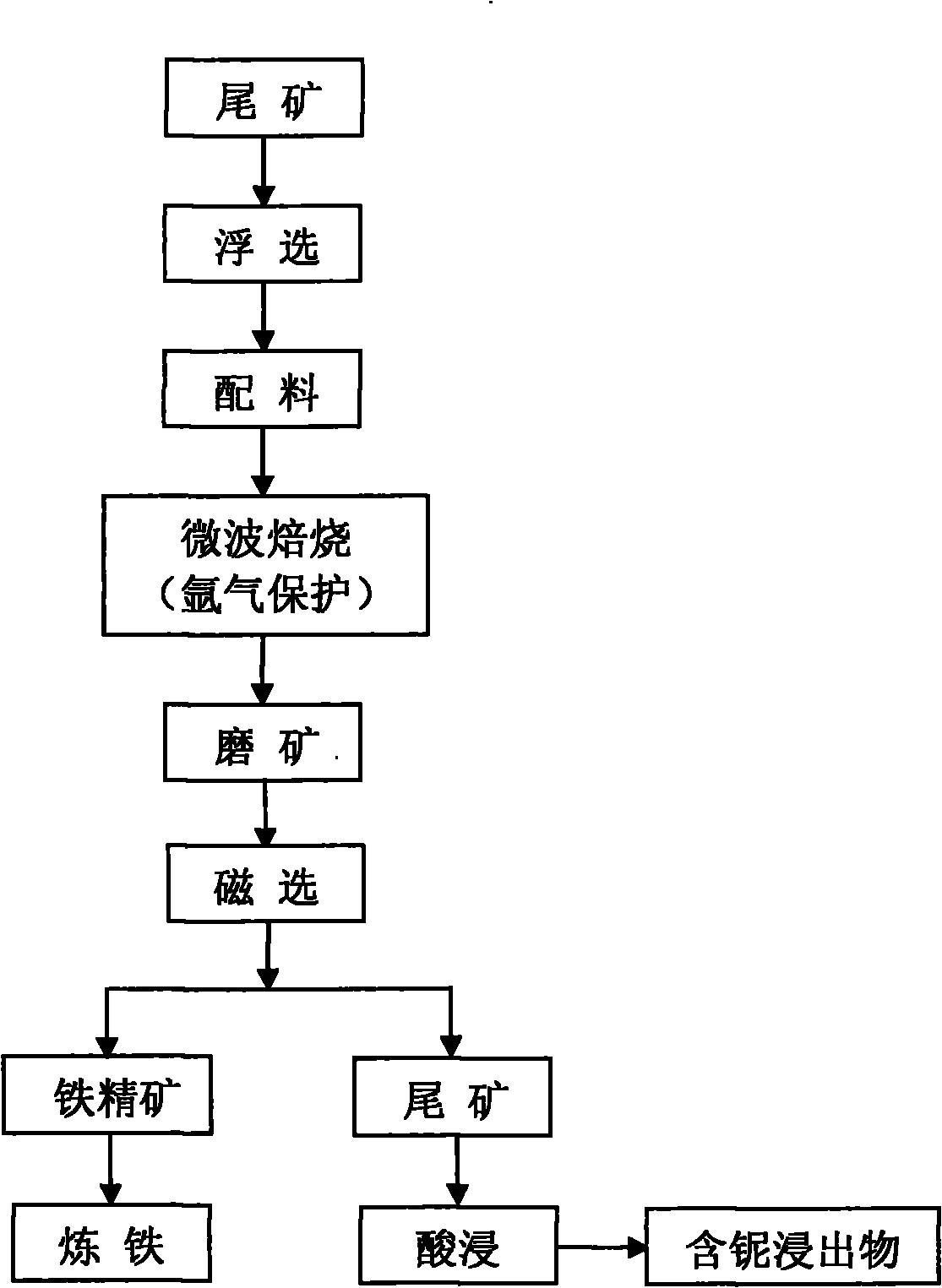
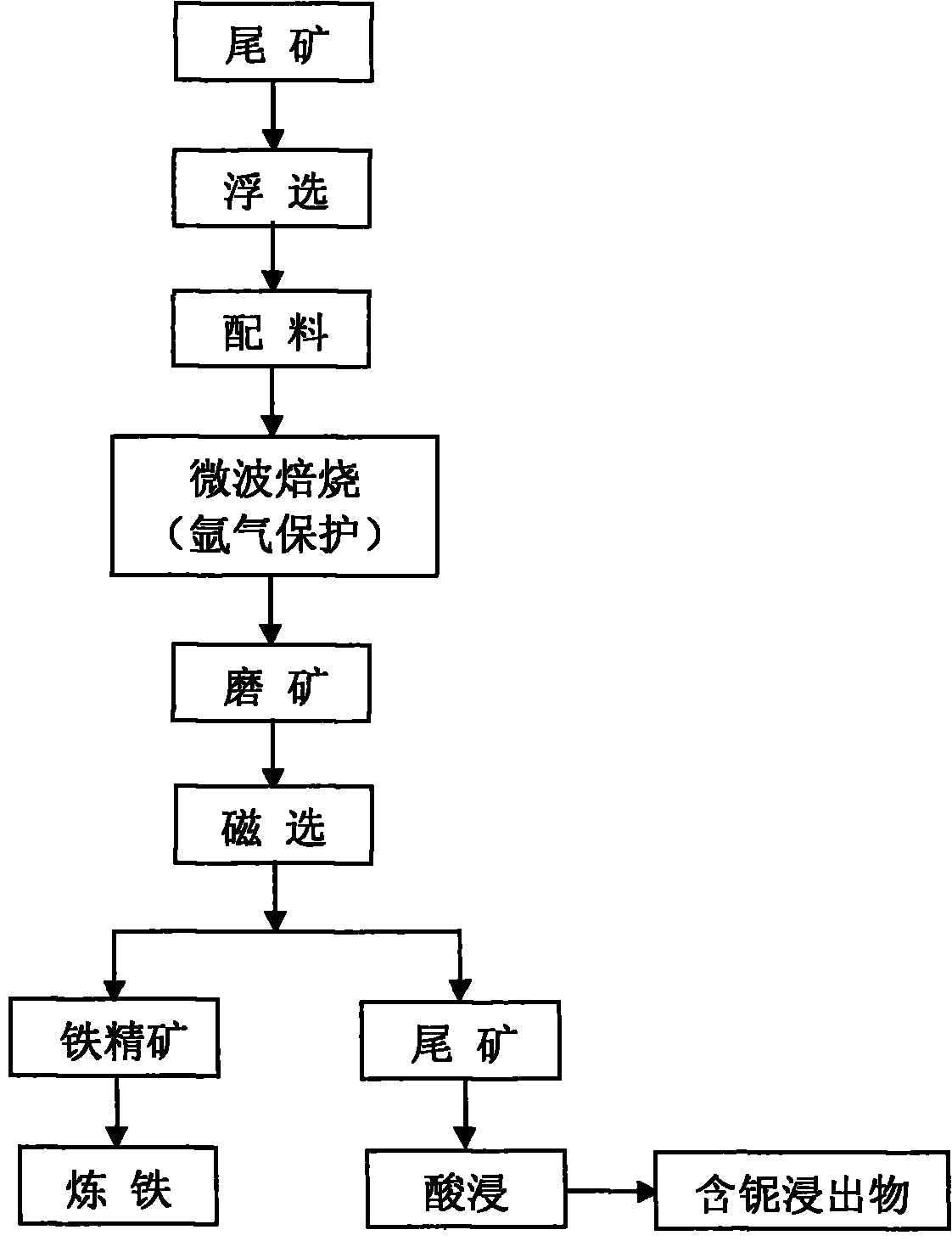
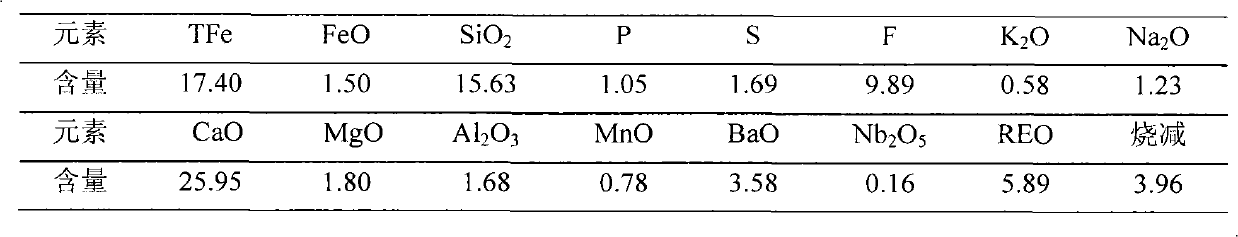
Method for extracting niobium from tailings
The invention relates to a method for extracting niobium from tailings, belonging to the technical field of mineral extraction metallurgy. The method includes the steps as follows: (1) treating the tailings with a flotation method so as to float out iron and niobium minerals from the tailings; (2) using a microwave magnetizing-roasting method and adding carbonaceous reducing agent in the floated minerals so as to convert the haematite in the minerals into magnetite; (3) separating the magnetite out from the roasted minerals by adopting a low-intensity magnetic separation method, thus enriching the niobium minerals in the tailings subjected to magnetic separation; and (4) leaching the obtained niobium minerals out in a high-pressure kettle with concentrated acid so as to obtain niobium-containing extract. The method flow is short, flotation agent types are few and the flotation effect is good; the mineral roasting time is short, the consumption quantity of reducing agent is less and the cost is low; the content of hazardous elements such as S, P and the like in the magnetite obtained by low-intensity magnetic separation is low simultaneously when niobium is enriched, niobium is an excellent material for making iron with a blast furnace, and environment pollution caused by the tailings is solved to a large extent.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
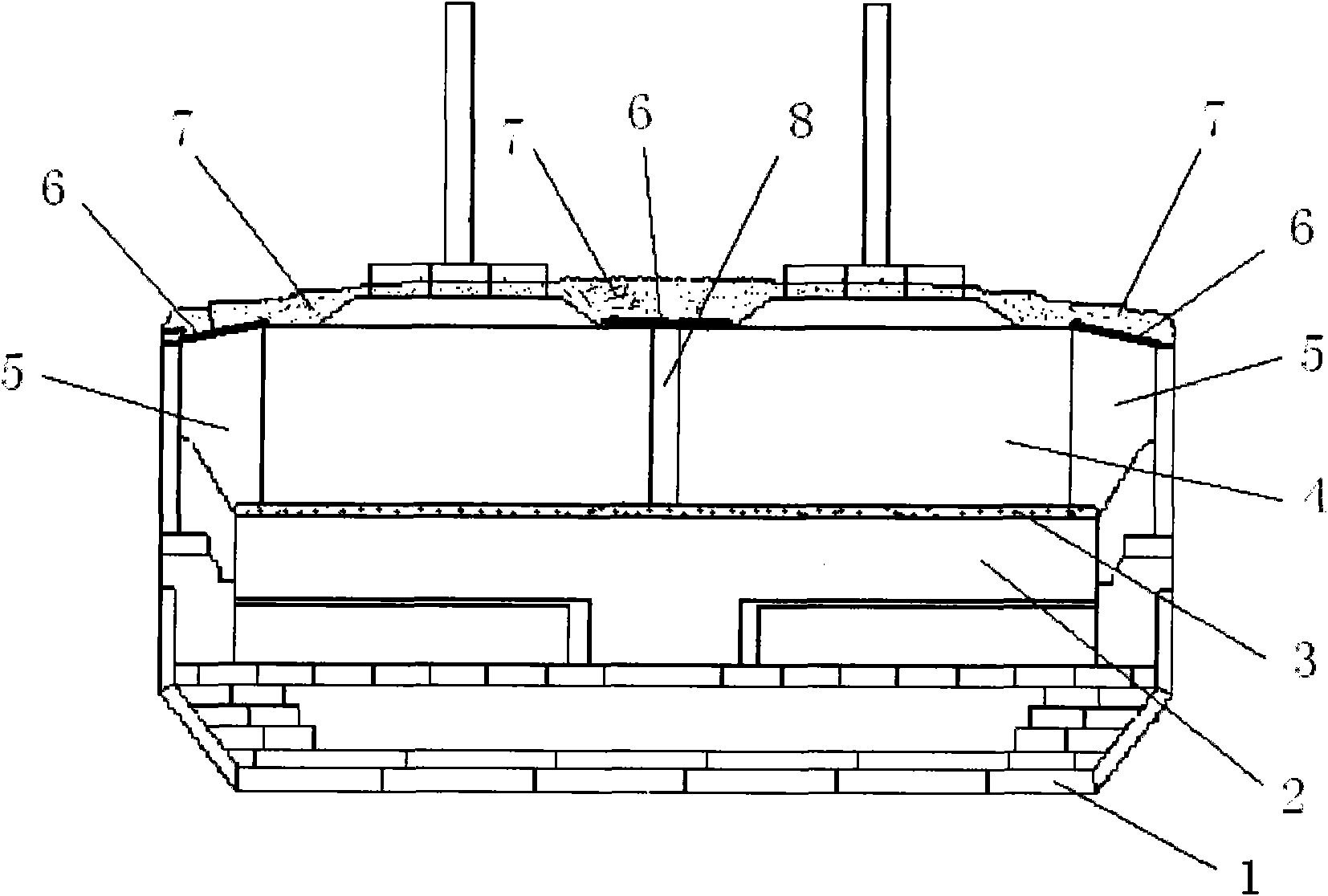
Method for preparing casting shell of fired mold
InactiveCN105414485AShorten roasting timeLow firing temperatureFoundry mouldsFoundry coresSurface layerNanotechnology
The invention discloses a method for preparing a casting shell of a fire mold. The method comprises a surface layer preparing step, a transition layer preparing step, a back layer preparing step, a dewaxing step and a roasting step. According to the method for preparing the casting shell of the fire mold, the roasting time of the shell is shortened, the roasting temperature of the shell is reduced, and energy can be saved; and the residue strength of the shell is reduced, the shell removing performance of the shell is improved, cleaning of the shell after casting is facilitated, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUZHOU NANFENG MACHINERY MFG
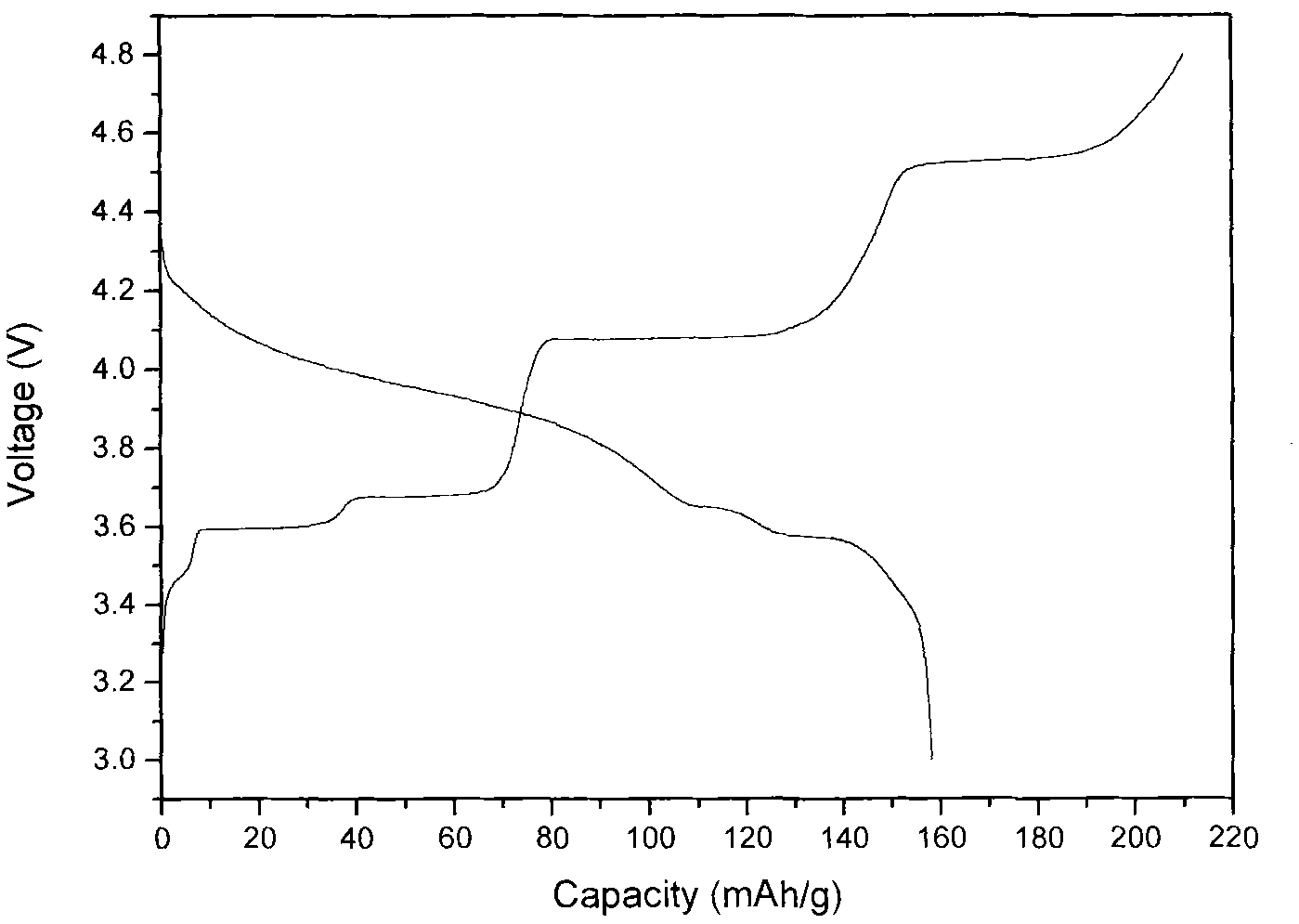
Method for preparing cathode material lithium vanadium phosphate of lithium ion battery by using fast sol-gel method
InactiveCN101841024AAvoid overgrowthGrowth inhibitionCell electrodesCooking & bakingSodium-ion battery
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cathode material lithium vanadium phosphate of a lithium ion battery by using a fast sol-gel method, which specifically comprises the following steps of: (1) adding vanadic oxide into the solution of a reducing acid, heating the mixed solution to 60 to 80 DEG C and stirring the mixed solution for 10 to 50 minutes at a constant temperature to obtain blue solution; (2) adding lithium salts into the blue solution, wherein a stoichiometric ratio of the lithium salts to the vanadic oxide is 3-3.2: 2.9-3.05: 0.95-1.05; (3) treating an obtained powder material in an inert atmosphere at 200 to 400 DEG C for 2 to 4 hours to obtain a precursor; and (4) mixing and grinding uniformly the obtained precursor and another carbon source and cooling the mixture to obtain the cathode material lithium vanadium phosphate of the lithium ion battery. The method has the advantages that: (1) a synthesis process is simplified, the cost is reduced and the method is applied to industrial production; (2) the baking time is greatly shortened, the granularity of the product is reduced and the synthesized material has a nano-size; and (3) the carbon source is mixed before baking, carbon granules also can prohibit the growth of material granules and the synthesized material granules are uniform and fine.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
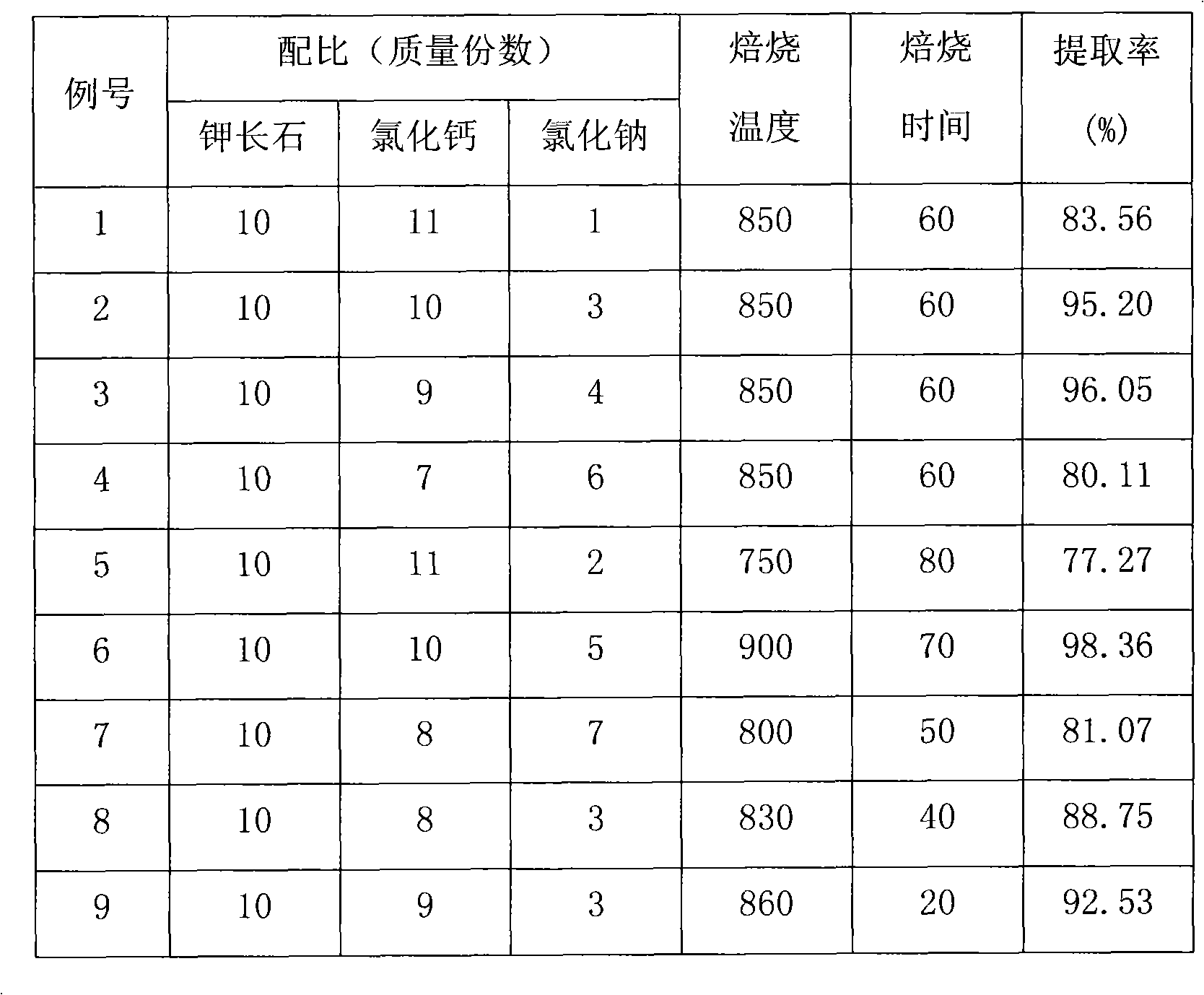
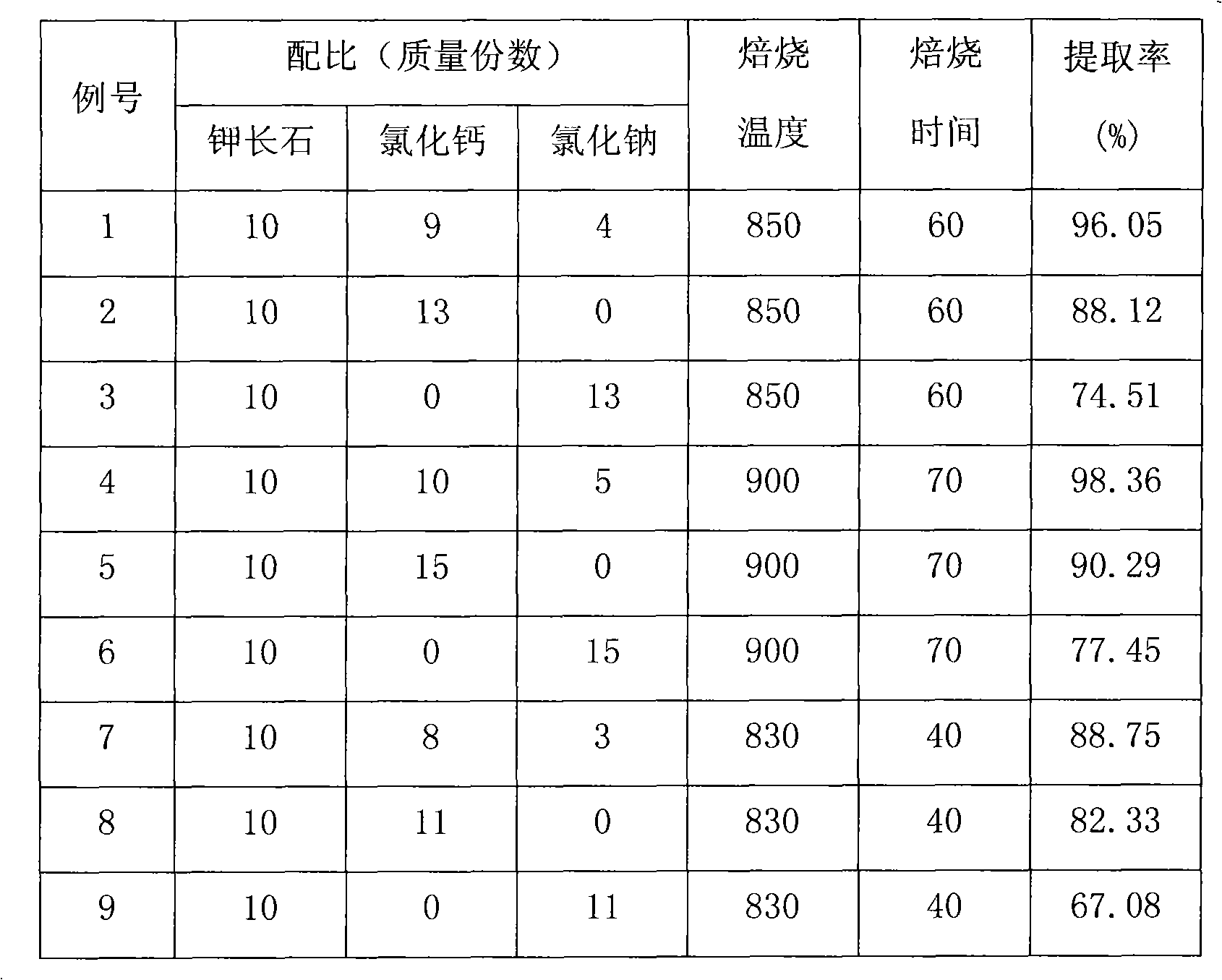
Method for decomposing potassium feldspar to extract soluble potassium
InactiveCN101831561AHigh extraction rateLow firing temperatureProcess efficiency improvementPotassium feldsparAnorthite
The invention discloses a method for decomposing potassium feldspar to extract soluble potassium, comprising the following steps of: crushing and grinding potassium feldspar used as a raw material; mixing with the ground potassium feldspar, calcium chloride and sodium chloride which are used as a combined assistant, and fully stirring, wherein the ratio by mass part of the potassium feldspar to the calcium chloride to the sodium chloride is 10:(7-11):(1-6); roasting the mixture at the temperature of 750-900DEG C for 20-80 minutes; leaching the product with water; and evaporating, condensing and separating the filtered filtrate to obtain a potassium chloride product. The potassium chloride product can be used for producing potassic fertilizer; and main components of filter residue are anorthite and soda feldspar which can be used for producing cement, microcrystalline glass and other building materials. In the method, the selected assistant has low price and wide sources and the obtained potassium extract rate is high; in addition, the method is applicable for the production of extracting the potassium from the potassium feldspar.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing oxidated pellets from pure hematite concentrate
