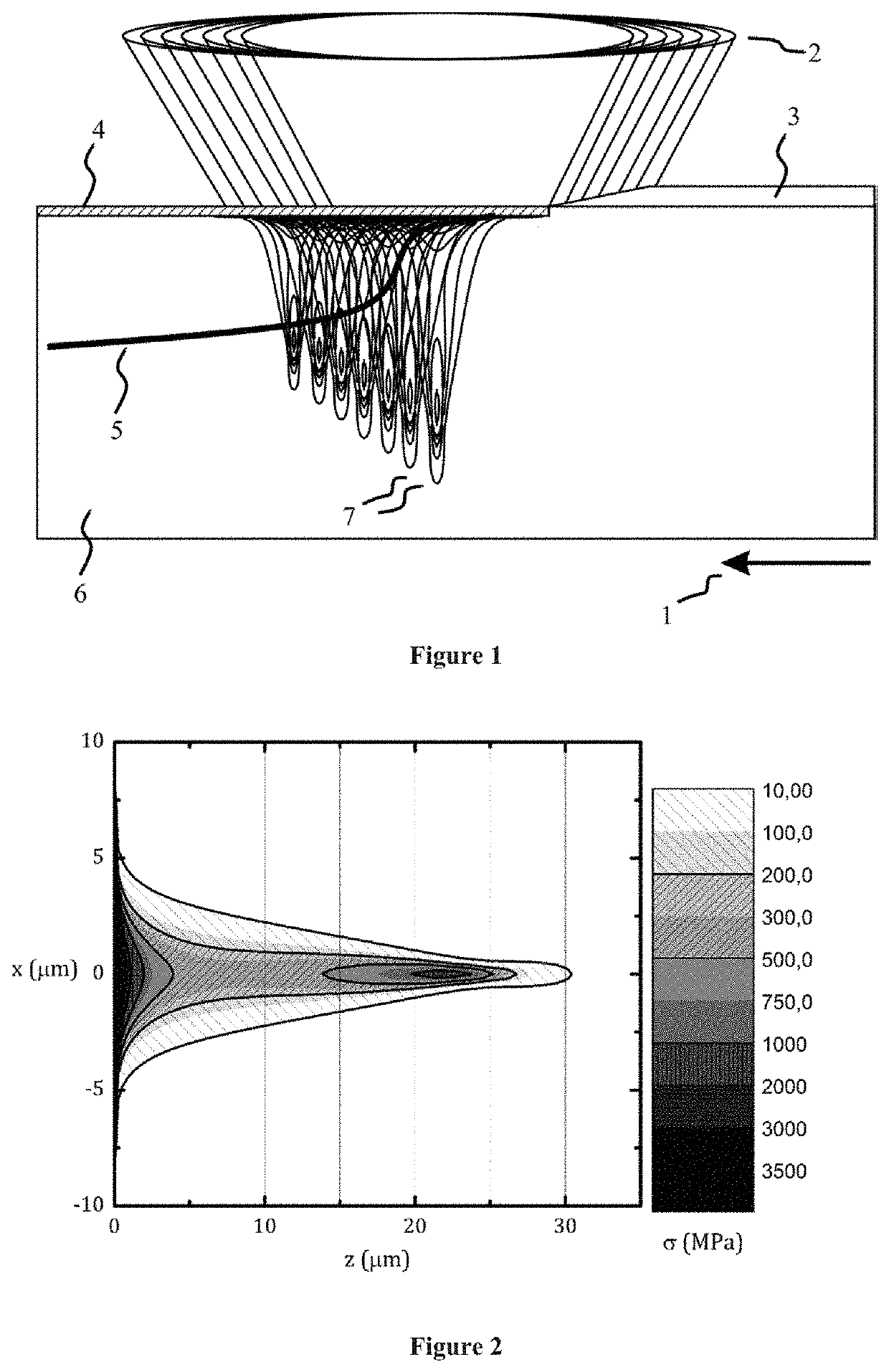
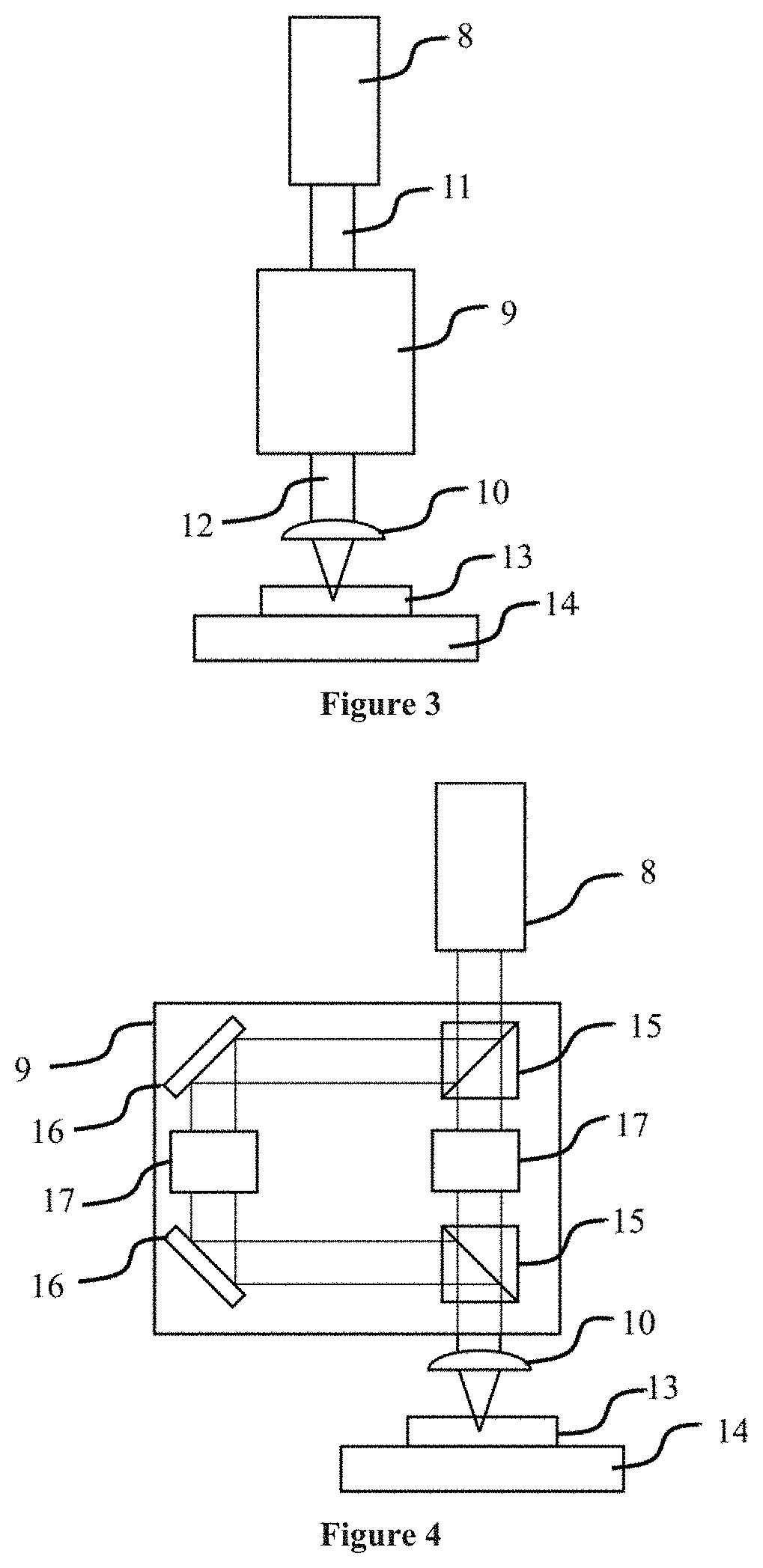
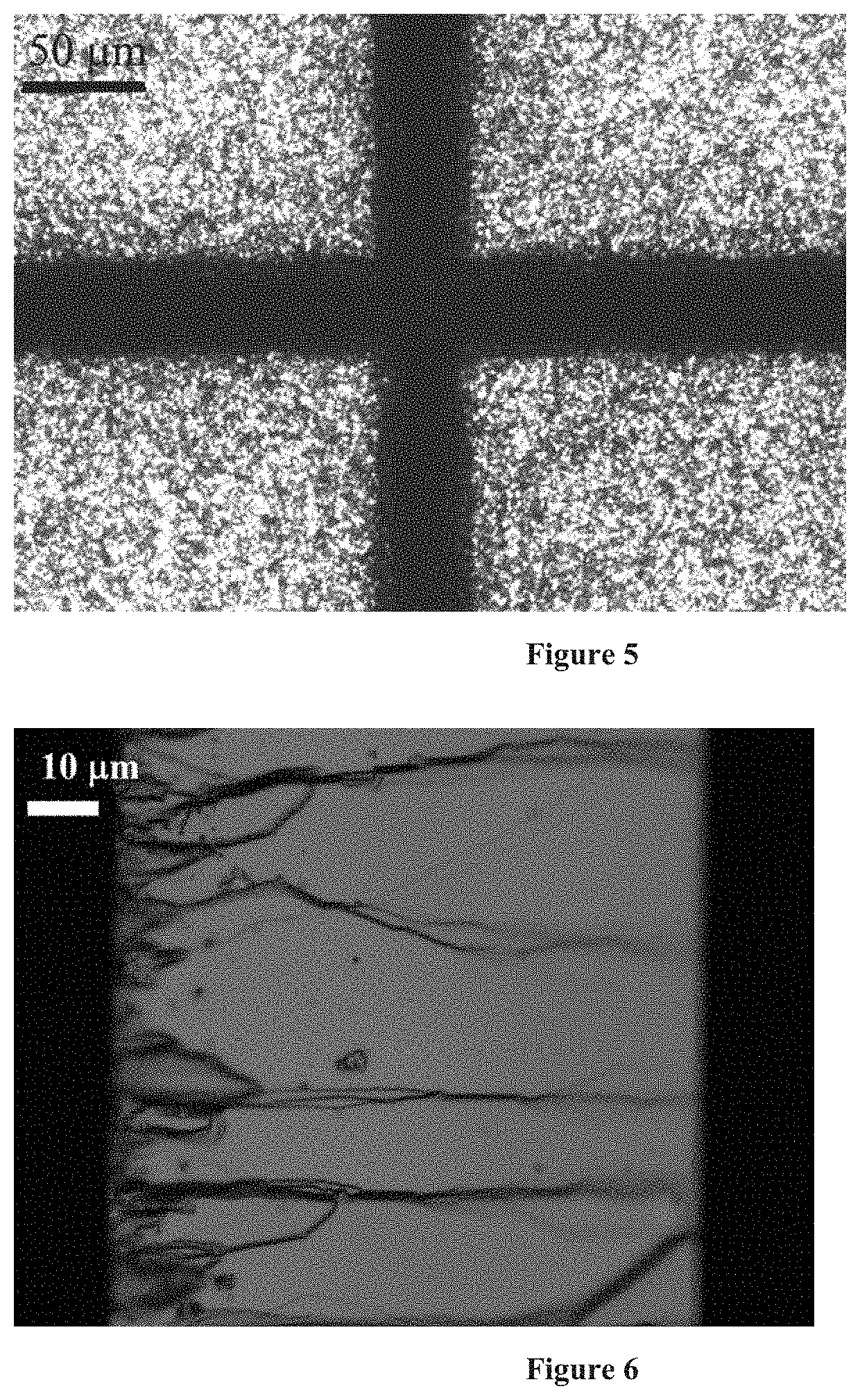
Method of laser scribing of semiconductor workpiece using divided laser beams
a laser beam and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device details, manufacturing tools, welding/soldering/cutting articles, etc., can solve the problems of prior art methods imposing limitations on substrate thickness, material type and processing quality used for wafer separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0031]Workpiece substrate material is SiC (4H—SiC) with a single metal coating of gold. Primary and secondary pulse energy equally combined is 10 mikrojoules. The laser source is a femtosecond laser having an output radiation wavelength 1030 nm, pulse width below 300 fs (full width at half maximum / 1.41), set at an output frequency of 200 kHz. Both primary and secondary beams are altered with non-linear second harmonic generation crystal to be of 515 nm wavelength. Primary and secondary pulses are set with a delay of 100 ps. The focusing unit is arranged with a 0.15 NA focusing objective lens, as the beam converging means, with a focal length of 15 mm. Linear workpiece translation speed is set to 100 mm / s. Result of such processing are summarized in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal relaxation time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal relaxation time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy bandgap | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com