Selective catalytic reduction of NO, enabled by side stream urea decomposition
A tributary, urea technology, applied in the direction of dissolution, separation methods, fluid mixers, etc., can solve problems such as deposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
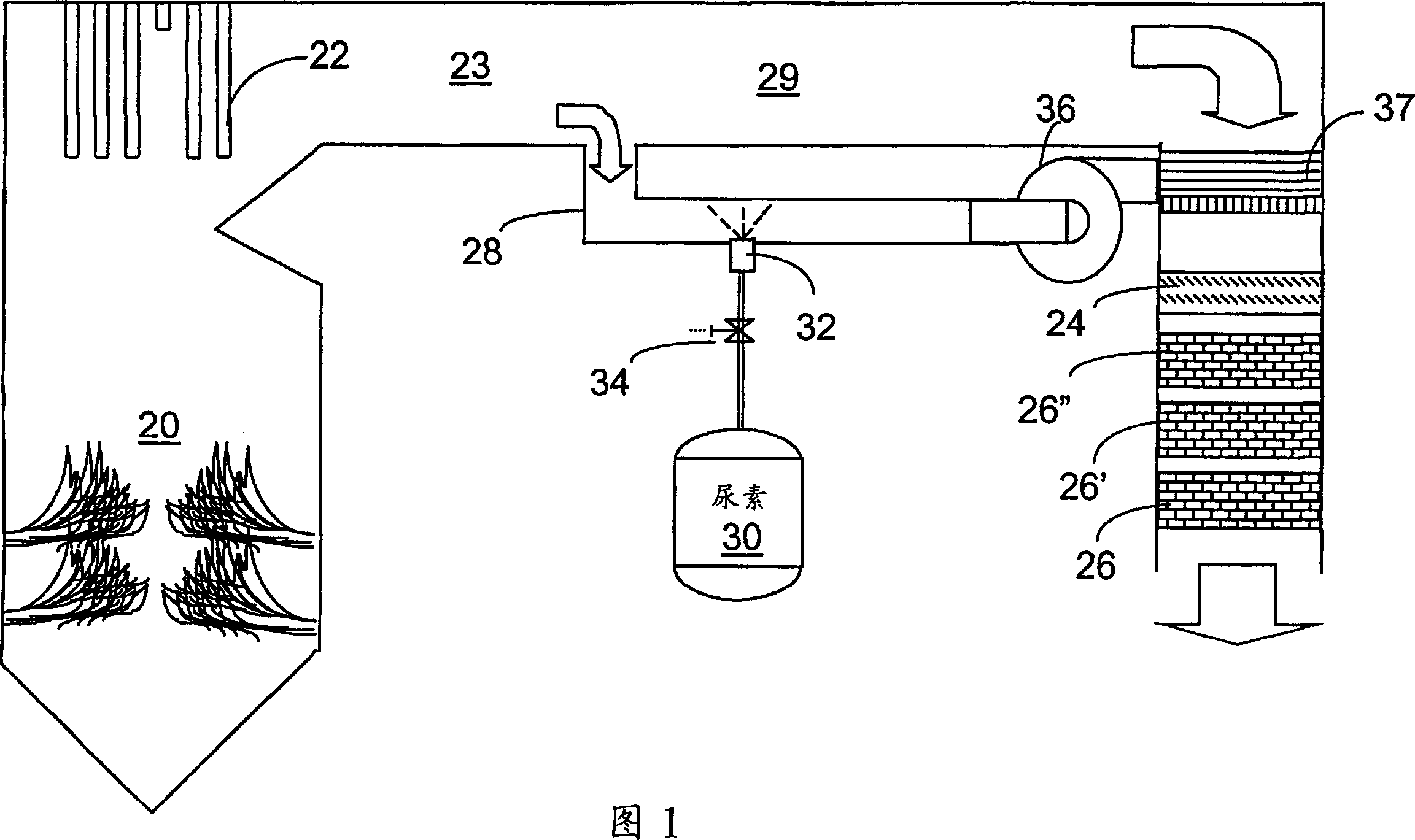
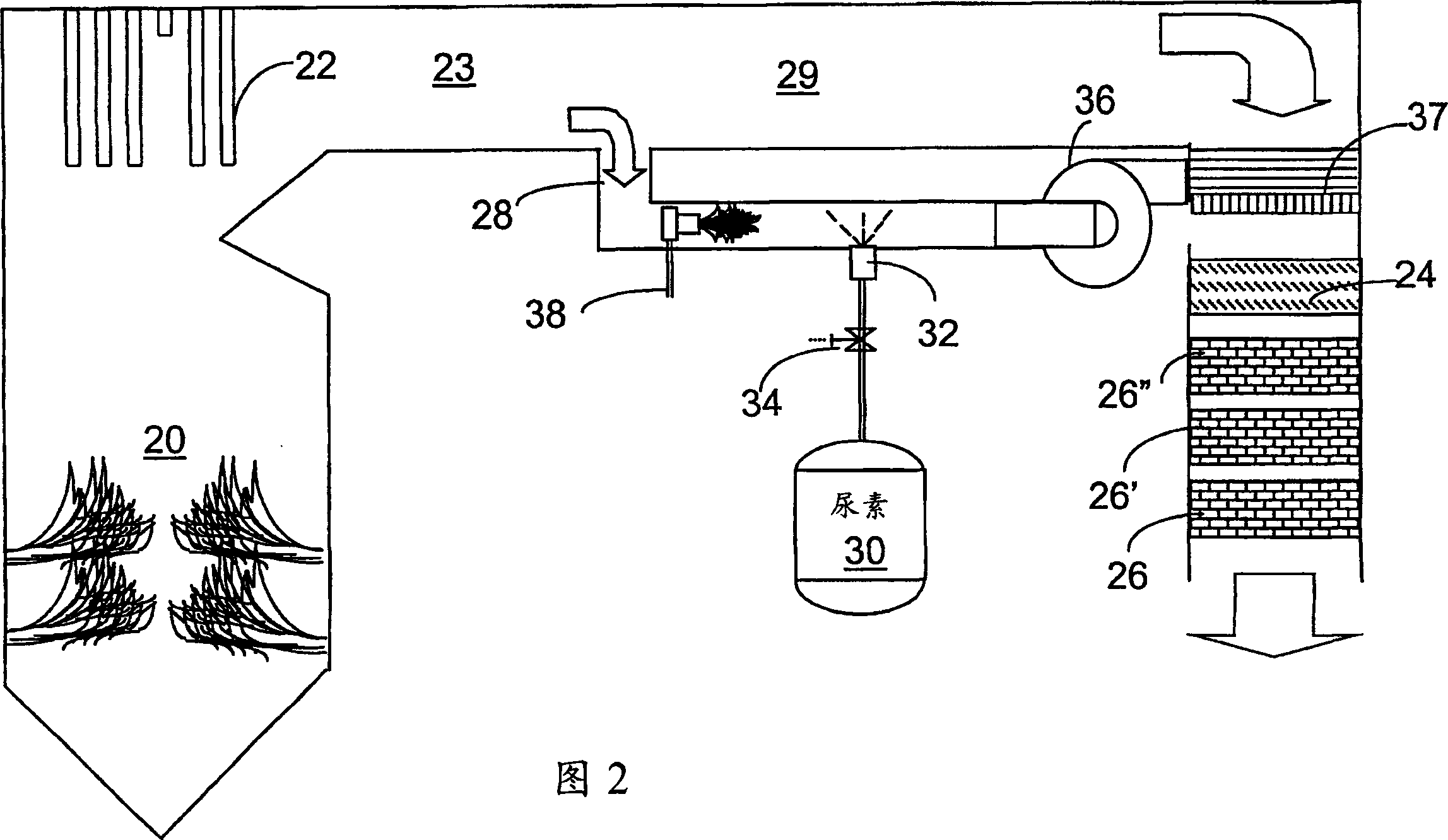
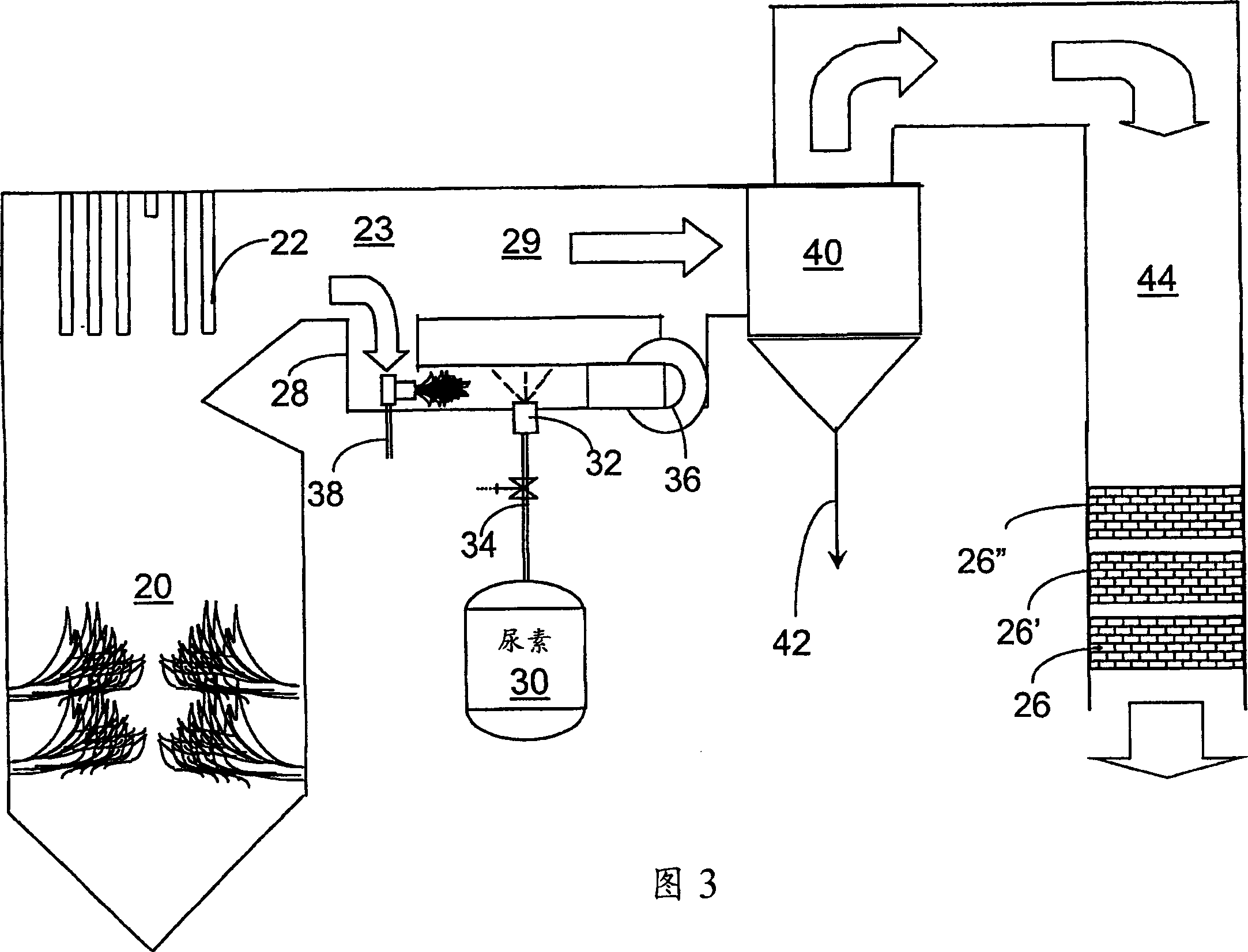
[0034] The present invention provides a urea-based SCR method, which can advantageously utilize the enthalpy of fuel gas (supplemented when necessary) to convert urea into ammonia. There are several embodiments, which will be described in their preferred forms. However, various features of the described embodiments may be used in combination with embodiments other than those specifically recited. Identical elements and drawing features will be provided with the same reference numerals throughout the drawings.
[0035] This new method takes advantage of the easy-to-handle characteristics of urea reagent, using side stream gas to provide complete vaporization and good mixing to provide high NO x Thorough mixing required for reconstitution. In a particularly advantageous embodiment, the heat required for the gasification comes from the enthalpy of the combustion gases.
[0036] The method can be carried out with urea, but other NO which can generate ammonia-containing reactant...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com