A method for preparing oxidated pellets from pure hematite concentrate includes the following steps: after the hematite concentrate is preprocessed until the specific surface area is larger than or equal to 1300cm2.g-1, compound additive which accounts for 0.5 to 1.6 percent by weight of the total amount of hematite concentrate is added, damp milling is then carried out, pelletizing, drying, preheating and roasting are sequentially carried out after damp milling, and thereby the finished oxidated pellet product is obtained. The compound additive is the mixture of humic acid, calcium peroxide and paigeite, the mixture is ground to the grain size of negative 0.074mm after mixing, and the percentage by weight is not lower than 95 percent. The method solves the problems in the preparation of oxidated pellets from the hard-to-pelletize, hard-to-roast hematite concentrate, such as poor pellet quality, high preheating and roasting temperatures, long time, low finished pellet product strength. The method is simple, the quality of the prepared hematite concentrate pellets is high, the preheating and roasting temperatures are low, the time is short, and the method is suitable for the preparation of the oxidated pellets from the hematite concentrate, particularly the preparation of the oxidated pellets from hard-to-pelletize, hard-to-roast spiegeleisen concentrate. The method can realizeindustrialized production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Electrolyzer circumfluence calcination method
The present invention provides electrolyzer circumfluence calcination method, when installing the electrolyzer, between the anode seam, center seam and inside edge cavity are provided with no materials, installing the electrolyzer in full cavity mode, then using the medium generated heat to calcine cathode lining of the electrolyzer in multiple heat transferring modes of radiation, convection and heat transmission etc, smoke generated by pressure difference during calcination circumfluence in the electrolyzer to make sure calcination temperature of all the sections is uniform, and avoids problem of heat stress centralization and sodium enriching in part effectively; a high-temperature insulation thermal insulating layer is lay in anode seam cavity, center seam cavity and top of edge cavity in the electrolyzer for reducing heat loss effectively, improving warming speed, shorting calcination time, saving energy sources and helpful for earlier regular production of the electrolyzer, meanwhile can reduce calcination energy consumption effectively and improve affect of radiation on operation environment; and the most important is that, using full electrolytes powder to instead of cryolite can reduce calcination startup cost greatly.
Owner:YUNNAN RUNXIN ALUMINUM
Method for extracting beryllium oxide from low-grade beryllium ore
InactiveCN102168184AIncrease concentrationLow firing temperatureProcess efficiency improvementKeroseneSlag
The invention discloses a method for extracting beryllium oxide from low-grade beryllium ore. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: grinding the low-grade beryllium ore, pelletizing, drying, roasting, and crushing to obtain a roasted material; adding concentrated sulfuric acid, stirring, leaching, and separating to obtain acidified liquid and acidified slag; adding the acidified liquid into the other roasted material, and stirring and leaching to obtain primary steep and primary leaching residue; adding concentrated sulfuric acid into the primary leaching residue, adding water, and stirring and leaching to obtain secondary steep and secondary leaching residue, wherein the acidified liquid is replaced by the secondary steep for recycling; extracting the primary steep by adopting an extracting agent in a volume ratio of phosphors extracting agents: alkanol: kerosene of (25-45):(5-1):(50-70) to obtain a beryllium-loaded organic phase and raffinate; washing the beryllium-loaded organic phase by adopting solution of oxalic acid, and performing back extraction by using solution of NaOH to obtain a blank organic phase and stripping solution; and regulating the concentration of hydroxyl ions in the stripping solution to ensure that beryllium is hydrolyzed and precipitated, and calcining a precipitate to obtain the beryllium oxide. The method is easy to operate, the cost is low, the beryllium oxide with the content of over 97 percent is obtained, and the recovery rate of the beryllium is about 80 percent. The method is suitable for extracting the beryllium oxide from low-grade beryllium ore with low BeO content and high CaF2 content.
Owner:广东省资源综合利用研究所
Method for preparing LiNi1-XCOXO2 of anode material of lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveCN1843930AHigh specific capacityImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesAlcoholNickel compounds
