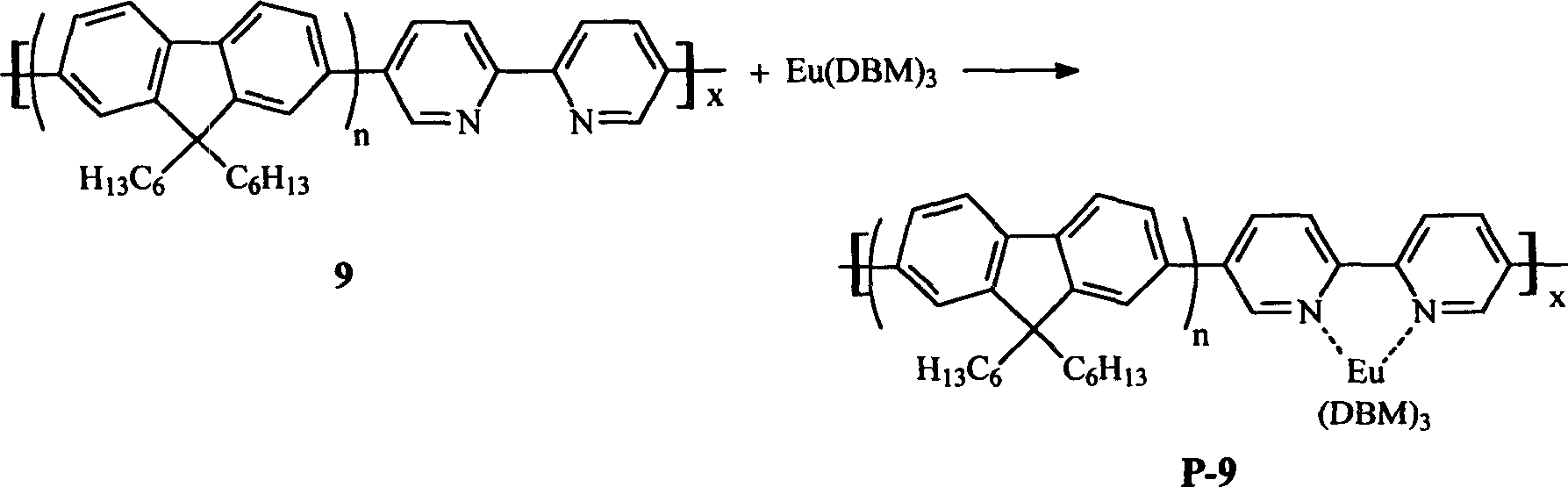Polymer material for electroluminescent device and its preparing method
A technology of electroluminescent devices and polymer materials, applied in the directions of luminescent materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of poor film-forming properties, unbalanced electron and hole injection and transport properties, and poor stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
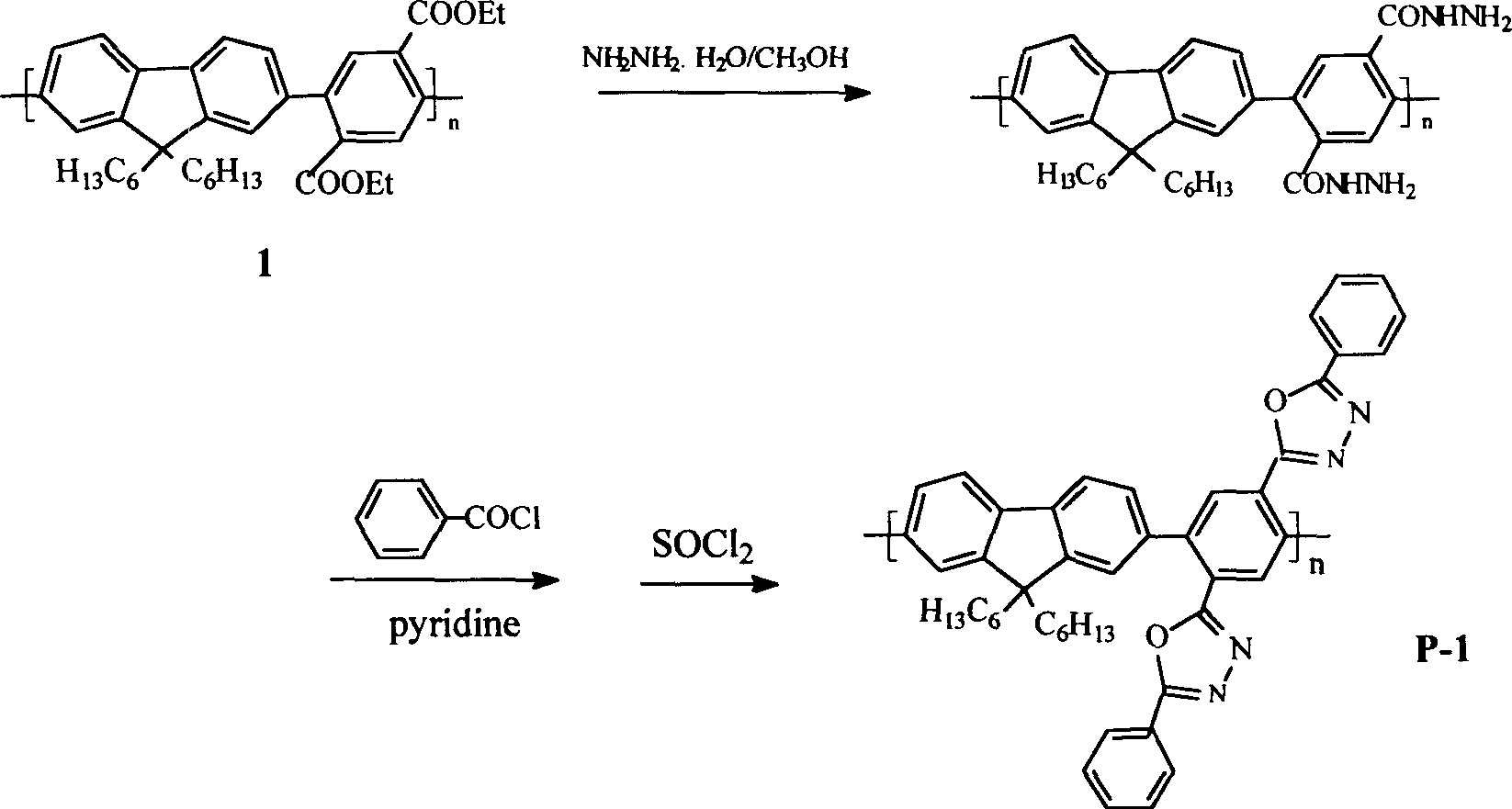
[0038] Add hydrazine hydrate to the fluorene-benzene alternating copolymer I in methanol, reflux for 16 hours under the protection of nitrogen, pour water after the reaction is completed, then extract with ethyl acetate, and rotary evaporate to obtain a white solid;
[0039] Dissolve the above white crystals and benzoyl chloride in pyridine. The reaction was refluxed under the protection of nitrogen, returned to room temperature at the end, the reaction product was poured into ethanol, and frozen to obtain a flaky white solid;
[0040] Add SOCl to the above flaky white solid 2 , and then refluxed for 5h under the protection of nitrogen. the excess SOCl 2After evaporation, the residue was poured into water to obtain a crude product, which was purified to obtain a fluorene-benzene alternating copolymer (P-1) with 1,3,4-oxadiazole-benzene flanking it.
[0041] The original polymer 1 is an electroluminescent material with good luminescence performance, but its electron injectio...
