Vibrating motor and portable terminal apparatus using same
A technology of vibrating motors and stator yokes, applied in the direction of using vibrating fluids, manufacturing motor generators, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of difficult rotating torque, difficult assembly, restrictions, etc., achieve effective driving torque, and achieve uniformity , the effect of imbalance suppression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0060] (structure)
[0061] A typical embodiment of the vibration motor of the present invention includes a stepping motor.
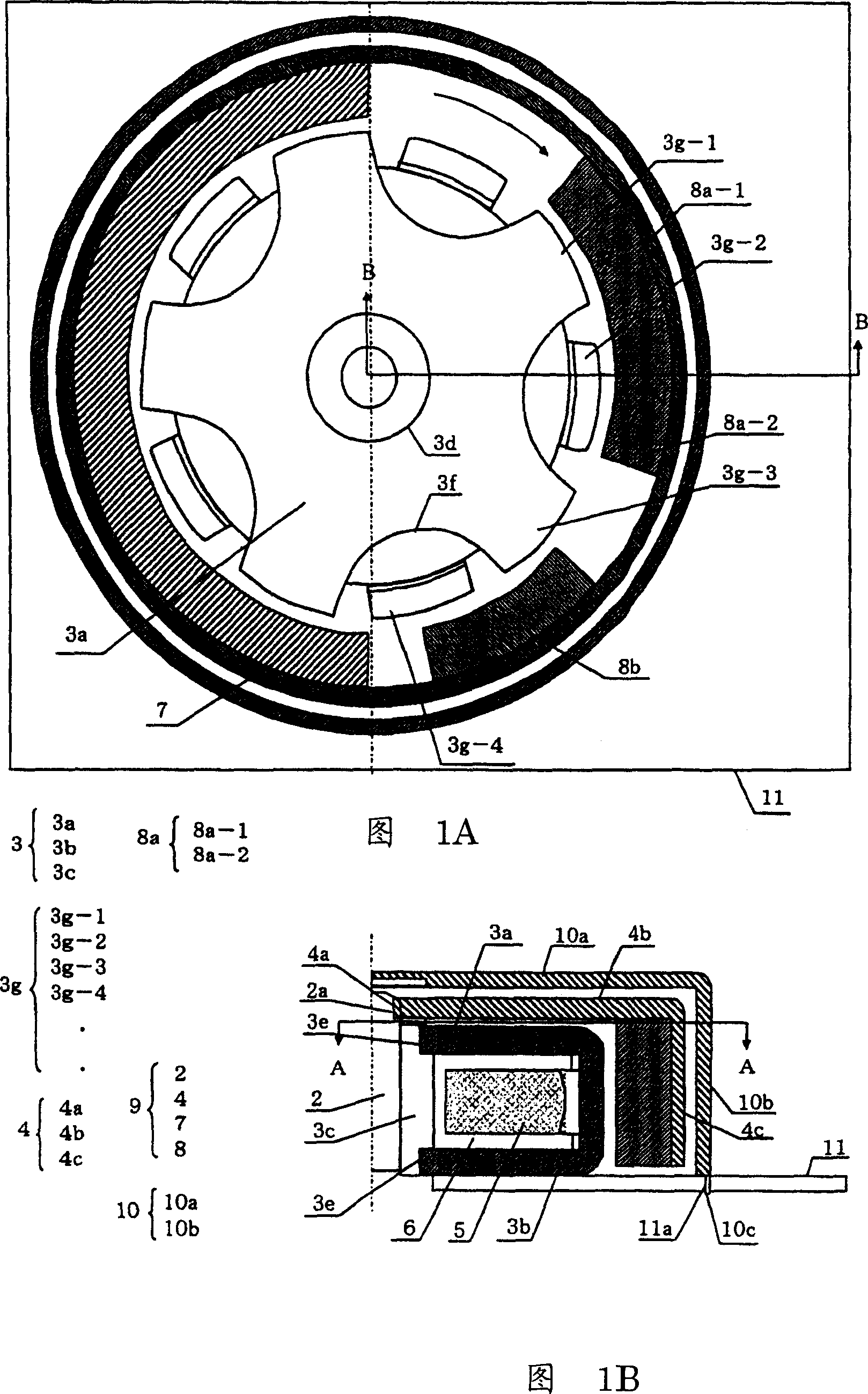
[0062] 1A and 1B are structural diagrams of a vibration motor applying an outer rotor type stepping motor according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. Fig. 1A is a sectional view along line A-A in Fig. 1B, and Fig. 1B is a sectional view along line B-B in Fig. 1A.
[0063] The vibration motor 1 includes a rotating shaft 2 and a rotor frame 4 having a third stator yoke 3c also serving as a bearing. The diameter of the rotating shaft 2 is, for example, 0.8 mm, and the outer diameter of the third stator yoke 3 c which also serves as a bearing is, for example, 1.8 mm.
