Methods and systems for producing ethanol using raw starch and fractionation
A fractional separation and ethanol technology, applied in the production of high-alcohol fermented mash, and the production of high-protein dry distiller's grains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
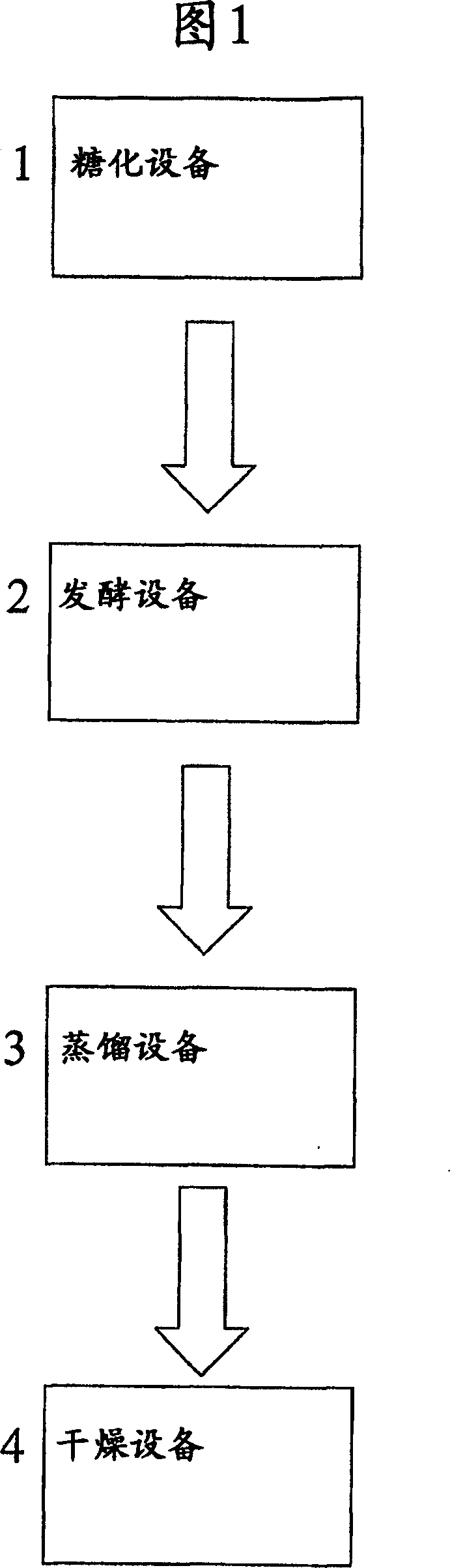
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] Preparation of plant material
[0029] The present method converts starch from plant material (eg, fractionated plant material) to ethanol. Plant material (eg, fractionated plant material) can be comminuted by various methods, such as by milling, so that the starch is available for saccharification and fermentation. Other methods of comminuting plant material are also available. For example, vegetable material such as corn kernels can be ground using ball mills, roll mills, hammer mills, or other mills known for grinding vegetable material, and / or other materials, to reduce particle size. The surface area of plant material (eg, fractionated plant material) can be increased while increasing the flow efficiency of the liquefied medium through the use of emulsification techniques, rotary pulsation, and other particle size reduction methods. Prepared plant material (eg, fractionated plant material) may be referred to as or include "raw starch."
[0030] Fine grinding e...