Embodiment 2
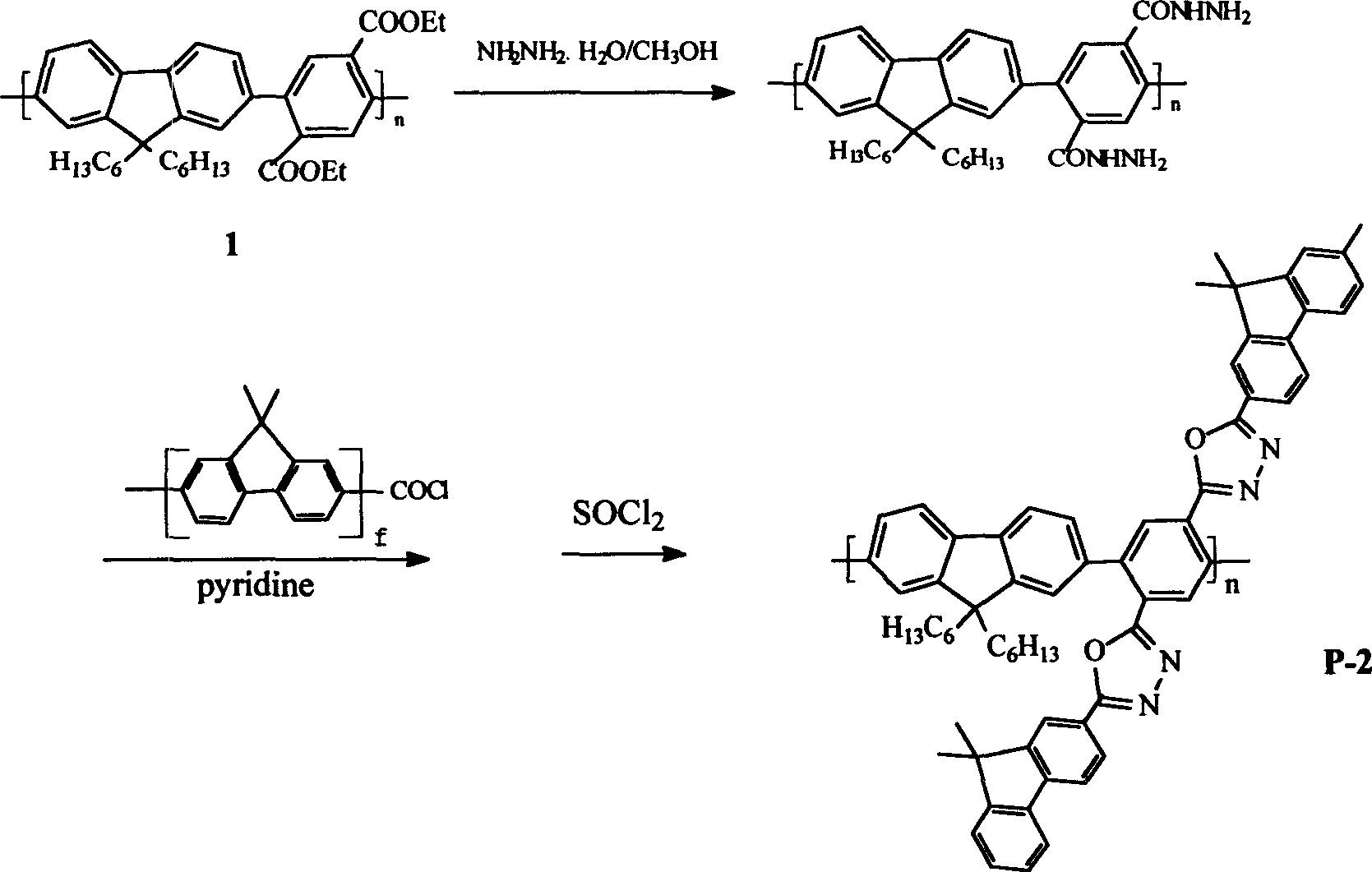
[0044] Others are the same as in Example 1, add hydrazine hydrate to the polymer I in methanol, reflux for 16h under nitrogen protection, pour water into after the reaction is finished, then extract with ethyl acetate, and spin evaporate to obtain a white solid;
[0045] Take the above-mentioned white crystal and a fluorene polymer (f=3) with an acid chloride at one end, wherein the substituent at position 9 is -C 8 h 17 ) added to pyridine. Reflux the reaction under the protection of nitrogen, and return to room temperature at the end, pour the reaction product into ethanol, and freeze to obtain a white solid; add SOCl to the white solid 2 , and then refluxed for 5h under the protection of nitrogen. the excess SOCl 2 Evaporated off, the residue was poured into water to obtain a crude product, which was purified to give the product as a fluorene-benzene alternating copolymer (P-2) with 1,3,4-oxadiazole and oxadiazole-benzene as side linkages.
[0046] Compared with polymer...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Others are the same as in Example 2, the degree of polymerization of the fluorene polymer with acid chloride at one end is f=6.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com