Dispersible nonwoven fabric and production thereof
A technology for non-woven fibers and woven webs, which can be used in non-woven fabrics, textiles, papermaking, textiles, etc., and can solve problems such as non-woven webs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0052] experiment method
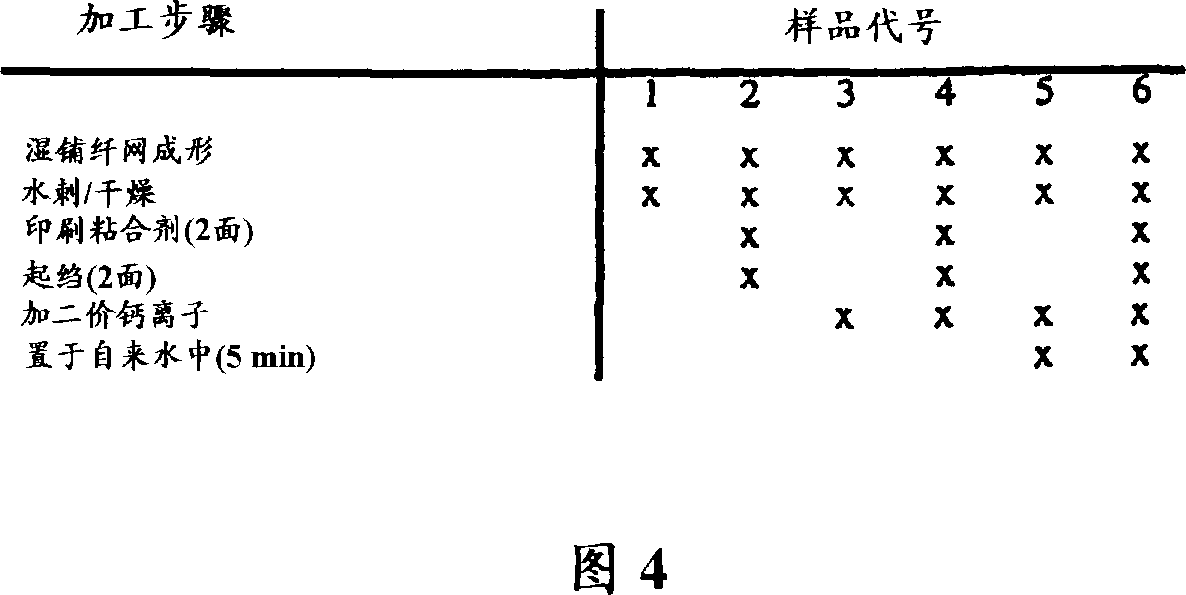
[0053] Holding Tensile Test: The holding tensile test is to measure the breaking strength and elongation or strain of the fabric when it is subjected to unidirectional stress. This test is known in the art and performed in accordance with Federal Test Methods, Standard 191A, Method 5100 (ASTM Standard, D-1117-6 or D-1682). Results are expressed as pounds to break and percent elongation before break. The higher the number, the stronger and more stretchable the fabric. The term "load" refers to the maximum load or force, expressed in units of weight, required to break or break a specimen in a tensile test. The term "strain" or "total energy" refers to the total energy under the load-elongation curve, expressed in weight-length units. The term "elongation" refers to the increase in length of a sample during a tensile test. Bar tensile strength and elongation values are obtained using fabric samples of specified width, typically 1 inch (25 mm), spe...
