Immunomodulatory methods using oligosaccharides
a technology of immunomodulatory methods and oligosaccharides, which is applied in the field of immunomodulatory methods using oligosaccharides, can solve the problems of not showing whether human immune cells (e.g., human immune cells in the absence of i>s. mansoni /i>infection) are responsive to lewis antigen-containing compounds, and not showing whether cell types, produce il-, and other cytokines that regulate the development o
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
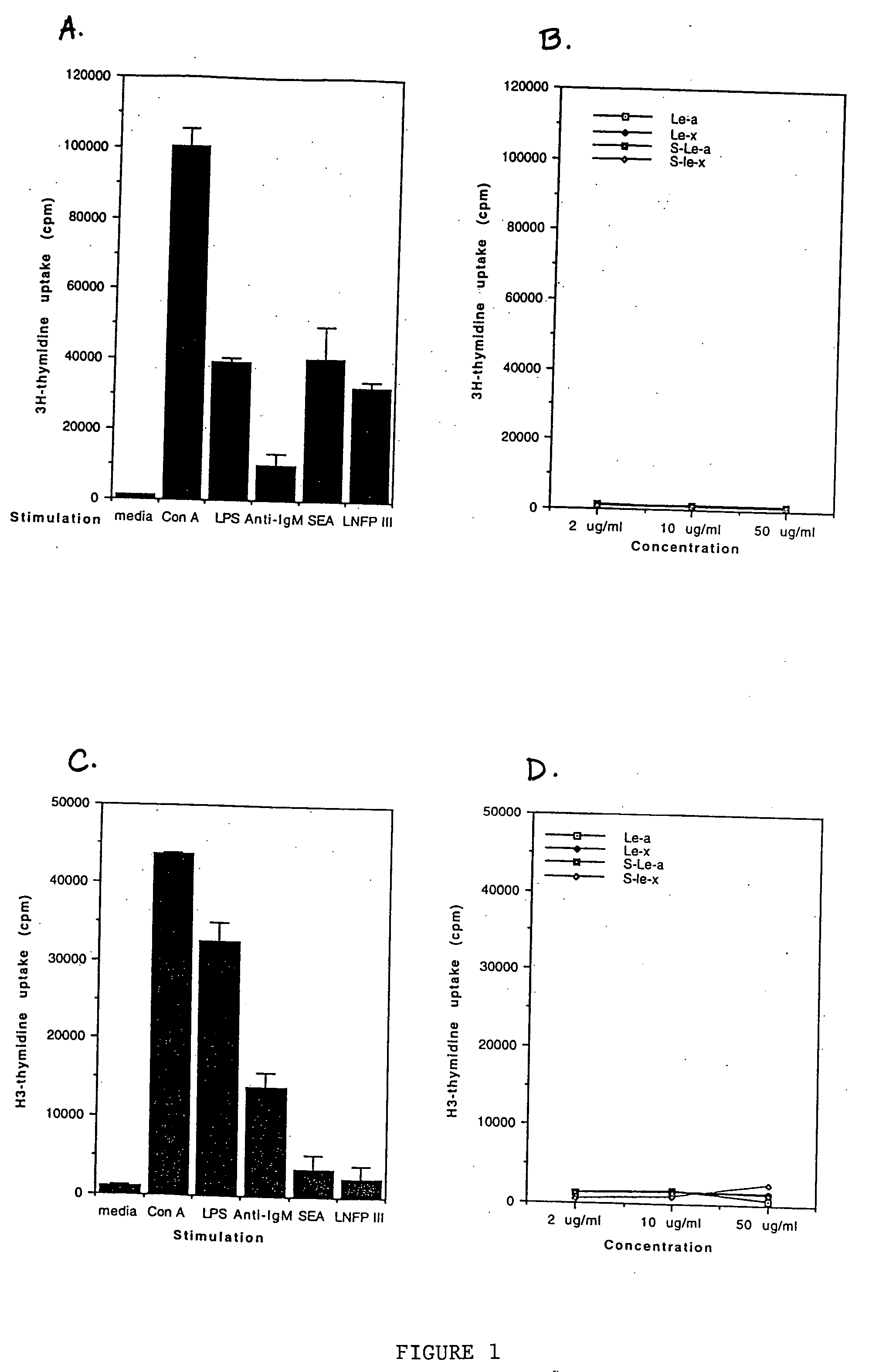
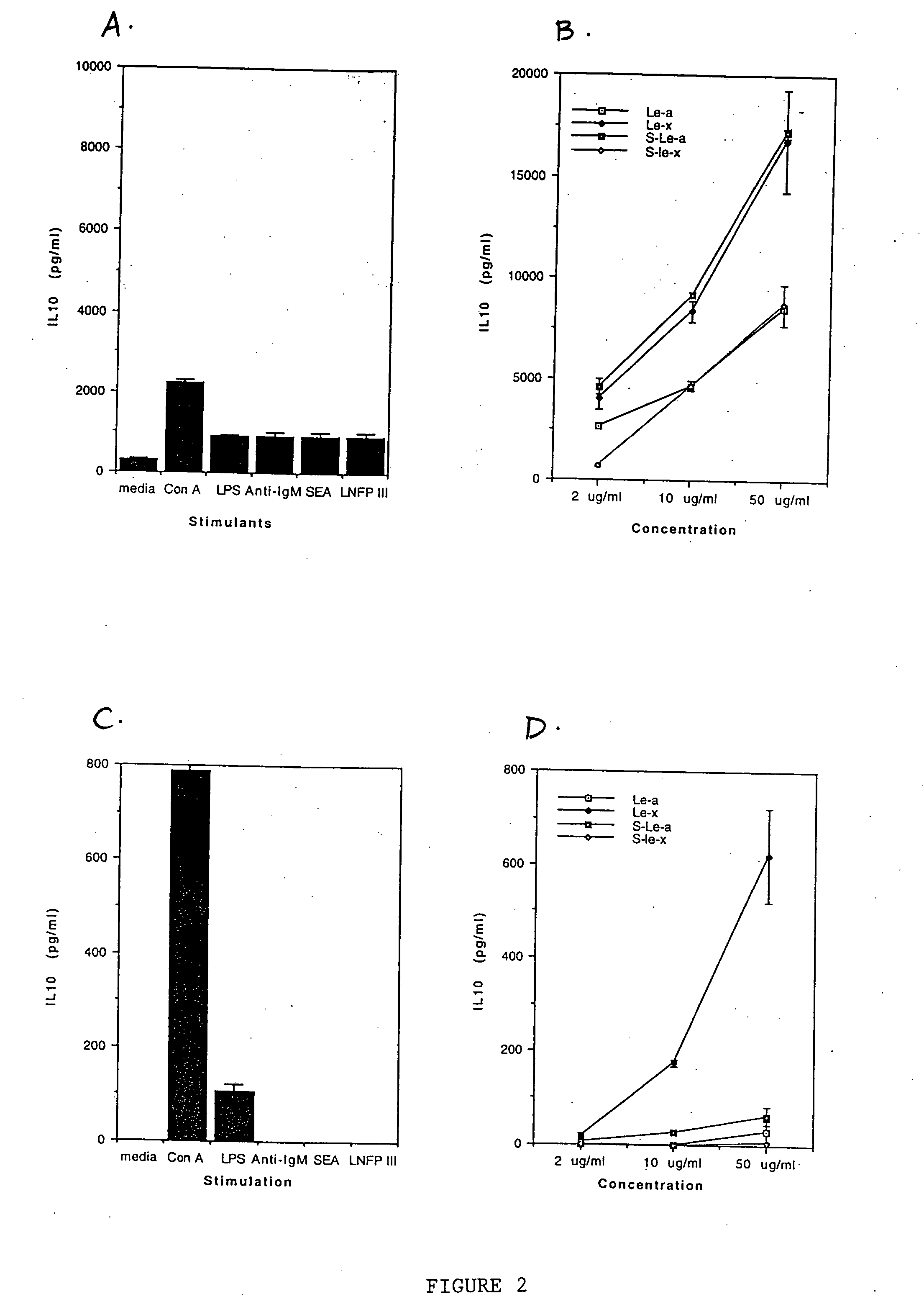
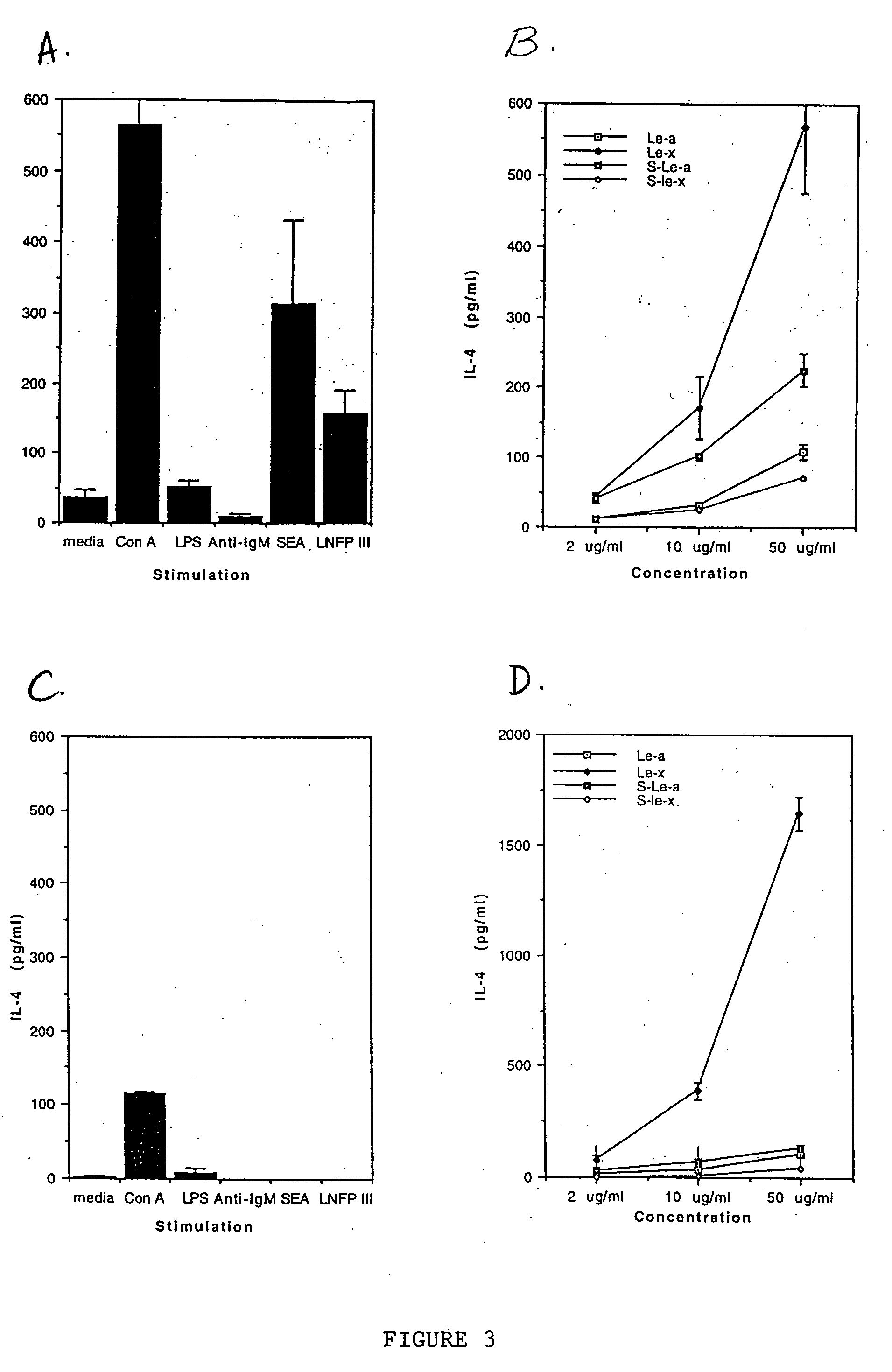
[0088] In this example, the ability of macrophages to produce IL-10 upon stimulation with various oligosaccharide conjugates was examined. Granuloma macrophages were prepared from C57BL / 6 mice as described in Flores Villanueva, P.O., et al. (1994) J. Immunol. 153:5190-5199 and Flores Villanueva, P.O., et al. (1994) J. Immunol. 152:1847-1855. Two million cells in 1 ml of DMEM, 10 % FCS were incubated with either no stimulant (i.e., medium alone; a negative control), lipopolysaccharide (LPS; at 20 μg / ml; a positive control), schistosome egg antigen (SEA; at 10 μg / ml), various sugars conjugated to human