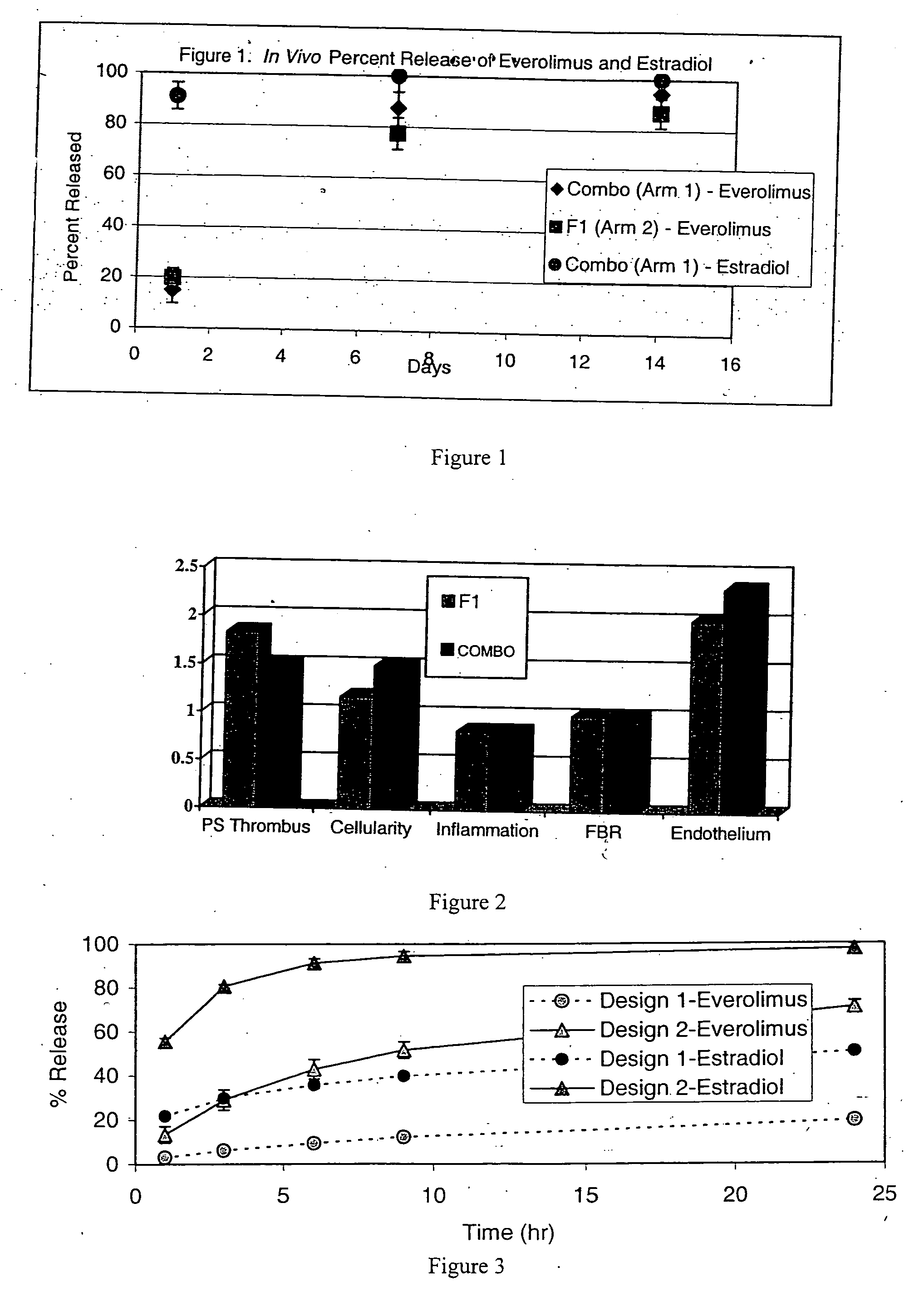
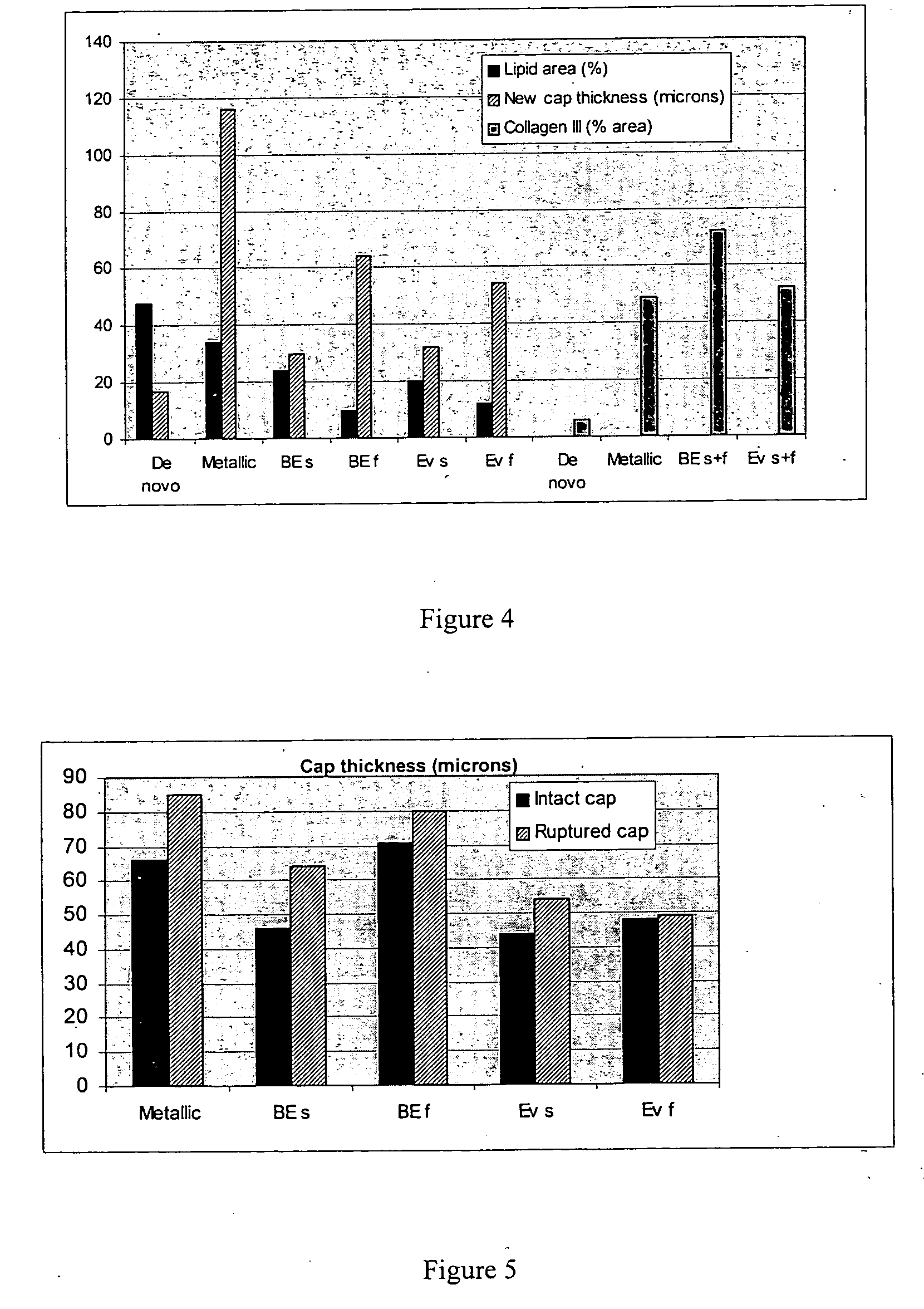
Drug-delivery stent formulations for restenosis and vulnerable plaque
a technology of vulnerable plaque and stent, which is applied in the direction of prosthesis, drug composition, extracellular fluid disorder, etc., can solve the problems of high risk, thrombosis-prone atherosclerotic plaque, and significant morbidity and mortality associated with vascular plaques
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0048] The embodiments of the present invention will be illustrated by the following set forth examples. All parameters and data are not to be construed to unduly limit the scope of the embodiments of the invention.
examples 1-2
Drug-Eluting Coatings Having a Fast and Slow Release of Estradiol from 13 mm Penta™ Stents
[0049] Penta™ stents (available from Guidant) can be coated according to the configurations defined in Table 1 to provide a fast release or a slow release of estradiol.
