Vertical replacement-gate junction field-effect transistor
a technology of junction field and transistor, applied in the field of semiconductor devices, can solve the problems of lithographic process, lithographic process, and current lithographic process nearing the point where it is impossible to accurately manufacture devices at the required minimal size demanded by today's device users, and achieve the effect of higher doping density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
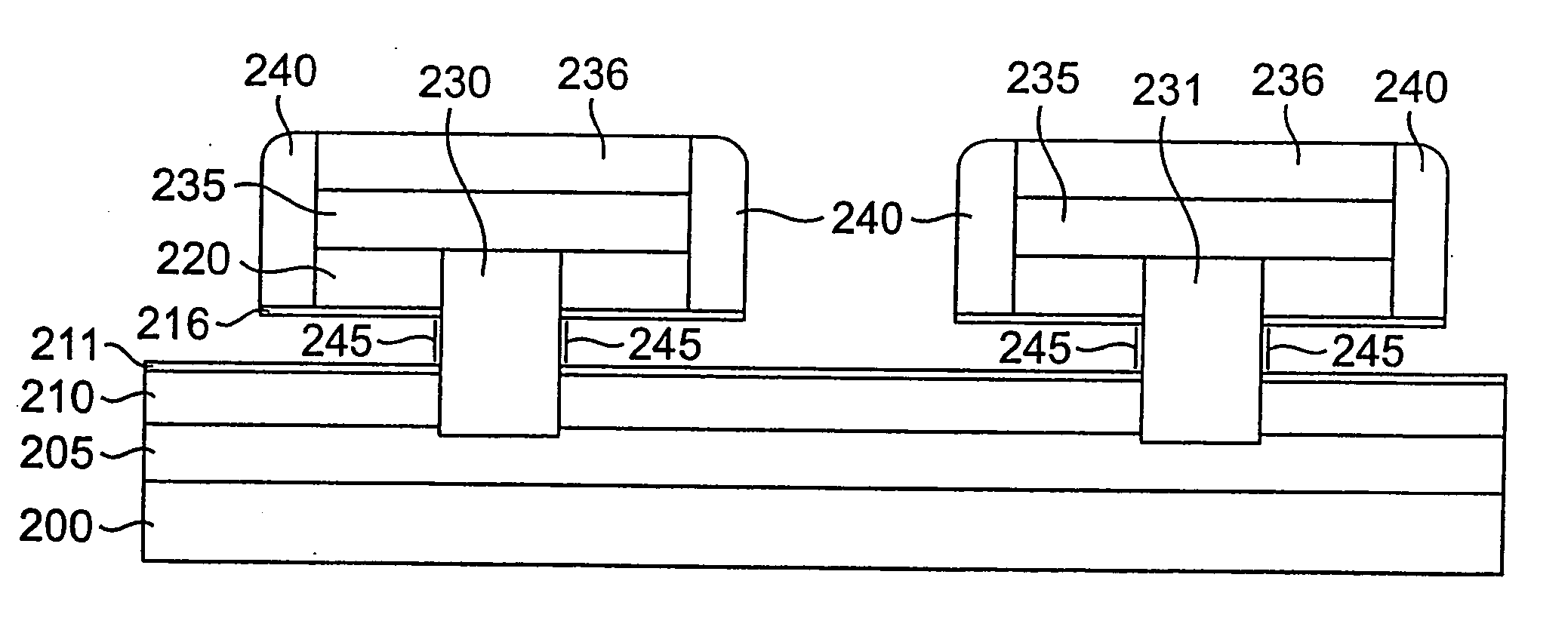
[0015] With regard to the fabrication of transistors and integrated circuits, the term “major surface” refers to that surface of the semiconductor layer in and about which a plurality of transistors are fabricated, e.g., in a planar process. As used herein, the term “vertical” means substantially orthogonal with respect to the major surface. Typically, the major surface is along a plane of a monocrystalline silicon layer on which the field-effect transistor devices are fabricated. The term “vertical transistor” means a transistor with individual semiconductor components vertically oriented with respect to the major surface so that the current flows vertically from source to drain. By way of example, for a vertical JFET the source, channel and drain regions are formed in relatively vertical alignment with respect to the major surface.
