Specific antibody fragments for the human carcinoembryonic antigen (cea)
An antibody fragment and specific technology, applied in the field of immunology, can solve the problems of no development, abnormal biodistribution, low affinity of immobilized antigen, etc., and achieve the effect of good tissue penetration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
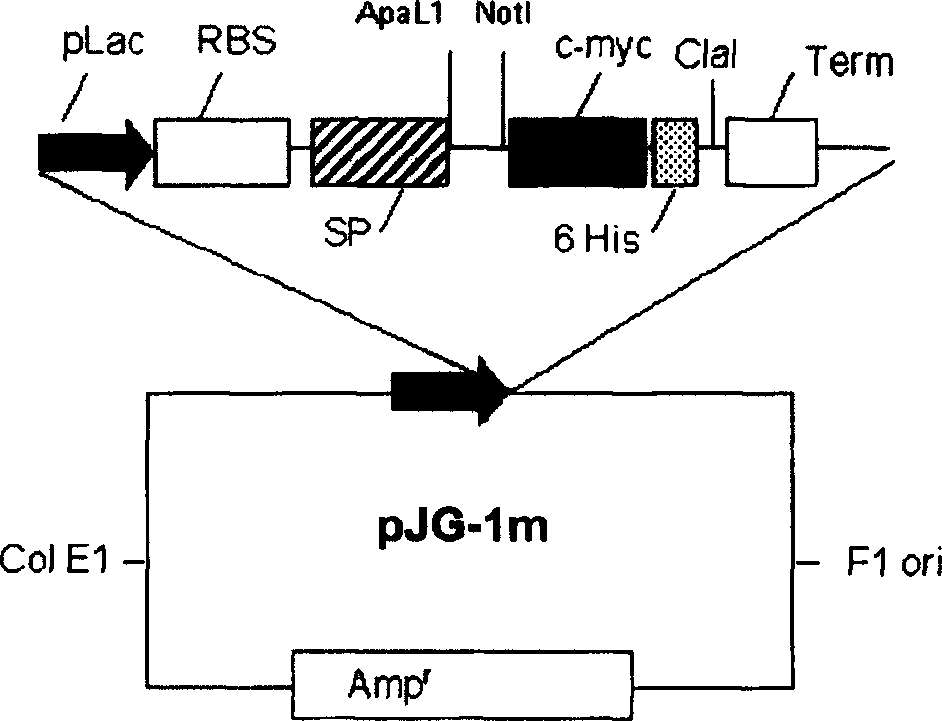
[0026] Specific polypeptide molecules formed by one or more antigen-binding sites from a mouse Mab specific for human CEA are obtained by the present invention. Depending on how the polypeptide molecule is constructed, antigen binding sites are assembled into monovalent, bivalent, and other forms of antibody fragments.
[0027] A polypeptide molecule in the form of a monovalent scFv fragment specific to human CEA exhibits an affinity constant for the antigen of (5.0±0.4)×10 9 Lmol -1 , which comprises VH and VL domains connected in this order by a joint segment (linker) of 14 amino acids, the amino acid sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO16.
[0028] The polypeptide molecule in the form of a bivalent scFv fragment (dibody) specific to human CEA exhibits an affinity constant for the antigen of (2.8±0.3)×10 10 Lmol -1 , which comprises pairs of two identical molecules, each formed by VH and VL domains connected in this order by a joint segment (linker) of 5 amino acids, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com