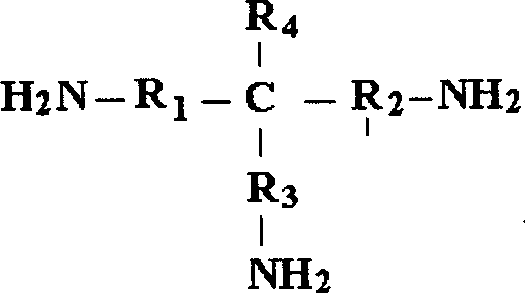Control agent for pitch for pitch trouble in use for paper making and preparation method
A control agent and barrier technology, applied in papermaking, textiles and papermaking, paper, etc., can solve the problems of no charge or weak electricity, resin deposition, etc., to prevent accumulation and deposition, and improve lipophilicity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0032] Example 1: Preparation of polyamide polyamine
[0033] Polyamide polyamine A: After mixing 103.17 parts of diethylenetriamine and 11.5 parts of 12.7% hydrochloric acid, slowly add 146.15 parts of adipic acid, then raise the temperature of the mixture to 146-148 ° C, and react for 5 hours , the condensation water is removed by distillation. After the product was cooled, it was dried at low temperature to obtain polyamide polyamine A in the form of light yellow resin.
[0034] Polyamide polyamine B: Repeat the preparation process of polyamide polyamine A, but adjust the reaction time to 15 hours. After the product was cooled, it was dried at low temperature to obtain a pale yellow resinous polyamide polyamine B.
[0035] Polyamide polyamine C: repeat the preparation process of polyamide polyamine A, but replace 103.17 parts of diethylene triamine with 146.19 parts of triethylene tetramine, and control the reaction temperature between 158-160 °C , The reaction time is 2...
example 2
[0036] Example 2: Preparation of polyamide polyamine and inorganic bentonite composite
[0037] 1. Aqueous solution method
[0038] Compound A1 of polyamide polyamine A and sodium-calcium-based bentonite: gradually add 6 parts of bentonite (bentonite layer spacing 13.76 Å) to 47 parts of 0.1N hydrochloric acid containing 1 part of polyamide polyamine A under stirring In an aqueous solution, stir and react at room temperature for 12 hours, centrifuge and discard the supernatant. After drying, it is ground into powder to obtain composite A1 of polyamide polyamine A and sodium calcium bentonite.
[0039] Compound B1 of polyamide polyamine B and sodium-calcium-based bentonite: 6 parts of sodium-calcium bentonite (distance between layers of bentonite 13.14 Å) was gradually added to 190 parts of calcium-based bentonite containing 4 parts of polyamide polyamine B under stirring. hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, and the temperature was raised to 80 ° C, continued to stir and reac...
example 3
[0045] Example 3: Preparation of polyamide polyamine and organic bentonite composite
[0046] 1. Preparation of organobentonite
[0047] 1,12-diaminododecane as a swelling agent: dissolve 5 parts of 1,12-diaminododecane in 5000 parts of 0.01M HCl and filter to remove undissolved impurities, and then stir Slowly add 50 parts of sodium calcium-based bentonite (bentonite interlayer distance 13.14 Å) powder into the solution, heat up to 60°C, continue stirring and reacting for 3 hours, then centrifuge and discard the supernatant. The sample was washed with deionized water until the eluate was filled with AgNO 3 Cl cannot be detected - Until then, dry the washed sample at low temperature. The dried sample is ground into powder, which is 1,12-diaminododecane modified bentonite.
[0048] Use p-phenylenediamine as a swelling agent: dissolve 5.4 parts of p-phenylenediamine in 5000 parts of 0.01M HCl and filter to remove undissolved impurities, then slowly add 50 parts of sodium bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com