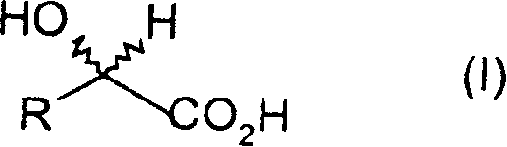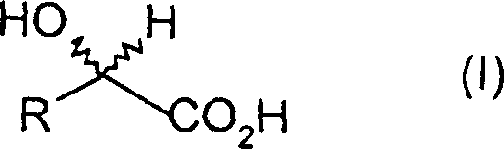Method for the microbiological isomerisation of alpha-hydroxy carboxylic acids
A technology of hydroxycarboxylic acid and microorganism, which is applied in the field of microbial isomerization of α-hydroxycarboxylic acid, which can solve the problems of high substrate specificity and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0136] a) Racemization of the [alpha]-hydroxycarboxylic acid after withdrawal of the desired product in order to recycle the stereoisomer which is not desired in conventional racemate separations. The advantage is a purely enzymatic racemization reaction; in contrast, chemically catalyzed racemization reactions usually react under severe reaction conditions leading to decomposition, formation of secondary products and side reactions (elimination, etc.). (cf. also: Kontrollierte Racemisierung von organischen Verbindungen [Controlled racemization of organic compounds]: E.J. Ebbers, G.J.A. Arians, J.P.M. Houbiers, A. Bruggink, B. Zwanenburg, Tetra-hedron, 1997, 53, 9417-9476).
[0137] b) Stepwise deracemization of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids. If the racemase cannot be used directly in the (chemical and enzymatic) enantioselective step in a "one-pot approach" (e.g. due to the required reaction conditions), then enzymatic racemization can be performed after the enantioselective step...
Embodiment 1
[0186] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of substrate and standard substance
[0187] a) Synthesis of Enantiomerically Pure 2-Hydroxy-3-Phenylalanine
[0188] Reaction mixture: 1 g of enantiomerically pure phenylalanine (6.05 mmol) was dissolved in 12 ml of H 2 SO 4 (1M). Add 1.66 g (24 mmol) of ice-cold NaNO in portions 2 . After the addition, the cooling system was removed and the reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature.
[0189] Procedure (Work-up): In each case the aqueous solution was extracted 3 times with 4 ml of diethyl ether, the organic phase was washed with saturated sodium chloride solution and the sodium chloride solution was extracted again with diethyl ether. Combine the organic phases and wash with Na 2 SO 4 Dry and evaporate the solvent on a Rotavapor. The yellow oily residue was treated with 2 mL of hexane and crystallized by scraping with a glass rod. A white crystalline precipitate formed. The crystals were washed three times with abo...
Embodiment 2
[0211] Example 2: Screening for racemase activity
[0212] To get a first indication of the racemic activity of microorganisms, observe their reaction to the (natural) substrate (S)-lactic acid 1 and / or the (unnatural) substrates (S)-phenyllactic acid 2 and (S)- Racemization of 4-fluorophenyllactate 3.
[0213] For screening, approximately 10 mg of freeze-dried cells were rehydrated in 900 μl of Bis-Tris buffer (50 mM Bis-Tris, pH=6) in Eppendorf flasks for 1 hour at 42° C. and 150 rpm. Then, 10 mg of substrate were added in each case, which had been previously dissolved in 100 μl of buffer and adjusted to pH 6-7 with NaOH. Incubate the reaction mixture at 42 °C and 150 rpm in a shaker incubator. A blank was measured in parallel with each reaction mixture, in which the same reaction conditions were maintained but without the addition of cells. Since all control experiments were negative, spontaneous racemization under these given reaction conditions could be ruled out.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com