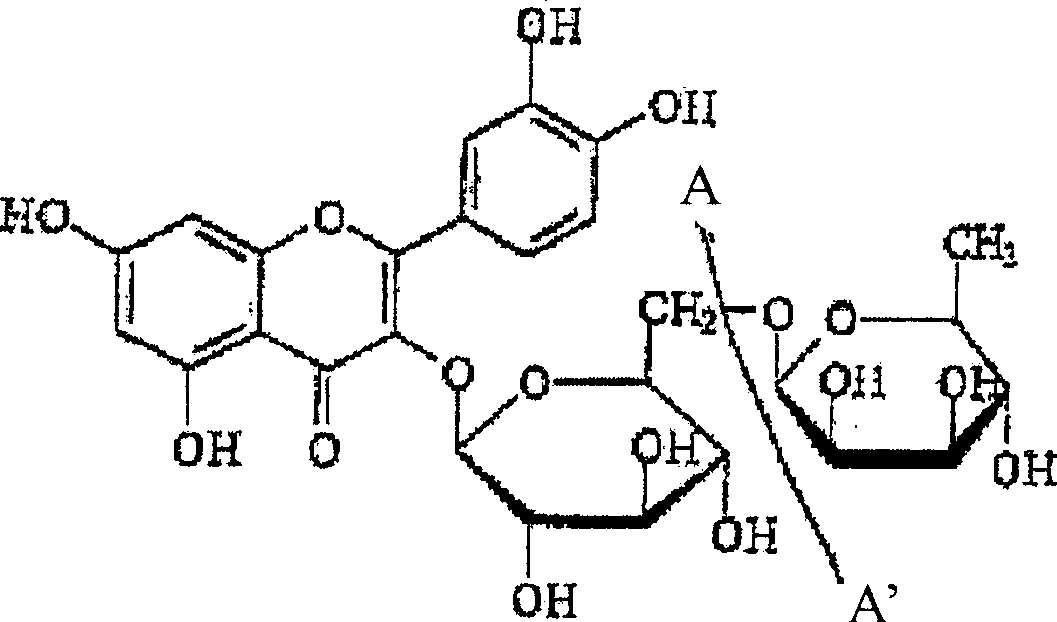
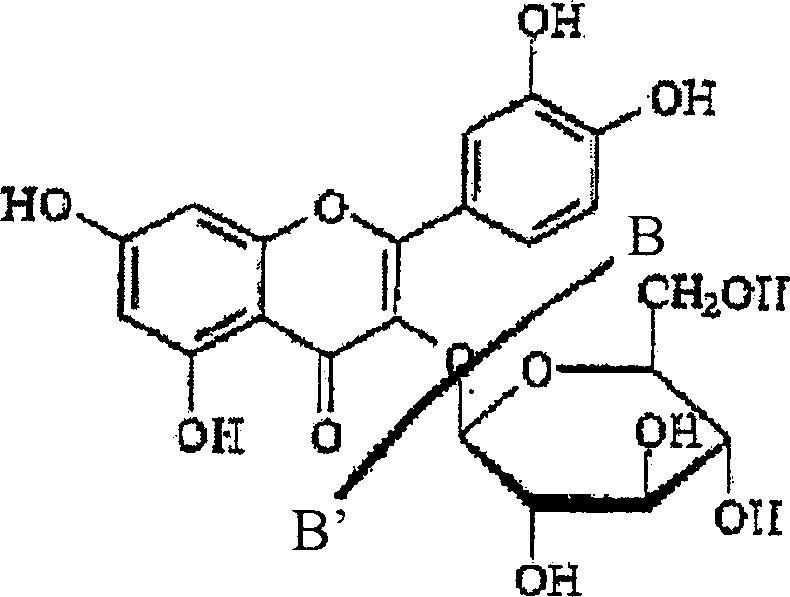
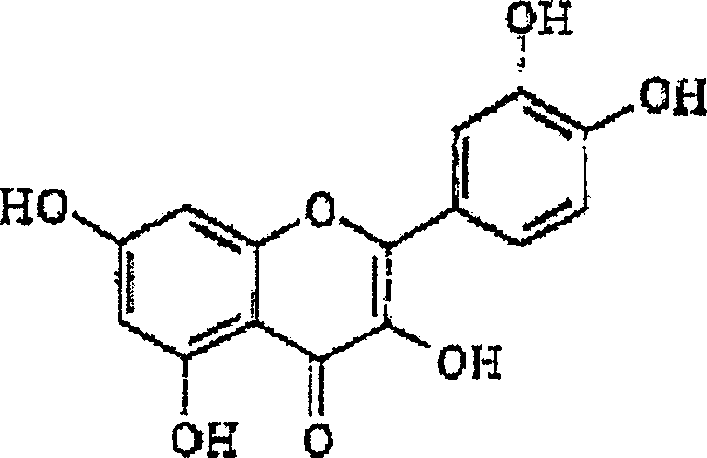
Extraction, purification and conversion of flavonoids from plant biomass
A compound, flavonoid technology, applied in the field of extraction, purification and conversion of flavonoids from plant biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] Example 1: Aqueous extraction, concentration and precipitation of rutin from buckwheat leaf material
[0138] After harvesting and drying, buckwheat leaves were ground on a Wiley mill to pass through a 2mm sieve, thereby preparing buckwheat leaves for extraction. Extraction was carried out by 1 kg of ground buckwheat leaves (3.74% rutin content, based on dry weight) in 10 L of water with continuous stirring at 90° C. for 1 hour. The resulting suspension was filtered, and the filter cake was washed twice with 300 ml of hot (95° C.) water. The washed filtrate was mixed with the extract to obtain a combined extract with a volume of 8.6 L. This aqueous extraction method recovered 36% of the available rutin from the leaves.
[0139] The extract was concentrated under reduced pressure to about 1 / 5 and 1 / 10 of its original volume. The concentrated extract was stored in the refrigerator (4°C) overnight, at which time the flavonoid compounds precipitated out of solution. The...
Embodiment 2
[0140] Example 2: Aqueous Alcoholic Extraction, Concentration and Precipitation of Rutin from Buckwheat Leaf Material
