High efficiency switching amplifiers
A switching amplifier and switching technology, used in amplifiers, low-frequency amplifiers, improving amplifiers to improve efficiency, etc., can solve problems such as no bidirectional energy transmission capability, slowing down signal leakage inductance, and difficulty in compensating for transformer delays.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
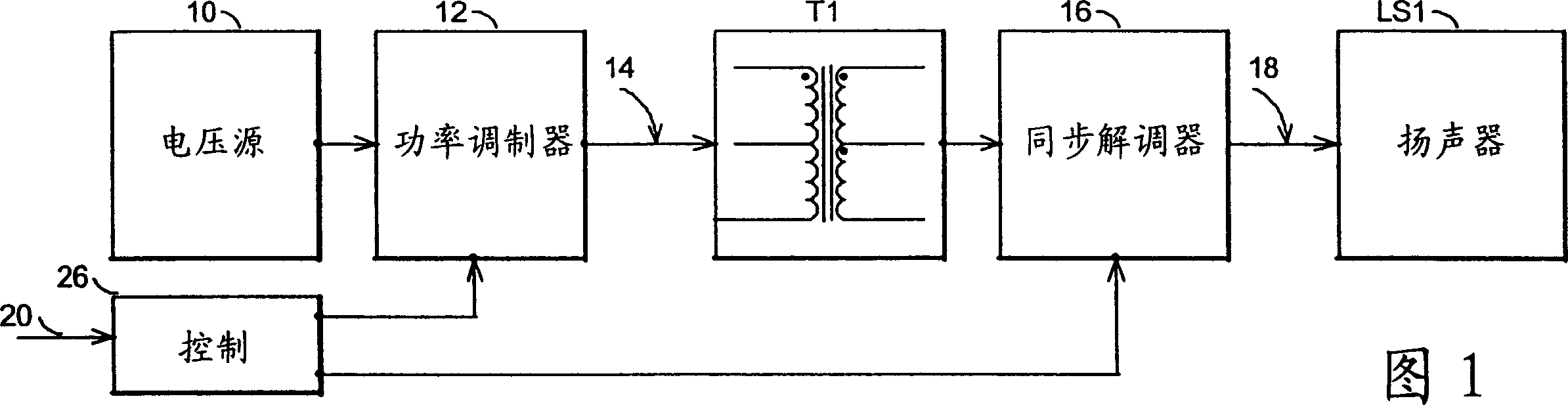
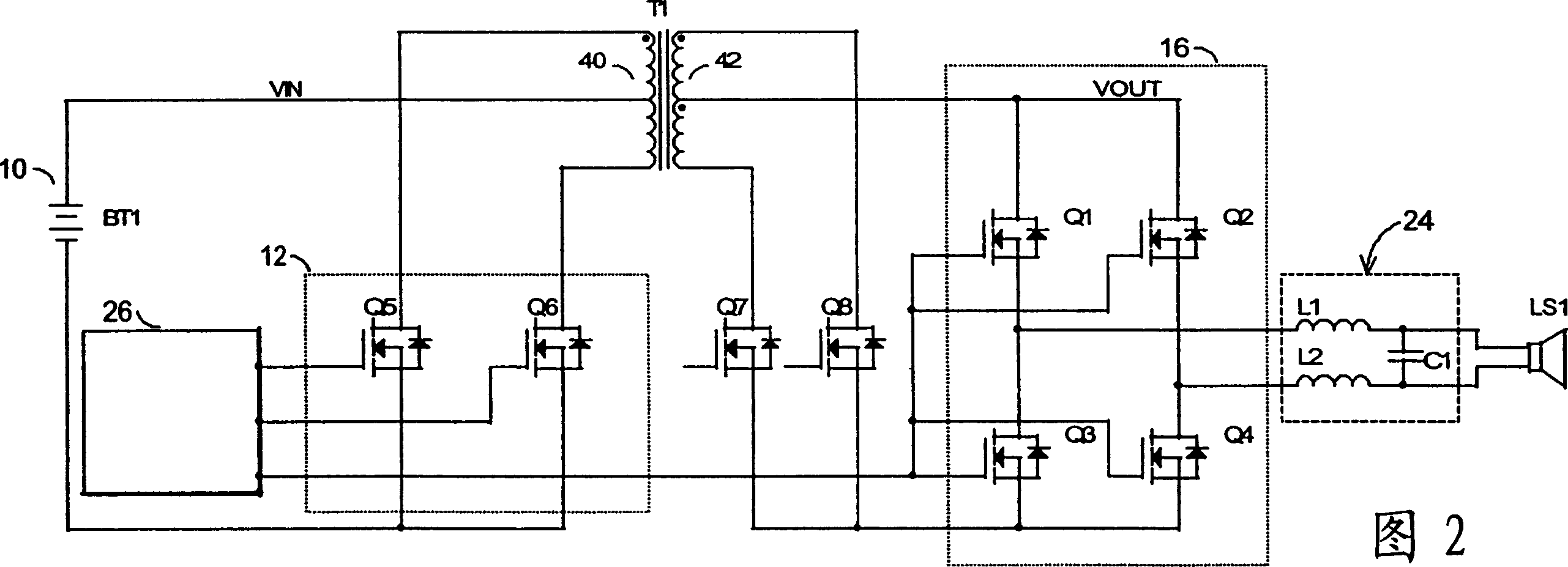
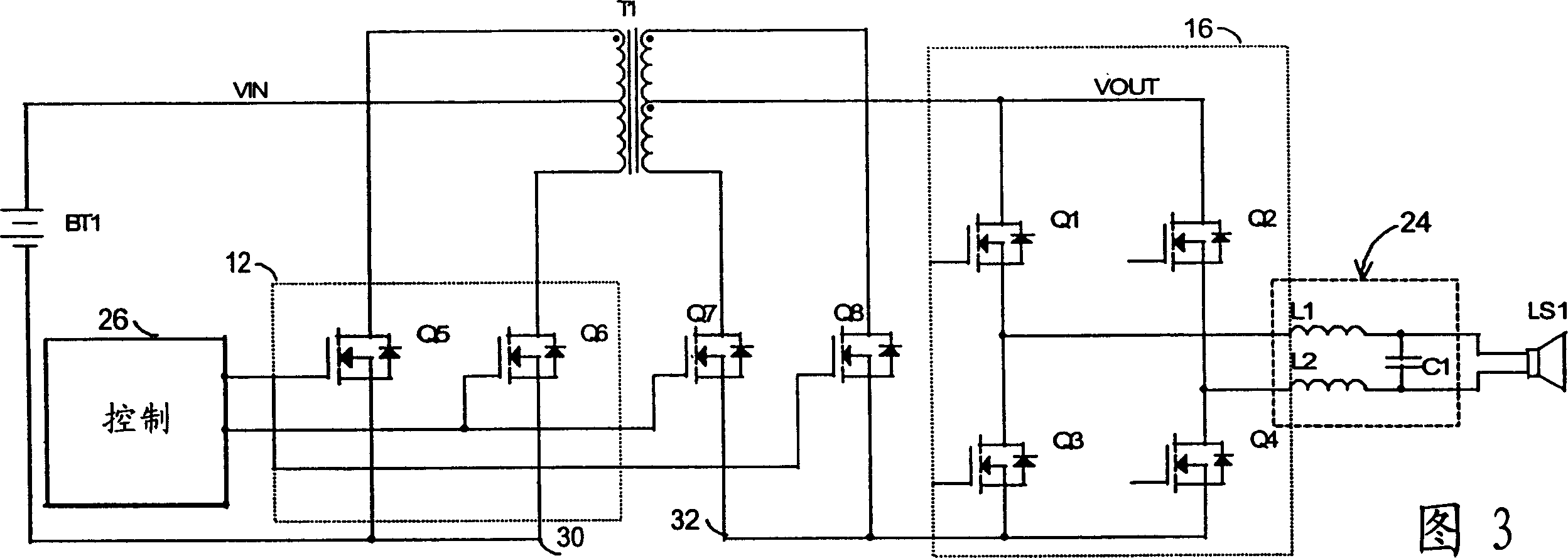
[0026] In the general block diagram of FIG. 1, the class N switching amplifier series of the present invention includes a voltage source 10 supplying power to a power modulator 12 which generates a PWM (pulse width modulated) voltage 14 to drive a transformer T1. Synchronous demodulator 16 reconstructs the signal from PWM voltage 14 conducted by transformer T1 into an amplified audio signal 18 to drive speaker LS1. A controller 26 receiving an audio signal 20 as input controls the operation of the power modulator 12 and synchronous demodulator 16 by driving them with corresponding pulses. The power modulator 12 and its matched synchronous demodulator 16 process the PWM voltage 14 substantially simultaneously.
[0027] To clarify definitions and terminology, a modulator is typically an electronic circuit or device capable of providing a pulse or waveform of which at least one of its characteristics such as amplitude, frequency, phase, pulse duty cycle, energy, etc. Variety. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com