High-temp. resistant isocitric dehydrogenase gene, its coded polypeptide and its preparation method
A technology of isocitrate dehydrogenase and high temperature resistance, applied in the field of mutation or genetic engineering, can solve the problems of no tricarboxylic acid cycle, lack of respiratory chain, and the inability of isocitrate dehydrogenase to generate acetate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
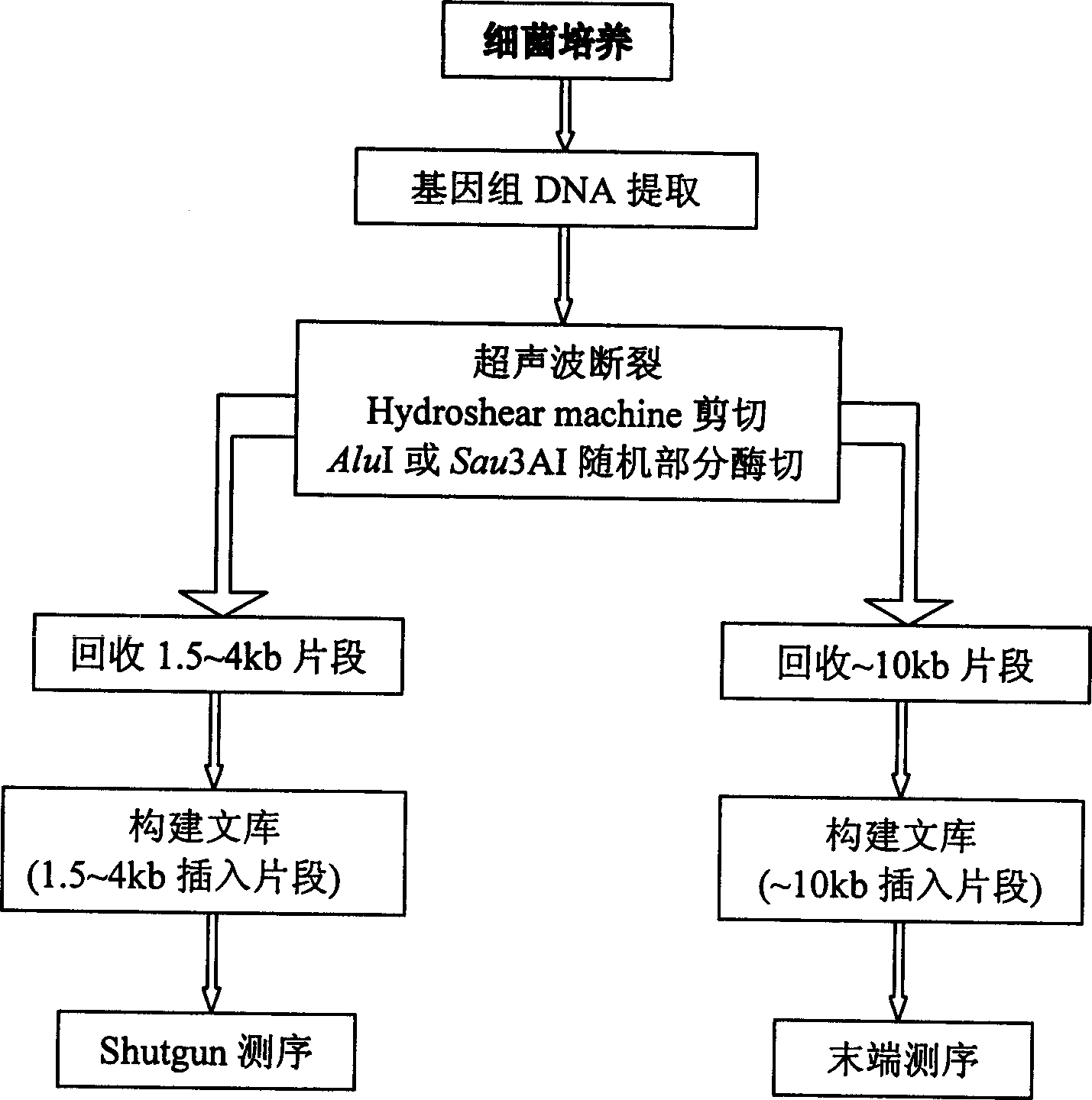
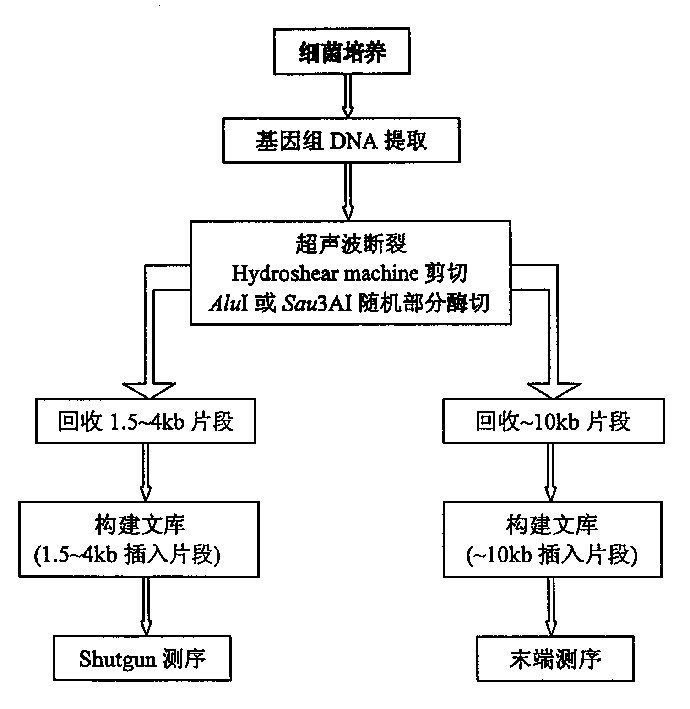
[0034] Example 1: Construction of a sequencing library
[0035] The sequencing library was constructed using the genome-wide shotgun method. Firstly, Tengchong thermophilic anaerobic bacteria were cultured according to (Yanfen Xue, 2000) modified MB medium (Balch et al., 1979), bacteria were collected according to Marmur (1961) method, and total DNA was extracted. In order to ensure the randomness of sequencing library construction and avoid the problem of hot spots of breakage to the greatest extent, a variety of methods and principles