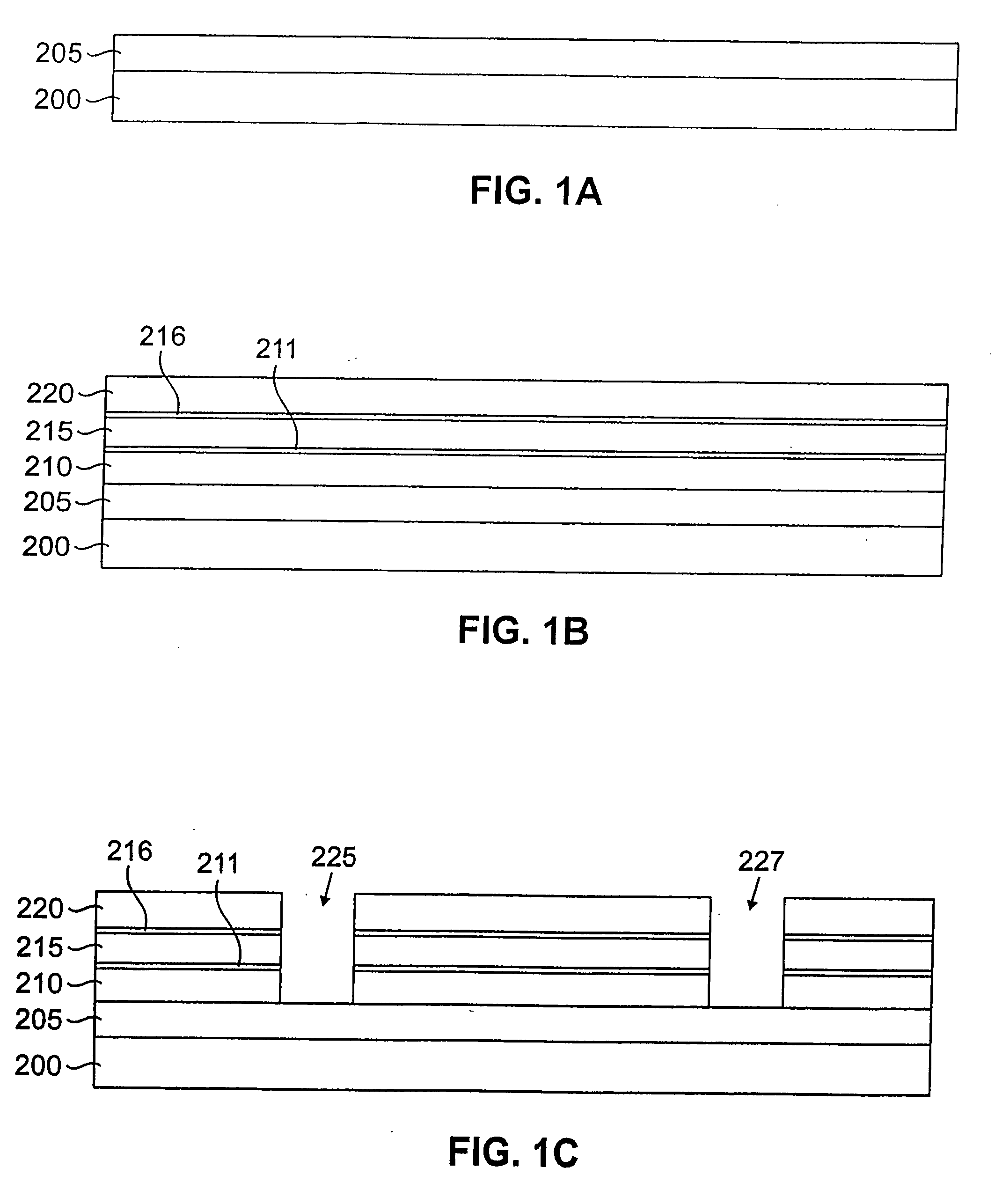
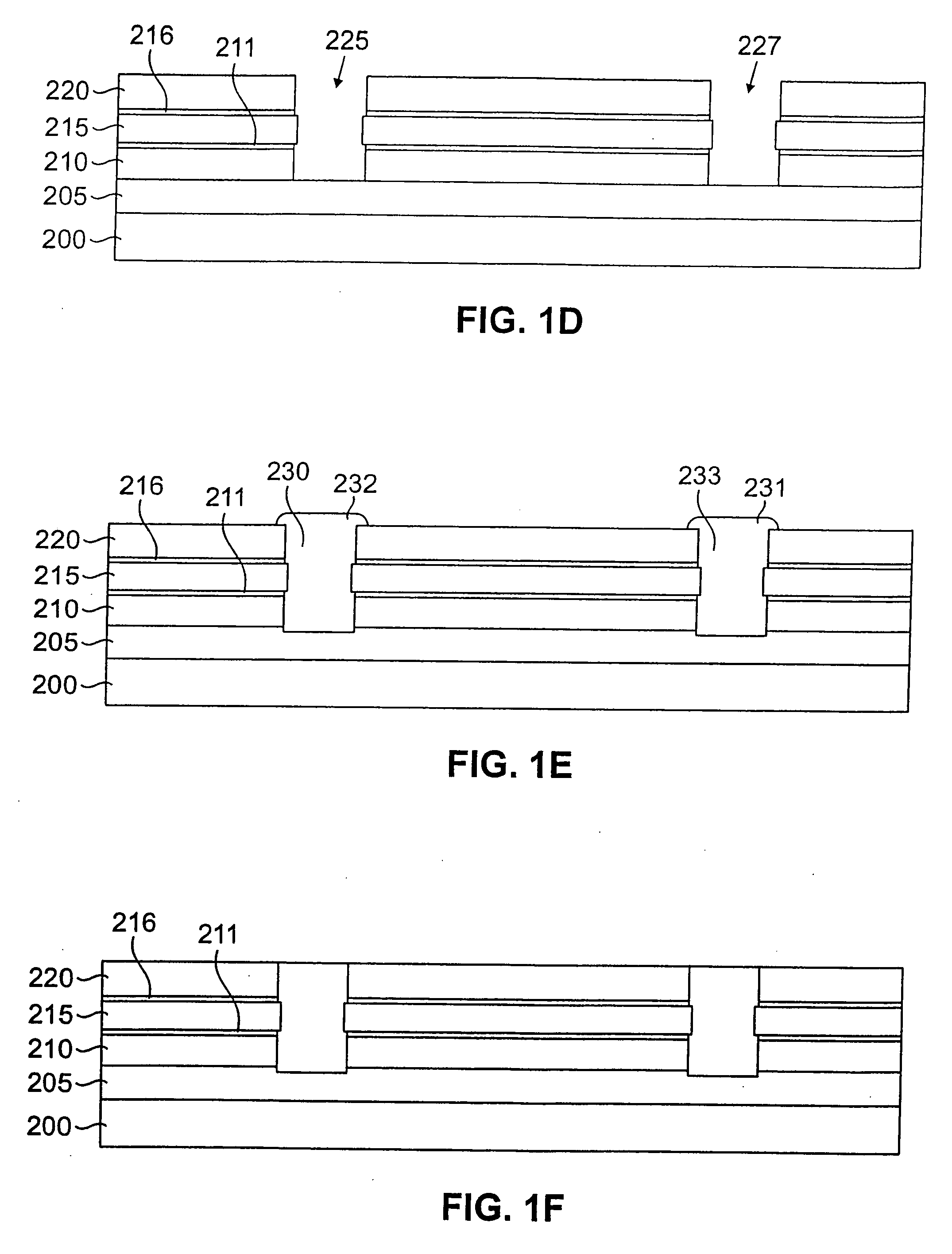
[0016]FIGS. 1A through 1R illustrate cross-sectional views of an integrated circuit structure 200 during various stages of fabrication to form an exem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com