Osteostimulating elastomeric bone filling compositions
a technology of elastomeric bone filling and composition, which is applied in the field of bone filling composition, can solve the problems of not transmitting stress, not providing any therapeutic effect, and inability to mold to fit the defect geometry
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0060]A porous thermoset PGS flour was produced by first adding about 15 grams (g) of hot (≥90° C.) PGS resin to about 30 g of sieved, crystalline NaCl salt having an average particle size about 106 μm or less. The materials were mixed by a mixer (FlackTek, Inc., Landrum, S.C.) at 2000 revolutions per minute (rpm) for about 2 minutes. The resultant paste was placed into a round aluminum dish and smoothed to a film about 2 millimeters (mm) thick. The film was thermoset at a temperature of about 120° C. and a pressure of about 10 Torr for about 24 hours. The resultant solid film was removed from the aluminum dish in crumbled pieces and placed into a jar and then mixed by the FlackTek mixer at 2000 rpm for about 1 minute to break / grind the flour to smaller particle sizes.
[0061]About 50 mL of deionized water (diH2O) was added to the jar and the jar was sonicated for about 5 minutes to dissolve away the NaCl salt. The solvent was decanted, and the dissolve step was repeated three times. ...
example 2
[0062]A PGS bone filling composite was produced by adding about 2.5 g of the porous thermoset PGS flour from Example 1 to about 4.4 g of TCP particles having a particle size in the range of about 50-150 μm and about 0.6 g of glycerol. The materials were mixed by a FlackTek mixer at about 2000 rpm for about 30 seconds, followed by a dwell time of about 20 minutes. To this mixture, about 2.5 g of hot (≥90° C.) PGS resin was added as a carrier and mixed at about 2000 rpm for about 1 minute. The resultant bone filling composite was soft and moldable. The bone filling composite was characterized by manual manipulation and by SEM / energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) for organic / mineral homogeneity.
example 3
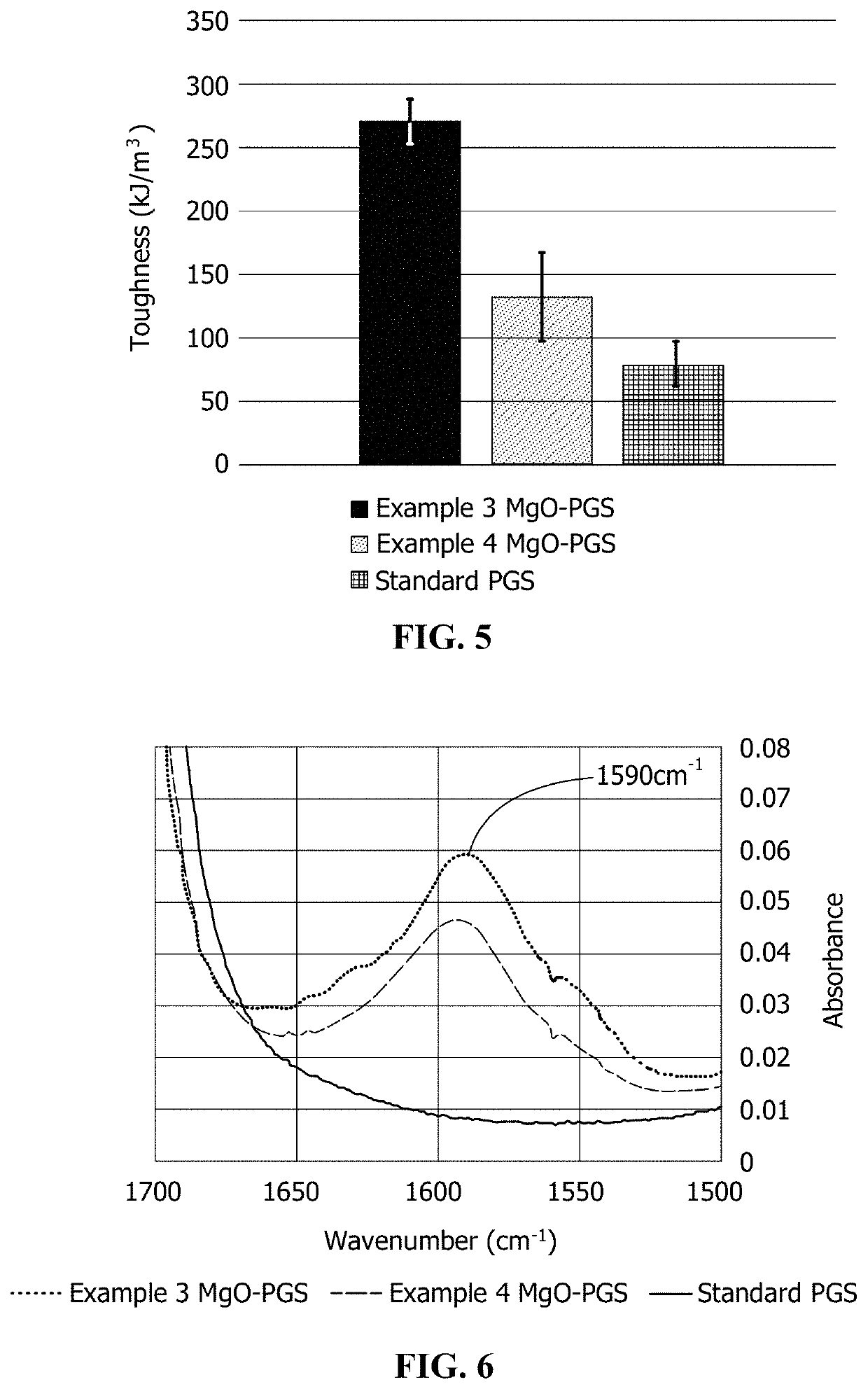
[0063]An MgO-doped PGS resin was formed in a water-mediated reaction based on a method described in U.S. Pat. No. 9,359,472, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety, where the MgO particles were introduced before the 24-hour distillation step. The MgO was provided in an amount of about a 1:200 weight ratio with respect to the PGS resin. Glycerol was added to a reaction vessel with water under stirring. After dissolution of the glycerol, sebacic acid was added to the reaction vessel. The amounts of glycerol and sebacic acid were selected to provide about a 3:2 molar ratio of free hydroxyl groups to free carboxyl groups. The reaction vessel was then fitted with a condenser to reflux water during the melt and stir steps of the polymerization, with the condenser temperature being set to 2.5° C. The reaction vessel was then heated to a temperature of 160° C. under stirring for approximately 70 minutes.
[0064]After the sebacic acid melted, the temperature was set to 150° ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com