Polyamino acid chemical-modification bacterium and its preparation method and use
A technology of polyamino acid chemistry and drying bacteria, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, fixed on/in organic carriers, etc., can solve the problem of loose surface structure, poor mechanical strength, and weak adsorption capacity and other problems, to achieve the effect of good regeneration performance, high adsorption efficiency, and simple production method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
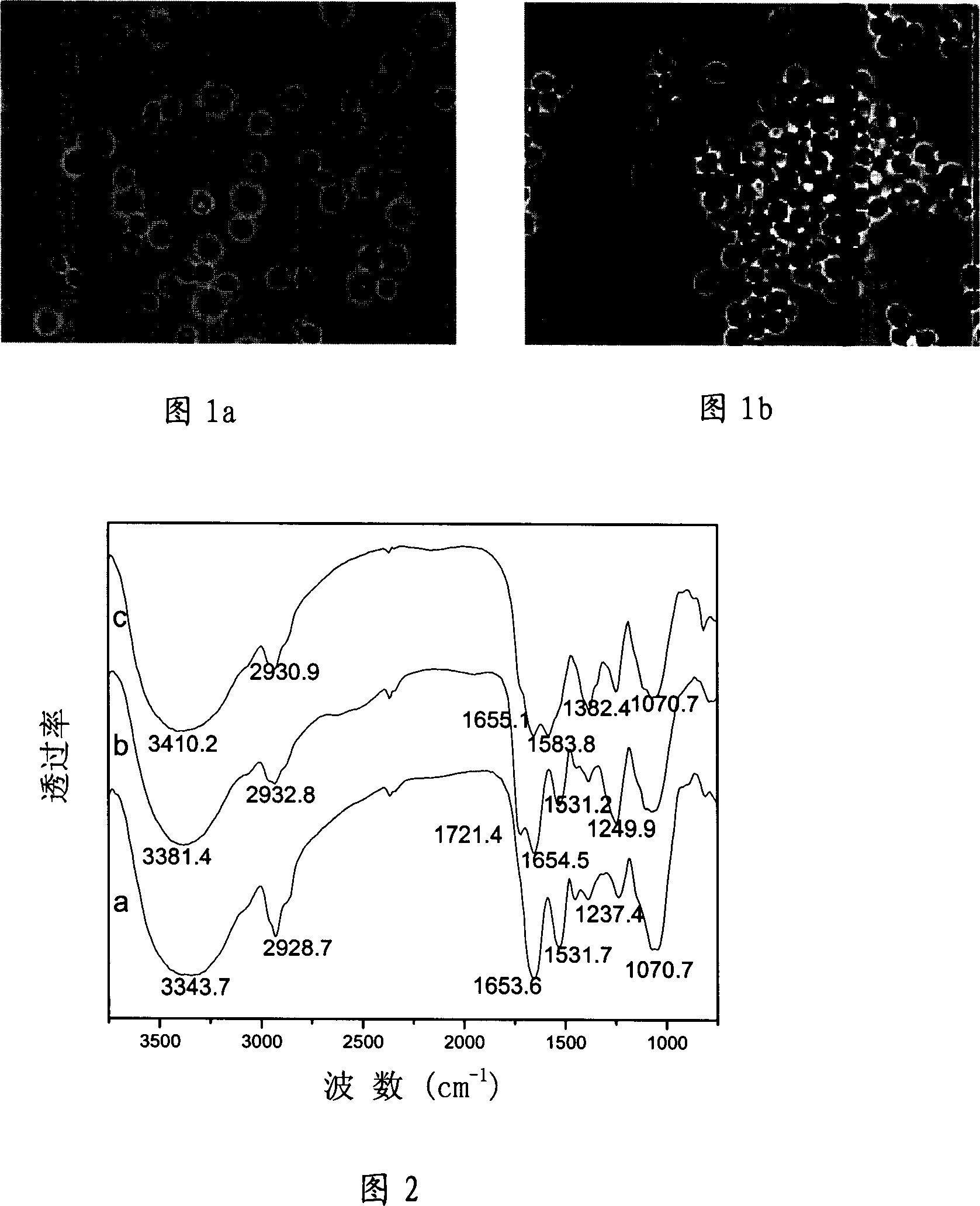
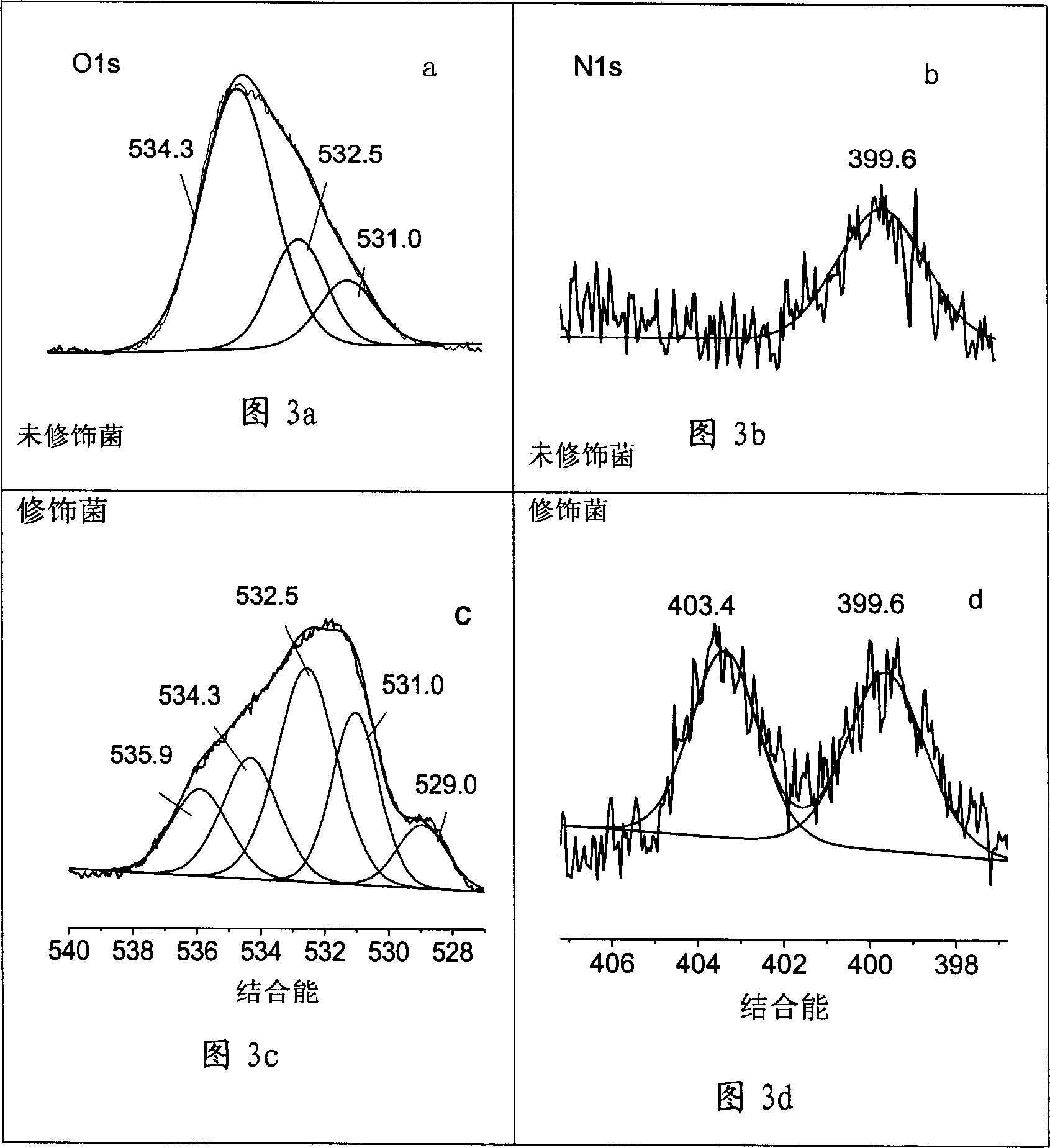
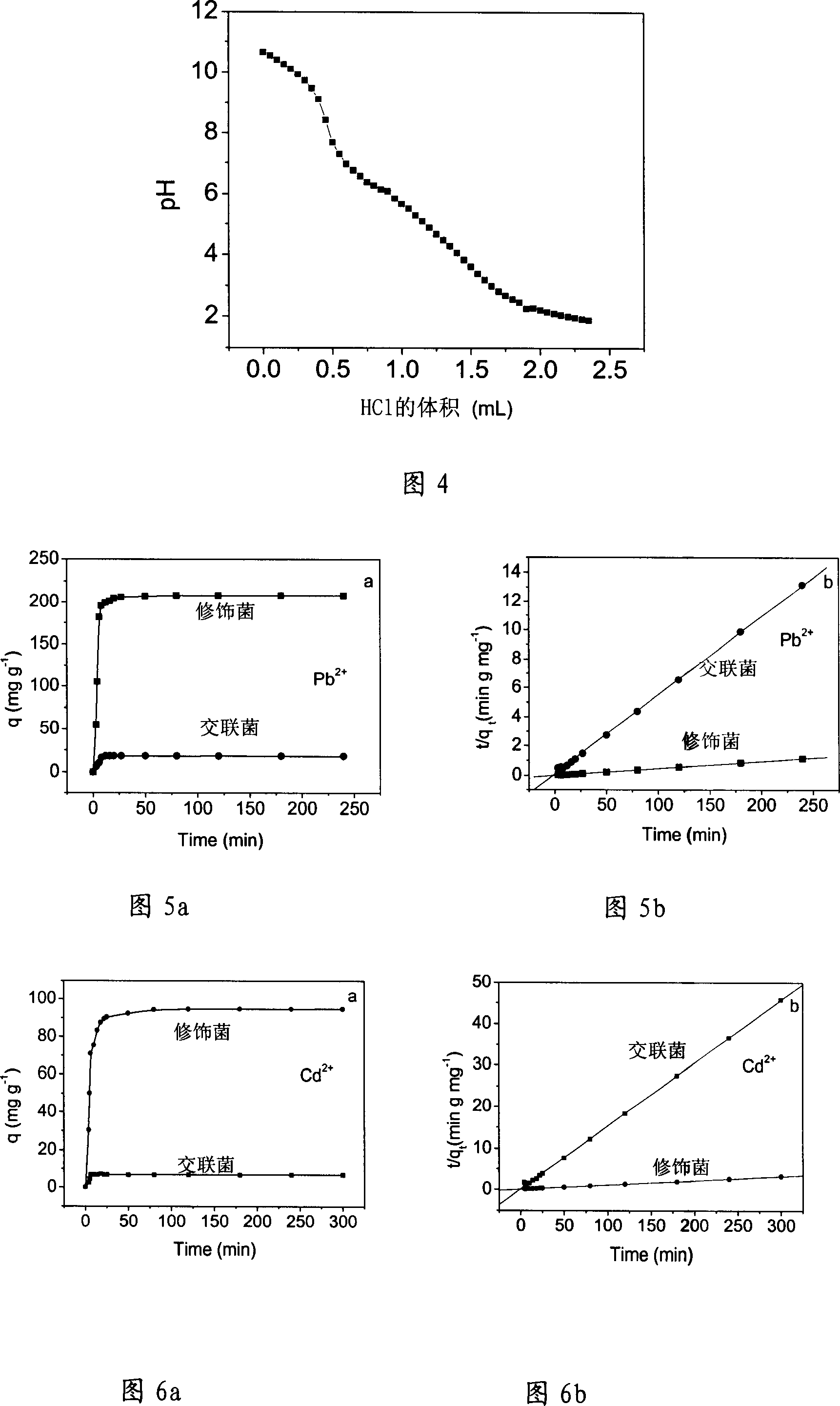
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Synthesis of polyamino acid modified yeast
[0043] 1. First add 15g of dry yeast to 75mL of 1.0% (w / w) glutaraldehyde aqueous solution, shake and react for 14 hours, centrifuge, wash with water, and dry to obtain glutaraldehyde-crosslinked bacteria;