example 1
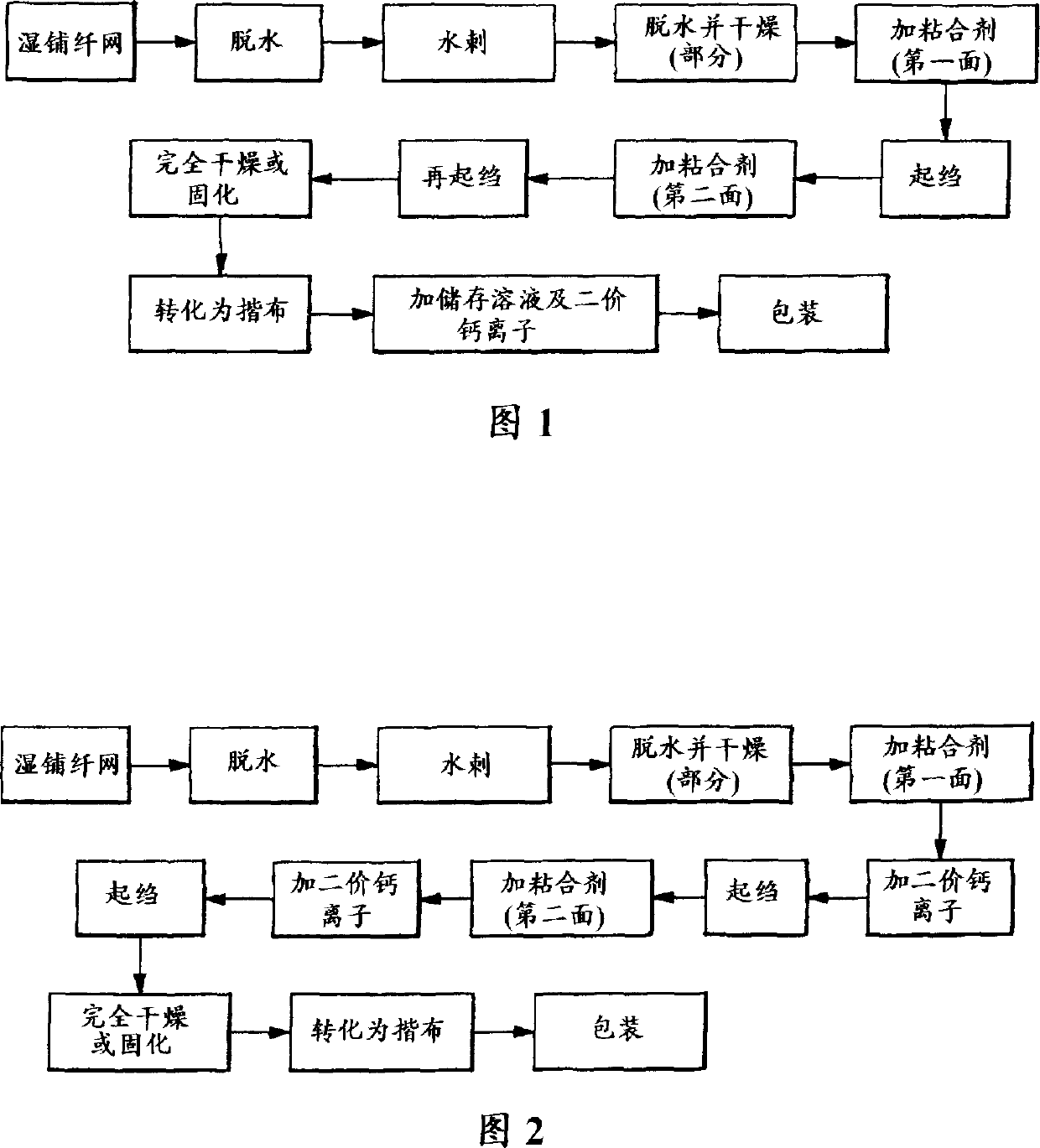
[0054] Example 1 - Moist wipe formation (see Figure 1)
[0055] A. wet laying method
[0056] The pulp of basic composition is as follows, 50wt% northern softwood unrefined log fiber pulp (Longlac 19, Kimberly-Clark company provides); 30wt% secondary (wastepaper) fiber pulp (wastepaper pulp of BJ deinking ( Ponderosa Pulp Products, Inc., a division of Ponderosa Fiber Corporation Americas, Atlanta, Ga.); 20 wt% Southern Softwood Kraft Pulp; and 0.33% Aerosurf PA-227 Debonding Agent, Aerosurf-Witco Inc. (Dublin, Ohio), as per Traditional papermaking technology wet-laid on the multi-layer wire mesh fabric. This supporting wire mesh is PRO 47, and the forming concentration is 0.187%. The pulper is 45#, and each batch produces a roll of material. The speed of the production line is 50 feet per minute, basis weight 65 gsm, width 22 inches. The web (ie, web) was dewatered to a moisture content of about 500% dry weight of the web.
