Laser machining apparatus
A laser processing and laser technology, which is applied in laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, optics, etc., can solve the problems of focus distance change, reduced productivity, and processing position offset, etc., to achieve the effect of stabilizing laser processing and avoiding temperature changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
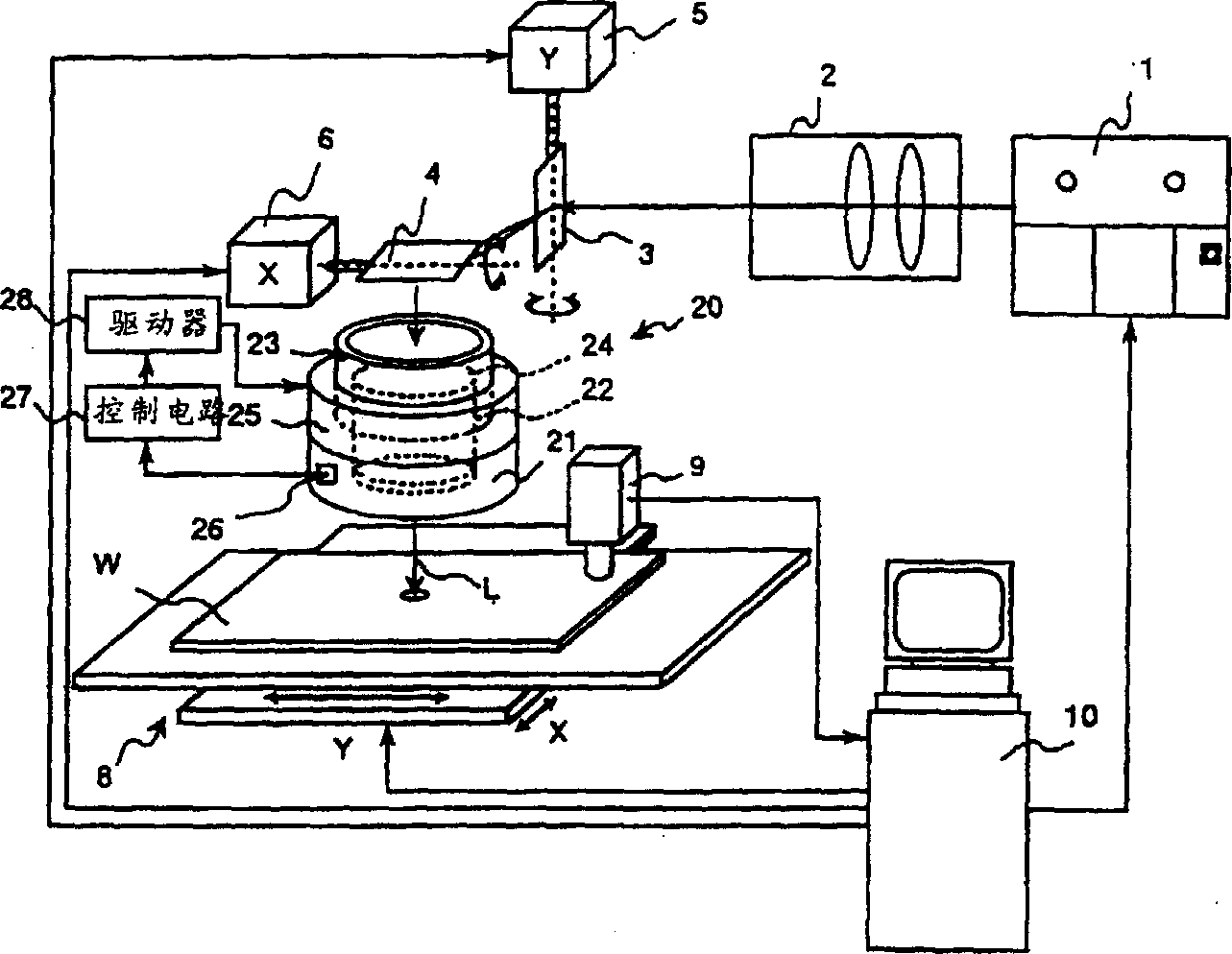
[0165] figure 1 It is an overall configuration diagram showing Embodiment 1 of the laser processing apparatus of the present invention.
[0166] The laser processing apparatus of Example 1 has a lens position adjustment device that changes the relative position between the lenses of the focus lens according to the temperature of the focus lens in order to eliminate the temperature change of the refractive index of the lens of the structure focus lens.
[0167] exist figure 1 , the focusing lens is denoted by reference numeral 20 . The focusing lens 20 is an fθ lens, and injects the laser light L deflected by the Y-axis galvano mirror 3 and the X-axis galvano mirror 4 to focus the laser light as in the conventional device.
[0168] In the laser processing apparatus of the present embodiment, the focus deviation of the focus lens 20 caused by the temperature change of the focus lens 20 is corrected by autofocusing (focusing) compensation.
