Bidirectional-light silicon controlled chip
A technology of silicon chip and two-way light, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, thyristors, electronic switches, etc., can solve the problem that the main silicon 4 cannot be cancelled, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
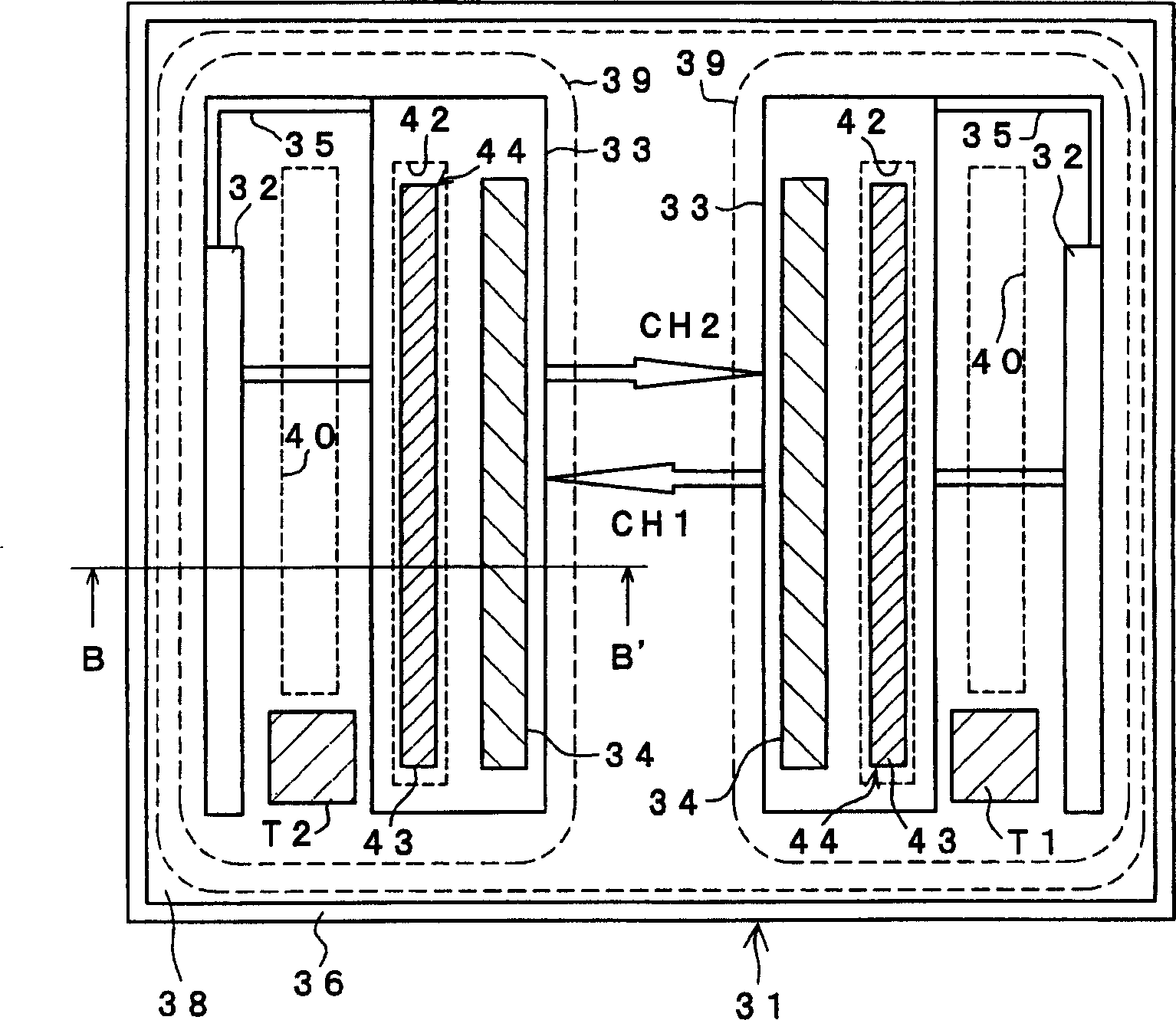
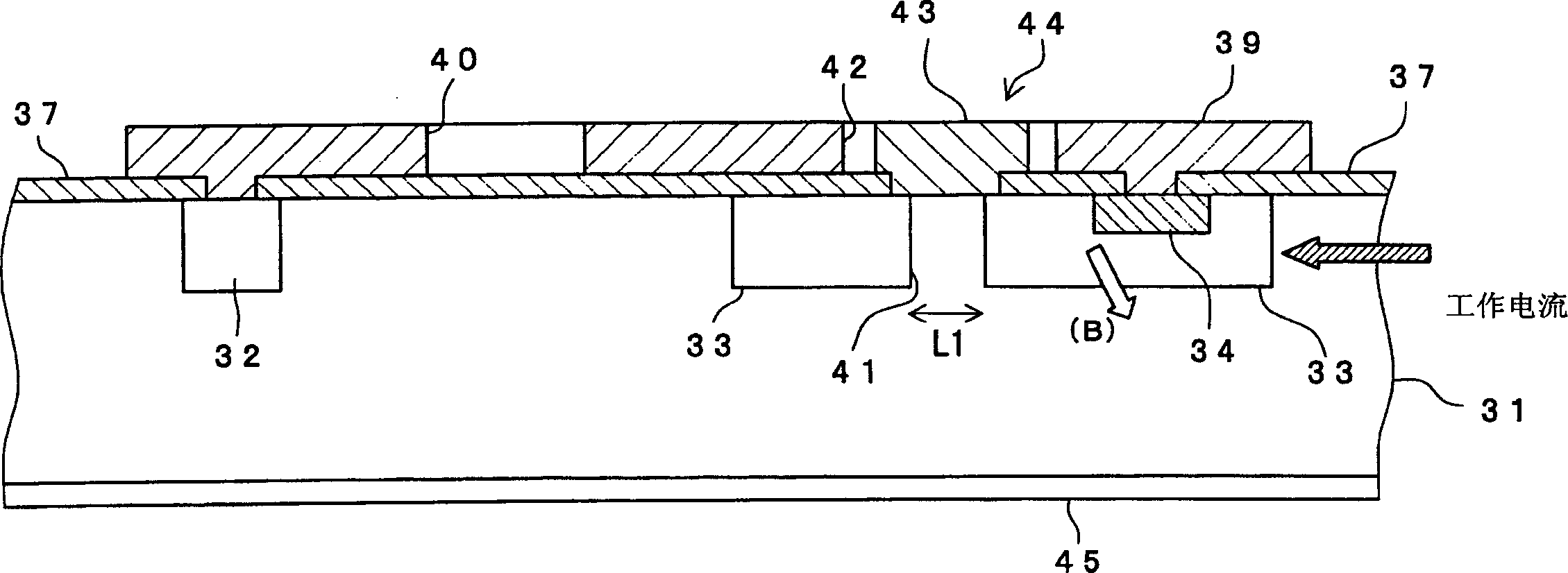
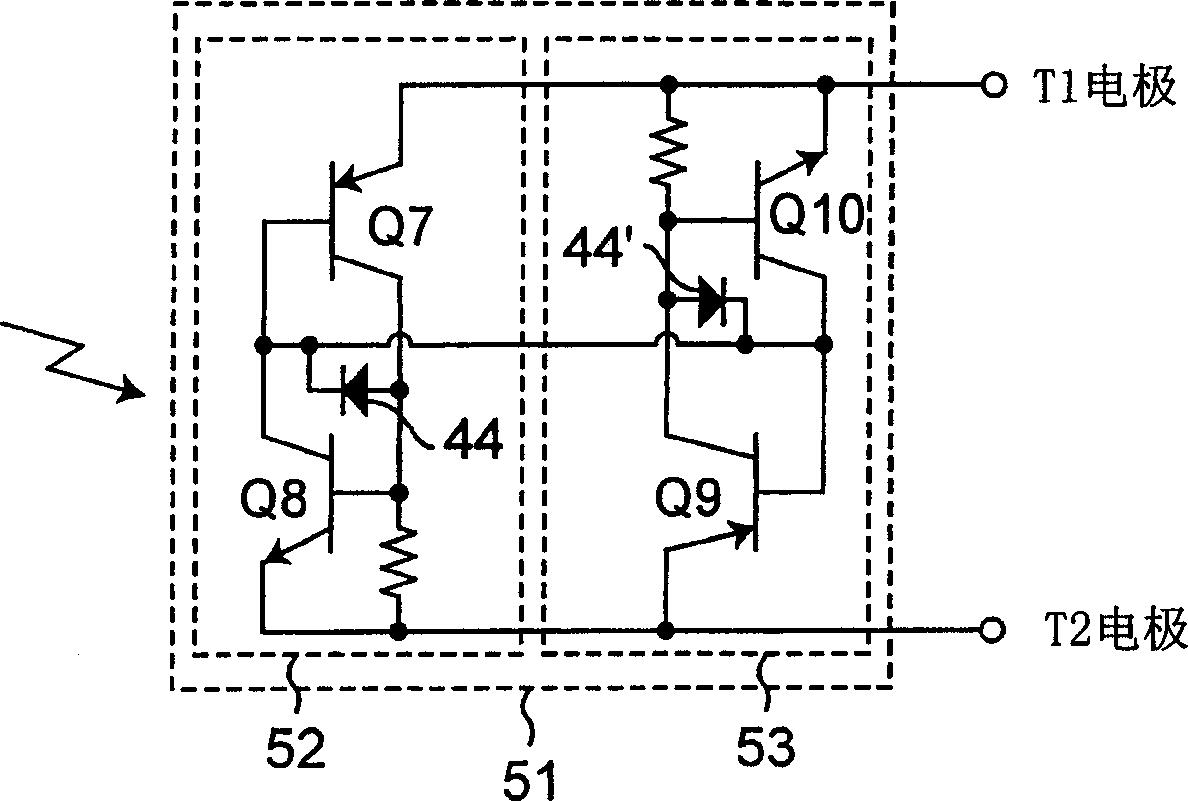
[0060] figure 1 A schematic diagram arrangement of the bidirectional phototriac chip of the present embodiment is shown. figure 2 is along figure 1 A cross-sectional view taken along the arrow B-B'. image 3 It is the equivalent circuit diagram of the bidirectional phototriac chip of this embodiment. Please note that the graphic arrangement of this phototriac chip is basically the same as Figure 11 The same as shown for the conventional triac 2.
[0061] The structure of the bidirectional phototriac chip is as follows: that is, two anode diffusion regions (P-type) 32 and two P gate diffusion regions (P-type) 33 opposite to them are symmetrically arranged with a horizontal flip axis in the figure On the front side of the