Continuous microlens array amplifying displaying antifogery method
A microlens array, magnifying display technology, applied in the direction of lenses, decorative arts, patterns characterized by light projection effects, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient observation, unrecognizable graphics and fonts, etc. produce a variety of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
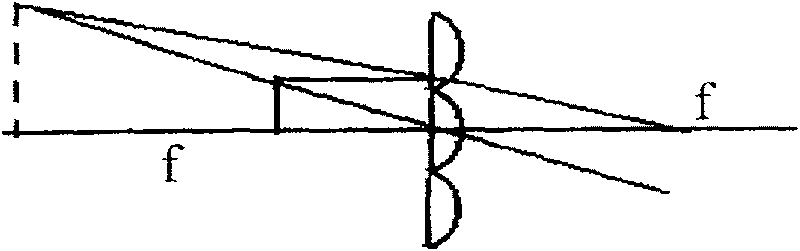
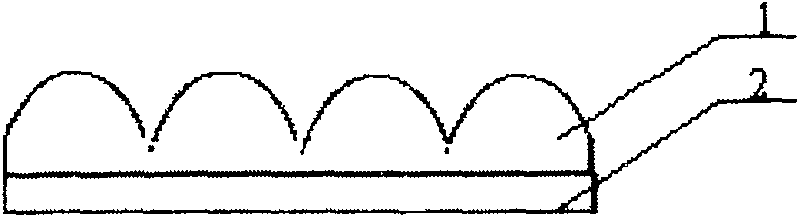
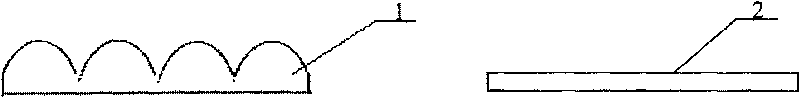
[0032] Example 1, such as figure 1 , Figure 4 As shown, first make micro-graphics or micro-structures, using a relatively simple method of filming to complete, design the aperture of each sub-pattern to be 200 μm, and the figure is crescent-shaped, and the output is generated by the filming machine, formed on organic materials, such as plastic film Above; secondly, use the method of microfabrication to manufacture microlens arrays with diameters of 200 μm and shapes that match the micrographics. The continuous microlens arrays are formed on the surface of gelatin photoresist materials by moving masks. The method can be dry or wet etching or a combination of dry and wet methods, and the pattern is transferred to the surface of the organic plastic by copying. The microphotograph of the microlens is as follows: Figure 5 Shown; Finally, combine the two with the combination glue method, such as figure 2 As shown, it is combined into a micro-graphic and a micro-lens array to ob...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2, making and displaying μ characters.
[0034] First, make micro-graphics or micro-structures, use the laser direct writing method to make a mask to obtain micro-graphics or micro-structures, the designed sub-graphics have an aperture of 100 μm, and the graphics are μ characters, which are directly produced on the surface of the chromium layer on the glass substrate, such as Figure 7 shown. The continuous microlens array is molded by grayscale mask method, and formed on the surface of optical materials (such as fused silica, K9) by direct etching, such as Figure 8 Shown is a 3D profile of the microlens array. Using separate methods, such as image 3 shown. The display results obtained during observation are as follows Figure 9 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3, the display of various graphics.
[0036] First, laser printing is used to obtain fine graphics, the sub-graphics have a diameter of 150 μm, and the graphics are square and circular, such as Figure 10 Shown; Make the microlens array again, use the grayscale mask method to form on the photoresist material, and then press the microlens on the plastic surface, and then combine the two through film pressure.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com