[0057] B. Spunlace processing
[0058] The suppor...
example 2
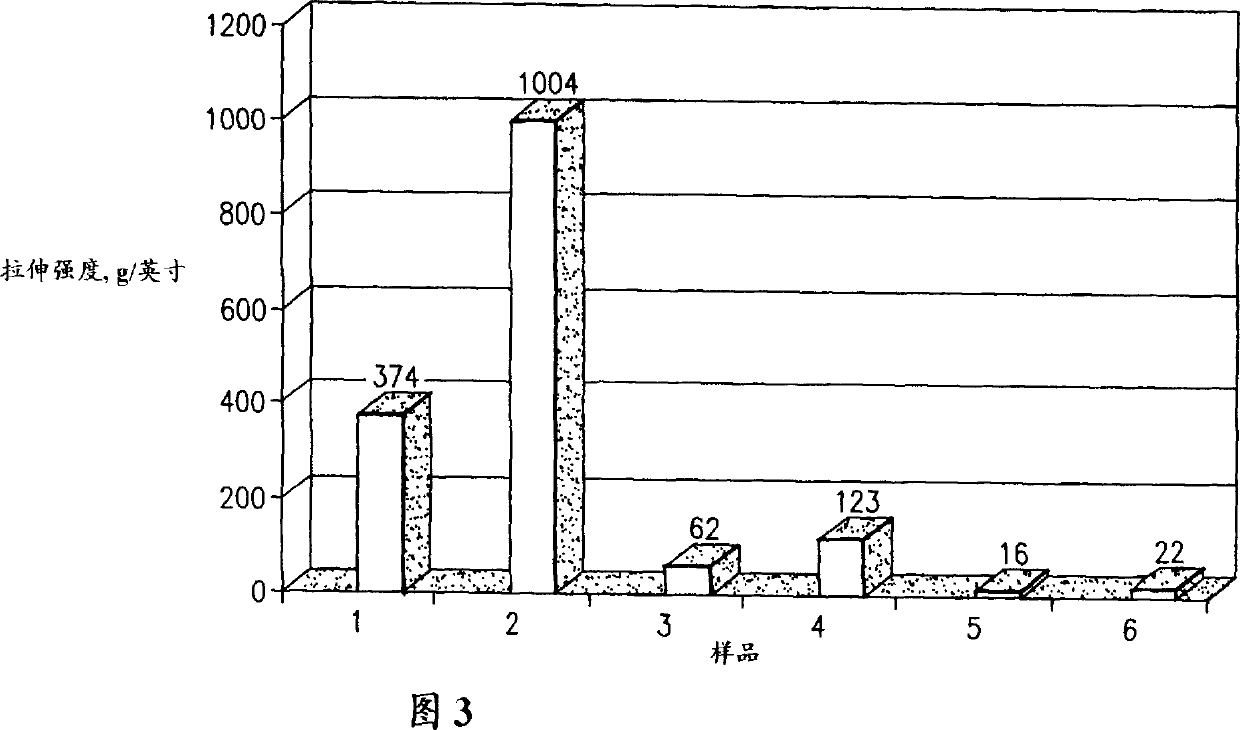
[0079] Example 2 - Dry wipe forming (see Figure 2)
[0080]Fiber web is formed according to the method for example 1, steps A~C. After the adhesive composition was applied on the first side, the calcium ion solution was sprayed on the same side to obtain an application level of calcium ions of about 100 ppm based on the basis weight of the paper web. The web was creped and adhesive was applied on the second side as described in Example 1, Steps E and F. The calcium ion solution was sprayed on the second side to obtain an applied amount of calcium ions of about 100 ppm based on the basis weight of the paper web. The web was then recreped and dried as described in Example 1, Steps F and G. As a finishing touch, the web is completely dried and made into a dry wipe product.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com