Frequency multiplier and semiconductor integrated circuit
A frequency multiplication circuit and circuit technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, modulation, transmission systems, etc., to achieve the effect of characteristic stabilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
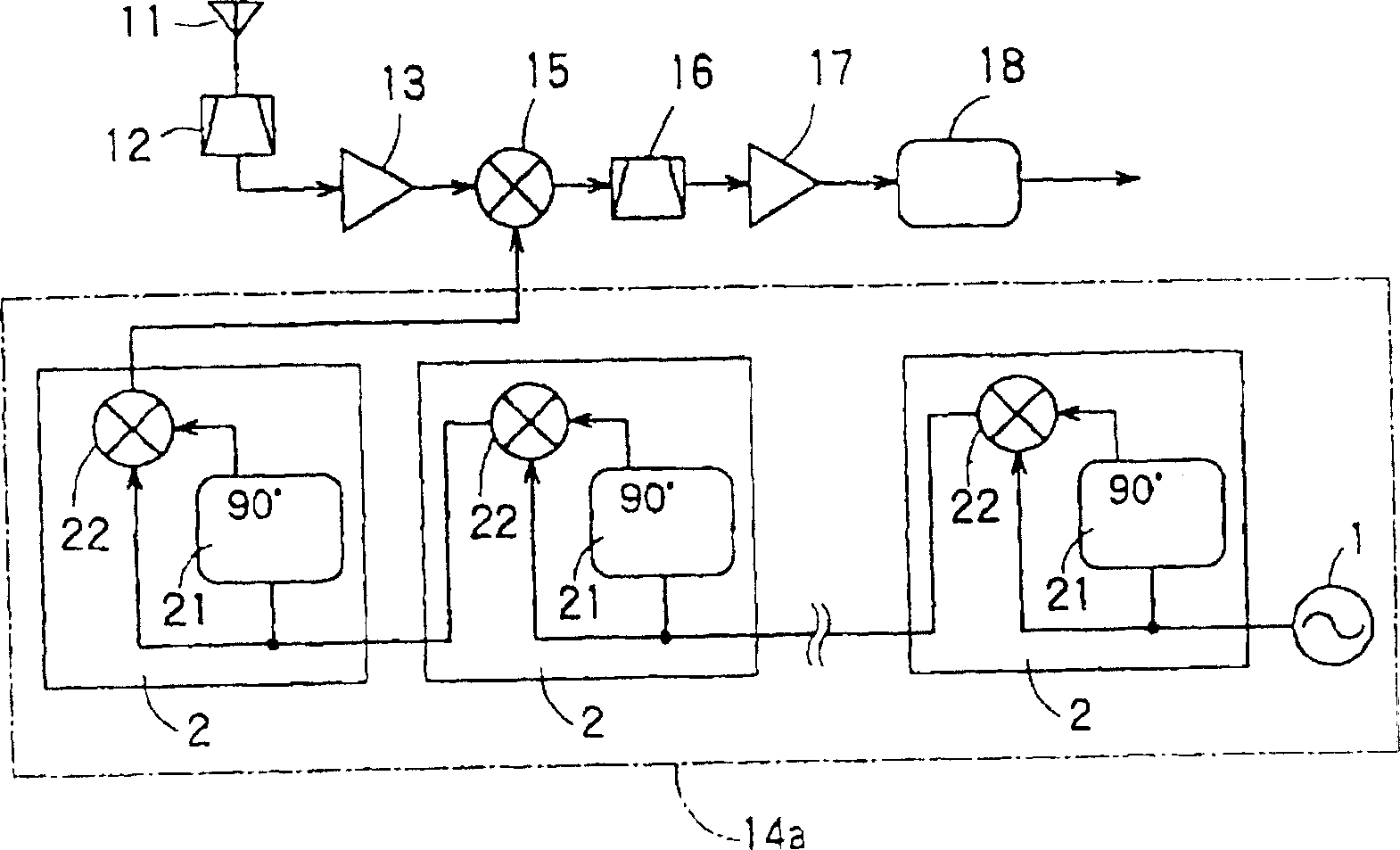
[0058] figure 1 It is a block diagram of Embodiment 1 of the receiver using the frequency multiplication circuit of the present invention. figure 1 The receiver, except for the source oscillation circuit 1 and the antenna 11, has been integrated into a single chip. in figure 1 In, for and Figure 15 The common parts are given the same reference numerals, and the differences are explained below.
[0059] figure 1 The frequency multiplier circuit, except the structure of the local oscillator circuit 14a that generates the local oscillator signal and Figure 15 The frequency multiplier circuit is different from Figure 15 The same composition.
[0060] figure 1 The local oscillation circuit 14a has a source oscillation circuit 1 that generates a source oscillation signal and a plurality of frequency multiplication circuits 2 connected in cascade. The frequency multiplier circuit 2 is actually a double frequency circuit that doubles the frequency of the input signal. A 90-degr...