The invention relates to a method for preparing LiNi1-xCoxO2 used as lithium-ion secondary battery anode material. It comprises following steps: dissolving nickel compounds and cobalt compounds into distilled water according to proportion; adding mixing solution of basic precipitant and oxidant and stirring strongly to make Co2+,Ni2+ deposite in form of Ni1-xCoxOOH; washing the deposition with distilled water and drying; mixing said deposition with lithium compounds, adding alcohol, water or mixture of that; grinding to make it be changed into flowing deformation phase pioneer matter; making lithium compound and Ni1-xCoxOOH mixed completely; drying said pioneer matter; and putting it into high temperature furnace, preheating, calcining, cooling and getting said LiNi1-xCoxO2. The invention is characterized by simple process, low cost, easy for industrial production, fine electrochemical property of got anode material and good circularity.
Owner:CHENGDU ORGANIC CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tantalum-doped cubic garnet structure Li7La3Zr2-xTaxO12 material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105244536AReduce high temperature lossLow content requirementSolid electrolytesSecondary cellsLithiumPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a tantalum-doped cubic garnet structure Li7La3Zr2-xTaxO12 material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1, lanthanum zirconate, a lanthanum source, a lithium source and a doped element being a tantalum source are weighed; the materials are placed in a container successively, a complexing agent is added into the container, and then stirring is performed for 4-6 h; 2, the temperature is gradually increased to 80 DEG C and kept till excessive moisture is removed, and a precursor processed in a high-temperature solid-phase mode is obtained; 3, the precursor is preheated for 3-5 h at the temperature of 400 DEG C, and a product is taken out, sufficiently and evenly ground and roasted for 1.5-5 h at the temperature of 900 DEG C to obtain a primary roasted product, wherein the value of x is 0.25-0.6. The method is simple in process, the requirement for the content of the doped materials is lowered, energy consumption and lithium high-temperature losses are reduced in the preparation process due to the fact that the roasting time is shortened, energy is saved, the cost is greatly reduced, and the preparation method is quite suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER ENERGY STORAGE BATTERY SYST ENG TECH +1
Composite additive for preparing hematite concentrate pellet and application thereof
A composite additive for preparing hematite concentrate pellets comprises the following components: humic acid, calcium peroxide, and paigeite. During application, the composite additive is added which has a mass percent of 0.5%-1.6% of the total mass of the hematite concentrates, and the finished product pellets are obtained by pelletization, preheating, and roasting. Compared with pellets prepared by traditional technology, the hematite pellets prepared by the composite additive of the invention have improved falling strength of the green pellets, and compression strength of the finished product pellets; the preheating temperature and roasting temperature suitable for the pellets are reduced; both the preheating time and roasting time are shortened; the TFe grade is increased by 0.8%-1.2%. The composite additive of the invention has reasonable component ratios, is easy to process and manufacture, has a low using amount and a low residual amount, can significantly improve the pelletability of hematite concentrates which are difficult to be palletized, can improve the green pellet quality, has good heat stability, and can effectively reduce the preheating and roasting temperatures and shorten the preheating and roasting time of hematite concentrates. The composite additive of the invention is applicable to the production of oxidized pellets by hematites, and is especially applicable to the production of oxidized pellets by specularites. The composite additive of the invention is applicable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Rare-earth waste recovering and machining and treatment device system and rare-earth waste recovering and machining and treatment method
ActiveCN108411115ARapid and uniform thermal decomposition and oxidationReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionRare earth
The invention discloses a rare-earth waste recovering and machining and treatment device system and a rare-earth waste recovering and machining and treatment method. Rare-earth waste is placed in a roasting furnace, and is subjected to oxidizing roasting on the condition of heat preservation after being heated to 850-1000 DEG C; rare-earth substances in the rare-earth waste are all turned into rare-earth oxide materials; an appropriate amount of water is added to a reactor and is heated to 200-250 DEG C; the measured materials and hydrochloric acid with the concentration being 0.8-1 mol / L areproportionally added to the reactor by several times for acidification decomposition; a rare-earth solution subjected to the acidification decomposition is supplied into the reactor for extraction andiron contained impurities are removed; then the rare-earth solution after iron is removed is supplied to an extraction tank for extraction; a praseodymium neodymium oxide solution is subjected to extraction separation and sedimentation; and sediments are fired. According to the rare-earth waste recovering and machining and treatment device system, through practical application measurement, the comprehensive recovery rate is above 97%, the purity of obtained (Pr and Nd) 203 is greater than or equal to 98%, the purity of Dy 203 is greater than or equal to 99%, and the recovering and machining cost for per ton of rare earth oxides is lower than 15,000 yuan.
