Novel polynucleotides and polypeptides in pathogenic mycobacteria and their use as diagnostics, vaccines and targets for chemotherapy
a technology of mycobacteria and polypeptides, which is applied in the field of new polynucleotides and polypeptides in pathogenic mycobacteria and their use as diagnostics, vaccines and targets for chemotherapy, can solve the problems of resistant organisms, strains are unable to repair the constructed deletion mutation, and the truncated gene products cannot carry out the normal function of the gen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
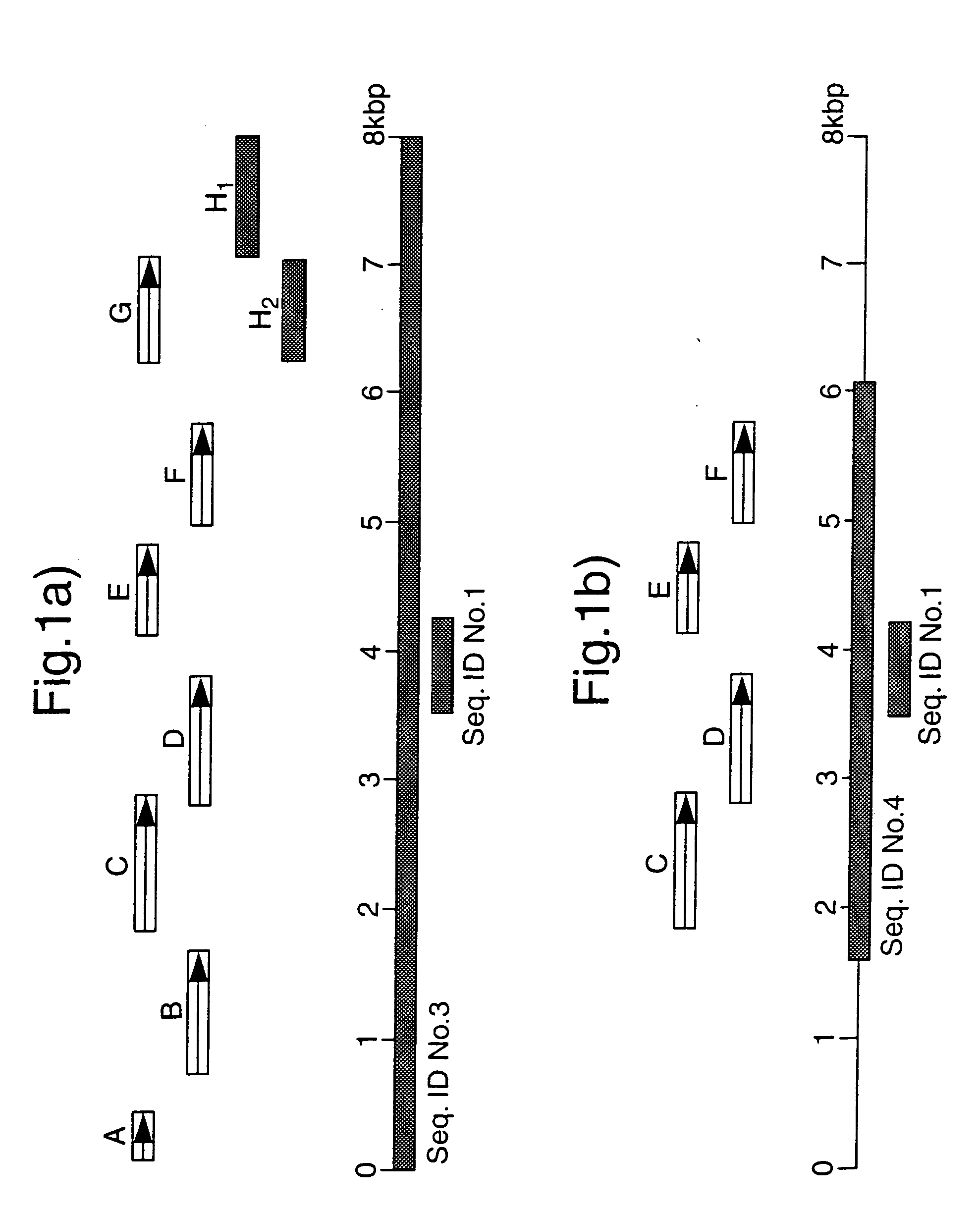
[0151] To obtain the full sequence of GS in Mavs and Mptb we generated a genomic library of Mavs using the restriction endonuclease EcORI and cloning into the vector pUC18. This achieved a representative library which was screened with .sup.32P-labelled identifier sequence yielding a positive clone containing a 17 kbp insert. We constructed a restriction map of this insert and identified GS as fragments unique to Mavs and Mptb and not occurring in laboratory strains of M.avium. These fragments were sub-cloned into pUC18 and pGEM4Z. We identified GS contained within an 8 kb region. The full nucleotide sequence was determined for GS on both DNA strands using primer walking and automated DNA sequencing. DNA sequence for GS in Mptb was obtained using overlapping PCR products generated using PwoDNA polymerase, a proofreading thermostable enzyme. The final DNA sequences were derived using the University of Wisconsin GCG gel assembly software package.
example 3
[0152] The DNA sequence of GS in Mavs and Mptb was found to be more than 99% homologous. The ORFs encoded in GS were identified using GeneRunner and DNAStar computer programmes. Eight ORFs were identified and designated GSA, GSB, GSC, GSD, GSE, GSF, GSG and GSH. Database comparisons were carried out against the GenEMBL Database release version 48.0 (9 / 96), using the BLAST and BLIXEM programmes. GSA and GSB encoded proteins of 13.5 kDa and 30.7 kDa respectively, both of unknown functions. GSC encoded a protein of 38.4 kDa with a 65% homology to the amino acid sequence of rfbD of V. cholerae, a 62% amino acid sequence homology to gmd of E. coli and a 58% homology to gca of Ps.aeruginosa which are all GDP-D-mannose dehydratases. Equivalent gene products in H.influenzae, S.dysenteriae, Y.encerocolitica, N.gonorrhoea, K.pneumoniae and rfbD in Salmonella enterica are all involved in `O`-antigen processing known to be linked to pathogenicity. GSD encoded a protein of 37.1 kDa which showed ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pharmaceutical composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com