Embodiment 2
[0110] In the first embodiment, when the shift of the phase shift by the phase shift circuit is not 90 degrees, the input waveform of the mixer contains a DC component. If a square wave is considered as a distorted wave, and when a square wave containing a DC component is multiplied by a mixer as an input waveform, in addition to (Equation 2), a square wave of the input signal will appear at the output of the frequency multiplier circuit. The frequency component of the wave. Consider the square wave as an even function when the interval from -X to +X is 1, and the other interval is -1, it can be expressed as
[0111] A(x-π / 2)+Asinxcosωt+A / 2·sin2xcos2ωt+A / 3·sin3xcos3ωt
[0112] +…+A / n·sinnxcosnωt
[0113] (Equation 3)
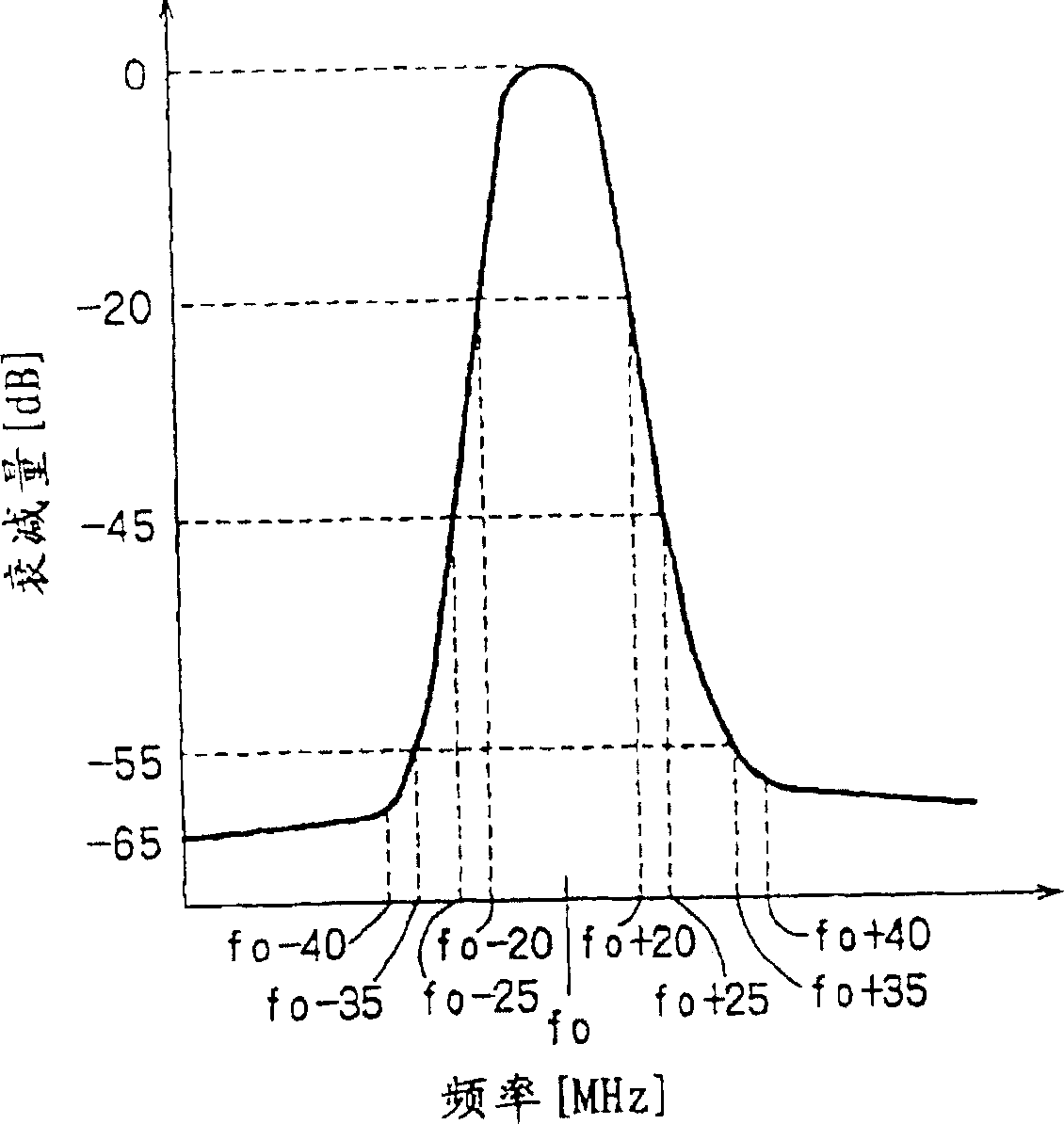
[0114] Among them, A is a constant, ω is the angular frequency 2πfL0, t is time, n is a natural number, and the first term is the DC component. For example, if n=2 and the source oscillation frequency is f0, the frequency output from th...