[0169] Therefore, the focusing le...
Embodiment 2
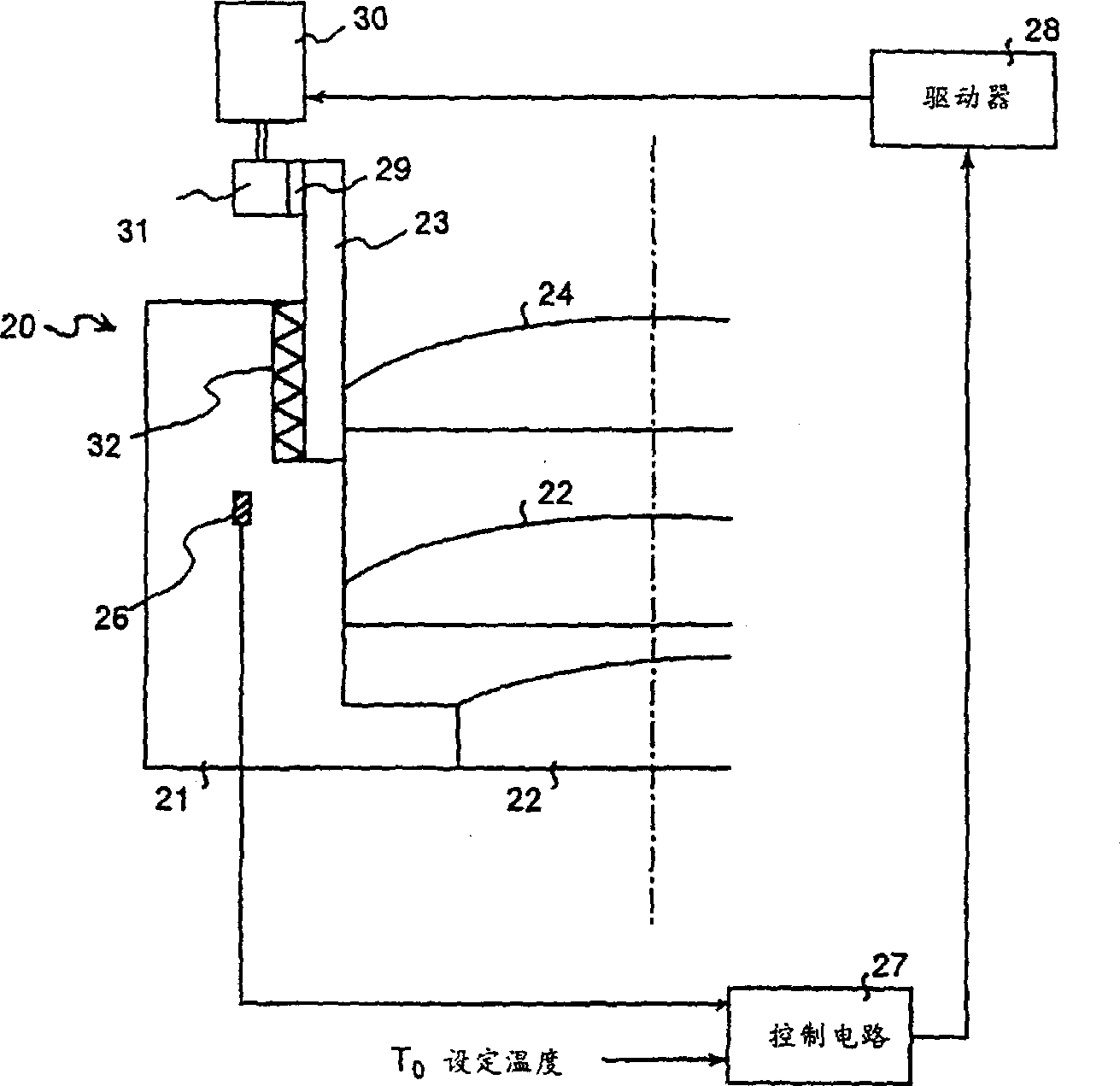
[0179] image 3 It is Example 2 which shows the laser processing apparatus of this invention.
[0180] In the laser processing device of this embodiment, the focus deviation of the focus lens 20 caused by the temperature change of the focus lens 20 is corrected by automatic focusing, and the movable lens 24 is supported on the lens holder 21 by a piezoelectric (piezo) element 33. The electric distortion of the electric element 33 directly displaces the movable lens 24 in the direction of the optical axis.
[0181] The control circuit 27 compares the preset set temperature T0 with the temperature of the focus lens 20 detected by the temperature sensor 26, and the deviation Δf of the focus distance f of the focus lens 20 produced by eliminating the temperature difference A command signal is supplied to the driver 28 of the piezoelectric element 33 in order to displace the movable lens 24 .
