Treatment of Mycobacterial diseases by administration of bacterial/permeability-increasing protein products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
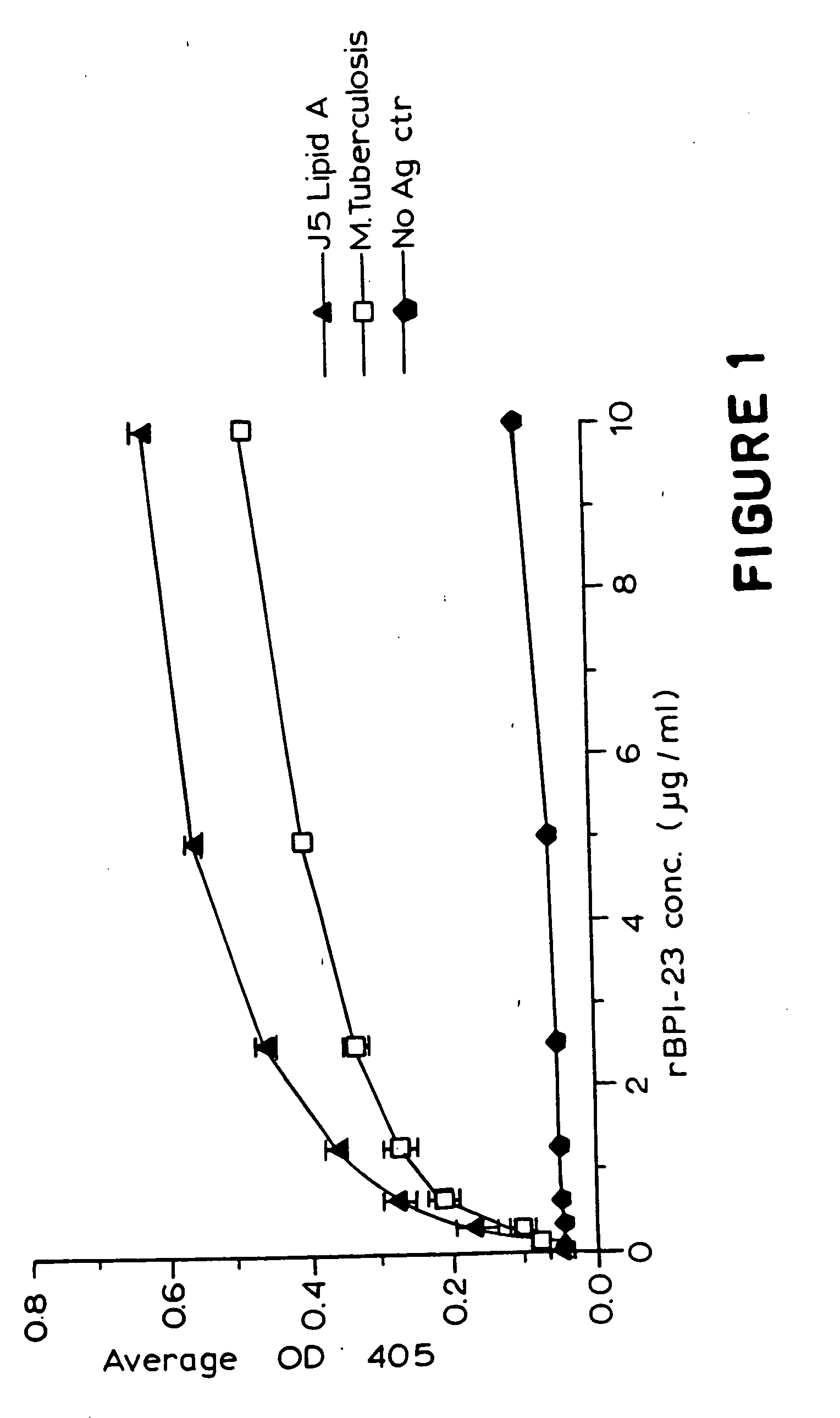
[0041] An enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was conducted to determine binding of a BPI protein product to M. tuberculosis. Specifically, non-viable, desiccated M. tuberculosis H37 RA (Difco, Detroit, Mich.) was suspended in DPBS (25 μg / ml) and used to coat microtiter wells overnight at 37° C. Wells were also coated with either 25 μg / ml Lipid A (E. coli J5 mutant, RIBI, Hamilton, Mont.) or 500 μl DPBS to demonstrate the functionality and specificity of rBPI23. After washing (3× with DPBS+0.05% Tween 20), the plates were blocked for 1 hr. at room temperature with 200 μl / well of DPBS+1% non-fat milk. After washing as above, 50 μl solutions of either various concentrations of rBPI23 (in DPBS containing 0.05% Tween 20) or DPBS (negative control) were added to the wells, which were then incubated for 1 hr. at 37° C. The wells were again washed as above, and the amount of rBPI23 bound to the wells was determined using an anti-rBPI23 mouse monoclonal antibody (designated αBPI MAb-2...
example 2
[0044] In this example, an ELISA Assay is conducted to determine binding of a BPI protein product to the lipoarabinomannan portion of Mycobacteria. The binding activity of BPI protein product (e.g., rBPI23) to LAM is demonstrated as described in the previous example, except LAM purified from a species of Mycobacterium, (e.g., M. tuberculosis or M. leprae) is substituted for the nonviable M. tuberculosis used to coat the ELISA plates in that example. Purified LAM is isolated as described by Hunter et al., J. Biol. Chew., 261: 12345-12351 (1986). Specific binding of biologically active BPI protein product is demonstrated by comparison of the OD 405 readings from the LAM coated wells with positive and negative controls.