Embodiment 3
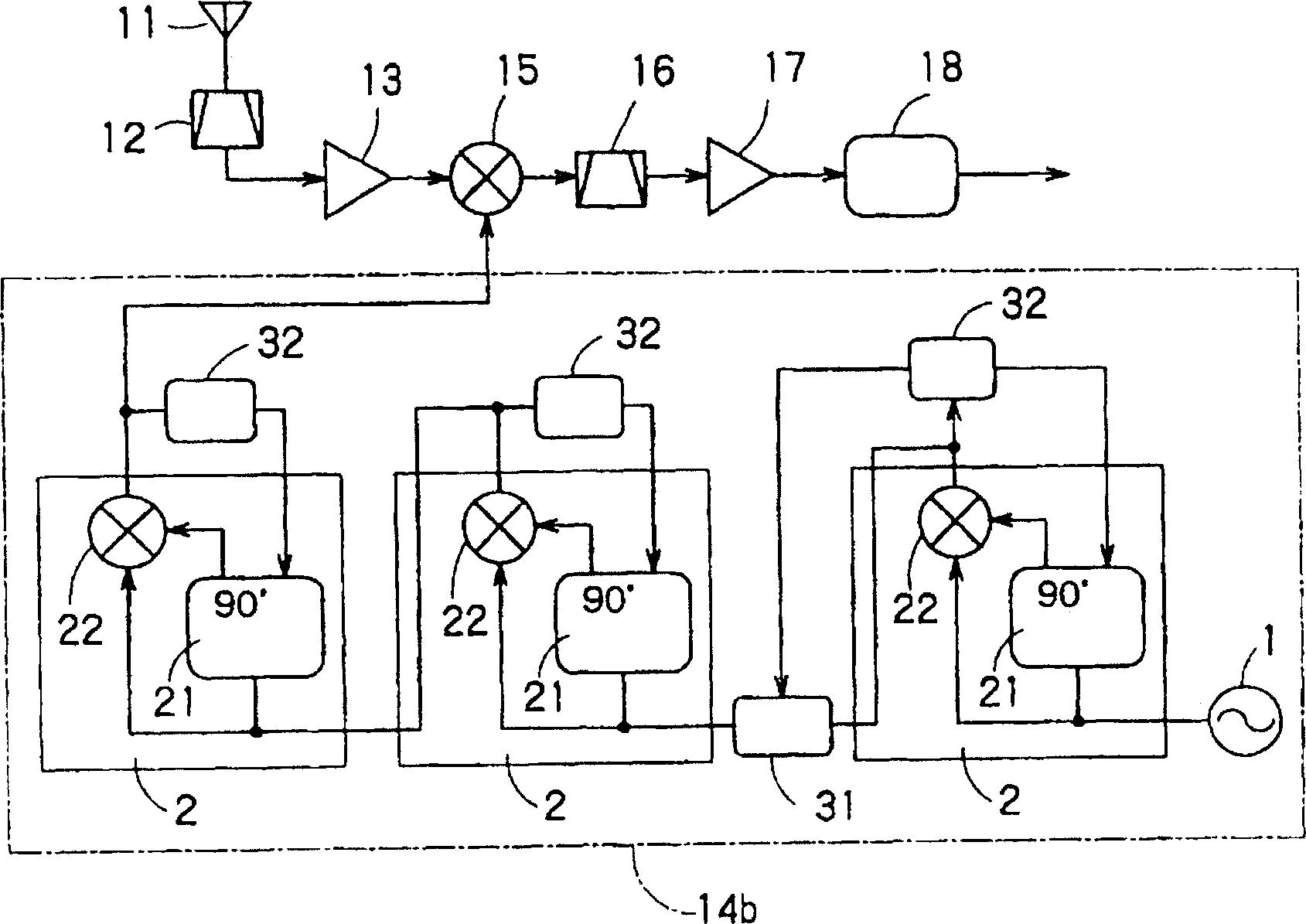
[0195] The frequency multiplier circuit of the third embodiment, the configuration of the 90-degree phase shift circuit 21 and the filter circuit 31 are different from those of the second embodiment.
[0196] Figure 6 The circuit diagram shows the detailed configuration of the 90-degree phase shift circuit 21a of the third embodiment. Figure 6 The 90-degree phase shifting circuit 21a is a CR phase-shifting circuit using semiconductor devices (transistors), and its composition is a 45-degree phase shifting part (first and second phase shifting parts) 60-level phase shifting 45 degrees in two stages Link up.
[0197] Figure 6 The 45-degree phase shifting part 60 has transistors Q1 and Q2 for supplying the output of the reference oscillator 41 to the base terminal, connected to the capacitor C5 between the emitter terminals of the transistors Q1 and Q2, and respectively connected to the emitters of the transistors Q1 and Q2. Current sources 61, 62 on the terminals. The current s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com