Medical internal marmem frame coated by high-molecular film for penetration therapy and its preparing process
A memory alloy and internal stent technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of poor biocompatibility, easy thrombosis, poor biocompatibility of metal stents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
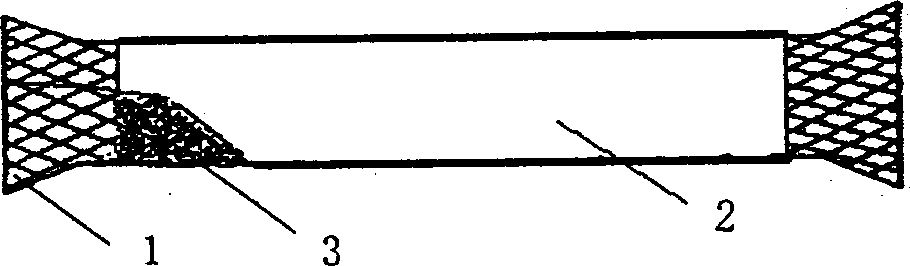
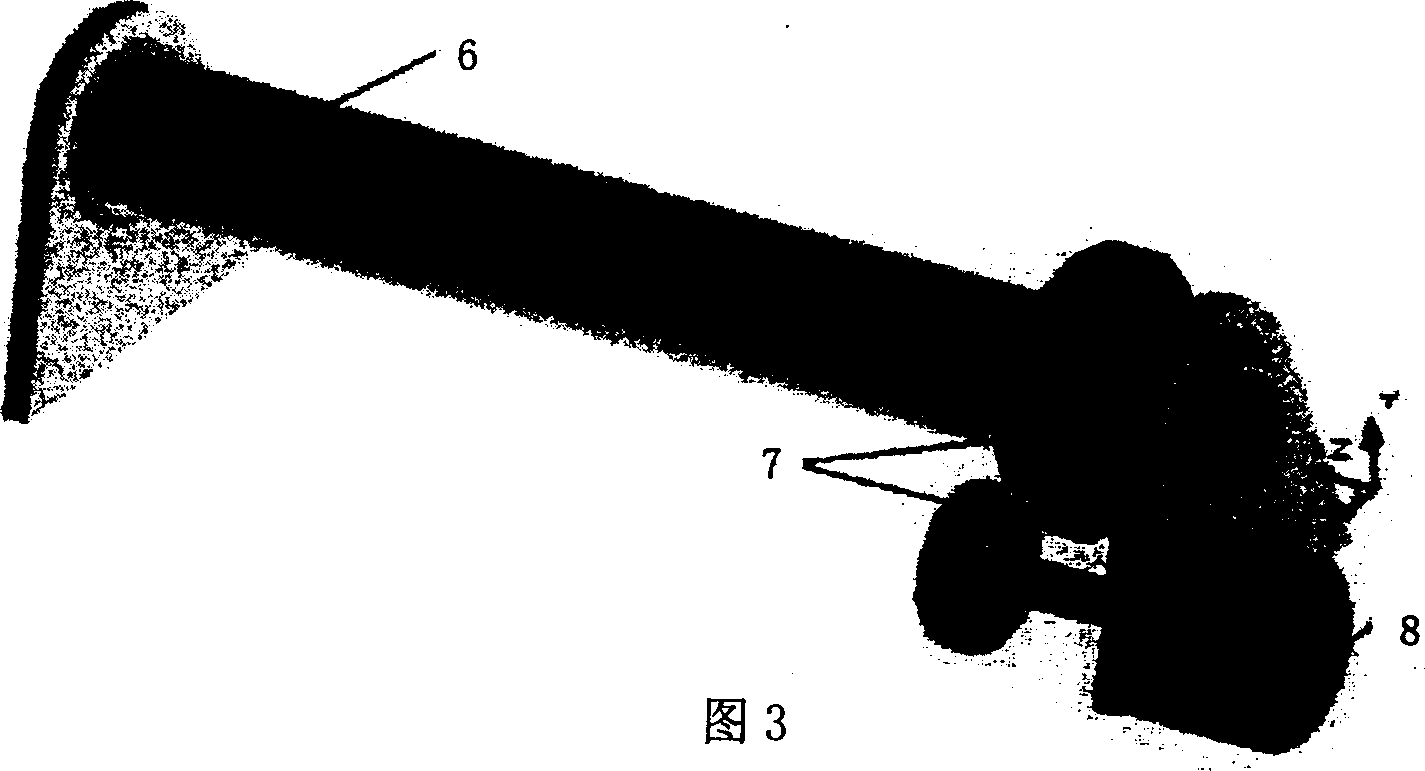
[0024] endometrial manufacture, such as figure 1 Shown is a stent covered with intima, and its production method is as follows: use soft polyethylene film to wrap the surface of the metal alloy stent (when wrapping, try to be as flat as possible to ensure the flatness of the formed intima), heat it slightly The film hardens. Then put 0.1 g / ml polyurethane tetrahydrofuran solution inside the bracket, and rotate the bracket to volatilize the solvent to form a film (just at room temperature). The motorized device shown in Figure 3 can be used for film formation, and the entire bracket is placed inside the sleeve, and the motor drives the rotation. After the polymer film is fully set (generally, the solvent can be fully developed for 3 to 4 hours at room temperature), the polyethylene film can be peeled off. The intima formed by this method has good uniformity, is solidly integrated with the metal stent, and has relatively strong impact resistance, which ensures that the membran...
Embodiment 2
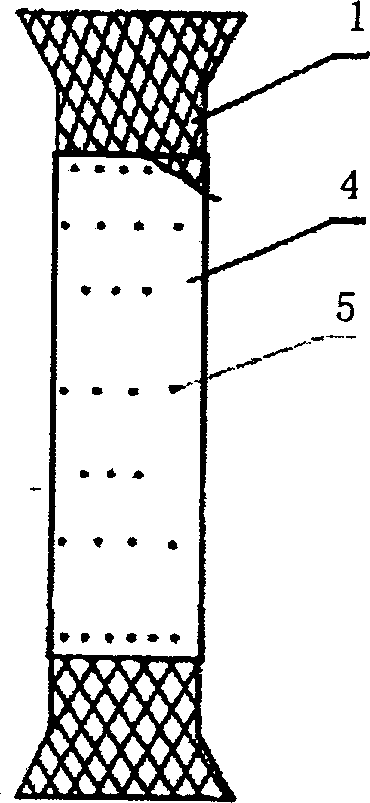
[0026] For the manufacture of the outer membrane, we adopt the process of film formation and membrane separation. First, prepare the sleeve of the outer membrane according to the size of the metal alloy stent (the outer membrane mold cylinder is not adhered to the polyurethane membrane). The device puts 0.1g / ml polyurethane tetrahydrofuran solution in the outer membrane sleeve, and rotates the sleeve to volatilize the solvent to form a film. The resulting outer membrane is removed, and then the outer membrane is bonded to the fulcrum of the alloy stent by using saturated polyurethane solution as an adhesive. When bonding, attention should be paid to taking more bonding points at both ends of the adventitia to improve the firmness of the adhesion between the adventitia and the stent. (See figure 2 )
Embodiment 3
[0028] To manufacture the microporous inner membrane, we add an appropriate amount of sieved pore-forming agent to the 0.1g / ml polyurethane solution (salt is used as the pore-forming agent in this example, and the specific sieving size depends on the micropore requirements for medical use. Examples employ 100 micron sieves). Experiments show that when the salt concentration is 0.06-0.07g / ml, the microporous membrane has a better porosity and does not affect the strength requirement of the membrane. The specific process of forming an inner film is similar to that of Example 1. Finally, wash away the salt grains on the stent that formed the intima with warm water.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com