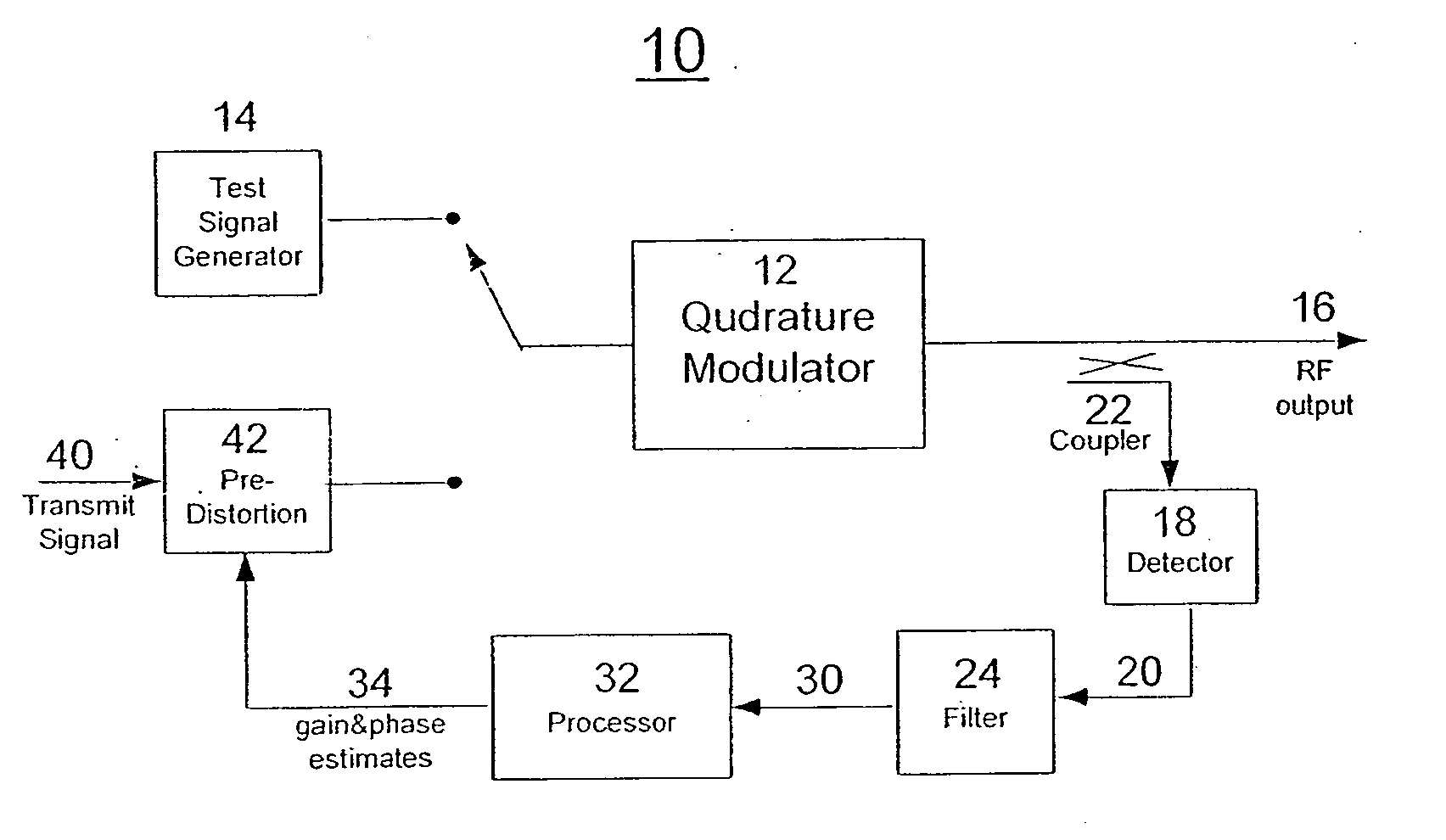
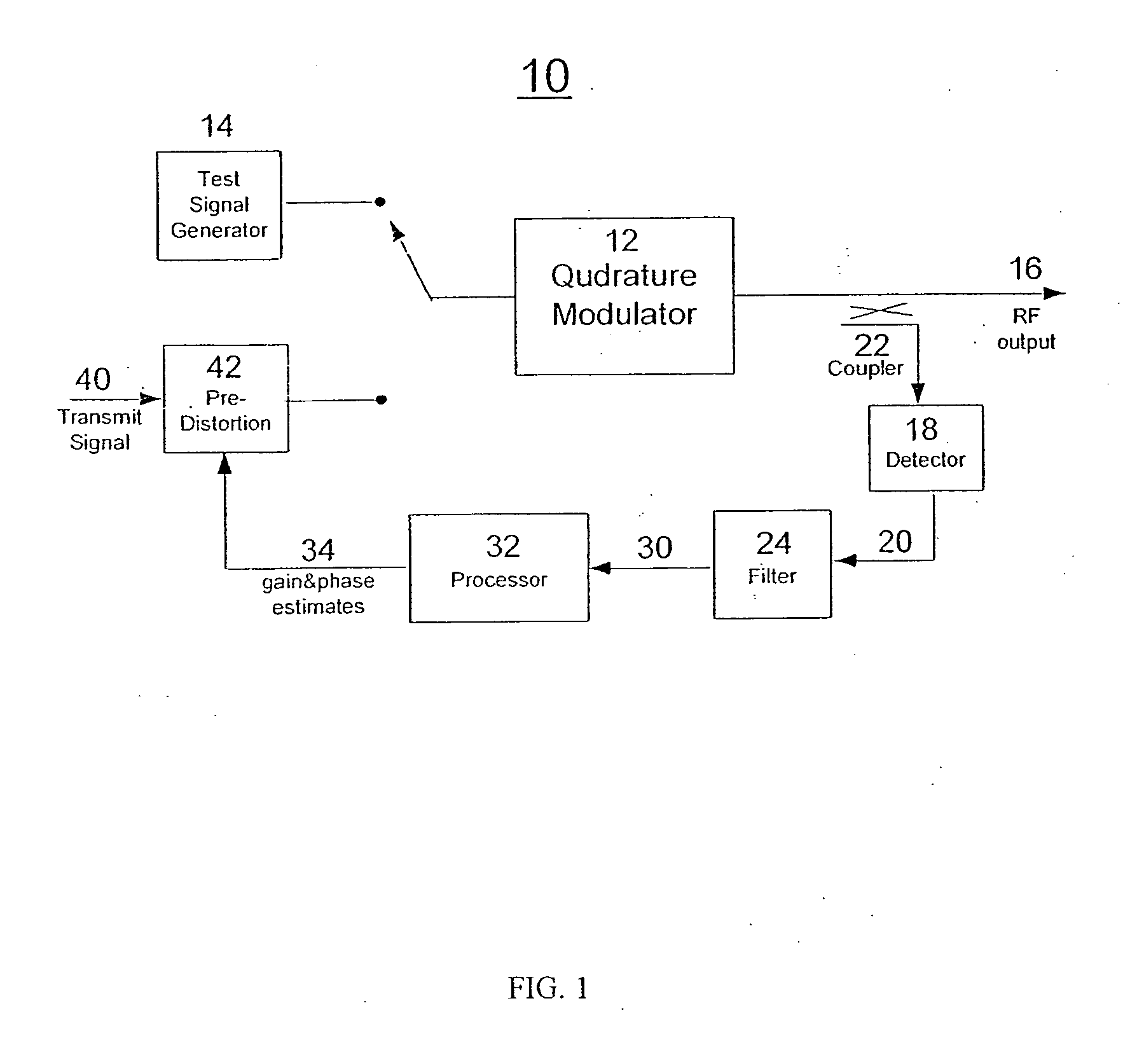
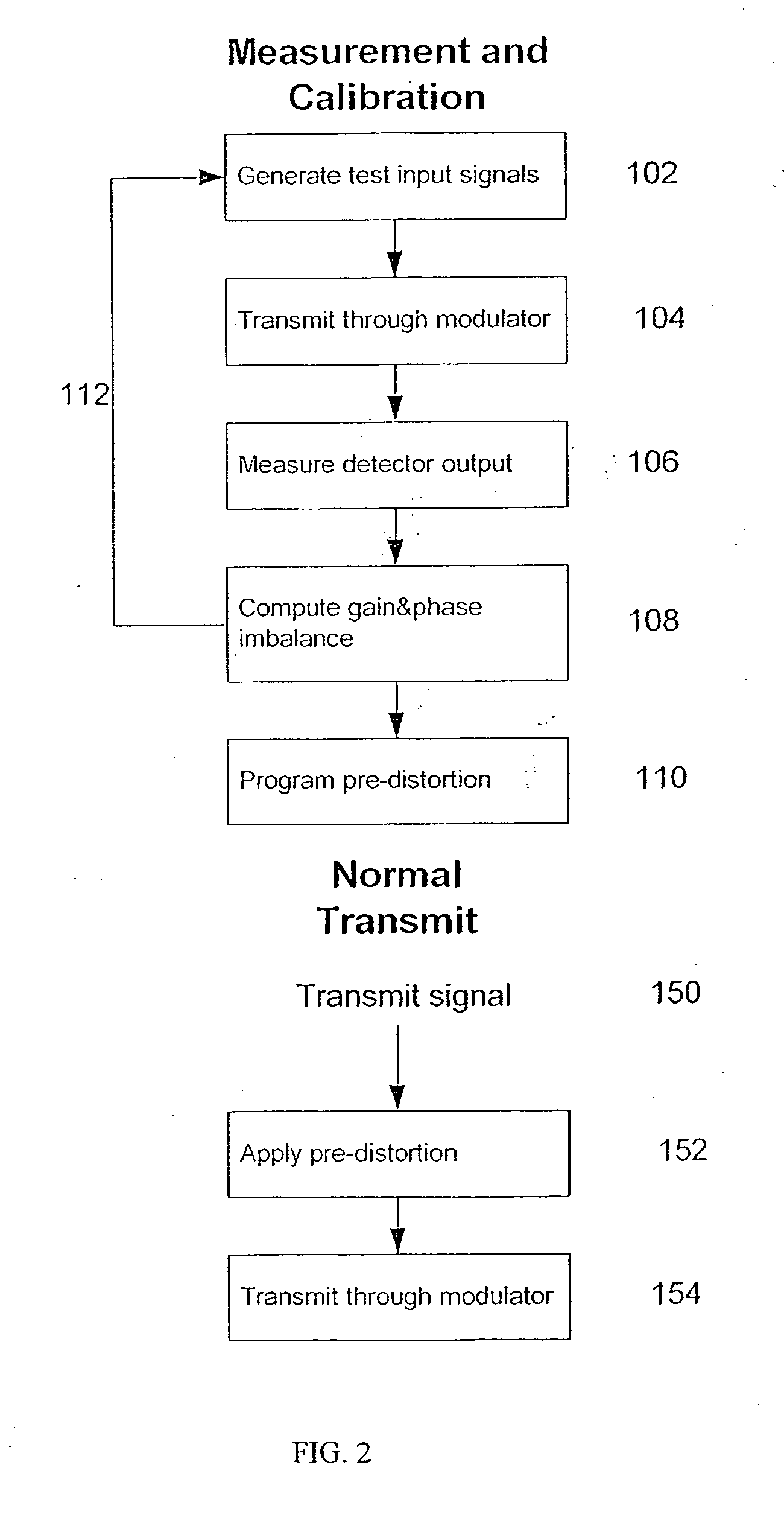
Method for measuring and compensating gain and phase imbalances in quadrature modulators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] I(t), Q(t) sine / cosine waveforms with equal amplitude and frequency, but shifted by 90 degrees one with respect to the other, e.g.:
I(t)=A cos (.omega..sub.it-90.degree.)=A sin (.omega..sub.it)
Q(t)=A cos (.omega..sub.it)
[0034] Ignoring the modulator imbalance we get:
Y(t)=A sin (.omega..sub.it) sin (.omega..sub.LOt)+A cos (.omega..sub.it) cos (.omega..sub.LOt)=A cos [(.omega..sub.LO-.omega..sub.i)t] (5)
[0035] i.e. the output contains a single sideband carrier at frequency f.sub.LO-f.sub.i=(.omega..sub.LO-.omega..sub.i) / 2.pi.. Now, for the same sine inputs waveforms, we compute the effect of gain and phase imbalances:
Y(t)=A(1+.epsilon.) sin (.omega..sub.it+.DELTA..epsilon.) sin (.omega..sub.LOt+.DELTA..phi.)+A cos (.omega..sub.it) cos (.omega..sub.LOt) (6)
[0036] By standard trigonometric manipulation we can show that:
Y(t)=S.sub.L cos [(.omega..sub.LO-.omega..sub.i)t+.psi..sub.L)+S.sub.U cos [(.omega..sub.LO+.omega..sub.i)t+.psi..sub.U) (7)
[0037] where: 1 S L = A ( 1 + ) cos 2( -...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com