[0064] The third stator yoke 3c, which also serves as a bearing, is made of an oilless metal magnetic material formed into a substantially cylindrical shape. (1) Most of the sides of the rotating shaft 2 are rotatably guided, (2) constitute a part of the magnetic circuit...
Embodiment 1
[0128] (Effect of Embodiment 1)
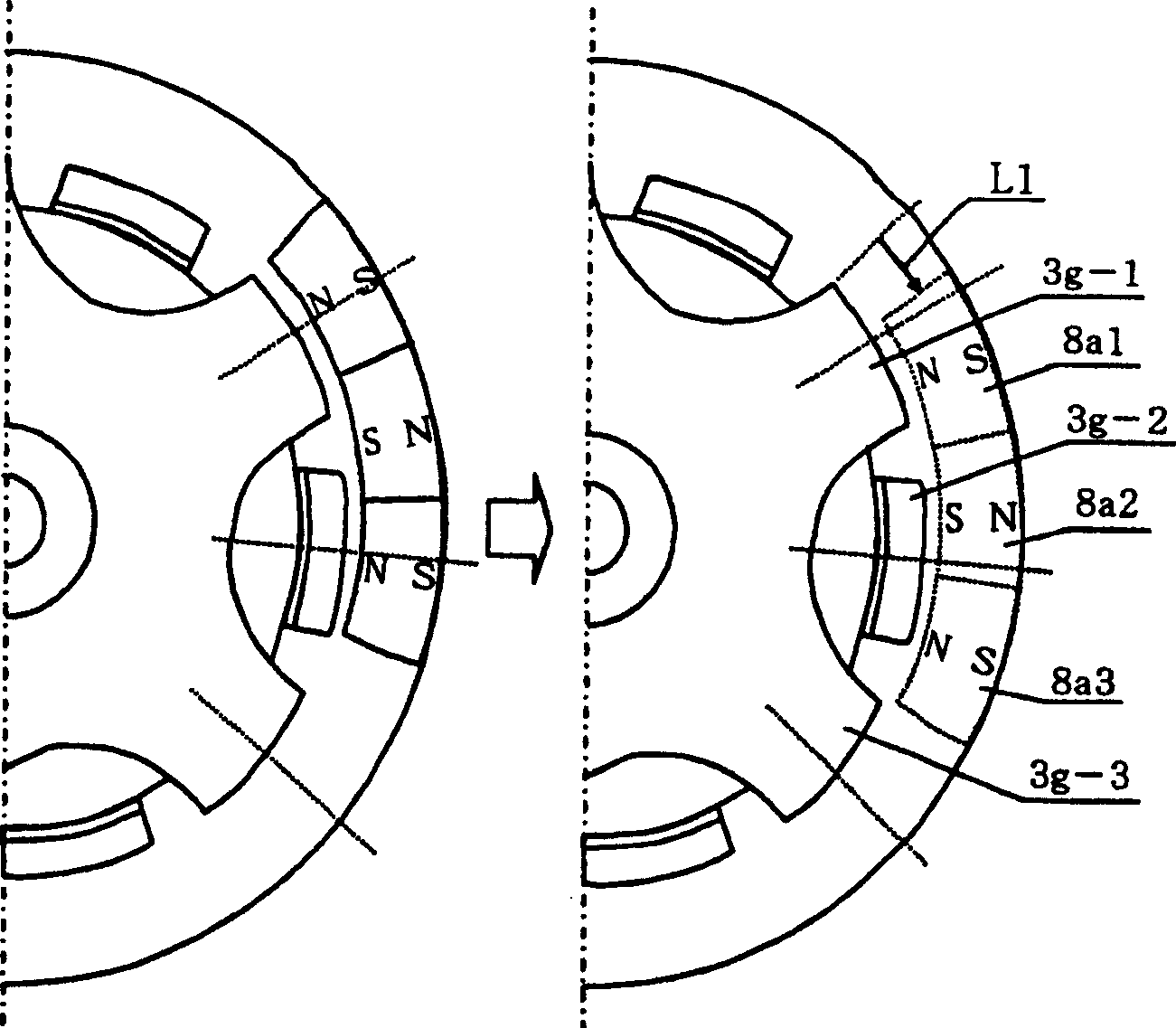
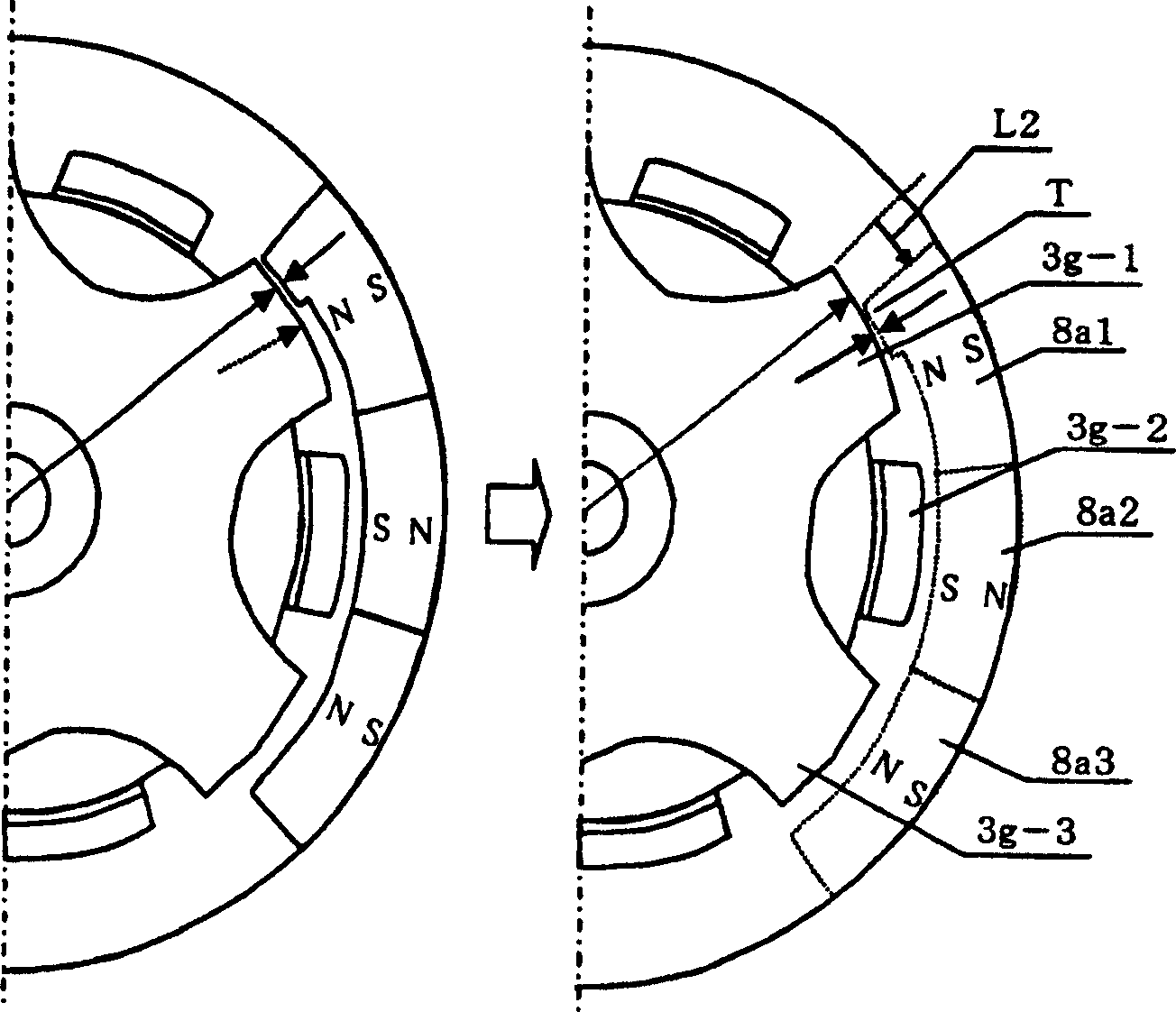
[0129] Since the outer rotor type incorporates eccentric weights in the same outermost rotating area as the magnets, the accommodation space for the eccentric weights can be shared with the magnets. Since the eccentric weight is arranged on the outermost side, the radius becomes long, strong vibration can be generated, and the part exposed to the outside can move. Also, since the stepping motor has no brushes, similar to other brushless motors, the need for maintenance is almost eliminated and its lifespan becomes longer.
[0130] In addition, when the control speed is synchronized with the input pulse, the amount of vibration can be adjusted linearly, and the braking time can be shortened.
[0131] Due to the single-phase, the excitation pulse current with alternating and reverse directions is input to the single-phase stator coil wound around the stator yoke. Since this coil has a single phase, it takes up less space and has a reduced thic...
no. 2 example
[0144] 5A and 5B are structural diagrams of an inner rotor type vibration motor according to a typical embodiment of the present invention. Figure 5A is along the Figure 5B The profile of C-C line, Figure 5B It is a sectional view taken along line D-D in FIG. 5A .
[0145] The bearing 12 is vertically arranged on the interface plate 21, just like the bearing shown in Embodiment 1, the cylindrical rotating shaft 19 is rotatably arranged on the bearing 12, the supporting body 22 is fixed to the rotating shaft 19, and the magnet 18 is arranged on The top of the support body 22. The magnets 18 include a rotor magnet 18a and an auxiliary pole magnet 18b. In the case of Embodiment 2, although the magnet 18 includes two magnets, the magnet may basically be constructed of one or more magnets. The magnetization, magnetic pole pitch, and the like of the rotor magnet 18 a and the auxiliary pole magnet 18 b are configured similarly to the case of Embodiment 1.
[0146] The stator i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com