[0141] After harvesting and drying, buckwheat leaves were ground on a Wiley mill to pass through a 2mm sieve, thereby preparing buckwheat leaves for extraction. 1 kg of ground buckwheat leaves (rutin content 3.74%, based on dry weight) were extracted in 10 L of 50% (v / v) aqueous methanol, specifically with continuous stirring at 40° C. for 3 hours. The resulting suspension was filtered, and the filter cake was washed with warm (40%) 50% (v / v) aqueous methanol. The washed filtrate was combined with the extract. This extraction method recovered 65% of the available rutin from the leaves. Figure 2A illustrates the concentration of rutin in methanolic extracts. The extract was concentrated to about 1 / 5 of its original volume under reduced pressure. The concentrated extract was stored in the refrigerator (4°C) overnight, at which time the flavonoid compounds p...
Embodiment 3
[0142] Example 3: Purification of rutin from a flavonoid-rich intermediate isolated from buckwheat leaves
[0143] The rutin-enriched product from Example 2 was dissolved in warm methanol with vigorous stirring on a magnetic stirrer to promote complete dissolution of the rutin. Any insoluble material was removed from the solution using vacuum filtration. The solution was evaporated to dryness at 40°C under reduced pressure. The residue was then suspended in hot (90°C) water with continuous stirring until most of the precipitate had dissolved. Allow the suspension to settle overnight in the refrigerator. The precipitate was removed by vacuum filtration and freeze-dried. The purified rutin precipitate was dissolved in methanol, filtered through a 0.45 μm nylon syringe filter, and analyzed by RP-HPLC to confirm product purity. After repeated dissolution / crystallization without chromatography, the rutin content increased to about 70% and higher.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com