Owner:萍乡泽昊新材料有限责任公司
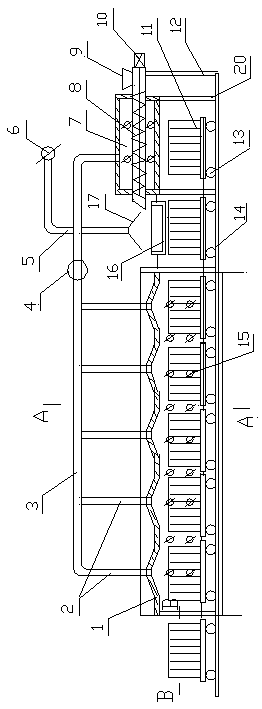
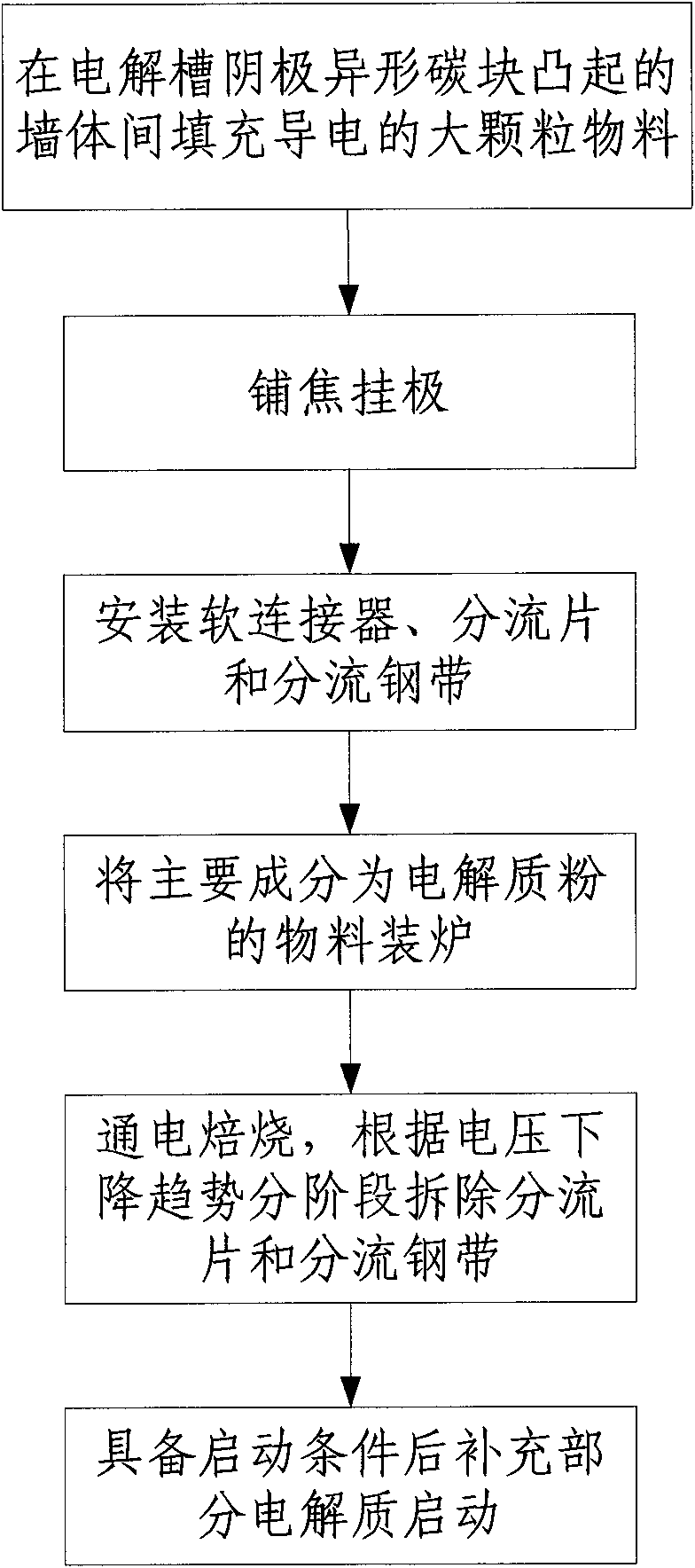
Method for roasting and starting aluminum electrolytic cell
The invention discloses a method for roasting and starting an aluminum electrolytic cell. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, evenly and compactly filling conductive bulky grain materials among wall bodies which are projected on cathode abnormal carbon blocks of the electrolytic cell; using coke grains for pouring cracks and filling gaps among the bulky grain materials; laying cokegrains on upper surfaces of the abnormal carbon blocks and the filled bulky grain materials; after laying coke grains of a group of anodes, placing a group of anodes thereon; then installing a soft connector, a current-dividing sheet and a current-dividing steel belt; filling the materials which takes electrolyte powder as the main component in a furnace and evenly laying the materials around theelectrolytic cell; detaching the current-dividing plate and the current-dividing steel belt by phases through electrifying and roasting according to the downtrend of voltage; and when most materials in the gaps of the anodes are smelted and communicated and both the electrolyte height and the roasting temperature meet requirements, supplementing part of electrolyte to the electrolytic cell and then starting the electrolytic cell. The method has the advantages of short roasting time, less electricity consumption, safe and reliable control of roasting process, low producing cost, and the like.
Owner:YANKUANG GRP CO LTD +1
Method for extracting molybdenum and nickel and enriching precious metals from nickel and molybdenum ores
ActiveCN103555933AEfficient separationLow melting pointProcess efficiency improvementSodium molybdateSulfur
The invention provides a method for extracting molybdenum and nickel and enriching precious metals from nickel and molybdenum ores. The method comprises the steps of (1) carrying out oxidized desulfurization and roasting; (2) smelting at high temperature to separate nickel and molybdenum: heating to 1250-1550 DEG C to enable the mixed furnace charge to be fused, and then, preserving the heat for 20-40min; (3) leaching and extracting the molybdenum for the first time; (4) leaching and extracting the molybdenum for the second time. The method provided by the invention is only used for removing sulfur in the nickel and molybdenum ores to be below 10%, so that the long roasting process is avoided, SO2 in the obtained smoke is high in concentration and can be directly used for preparing acids, meanwhile, the roasting time is greatly shortened, the production efficiency is remarkably increased, and the operation difficulty is lowered. The molybdenum can be converted into sodium molybdate and reserved in molten alkaline slag through adding sodium carbonate into the roasted clinker and melting the sodium carbonate under an alkaline condition, while the nickel is produced in an iced nickel or ferronickel way, so that the efficient separation of the nickel and the molybdenum is realized. The sodium carbonate is added in a melting process, so that the melting point and viscosity of the molten slag are reduced, and the iced nickel or ferronickel can be favorably settled and enriched.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
High density lithium iron phosphate and method for synthesizing
InactiveCN101399339AEnhanced mutual mass transferImprove conductivityElectrode manufacturing processesPhosphorus compoundsLithium iron phosphateHigh density
The public invented a high-density lithium iron phosphate and a synthesis method thereof, the molecular expression formula of the high-density lithium iron phosphate is: Li1-x MexFe(PO4)1-1 / 3xFx (x is not less than or equal to 0.01 and not more than or equal to 0.10), wherein, Me is a cation doped element and is one of Li, Na and Mg. The synthesis method of the high-density lithium iron phosphate comprises the following steps: step 1: lithium salt, ferrous salt, phosphate and a fluxing agent are mixed according to the calculation of the molecular expression formula; step 2: required amount of reductive ferric iron is added, water or ethanol is taken as a dispersion medium, and granules are prepared by milling, drying and re-milling after the drying; step 3: the prepared granules are transferred into an atmosphere protection furnace and the black lithium iron phosphate is prepared after the calcination in the N2 gas environment. The lithium iron phosphate which is synthesized by using the method has the advantages of high specific capacity, high tap density, good cycle performance, good rate property, simple process and low cost, thereby being applicable to industrial mass production.
Owner:BAK INT TIANJIN +2
Method and device for preparing nickel iron roasted ore by utilizing lateritic nickel ore
ActiveCN103468930AFast heat and mass transferShorten decrystallization wateChemical reactionLaterite
The invention discloses a method and a device for preparing a nickel iron roasted ore by utilizing a lateritic nickel ore. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, grinding the lateritic nickel ore into an ore powder, then carrying out high-temperature roasting of the obtained ore powder, during the high-temperature roasting process, allowing the ore powder to be in a pre-reduction system and carry out a high-temperature preheating reduction reaction, followed by allowing the high-temperature roasted ore to go into a rotary kiln for high-temperature calcination, thus obtaining a roasted ore containing nickel pig iron after completing high-temperature calcination, and then after dipping the roasted ore into water for cooling, separating to obtain the nickel iron roasted ore. The device comprises a hopper-type elevator, an air chute, a chute draught fan, a rotary feeder, a sluice valve, a rotary kiln, a water-cooling stirring tank, a burner, a hot wind mixing chamber, a high-temperature draught fan, a cyclone dust remover, a bag-type dust remover, a chain-type conveyor, a burner and a pre-reduction system. The preparation method and the device allow the heat transfer area of the ore powder to be large, enable each particle to be uniformly and fully subjected to a chemical reaction, have short reaction time, and have high utilization rate of the lateritic nickel ore.
