Method and device for transporting or binding-specific separation of electrically charged molecules
A molecular and metal ion technology, applied in measurement devices, biochemical equipment and methods, analytical materials, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and high cost of manufacturing microsensor chips
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
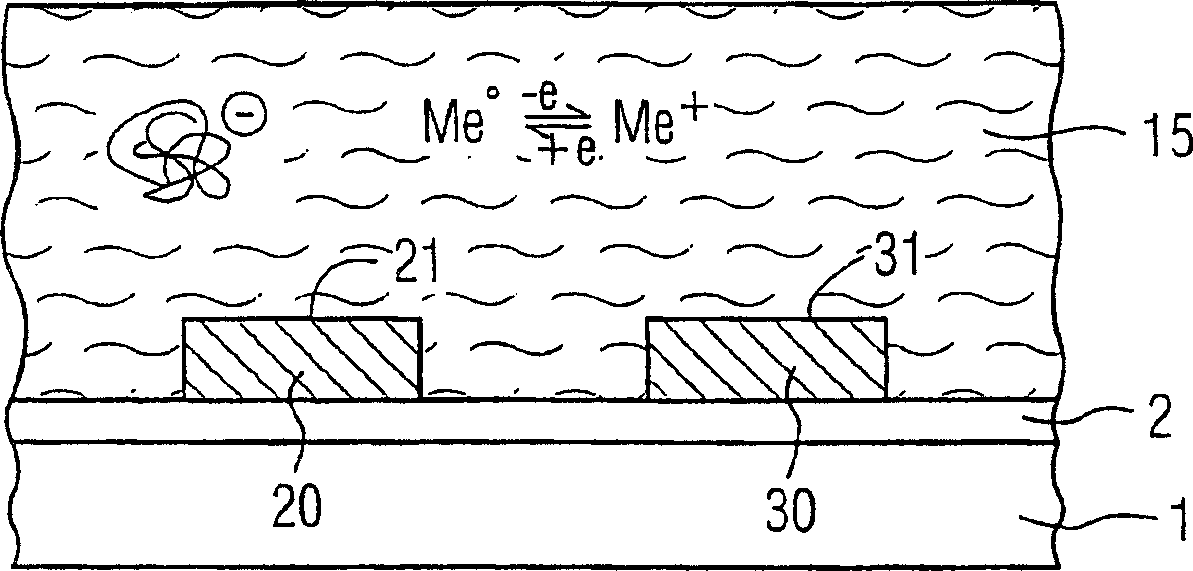
[0027] figure 1 The schematic structure of a general device for carrying out biochemical measurements is shown. 1 denotes a plate-shaped base made of, for example, silicon, on which a substrate made of, for example, silicon oxide (SiO 2 ) made of thin insulating layer 2. On the device are two measuring electrodes 20 and 30, which are preferably made of a noble metal, in particular gold. The entire measuring device is in contact with an aqueous solvent 15 .
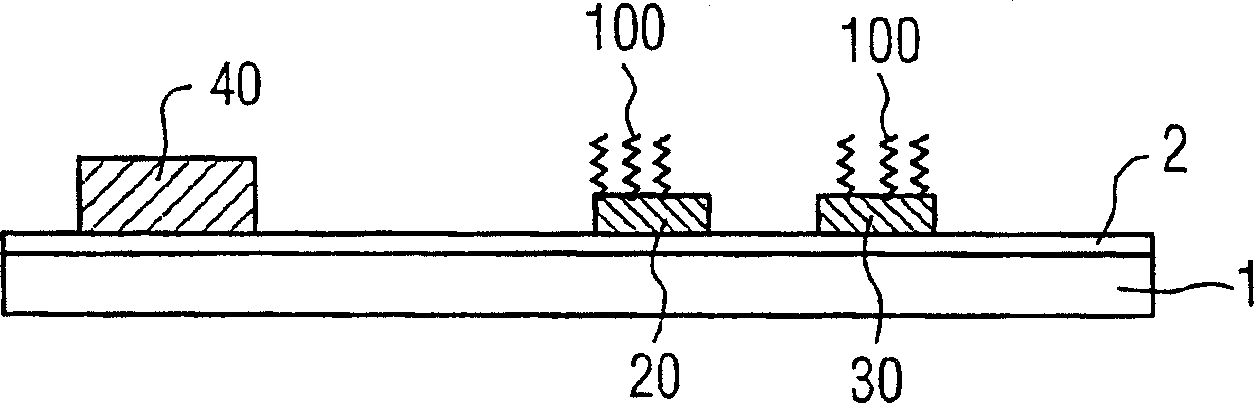
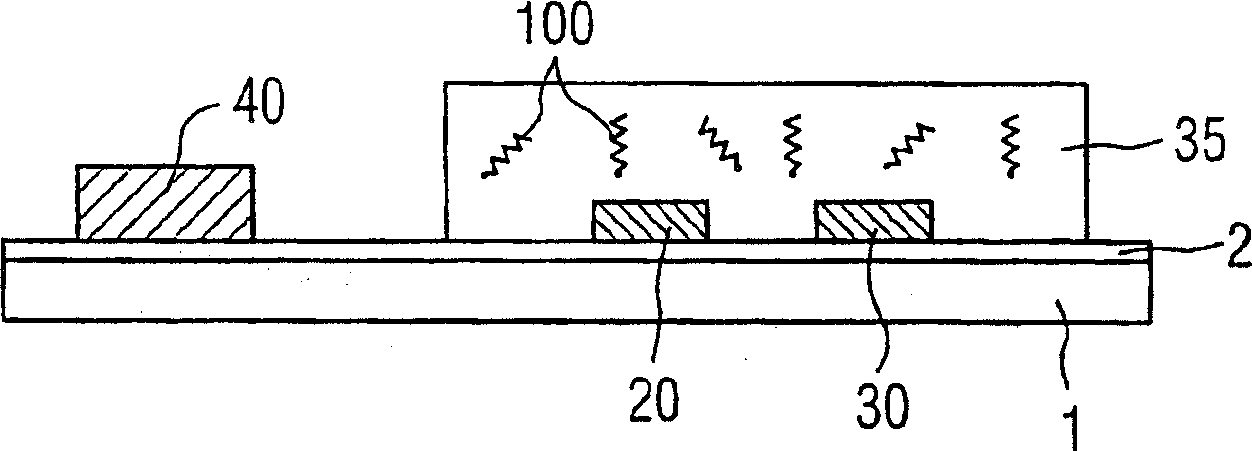
[0028] There are negatively charged macromolecules in the aqueous solvent 15, which in figure 1 Indicated by the thread ball structure, and in the back Figure 5 Use 200, 200' to mark respectively. The negatively charged molecules are supposed to migrate towards the measuring electrodes 20 , 30 and are also referred to below as target molecules. In the case of DNA analysis the target molecule is the DNA to be examined. By means of capture molecules, which can be immobilized, for example, in the hydrogel layer 35 , t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com