[0182] Therefore, the movable lens 24 is moved in the direction of the optical axis co...
Embodiment 3
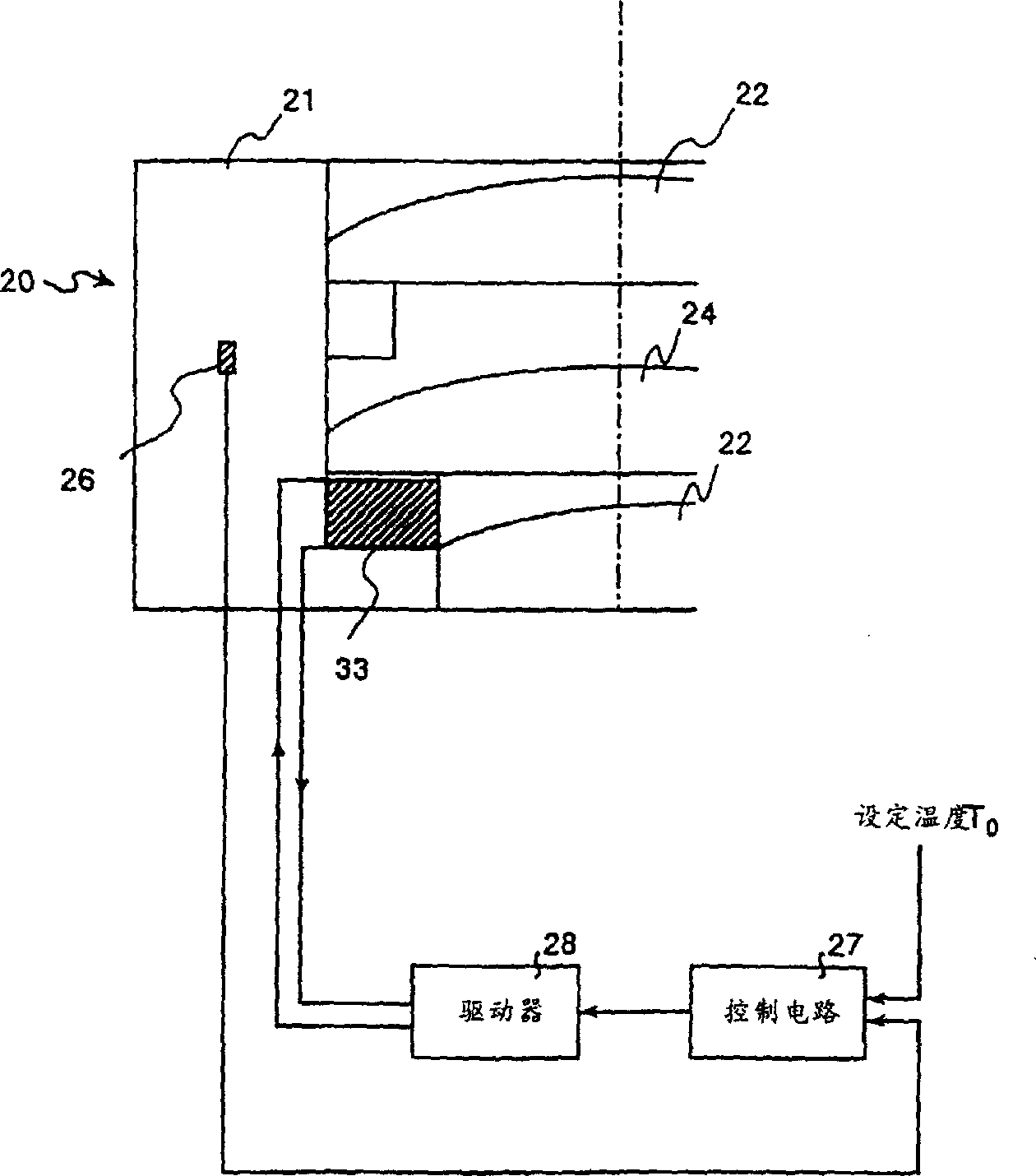
[0185] Figure 4 It shows Example 3 of the laser processing apparatus of this invention.
[0186] In the laser processing device of this embodiment, the focus deviation of the focus lens 20 caused by the temperature change of the focus lens 20 is corrected by automatic focusing, and the movable lens 24 is supported by the lens holder 21 by the temperature-elasticity holding part 34. Due to the temperature-elasticity The temperature expansion and contraction of the holding fitting 34 directly displaces the movable lens 24 in the direction of the optical axis.
[0187] For the temperature-elasticity holding fitting 34, select a material whose thermal expansion coefficient is negative for the fixed lens 22 and the temperature characteristic of the movable lens 24 (the temperature change rate of the focal distance f), for example, it can be made of calcite (CaCO3) and other structures, and the temperature changes The stretchability of the movable lens 24 displaces in the directio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com