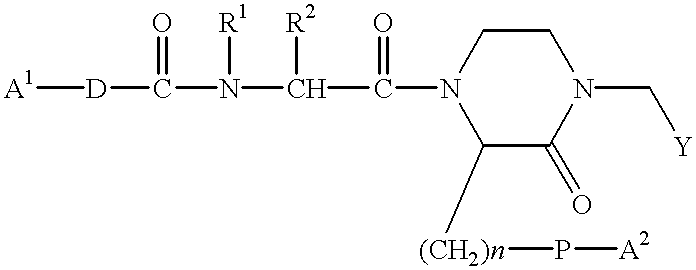
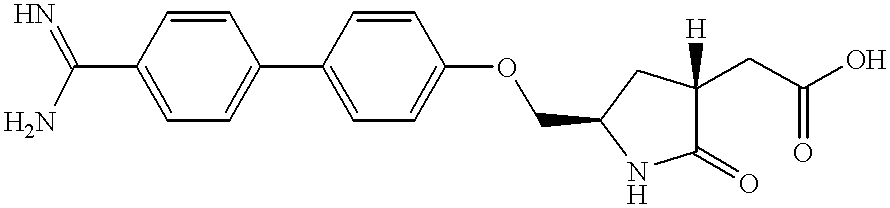
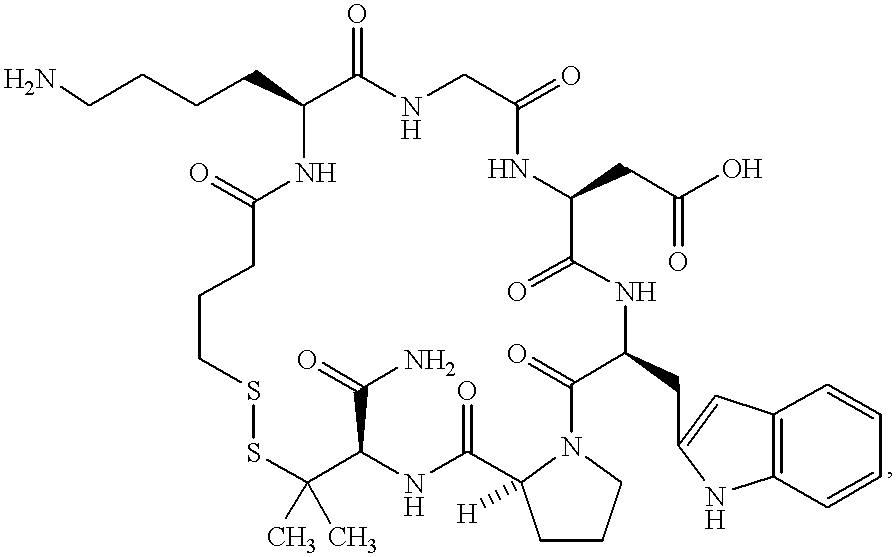
Process for producing sustained-release preparation
a technology of sustained release and preparation, which is applied in the direction of prosthesis, peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of not having a description on the process of producing microcapsules using a solution, no suggestion on application to the other bases, and no suggestion on the application of microcapsules to achieve the effect of suppressing initial release, simple and convenient, and suppressing initial releas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working example 1
[0171] In distilled water 1 ml were dissolved (S)-4-(4-guanidinobenzoylami-no)acetyl-3-[3-(4-guanidinobenzoyl-amino)]propyl-2-oxopiperazine-1-acetic acid (hereinafter, briefly referred to as Compound A) hydrochloride 500 mg and L-arginine 150 mg to give an inner aqueous phase. In methylene chloride 7.5 ml were dissolved lactic acid / glycolic acid copolymer (lactic acid / glycolic acid=50 / 50 (mole %), weight-average molecular weight 8,000) 3850 mg and vitamin E 500 mg to give an oil phase. The oil phase was added to the inner aqueous phase, and the mixture was emulsified with small homogenizer (Polytron) to give a W / O type emulsion. The W / O emulsion was emulsified in 0.1% PVA solution 800 ml (an outer aqueous phase) containing 2.7% NaCl which was cooled to 15.degree. C. with using homomixer to give a W / O / W type emulsion. Then, the W / O / W type emulsion was slowly stirred with a conventional propeller agitator for 3 hours. After hardening of the microcapsules with evaporation of methylene ...
working example 2
[0172] In distilled water 1 ml were dissolved Compound A hydrochloride 500 mg and L-arginine 150 mg to give an inner aqueous phase. In methylene chloride 8 ml were dissolved lactic acid / glycolic acid copolymer (lactic acid / glycolic acid=50 / 50 (mole %), weight-average molecular weight: 8,000) 4100 mg and vitamin E 250 mg to give an oil phase. The oil phase was added to the inner aqueous phase, and the mixture was emulsified with small homogenizer (Polytron) to give a W / O type emulsion. The W / O emulsion was emulsified in 0.1% PVA solution 800 ml (an outer aqueous phase) containing 2.7% NaCl which was cooled to 15.degree. C. with using homomixer to give a W / O / W type emulsion. Then, the W / O / W type emulsion was slowly stirred with a conventional propeller agitator for 3 hours. After hardening of the microcapsules with evaporation of methylene chloride, the microcapsules were collected by centrifugation. The collected microcapsules were washed with purified water, to which was added manni...
working example 3
[0173] In distilled water 2 ml were dissolved Compound A hydrochloride 750 mg and L-arginine 150 mg to give an inner aqueous phase. In methylene chloride 10 ml were dissolved lactic acid / glycolic acid copolymer (lactic acid / glycolic acid=50 / 50 (mole %), weight-average molecular weight: 9,000) 3600 mg and vitamin E 500 mg to give an oil phase. According to a similar method described in Working Example 2 the W / O type emulsion was prepared, and thereafter the W / O / W type emulsion was prepared, and finally freeze dried microcapsules was prepared. In the prepared microcapsules, content of arginine and vitamin E was respectively 1.5% (w / w) and 10% (w / w).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com