Owner:WUHAN BUILDING MATERIAL IND DESIGN & RES INST
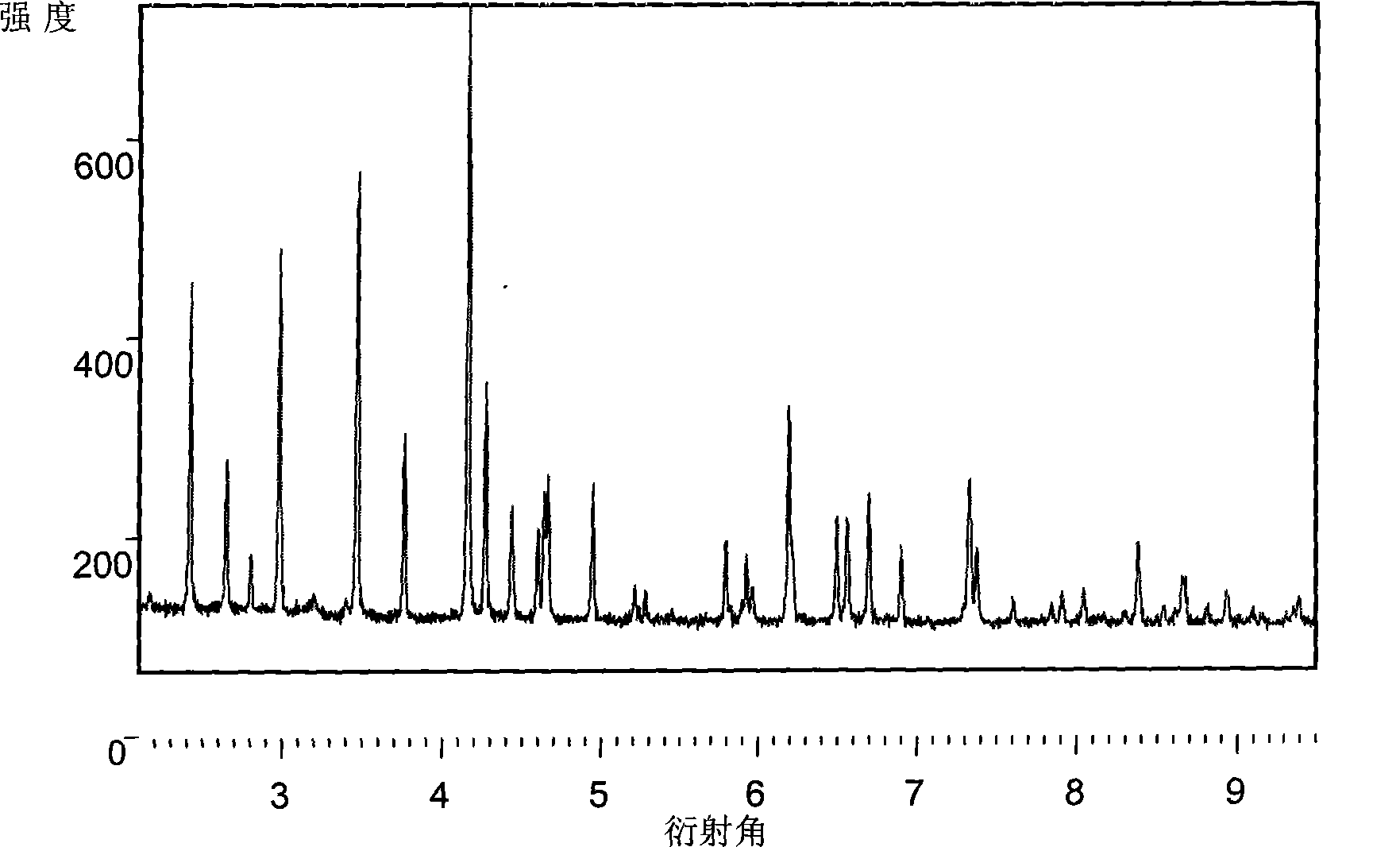
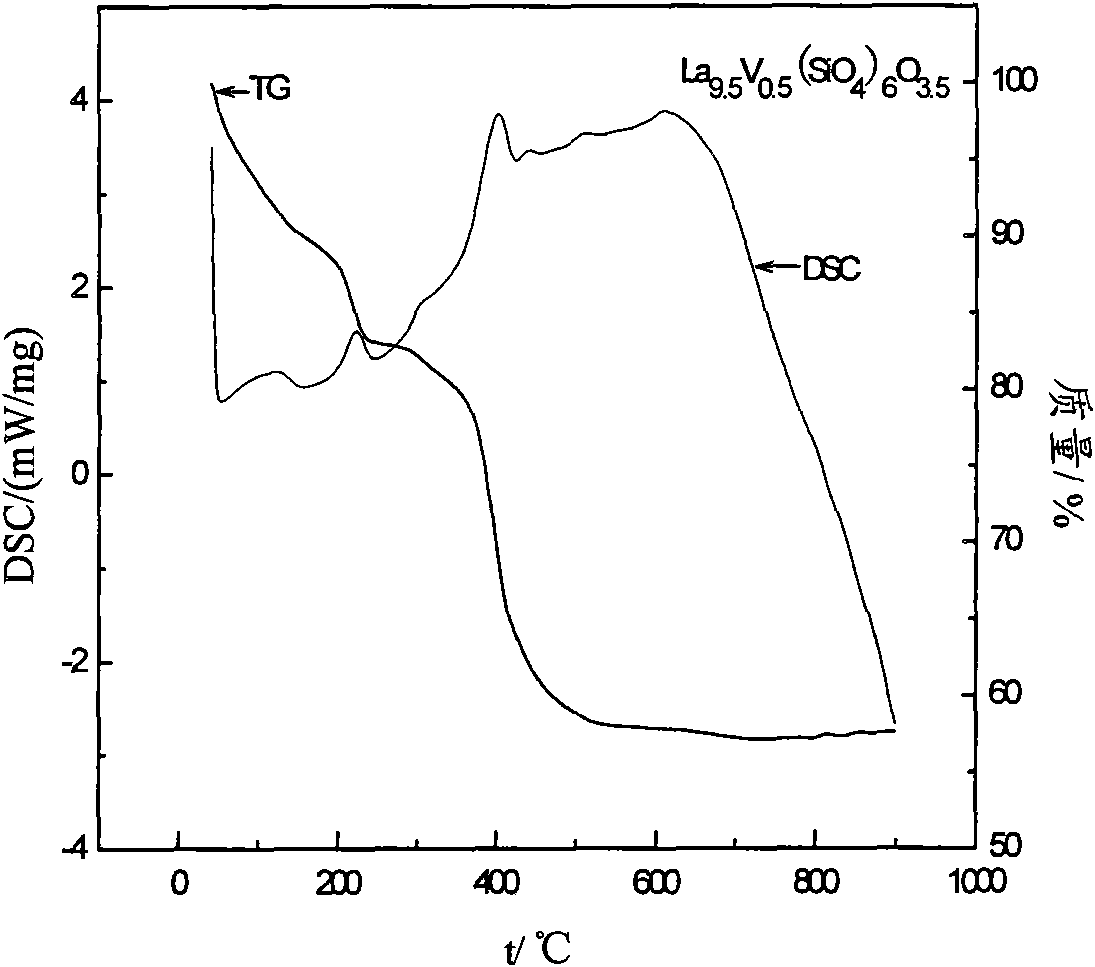
Vanadium-doped in lanthanum site apatite-type lanthanum silicate solid electrolyte material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101615679AExtended service lifeImprove conductivitySolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cell detailsSol-gelLanthanum
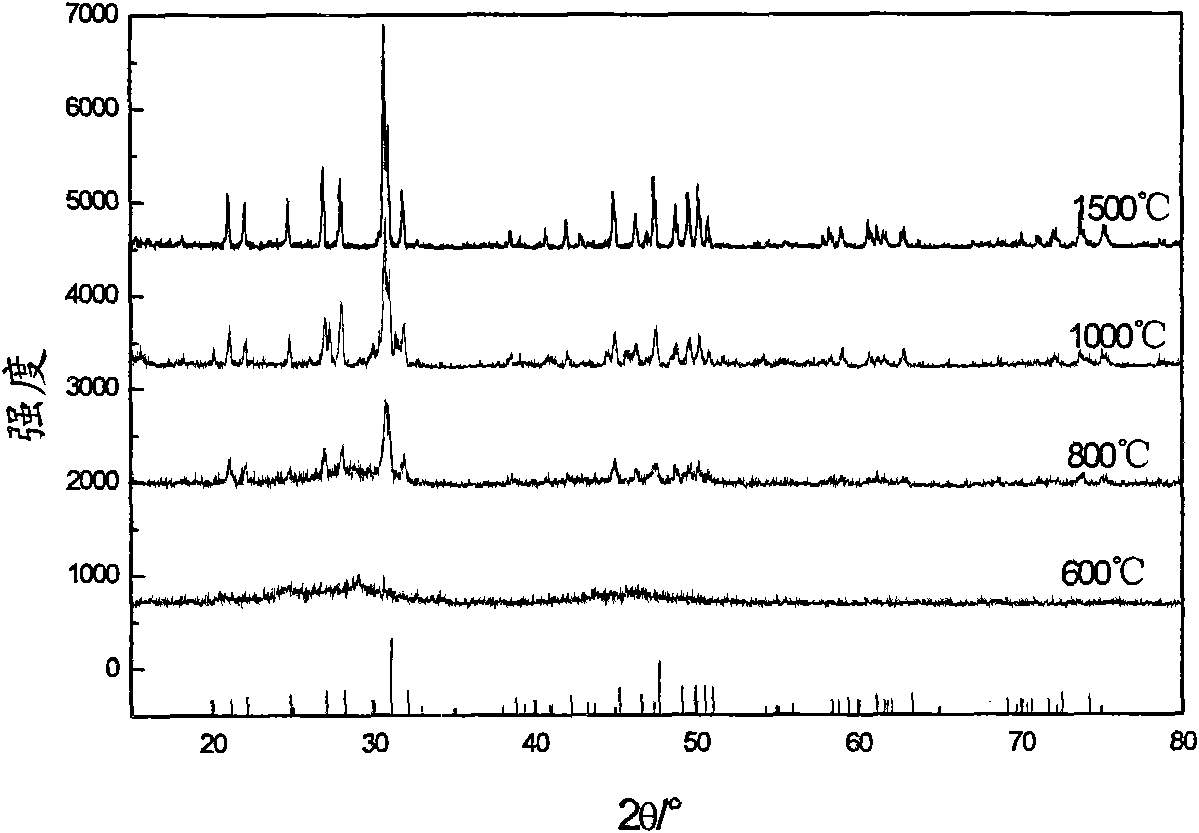
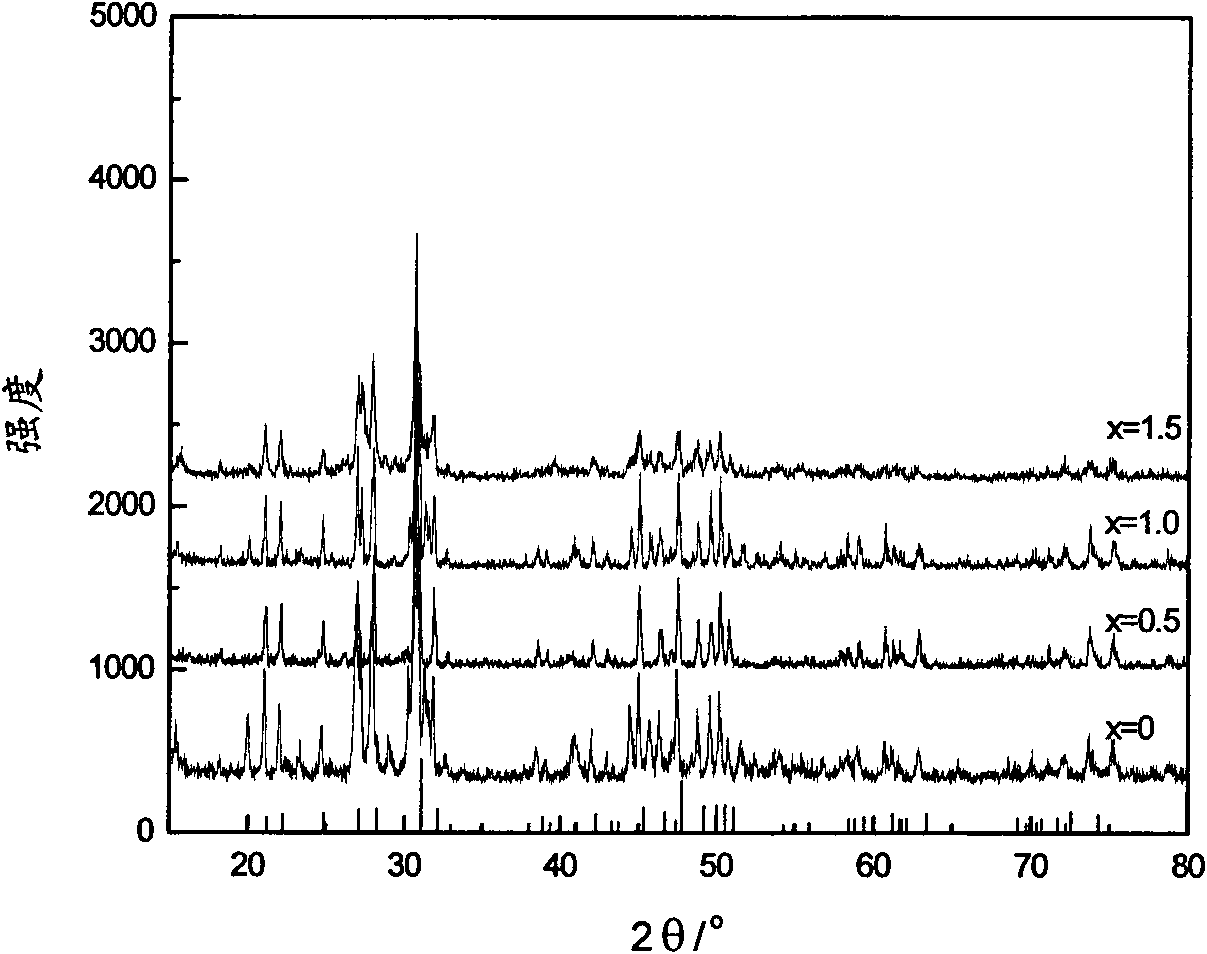
The invention discloses a vanadium-doped in lanthanum site apatite-type lanthanum silicate solid electrolyte material and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the solid electrolyte material is La10-xVx(SiO4)6O3+x; wherein, x is more than 0 and is not more than 1.5; the preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing apatite-type electrolyte material precursor through the sol-gel method with La(NO3)3-6H2O, tetraethoxy silane, glacial acetic acid and methanol in a molar ratio of 10-8.5:6:12:12, preparing membranes at 10-20MPa with the powder which is treated through drying and preroasting and finally roasting the membranes at 800-1500 DEG C for 2-6h. In the preparation method of the invention, the doping of vanadium in lanthanum site reduces the roasting temperature and time of the electrolyte material which has higher conductivity at the middle-low temperature(600-800 DEG C) and is used for the electrolyte layer of the solid oxide fuel cell so that the service life of cells can be effectively prolonged.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for performing microwave arsenic removal on high-arsenic iron ore
The invention discloses a method for performing microwave arsenic removal on high-arsenic iron ore and belongs to the technical field of mineral separation. The method comprises the following steps: crushing the high-arsenic iron ore until the granularity is less than 1mm, adding a proper amount of pulverized coal, uniformly mixing, performing microwave roasting in an industrial microwave oven, controlling the temperature at 800-1200 DEG C, wherein the roasting time is 5-30 minutes, the arsenic is separated from the iron ore in a gas state form, low-arsenic iron ore concentrate which meets the industrial requirements is obtained, and the generated arsenic-containing tail gas is recycled by virtue of a flue gas absorption device arranged on the industrial microwave oven. According to the method, effective separation between the arsenic and the iron ore is promoted by utilizing selective heating of microwave on the iron ore, the arsenic removal rate is over 90 percent, and the method is a high-efficiency low-cost method for removing arsenic from the iron ore.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
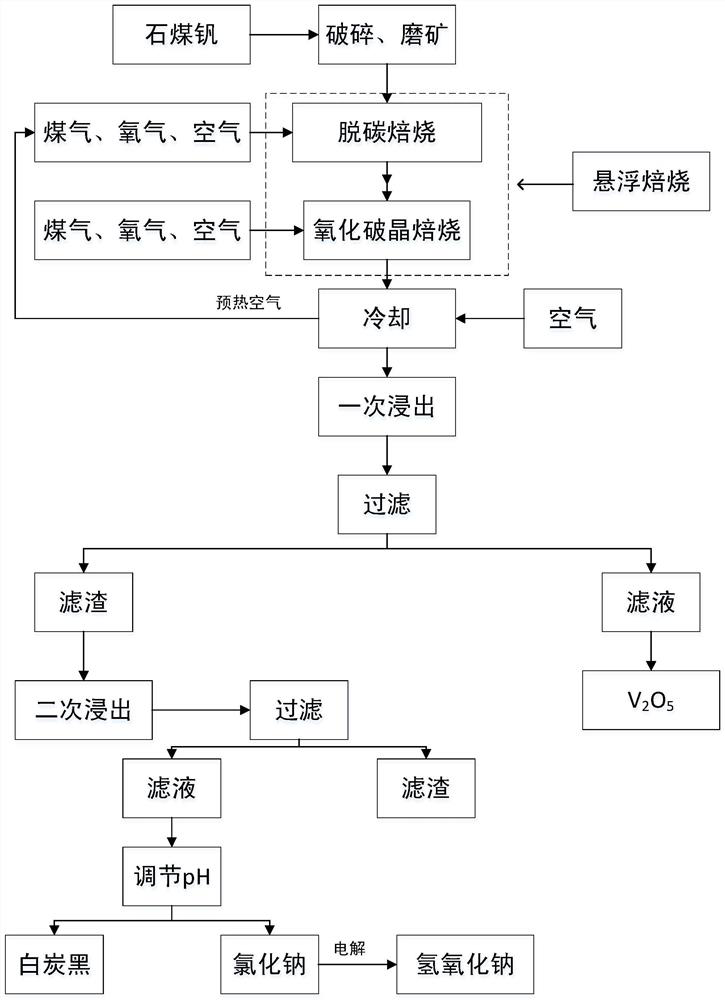
Stone coal vanadium ore oxidizing, crystal breaking, roasting and vanadium extracting comprehensive utilization system
ActiveCN111876616AHigh heat and mass transfer efficiencySolve problems such as secondary pollutionSilicaChemical industryDecarburizationCoal
The invention discloses a stone coal vanadium ore oxidizing, crystal breaking, roasting and vanadium extracting comprehensive utilization system. A crusher, a high-pressure roller mill, a first feeding belt, a feeding bin, a second feeding belt and a spiral feeder are sequentially matched with one another, and the discharging end of the spiral feeder is matched with a feeding port of a suspensiondecarburization roasting furnace; the suspension decarburization roasting furnace, a first cyclone separator, a suspension crystal breaking roasting furnace, a second cyclone separator and a cooler are sequentially communicated in series; a combustor and an air inlet are respectively arranged at the bottoms of the suspension decarburization roasting furnace and the