TABLE 1Coating configurations of Penta ™ stents for delivery of estradiolReservoirTopcoatPrimerDrugSolidTopcoatReleasePolymerPrimerPolymerContentTargetPolymerTarget1FastEVAL40 μgAEVAL300 μg600 mgBEVAL100μgC2SlowEVAL40 μgAEVAL300 μg600 mgBPBMA40μgD
A: 3% EVAL / 72% DMAC / 25% ethanol.
B: 2% EVAL / 1% Estradiol / 77% DMAC / 20% pentane.
C: 4% EVAL / 76% DMAC / 20% pentane.
examples 3-4
Drug-Eluting Coatings Having a Fast and Slow Release of Everolimus
[0050] Penta™ stents can be coated according to the configurations defined in Table 2 to provide a fast release or a slow release of everolimus.
TABLE 2Coating configurations of Penta ™ stents for delivery of everolimusReservoirTopcoatPrimerDrugSolidTopcoatReleasePolymerPrimerPolymerContentTargetPolymerTarget3FastEVAL40 μgAEVAL385 mg615 μgBEVAL40μgC4SlowEVAL40 μgAEVAL273 mg478 μgBPBMA189μgC
A: 3% EVAL / 72% DMAC / 25% ethanol.
B: 2% EVAL / 1% everolimus / 77% DMAC / 20% pentane.
C: 4% EVAL / 76% DMAC / 20% pentane
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com