[0044] 2. Dissolve 0.078mol of pyromellitic dianhydride and 0.026mol of arginine in 100mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, stir at room temperature for 1-2 hours, then add 6.0g of glutaraldehyde cross-linking bacteria, After continuing to react at 40-50°C for 2 hours, centrifuge and wash the product 4 times with N,N-dimethylformamide;
[0045] 3. Add the yeast obtained above to 50mL 0.1mol L -1 Alkaline in NaOH solution for 0.5 hour, centrifuge, wash until neutral, and freeze-dry to obtain polyamino acid-modified yeast.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Polyamino acid modified yeast synthesis
[0047] 1. First add 15g of dry yeast to 100mL of 1.0% (w / w) glutaraldehyde aqueous solution, shake and react for 15 hours, centrifuge, wash with water, and dry to obtain glutaraldehyde-crosslinked bacteria;
[0048] 2. Dissolve 0.208mol of pyromellitic dianhydride and 0.026mol of thiourea in 100mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, stir at room temperature for 2 hours, add 6.0g of glutaraldehyde cross-linking bacteria, 40-50 After continuing to react at ℃ for 3 hours, centrifuge and wash the product 4 times with N,N-dimethylformamide;
[0049] 3. Add the yeast obtained above to 50mL 0.1mol L -1 Alkaline in NaOH solution for 1 hour, centrifuge, wash until neutral, and freeze-dry to obtain polyamino acid-modified yeast.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: Synthesis of polyamino acid modified yeast
[0051] 1. First add 15.0g of dry yeast into 150mL of 1.0% (w / w) glutaraldehyde aqueous solution, shake and react for 16 hours, centrifuge, wash with water, and dry;
[0052] 2. Dissolve 0.14mol of pyromellitic dianhydride and 0.026mol of lysine in 100mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, stir at room temperature for 2 hours, add 6.0g of glutaraldehyde cross-linking bacteria, 40- After continuing to react at 50°C for 4 hours, centrifuge and wash the product 4 times with N,N-dimethylformamide;
[0053] 3. Add the yeast obtained above to 50mL 0.1mol L -1 Alkaline in NaOH solution for 0.75 hours, centrifuge, wash until neutral, and freeze-dry to obtain polyamino acid-modified yeast.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com