Embodiment 1
[0166] Example 1 - This method is derived from a grain dry milling operation (endosperm, fiber, and germ)
[0167] substrate provides improved efficacy
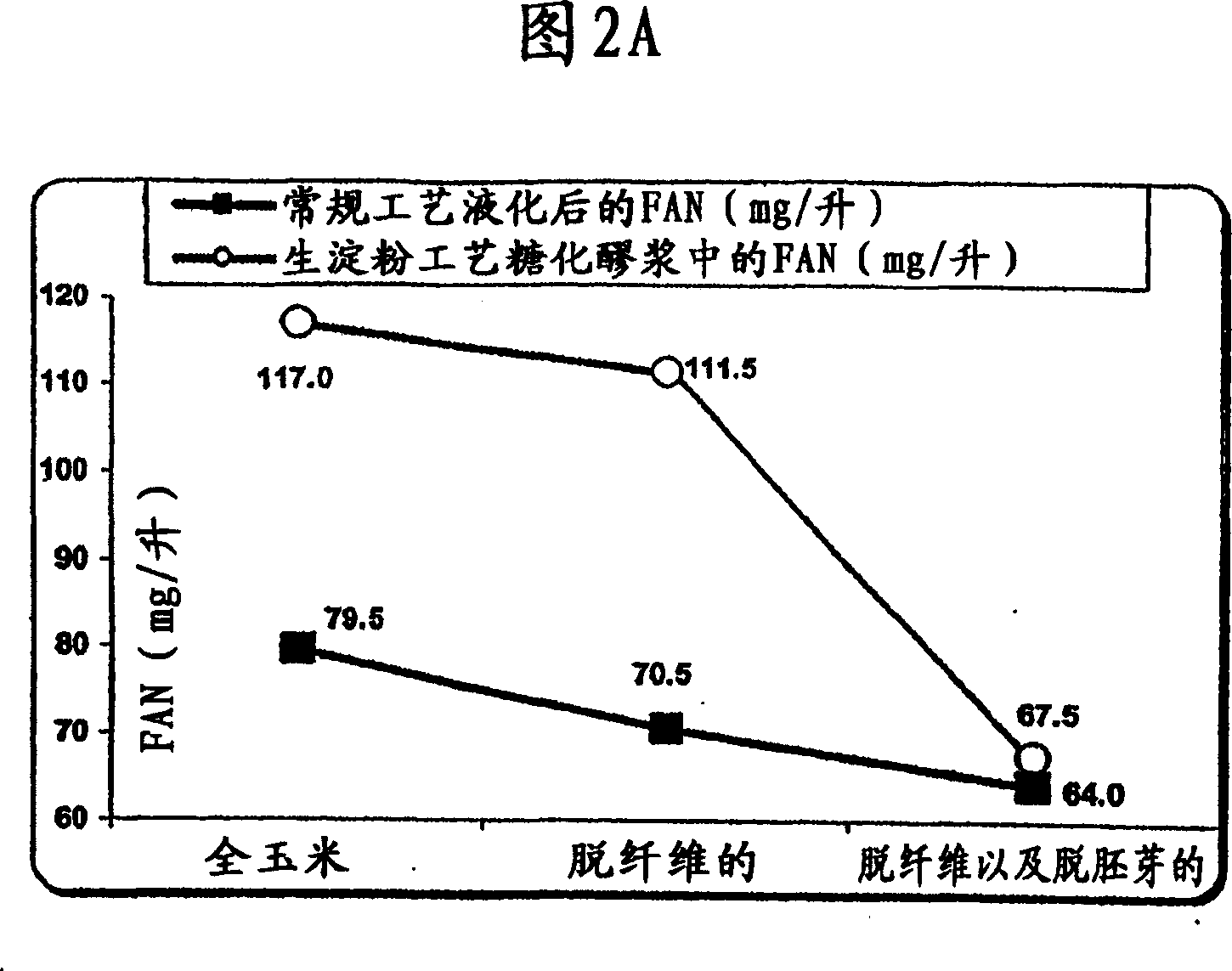
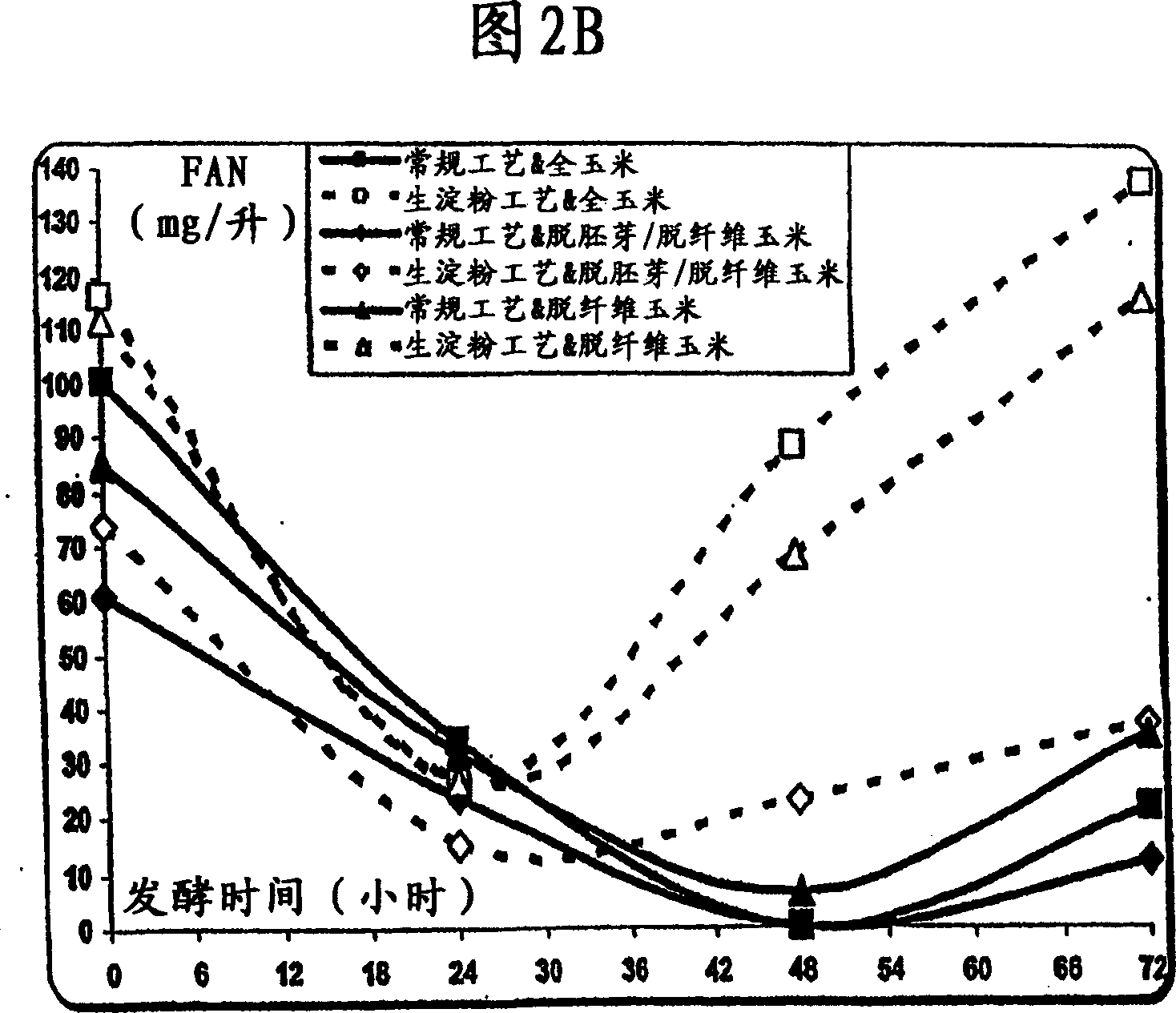
[0168] The present invention provides an improved method of fermenting substrates from grain milling (dry fractionation) processes. Since the removal of the germ results in reduced FAN levels in the mash, the present invention can be used to ferment the endosperm. This method facilitates endogenous enzyme activity in grains. Significant increases in FAN were achieved in whole corn and defiberized corn fermentations compared to the original mash slurry.
[0169] Results and discussion
[0170] This method can be used for endosperm fermentation because the removal of the germ results in reduced FAN levels in the mash, as shown in Figure 2A. FAN provides the nitrogen source required for yeast growth and reduces ethanol-related stress in high-gravity ethanol fermentation. Figure 2A reflects the negative effect...
Embodiment 2
[0173] Example 2 - This method produces high protein DDG from fractionated plant products
[0174] The present invention demonstrates that fractionating corn prior to fermentation can provide high levels of protein in the DDG produced.
[0175] Materials and methods
[0176] Corn was fractionated prior to fermentation by using a Satake fractionation system. After fractionation, saccharification using glucoamylase and acid fungal amylase. Corn is fermented according to the invention without cooking. Fermentation was carried out at 90°F and a pH of 5. After the corn solids are fermented, they are distilled to obtain ethanol. The remaining solids were then dried and samples of fiber, germ, and starch were obtained. All fractionated samples were ground on a Knifetec for 20 seconds. These samples were subsequently analyzed for starch, protein, fat, and neutral detergent fiber content. At the same time, the percentage yield of ethanol was calculated for each sample. Reference...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com