serum albumin (at 100 μg / ml) or human serum albumin alone (HSA; at 100 μg / ml; a negative control). The sugar conjugates tested were lacto-N-fucopentaose III (LNFP-III), lacto-N-neotetraose (LNT) and Lewisy (Ley). The oligosaccharide conjugates were obtained from Accurate Chemicals, Westbury, N.Y.
[0089] At various time points (24, 48 and 72 hours), the level of IL-10 in the supernatant ...
example 2
[0092] In this example, the ability of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from humans suffering from various disorders to produce IL-10 upon stimulation with various oligosaccharide conjugates was examined. Human PBMCs were obtained from: 1) an individual who was allergic to pollen; 2) an individual suffering from lung carcinoma and 3) an individual suffering from colon carcinoma. One million PBMC in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% human AB serum were incubated with either no stimulant (i.e., medium alone; a negative control), lipopolysaccharide (LPS; at 20 μg / ml; a positive control), various sugars conjugated to human serum albumin (at 100 μg / ml) or human serum albumin alone (HSA; at 100 μg / ml; a negative control). The sugar conjugates tested were lacto-N-fucopentaose I (LNFP-I), lacto-N-fucopentaose III (LNFP-III), lacto-N-neotetraose (LNT) and Lewisy (Ley).
[0093] After 24 hours, the level of IL-10 (in pg / ml) in the supernatant was determined by two-site ELISA as describe...
example 3
[0096] In this example, the ability of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from three humans with B lymphomas to produce IL-10 upon stimulation with various oligosaccharide conjugates was examined. One million PBMC in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% human AB serum were incubated with either no stimulant (i.e., medium alone; a negative control), lipopolysaccharide (LPS; at 20 μg / ml; a positive control), various sugars conjugated to human serum albumin (at 100 μg / ml) or human serum albumin alone (HSA; at 100 μg / ml; a negative control). The sugar conjugates tested were lacto-N-fucopentaose I (LNFP-I), lacto-N-fucopentaose III (LNFP-III), lacto-N-neotetraose (LNT), Lewisy (Ley) and lacto-N-difucohexose I (LND).
[0097] After 24 hours, the level of IL-10 (in pg / ml) in the supernatant was determined by two-site ELISA as described by in Example 2. Additionally, cellular proliferation was measured by standard 3H-thymidine uptake at 90 hours.
[0098] The results are shown below in Table...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com