suspension crystal breaking roasting furnace; an air inlet of the cooler is communicated with an air compressor; and a discharging hole in the bottom of the cooler is matched with a feeding hole of an acid mixing curing furnace; andthe acid mixing curing furnace, a first leaching tank, a first filtering device, a second leaching tank, a second filtering device, a pH value adjusting tank and a third filtering device are sequentially connected in series and matched with one another. The system provided by the invention is stable in operation, large in treatment capacity, low in energy consumption and cost of unit treatment capacity, and capable of easily controlling product properties and easily achieving large-scale equipment.
Owner:上海逢石科技有限公司
Preparation method for doped and modified spinel-type lithium manganite cathode material
InactiveCN102593460AReduce the amount of dissolutionLow melting pointCell electrodesPhysical chemistrySpinel
The invention provides a preparation method for a doped and modified spinel-type lithium manganite cathode material, which comprises the following steps of: mixing a lithium source compound, a manganese source compound, doped metal salt with a roasting accelerator to obtain a mixture; then, roasting the mixture to obtain metal element-doped spinel-type lithium manganite, wherein the roasting accelerator comprises one or more than one of acetylene black, active carbon powder, coke powder and charcoal powder. The preparation method provided by the invention is low in roasting temperature and is short in roasting time, and meanwhile, the obtained doped and modified spinel-type lithium manganite is stable in product quality and is uniform in performance.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Lithium ion battery anode material with LiCoO2 coated on surface and preparation method for lithium ion battery anode material
ActiveCN102324504AIncreased diffusion rateShorten roasting timeCell electrodesLithium compoundChemistry
The invention provides a lithium ion battery anode material with LiCoO2 coated on the surface and a preparation method for the lithium ion battery anode material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing an anode material, a low-melting-point salt, a lithium compound and a cobalt compound; raising the temperature to be between the melting point and the boiling point of the low-melting-point salt to form a molten salt medium; reacting for a certain period of time, and then cooling to the room temperature; and washing and drying to obtain the lithium ion battery anode material with the LiCoO2 coated on the surface. By the preparation method, the molten salt is used as a reaction medium, the process is simple, the synthesis temperature is low, the holding time is short, a layer of electrochemical active substance is formed on the surface of base material particles, the performance and the structure of the base material of the anode material are not changed, and advantages of a modified layer is obtained.
Owner:NINGXIA SINOCHEM LITHIUM BATTERY MATERIAL CO LTD
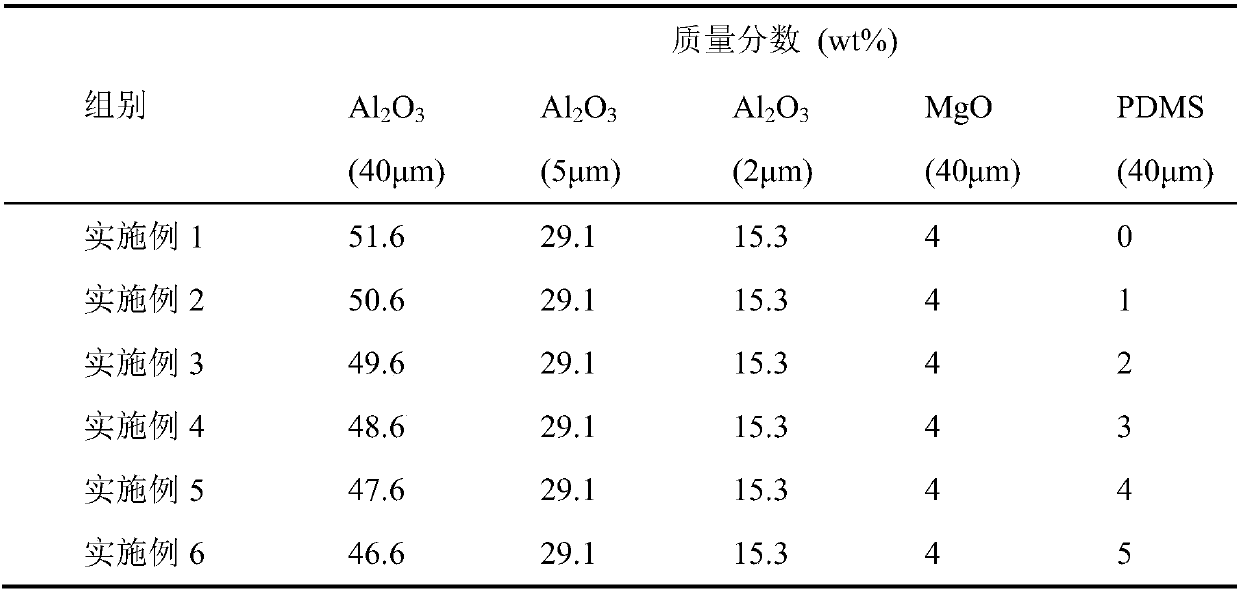
Method for improving degreasing strength of additive manufacturing formed ceramic part
InactiveCN109534794AImprove degreasing strengthSufficient strength marginUltrasound attenuationPrill
