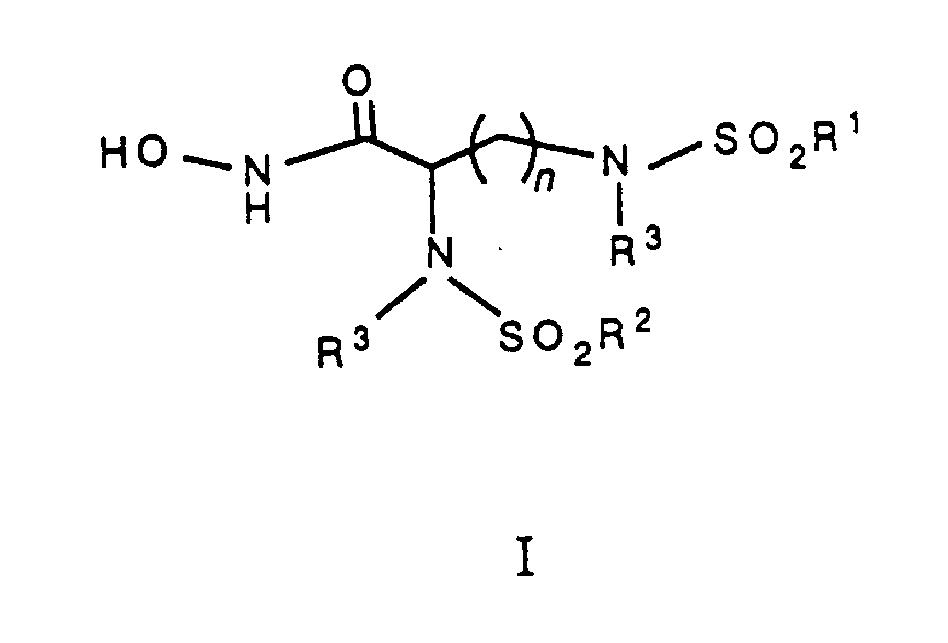
Bis-sulfonomides hydroxamic acids as MMP inhibitors
A compound, butanamide technology, applied in the direction of amide active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problem of no treatment method for preventing tissue damage and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The compound of the present invention can be prepared according to any one of the following two preparation methods. When the two sulfonamide groups are the same, the steps outlined in Scheme A are used. When the sulfonamide groups are different, the steps outlined in Scheme B are used.
[0029] As shown in Scheme A, bissulfonamide 2 can be prepared from amino acid 1 by the method described in the Proceedings of the American Chemical Society, Volume 59, Page 1116 (1937). Simply put, in the presence of 1N sodium hydroxide, the amino acid 1 is exposed to a predetermined at least 2 equivalents of sulfonyl chloride to obtain bissulfonamide 2. The starting reactant, amino acid 1, can be either a commercially available product or can be conveniently prepared according to the method disclosed in the Journal of the Chemical Society (English), No. 1564 (1939). Disulfonamide 2 reacts with a peptide coupling agent in the presence of o-benzyl hydroxylamine hydrochloride, 4-methylmorpho...
Embodiment 1
[0039] The following related examples can better understand the compounds and their preparations of the present invention. The purpose of the examples is to illustrate the present invention but does not limit the scope of protection of the present invention. Example 1 of N-hydroxy-2,4-bis-[[4-methylphenylsulfonyl]amino]butyramide
[0040] preparation Step 1. Preparation of 2,4-bis-[[4-methylphenylsulfonyl]amino]butyric acid
[0041] At room temperature, to a solution of 5.00g (26.2mmol) 2,4-diaminobutyric acid dihydrochloride and 130ml (130mmol) 1N sodium hydroxide was added 11.0g (57.6mmol) in 130ml ether at a time. Toluenesulfonyl chloride solution. The two-layer solution was stirred at room temperature for 16 hours. Separate the ether layer and acidify the aqueous layer to pH 2. The solid was collected, washed with water, air dried, and dried at 50°C under high vacuum. The product was crystallized from isopropanol / pentane to obtain 4.33 g of the title comp...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The o-benzyl hydroxamic acid intermediate (0.50 g, 0.94 mmol) and 0.10 g Pearlman's catalyst were hydrogenated in 75 ml methanol under 5 psi conditions for 2.5 hours. The mixture was filtered through Celite, the filtrate was evaporated, and the product was dried under vacuum to obtain 0.395 g of the title compound. 1 H NMR(CDCl 3 ) 1.88, 2.32, 2.35, 4.01, 7.21, 7.7; MS m / z[MH + ]442. Example 2. (R)-N-hydroxy-2,4-bis-[[4-methylphenylsulfonyl]amino]butyryl
[0047] Preparation of amine
[0048] According to the conventional method of Example 1 without important changes, but with (R)-2,4-diaminobutyric acid as the starting reactant, the title compound (melting point: 152-153°C) was prepared. [α] D =-8°(DMSO); 1 H NMR(DMSO) 1.54, 2.35, 2.37, 3.3, 7.28-7.36, 7.57; MS[MH + ]m / z 442.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com