Recording medium, recording apparatus and recording method
a recording medium and recording apparatus technology, applied in the field of data recording medium, can solve the problems of affecting the cooling process of the preceding mark, affecting the heat distribution, and significant loss of signal quality, and achieve the effect of reducing jitter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0177] The preferred embodiments of the present invention are described below with reference to the accompanying figures.
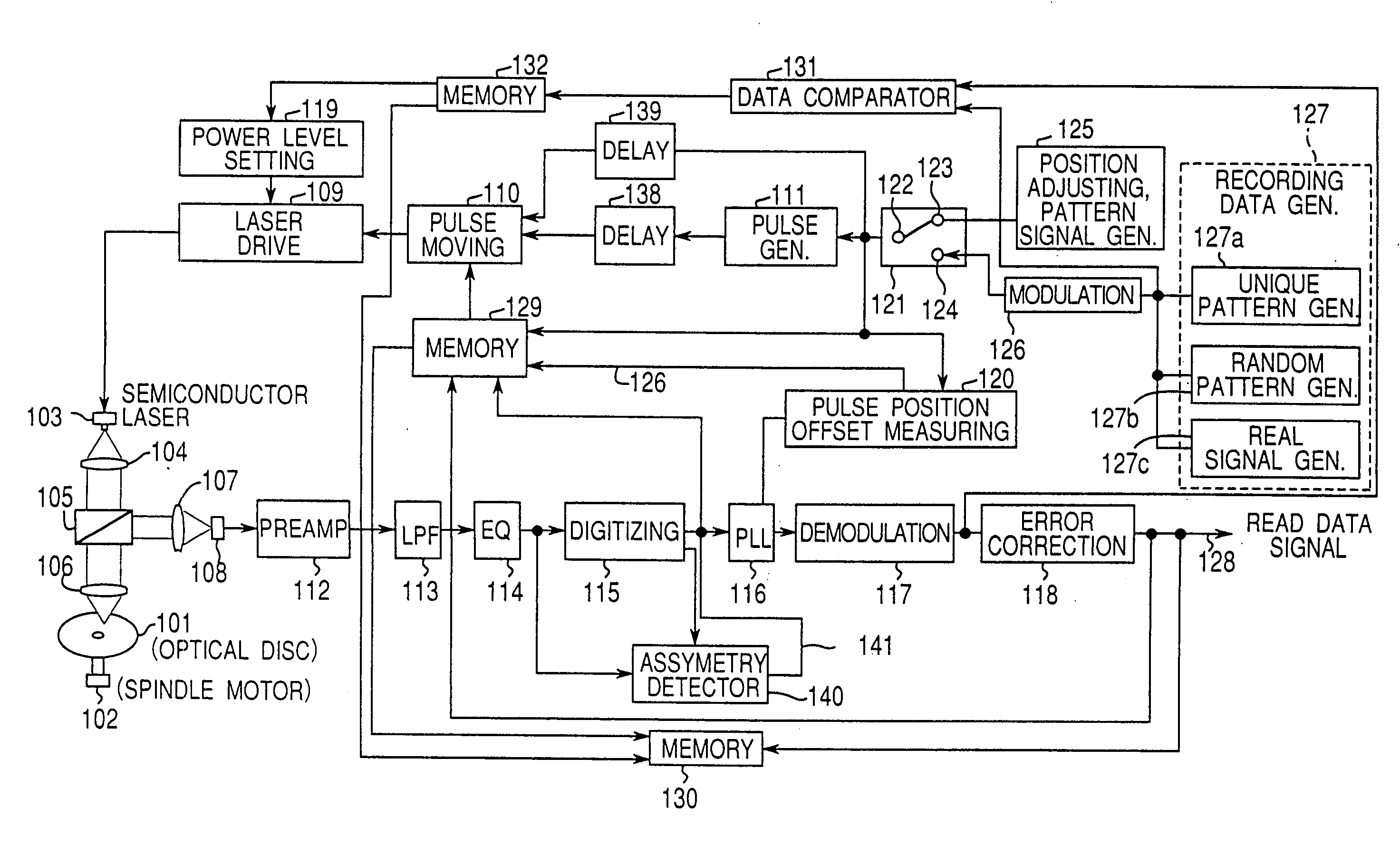
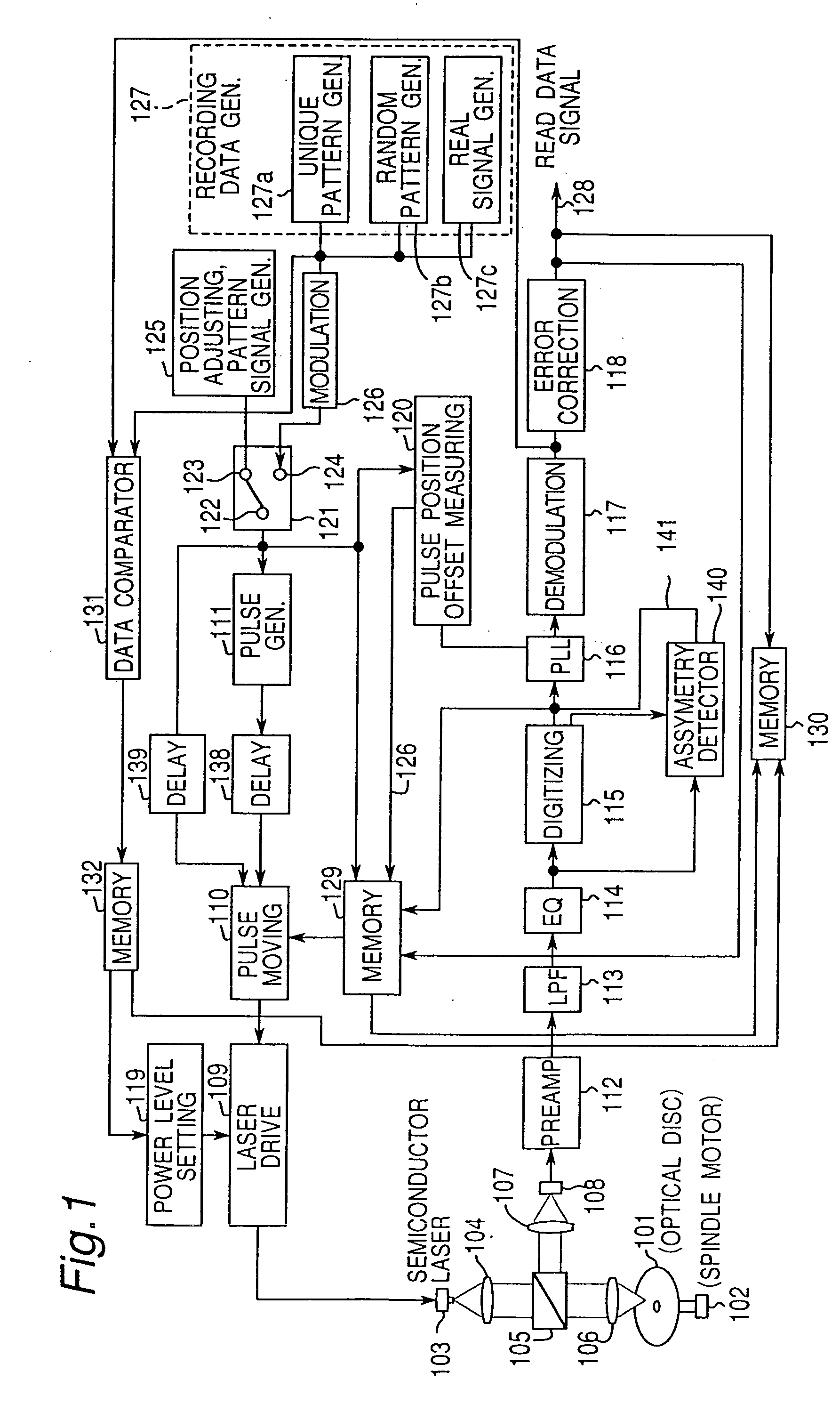
[0178]FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an optical data recording apparatus, referred to below as an optical disc recorder, according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention.
[0179] Shown in FIG. 1 are: an optical disc 101, spindle motor 102, semiconductor laser 103, collimeter lens 104, beam splitter 105, objective lens 106, collective lens 107, photodetector 108, laser drive circuit 109, pulse moving circuit 110, pulse generator 111, preamplifier 112, low pass filter 113, reproduction equalizer 114, digitizing circuit 115, PLL 116, demodulation circuit 117, error correction circuit 118, power level setting circuit 119, pulse position offset measuring circuit 120, switch 121, switch contacts 122, 123, and 124, pattern signal generator 125 for pulse position adjusting, modulation circuit 126, recording data generator 127, read data signal 128, memory 129,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com