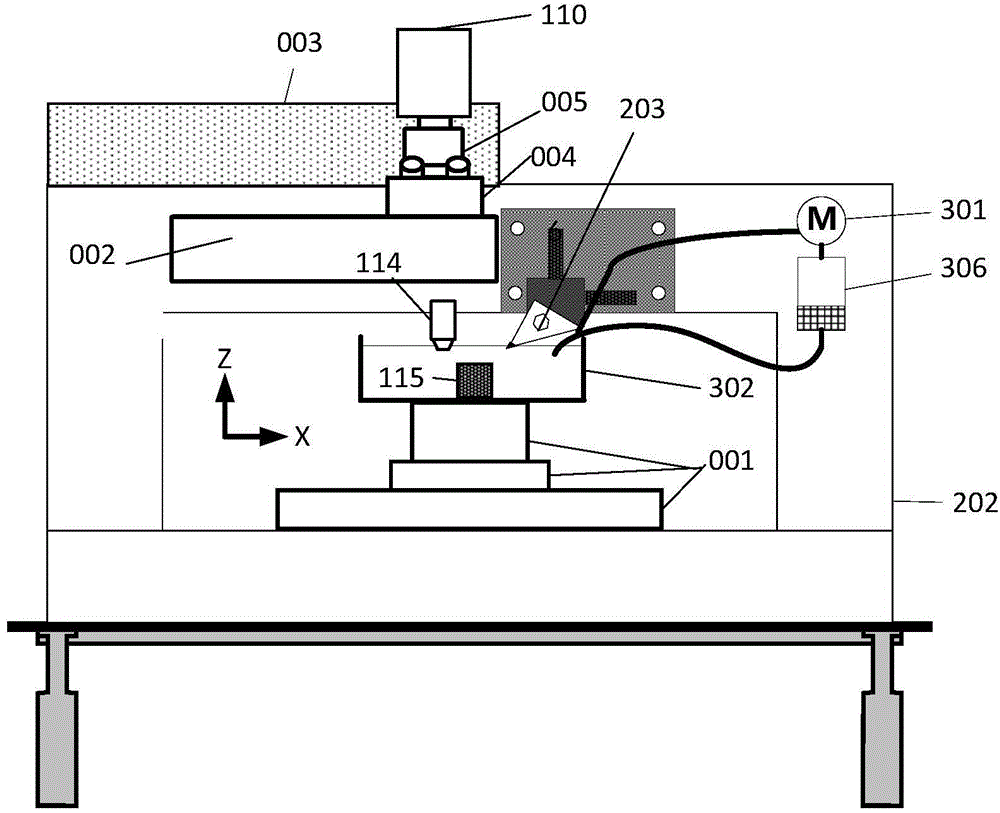
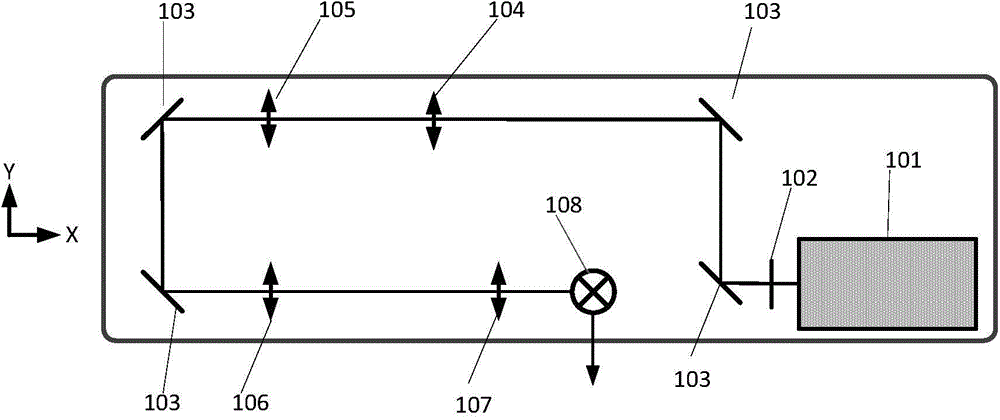
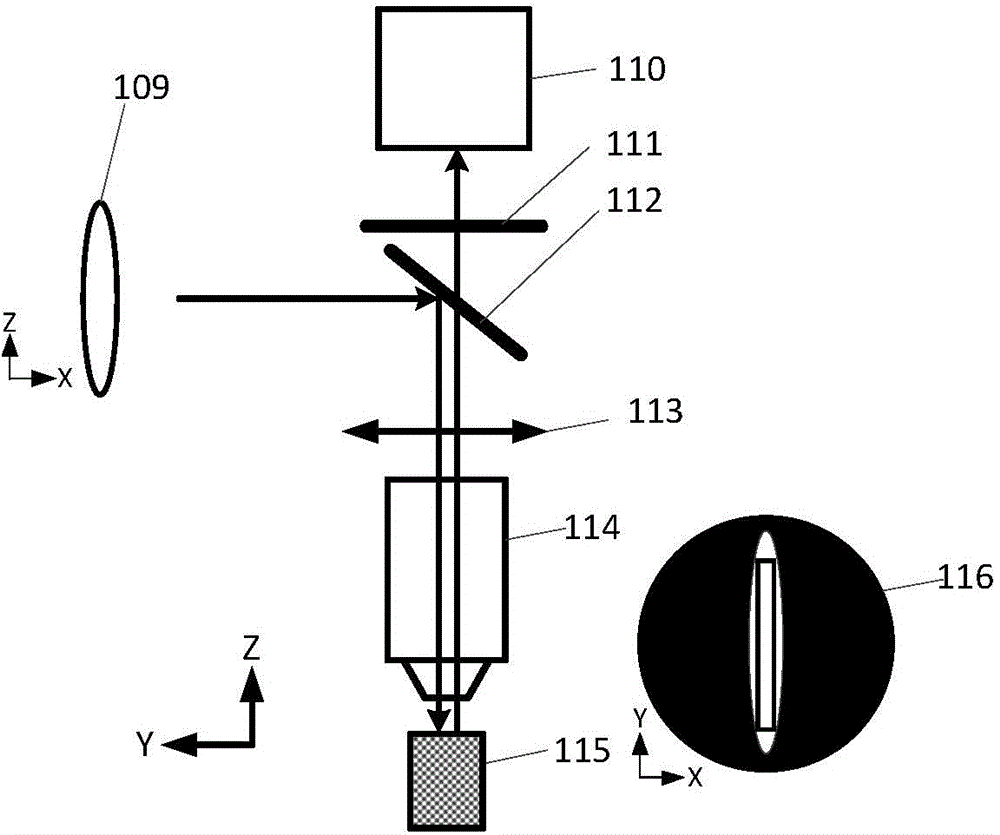
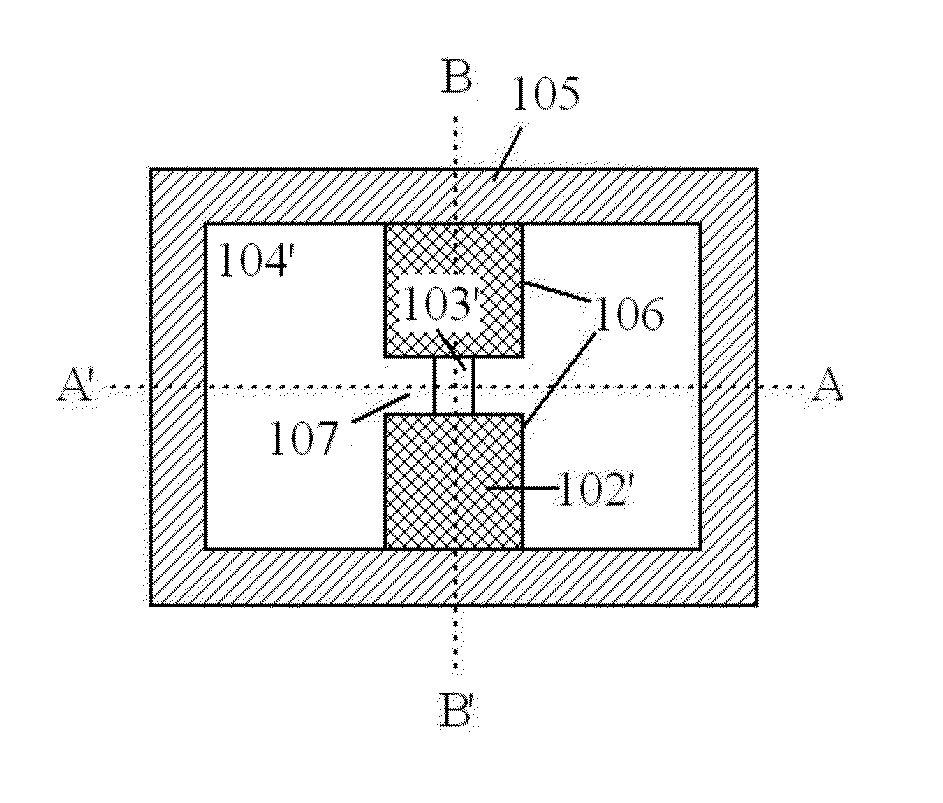
Patents
Literature
