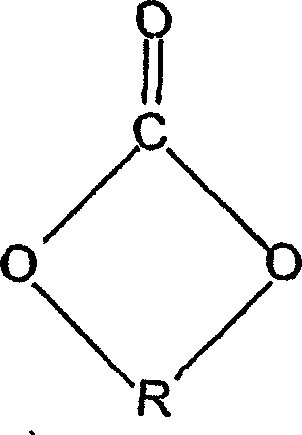
Melt spun polyether TPU fibers having mixed polyols and process
A technology of melt spinning and polyether, which is applied in the field of preparing melt-spun TPU fibers, which can solve problems such as loss of output and high cost of downtime
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1 is a comparative example of the prior art TPU, which shows that a single polyether intermediate and an aliphatic chain extender are used to prepare TPU. Example 2 is also a comparative example, which shows that a single polyether intermediate and an aromatic chain extender together with a chain extender are used to prepare TPU. Example 3 is the TPU of the present invention, which contains a mixed polyether intermediate and an aromatic chain extender. Example 4 is the most preferred TPU of the present invention, which is a TPU containing a mixed polyether intermediate and an aromatic chain extender together with a chain extender. Example 5 is similar to Example 4, except that Example 5 contains a higher amount of lower molecular weight polyether intermediate. Example 6 is a comparative example of the prior art TPU showing a polyester intermediate and an aliphatic chain extender. Example 7 represents a fiber melt-spun from each TPU of Examples 1-6, in which 10 wt% o...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 (comparative)
[0068] In a 40mm co-rotating twin-screw extruder, in the presence of 50 ppm stannous octoate as a catalyst, a mixture of substances preheated to 120°C or below was mixed with 17.5440 parts by weight of MDI and 0.4 parts by weight at a temperature of 200°C Lubricant reaction: 76.0761 parts by weight of molecular weight (Mn) 2000 polyether intermediate (PTMEG), 5.116 parts by weight of benzene glycol (HQEE) chain extender, 1.2435 parts by weight of hydroxyethyl resorcinol (HER ) Chain growth aid, 0.3 parts by weight of antioxidant and 0.3 parts by weight of UV stabilizer. The resulting polymer was pelletized underwater and collected in a silo heated at 105°C to dry the product. The molecular weight (Mn) of the resulting TPU was 150,000 Daltons, and was used in Example 7 to prepare melt-spun fibers.
Embodiment 3
[0070] In a 40mm co-rotating twin-screw extruder, in the presence of 50 ppm stannous octoate as a catalyst, a mixture of substances preheated to 120°C or below was mixed with 21.5760 parts by weight of MDI and 0.4 parts by weight at a temperature of 200°C Lubricant reaction: 54.8968 parts by weight of polyether intermediate (PTMEG) with molecular weight (Mn) 2000, 23.5272 parts by weight of polyether intermediate (PTMEG) with molecular weight (Mn) 1000, 8.2149 parts by weight of benzene glycol (HQEE) ) Chain extender, 0.3 parts by weight of antioxidant and 0.3 parts by weight of UV stabilizer. The resulting polymer was pelletized underwater and collected in a silo heated at 105°C to dry the product. The molecular weight (Mn) of the resulting TPU was 150,000 Daltons, and was used in Example 7 to prepare melt-spun fibers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com