N-type silicon substrate 31 . A cathode diffusion region (N type) 34 is provided on the side opposite to the anode diffusion region 32 in each P gate diffusion region 33 . Thus, a PNPN portion is formed extending from the anode diffusion region 22 on ...
no. 2 example
[0080] In the bidirectional phototriac substrate in the first embodiment, the working current regions of CH1 and CH2 cross each other, which can be clearly seen from their pattern layout. Therefore, the advantage of this chip is that the size of the chip can be reduced and the design is compact. But in turn, because the working currents of CH1 and CH2 cross each other, carrier interference will occur, although the injection of minority carriers (holes) into the N-type silicon substrate 31 is limited, and the number of residual carriers is reduced , but the rectification characteristic Icom is relatively low (drop). Therefore, in this embodiment, a bidirectional phototriac whose rectification characteristic Icom is further improved will be introduced.
[0081] Figure 4 A schematic pattern layout of the triac of this embodiment is shown. Although not shown Figure 4 sectional views and equivalent circuit diagrams, but they are basically similar to figure 2 and image 3 ....
no. 3 example
[0091] In the bidirectional phototriac chip of the second embodiment, the diffusion regions are arranged along two opposite sides of the chip periphery. Thus, the region in which the trench isolation region 70 is formed is a confinement region in the center portion, and CH1 and CH2 cannot be formed completely apart from each other. Thus, the rectification characteristic Icom cannot be sufficiently improved.
[0092] Furthermore, as described above, the lengths of the anode diffusion region, P gate diffusion region, and cathode diffusion region on the CH1 and CH2 sides are all shorter than in the case of the triac chip of the first embodiment. Therefore, due to the relatively short length of the diffusion region, the on-state voltage VT becomes very high, and the heat generation of the device increases.
[0093] Correspondingly, in this embodiment, a bidirectional phototriac chip capable of improving device characteristics and further improving rectification characteristics Ic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com