137 results about "Planar process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
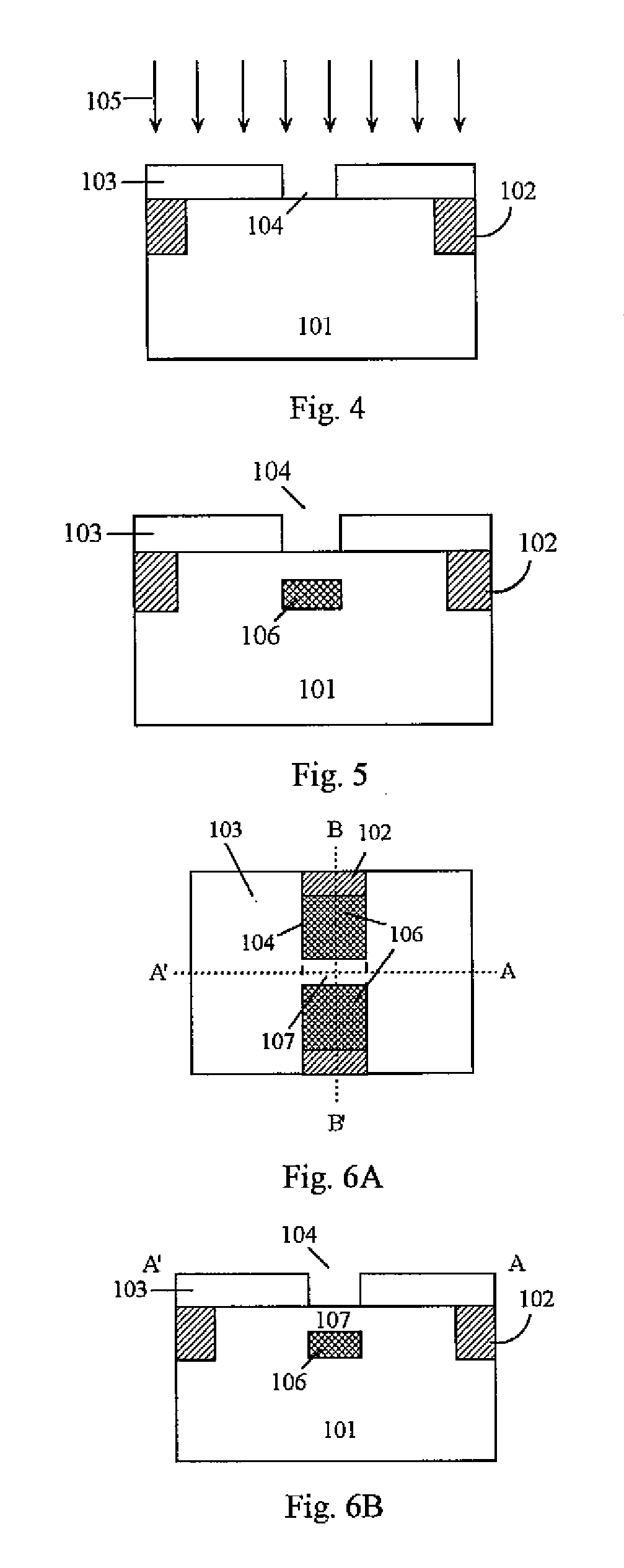
The planar process is a manufacturing process used in the semiconductor industry to build individual components of a transistor, and in turn, connect those transistors together. It is the primary process by which silicon integrated circuit chips are built. The process utilizes the surface passivation and thermal oxidation methods.