The invention discloses a method for improving the degreasing strength of an additive manufacturing formed ceramic part. The method comprises the following steps that polydimethylsiloxane is added into a ceramic powder material, and required raw material powder is obtained after even dispersing; the powder material and a liquid phase solvent are mixed, and ceramic slurry is prepared after even ball-milling; a ceramic part blank is formed through an additive manufacturing method, and after the blank is dried, degreasing and glue discharging are conducted; and in the degreasing heating process,the polydimethylsiloxane is softened and molten to permeate into adjacent ceramic particle gaps, and ceramic particles are wrapped. The polydimethylsiloxane is simple in molecular structure, low in carbon content and low in pyrolysis ignition lost rate, thus the wrapping bonding effect on the ceramic particles is small along with thermal attenuation of the temperature, the degreasing strength of the part can be established, and it is ensured that the blank has the sufficient strength margin to resist damage of gravity and thermal stress in a degreasing technology. The method can be used for improving the degreasing strength of the additive manufacturing ceramic part, and is especially suitable for additive manufacturing forming of ceramic parts of complex structures.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
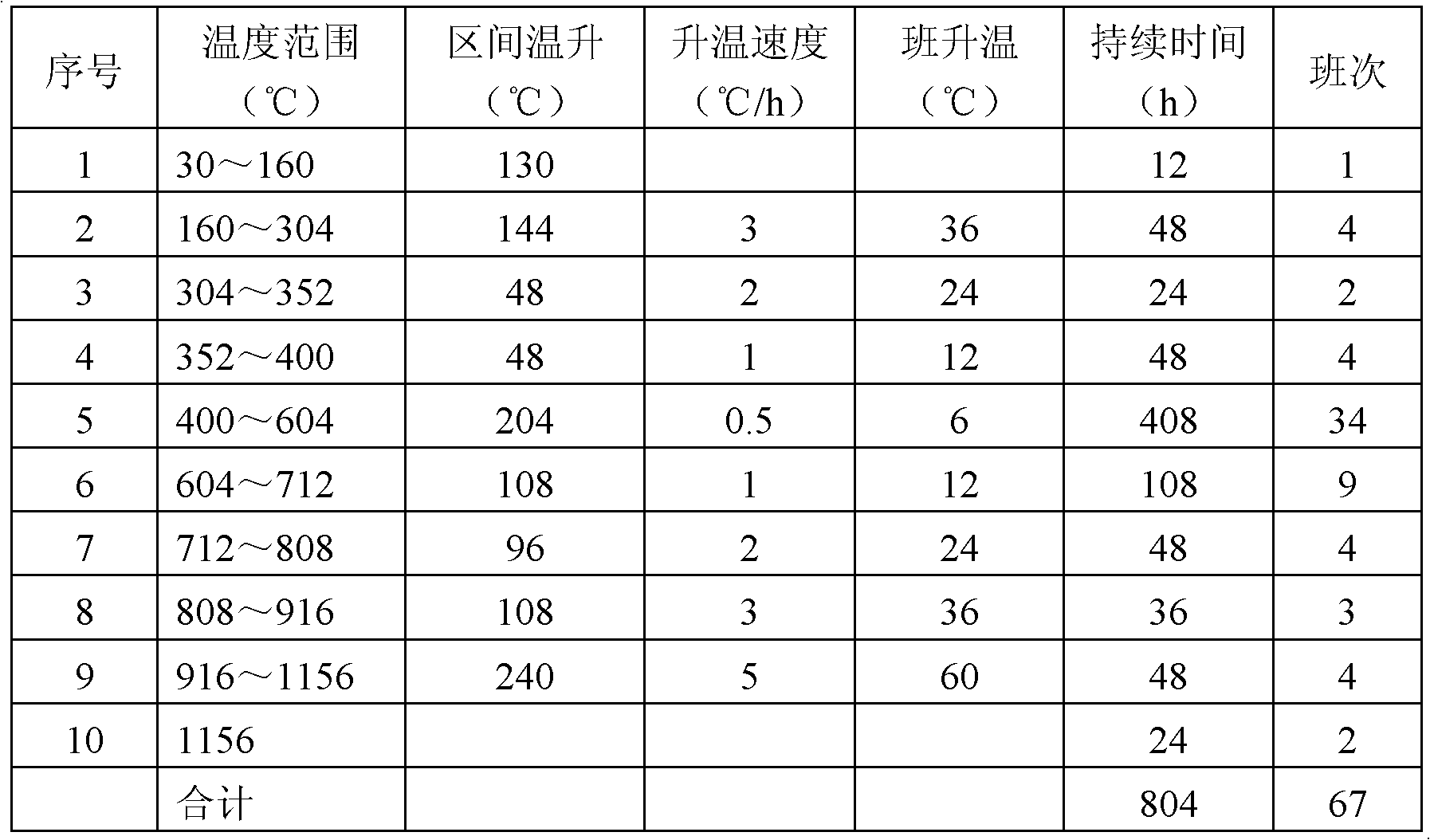
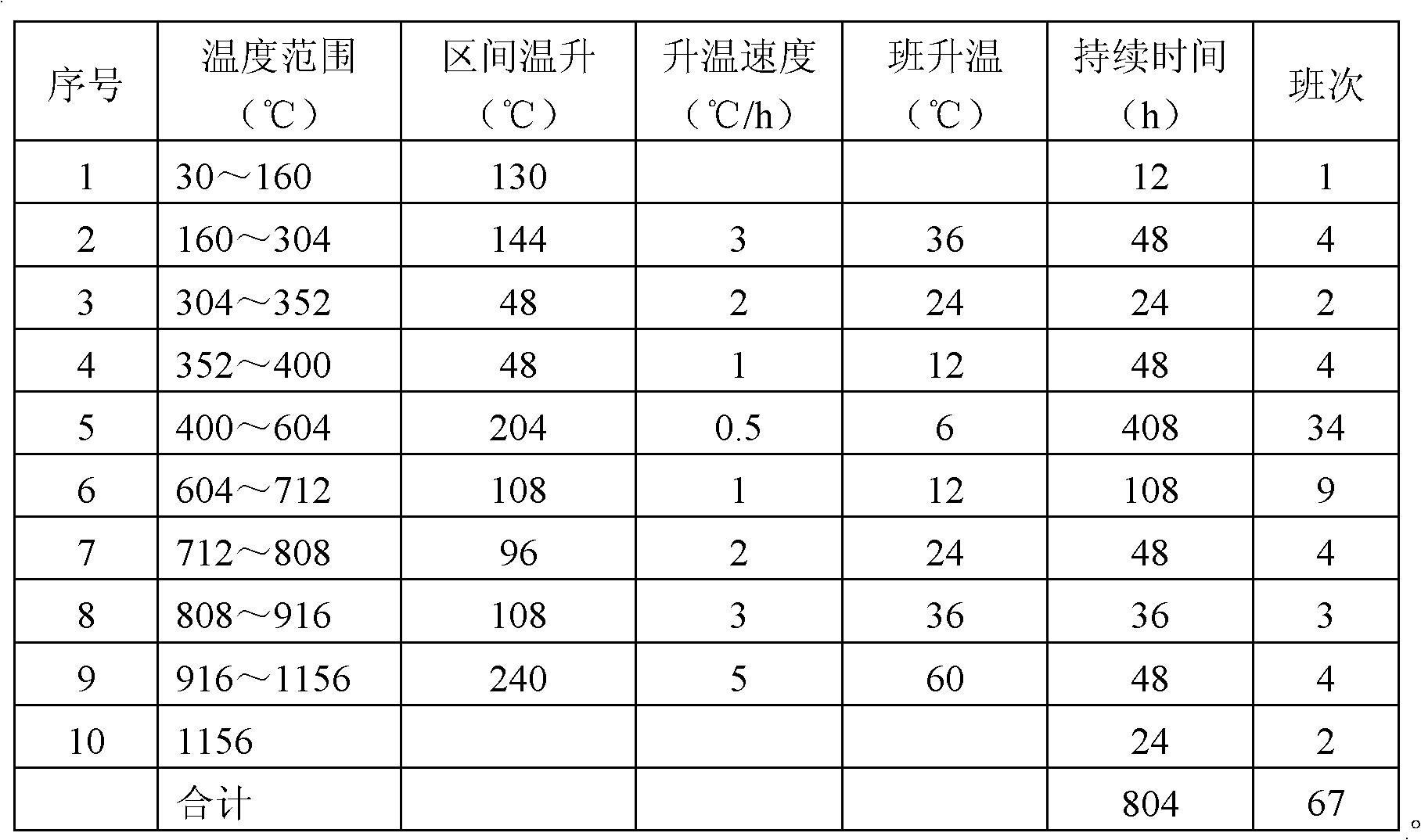
Pressurization roasting method for carbon
The invention provides a pressurization roasting method for carbon, and relates to a carbon roasting process. The pressurization roasting method for the carbon can avoid shell wastes, reduce the crack wastes caused by temperature difference and shorten the roasting time. The method comprises the following steps of: placing a compression green body product in a saggar, and filling a filler betweenthe product and the saggar; and after the product is filled in the saggar, sealing and vacuumizing, inflating nitrogen, placing in a roasting furnace, and heating, wherein the pressure is kept 2.5 to1.5 MPa, and when the pressure exceeds an upper limit, the pressure can be released through a valve and the valve is closed when the pressure is close to the lower limit. By using the anaerobic state, the shell wastes are avoided. By using the saggar, the periphery of the product is heated uniformly, the temperature difference among positions of the product can be reduced and the crack wastes caused by the temperature difference are reduced. An 804-hour roasting curve is performed for roasting and the roasting time can be reduced by about 12 percent. Through experiment, under the same condition, compared with the conventional carbon roasting method, the pressurization roasting method can obviously improve the product yield, coking rate, volume density and recovery yield.
Owner:福建兴朝阳硅材料股份有限公司
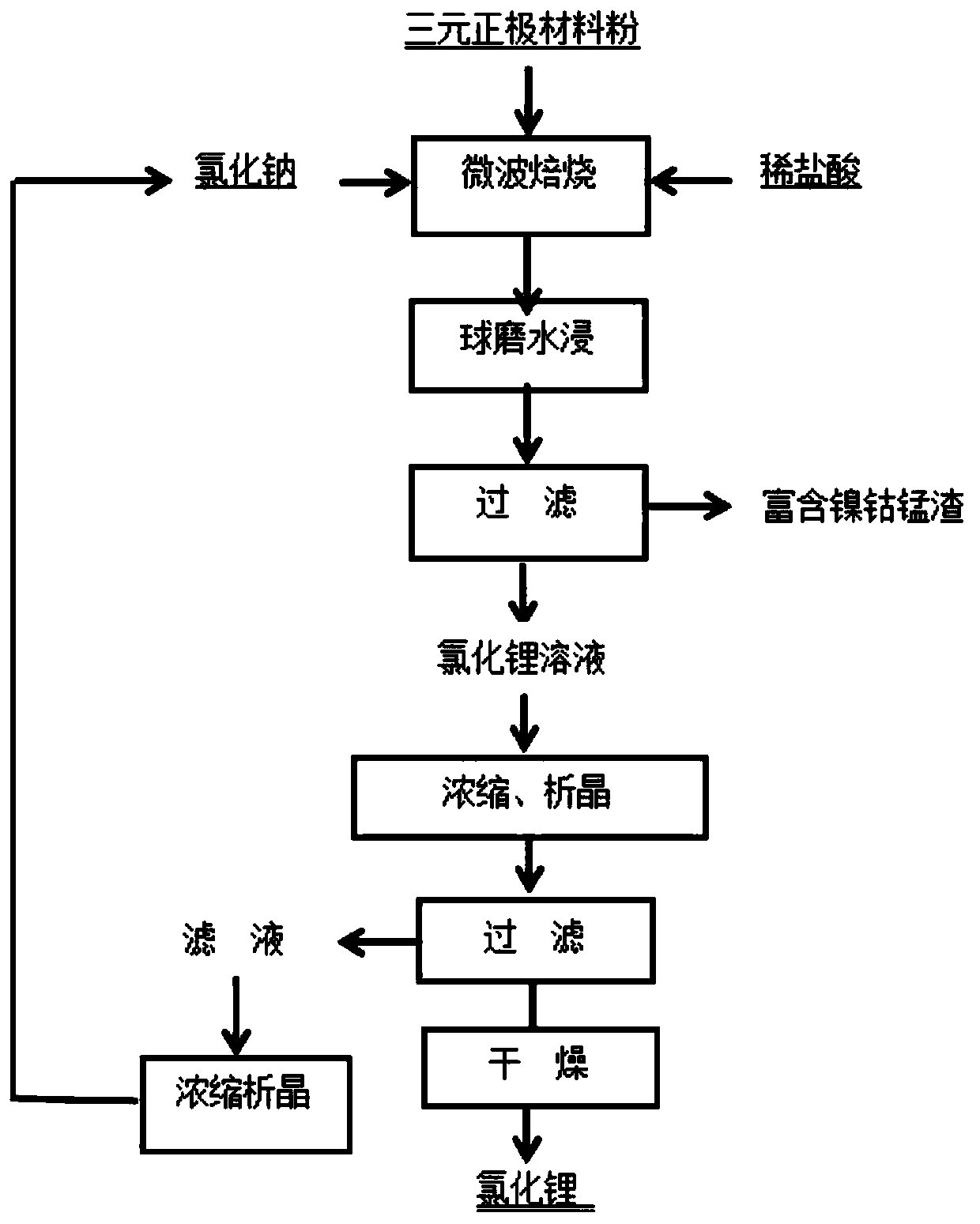
Method for recovering lithium in ternary positive electrode material by microwave roasting
ActiveCN110817905ALow ion contentLow firing temperatureLithium halidesBattery recyclingLithium chlorideRoasting
The invention relates to the technical field of lithium battery material recovery, and provides a method for recovering lithium in a ternary positive electrode material by microwave roasting, whereinthe method comprises the steps: mixing a waste ternary positive electrode material, diluted hydrochloric acid and an assistant, carrying out microwave roasting, carrying out ball milling and water leaching on the roasted product to obtain a lithium chloride solution, concentrating, crystallizing, carrying out solid-liquid separation, and drying to obtain lithium chloride. According to the method provided by the invention, conventional roasting is replaced with microwave roasting, materials are heated from inside to outside through microwaves, the roasting temperature is reduced, and the roasting time is shortened; ball-milling water leaching is adopted to replace crushing and water leaching or crushing and acid leaching in a traditional method, the water leaching process is accelerated through ball-milling water leaching, the leaching rate is increased, leachate hardly contains other high-valence metal ions, and lithium chloride can be directly prepared without purification and impurity removal.