example 3
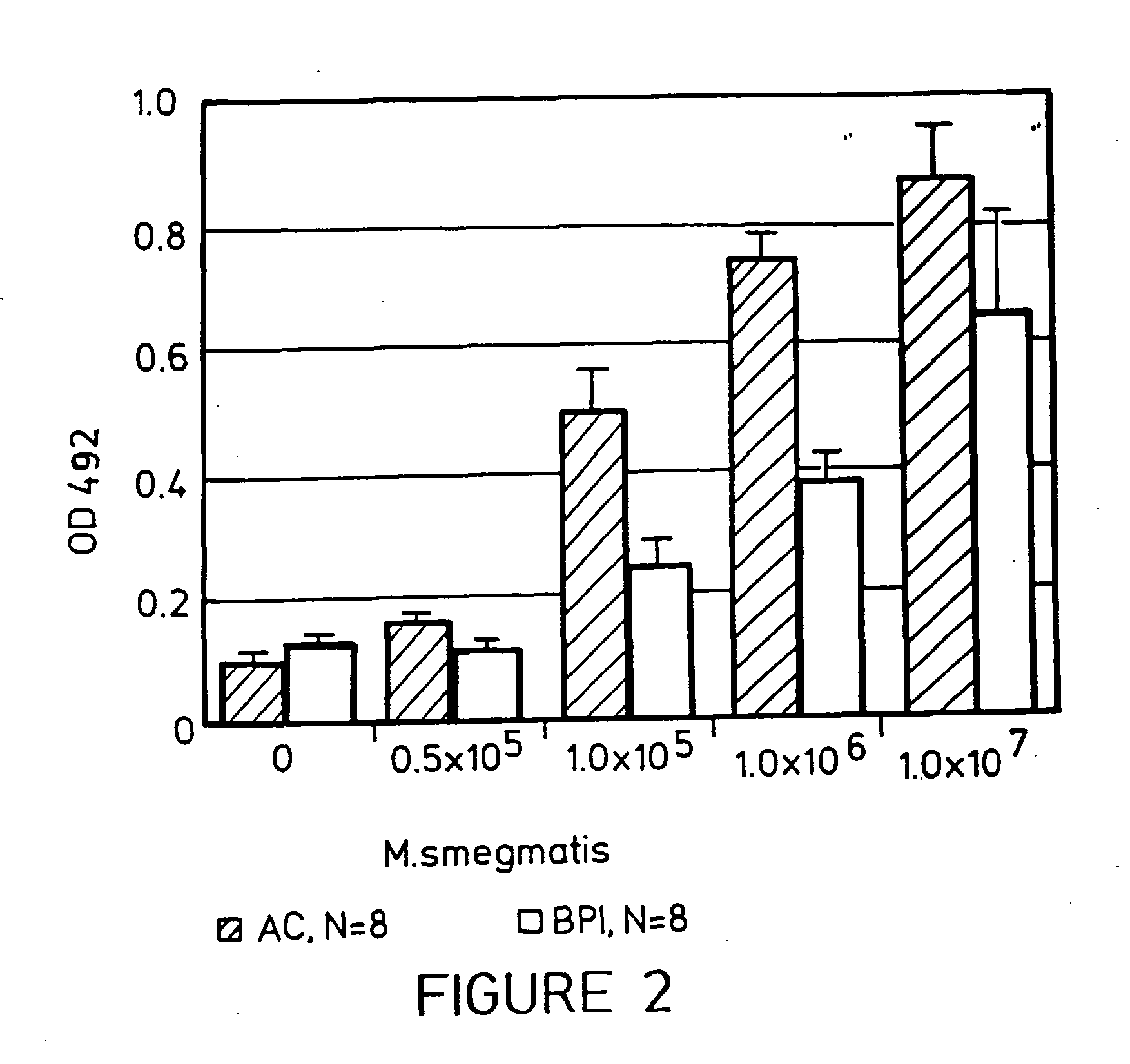
[0045] The following experiment was conducted to determine the effect of a BPI protein product, rBPI23, on Mycobacteria-induced cytokine production in whole human blood. Whole human blood from healthy volunteers was collected into Vacutainer tubes (ACD, Beckton Dickinson, Rutherford, N.J.). Aliquots of blood (225 μl) were mixed with either rBPI23 (10 μg / ml final) or the protein thaumatin (10 μg / ml final in 5 ml) as a negative control. RPMI medium (20 μl) was added to each sample. Varying dilutions (0-8 ng / ml) of either E. coli O113 LPS (Ribi, Hamilton Mich.) or of non-viable, desiccated M. tuberculosis H37 RA (0-100 μg / ml) (Difco, Detroit Mich.) were added to the samples, which were then incubated at 37 C for 6 hours. The reactions were stopped by the addition of 750 μl of RPMI medium, the samples were centrifuged at 500 g for 7 min, and stored at −20° C. until analyzed. The supernatant was assayed for cytokine (TNF) levels based on a standard curve, according to the manufacturers' ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Permeability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Immunogenicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com