of library construction under different conditions were adopted. Firstly, physical shearing method (including ultrasonic method and shearing with Hydroshear Machine) was used, and then AluI was selected for random partial enzyme digestion according to the genome characteristics of the bacteria. Different intensities were used to process samples during physical shearing, and samples were processed by setting enzyme gradients during enzyme diges...
Embodiment 2
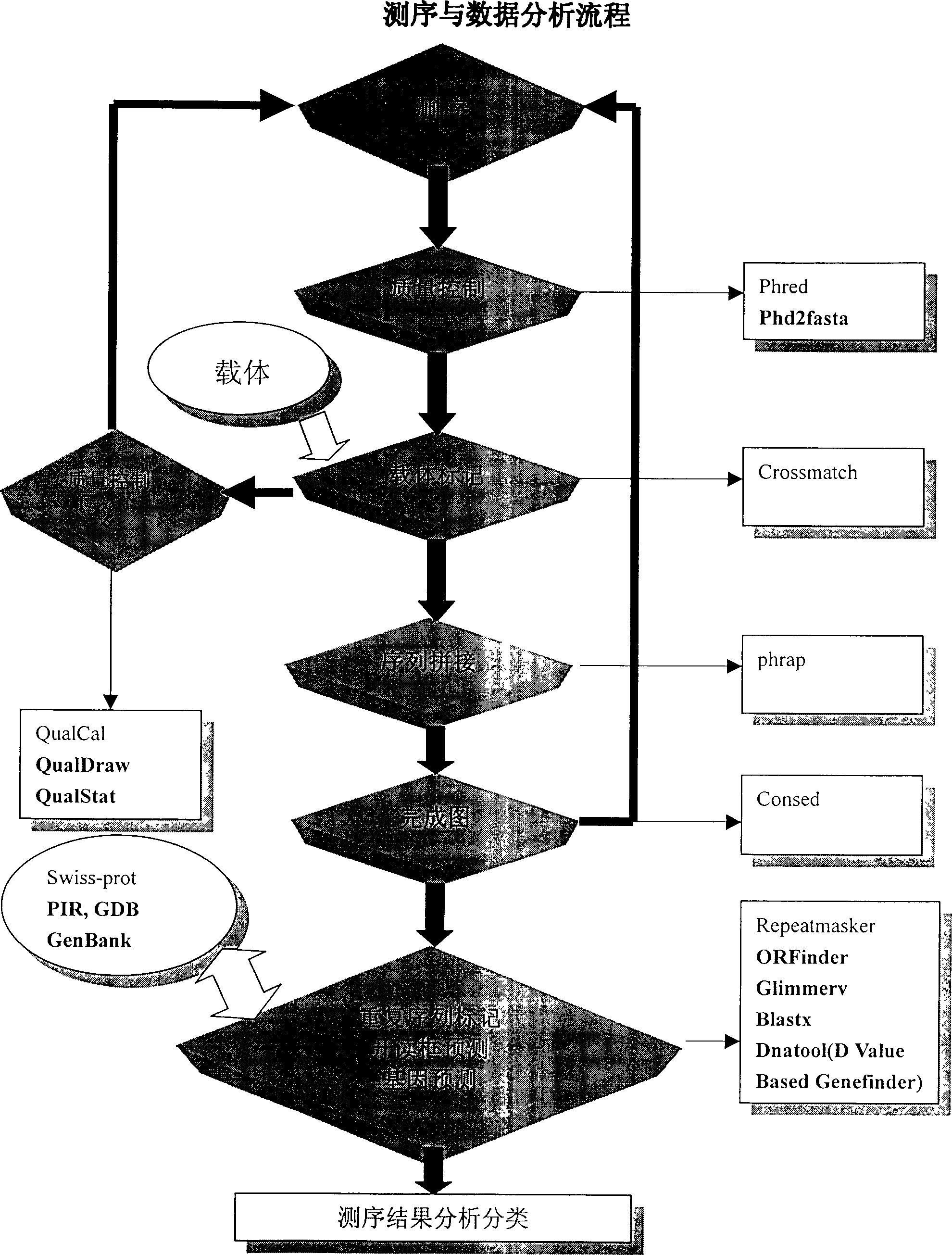
[0036] Example 2: Genome Sequencing
[0037] When sequencing the genome of thermophilic anaerobic bacteria in Tengchong, two automatic sequencers were mainly used: ABI377 and MegaBACE 1000. Both sequencers use the principle of electrophoresis for sequencing (see figure 2 ), 96 samples can be completed each time. ABI377 is a product of PE Company, which is a kind of ABI series. It belongs to the slab gel electrophoresis sequencer. MegaBACE 1000 is a product of Pharmacia, which belongs to capillary gel electrophoresis sequencer.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Basecalling and sequencing quality monitoring
[0039] The so-called basecalling refers to the process of obtaining the correct base sequence from the raw data file obtained on the sequencer. Since the sequencer obtains the intensity change traces (traces) of light of different wavelengths corresponding to the four bases A, T, G, and C, it is necessary to use a computer to adopt a certain algorithm to correctly identify the bases corresponding to the different traces. . We used Phred software (Ewing B, Hillier L, 1998) because its results are more reliable and its output is more convenient for further analysis by other programs in the same software package.
[0040] The algorithm principle of Phred's basecalling is to judge the base type based on the shape, distance, and signal-to-noise ratio of each peak in the trajectory, and at the same time give the credibility information for this base, that is, the sequencing quality of the base. In large-scale sequen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com