Owner:GANZHOU NONFERROUS METALLURGICAL RES INST
Device and method for extracting vanadium from vanadium slag in suspension state through oxidizing roasting-acid leaching
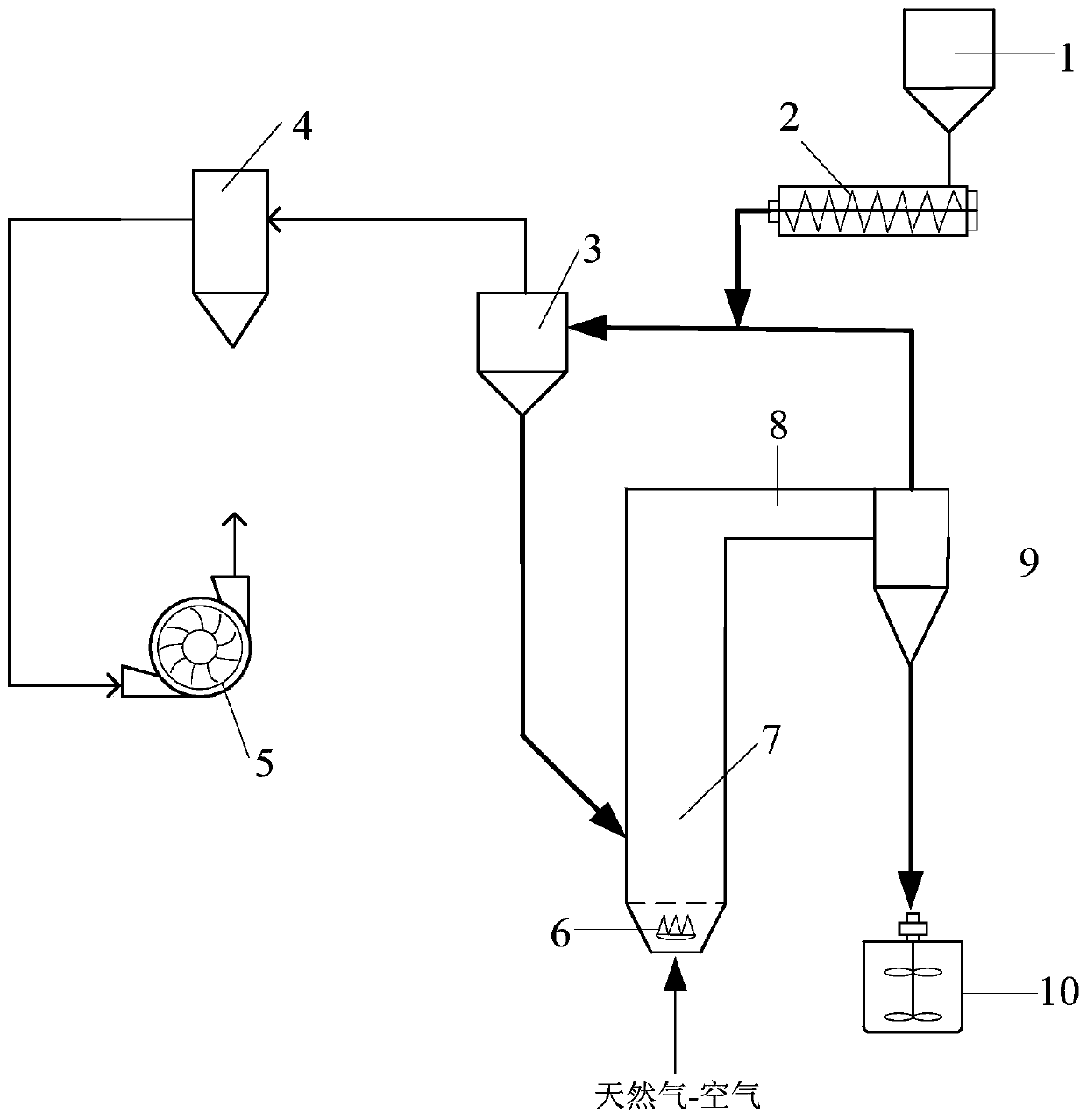
InactiveCN110172595AUniform temperatureAvoid High Temperature Bonding ProblemsProcess efficiency improvementCycloneCombustor
The invention provides a device and method for extracting vanadium from vanadium slag in a suspension state through oxidizing roasting-acid leaching. A stock bin, a screw feeder and a primary cycloneseparator in the device communicate with a suspension calciner in sequence, and the top of the suspension calciner communicates with a secondary cyclone separator; a discharging port of the secondarycyclone separator is opposite to an agitation leaching tank; and the bottom of the suspension calciner is provided with a burner. The method comprises the steps of placing vanadium slag powder into the stock bin, and conveying the vanadium slag powder to the primary cyclone separator through the screw feeder; enabling primary solid materials to enter the suspension calciner upon completion of gas-solid separation under the effect of negative pressure; holding the primary solid materials in a suspension flow state through high temperature oxidizing gas, and heating the primary solid materials to generate oxidization reaction; then, enabling secondary solid materials to enter the agitation leaching tank upon completion of gas-solid separation in the secondary cyclone separator; and performing stirring, leaching, filtering and separation. The device provided by the invention is high in gas-solid mass transfer and heat transfer efficiency, and high temperature bonding of the materials is avoided effectively; and the calcination time can be shortened greatly; and the production efficiency of the device is improved, and the energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for preparing water glass through extracting silicon oxide from chrysotile tailings by strong-base roasting method
ActiveCN105502426AReduce dosageShorten roasting timeMagnesium carbonatesAlkali metal silicatesPotassium hydroxideSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing water glass through extracting silicon oxide from chrysotile tailings by a strong-base roasting method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out processing, so as to obtain chrysotile tailing powder; (2) adding a strong base into the chrysotile tailing powder, carrying out uniform mixing, and carrying out a roasting reaction, so as to obtain a water glass containing active roasted product, wherein the strong base is sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, and the chrysotile tailing powder and the strong base are weighed in a mole ratio of SiO2 to (Na / K) being (1: 0.5) to (1: 6); (3) proportioning the active roasted product and industrial water in a solid-liquid mass ration of being (1: 5) to (1: 30), and carrying out a water soaking reaction for 20 minutes to 2 hours, so as to obtain a water glass containing suspension; (4) subjecting the suspension obtained in the step (3) to filtrating and dehydrating, so as to obtain a water glass filtrate and filtrated residue; (5) subjecting the water glass filtrate to spray drying, thereby obtaining the water glass. According to the method, the strong base serves as a chemical adjuvant and reacts with silicon oxide in the chrysotile tailings, and then, leaching is carried out so as to prepare the water glass, thus, the process flow and roasting time are short, the energy consumption is low, and the method is green and environmentally friendly and is beneficial to popularization and application.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stone coal vanadium ore oxidation grain breaking roasting comprehensive utilization method
ActiveCN111719054AHigh operating costsAdaptableSilicaProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionCyclonic separation
The invention discloses a stone coal vanadium ore oxidation grain breaking roasting comprehensive utilization method. The method is carried out according to the following steps (1) a stone coal vanadium ore is crushed and ground to obtain powder ore; (2) the power is delivered to a suspended decarburization roasting furnace for decarburization reaction; (3) a decarburized material is subjected tocyclone separation and then enters a suspended grain breaking roasting furnace to be subjected to a grain breaking oxidation reaction; (4) an oxidized material is discharged after cyclone separation;(5) cooling is conducted to 150-200 DEG C is conducted, acid mixing curing leaching, or directly leaching is conducted; (6) a leached material is filtered to obtain a V2O5 leaching solution; (7) filter residue is mixed with a sodium hydroxide solution for secondary leaching, and filtering is conducted to obtain a secondary filtrate; (8) hydrochloric acid is added into the secondary filtrate to generate white precipitate, and filtering is conducted to obtain third filter residue, and drying is conducted to obtain white carbon black. According to the method, sodium salt adding is not required byroasting, the problems of incomplete vanadium oxidation, low equipment processing amount, high operation cost and the like in a traditional process are solved, the process flow is simple, equipment and system operation are stable, and energy consumption and cost for unit processing amount are low.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
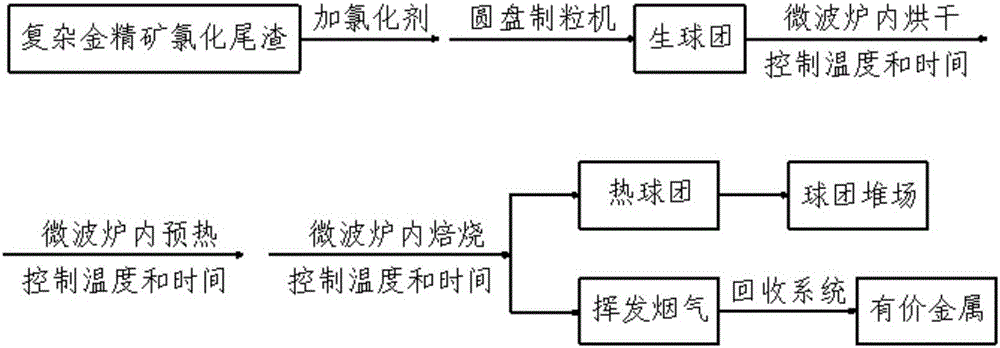
Method for treating complex gold concentrate cyanidation tailings through microwave chloridizing roasting and volatilization
InactiveCN105969979AShorten roasting timeEasy to recycleProcess efficiency improvementMicrowave ovenCyanide
The invention relates to a method for treating complex gold concentrate cyanidation tailings through microwave chloridizing roasting and volatilization. The method comprises the following steps: feeding a complex gold concentrate cyanide tailing mixture containing a chlorinating agent into a disk granulator, so as to obtain green pellets; sending the green pellets into an industrial microwave oven, setting certain temperature and time, and carrying out drying, preheating and roasting volatilization in sequence, so as to obtain volatilized flue gas and hot pellets, wherein the obtained flue gas contains valuable metals such as gold, silver and copper; leading the flue gas into a wet process recovery system via a draught fan for recovery; and sending the hot pellets into a pellet storage yard for sale after cooling. According to the method, the grade of gold in the tailings can be substantially lowered, the operation is easy and the technological process is short, the reaction temperature and time are reduced, and the subsequent treatment of the valuable metals such as gold in the discharged flue gas is relatively easy, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:新疆星塔矿业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com