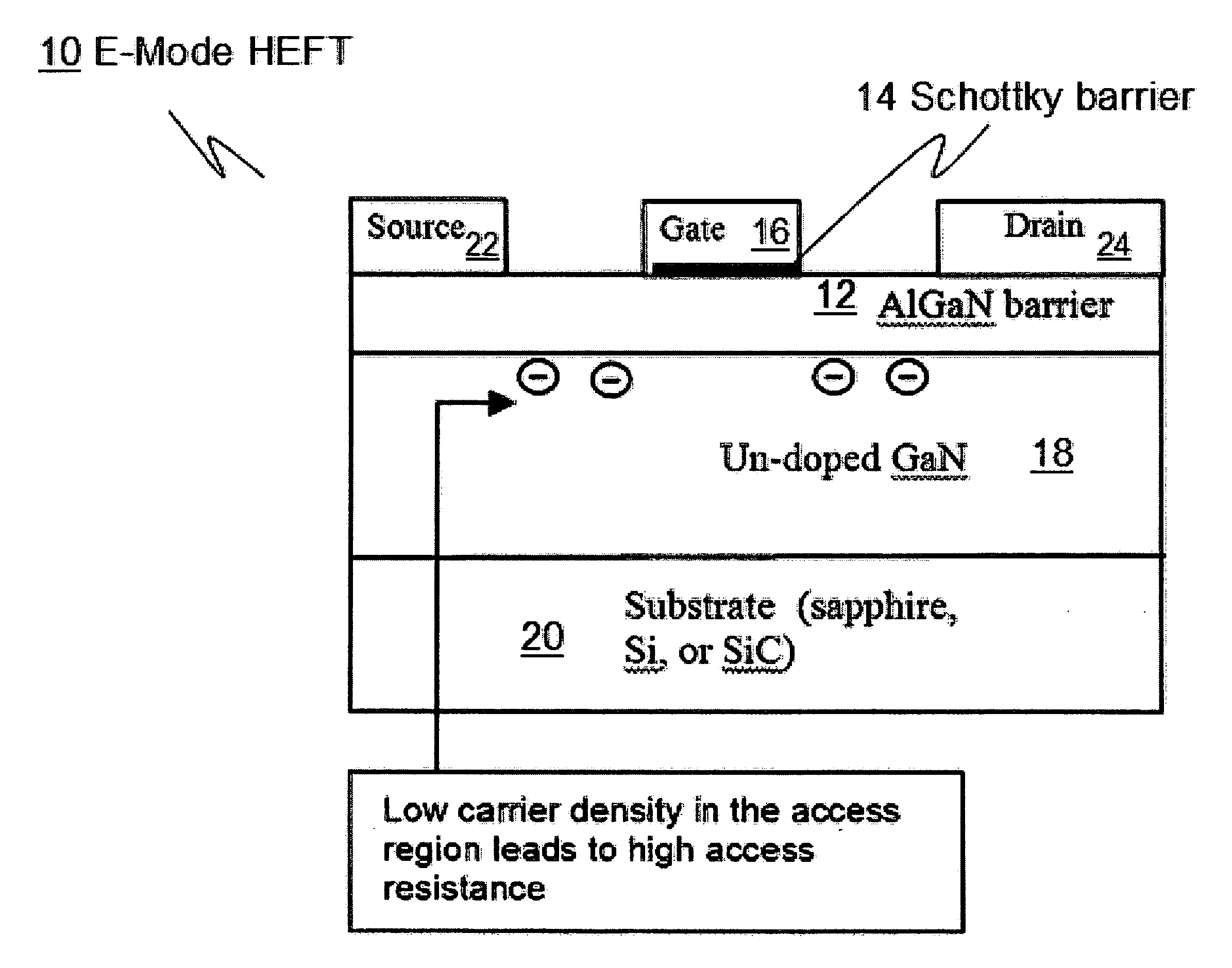
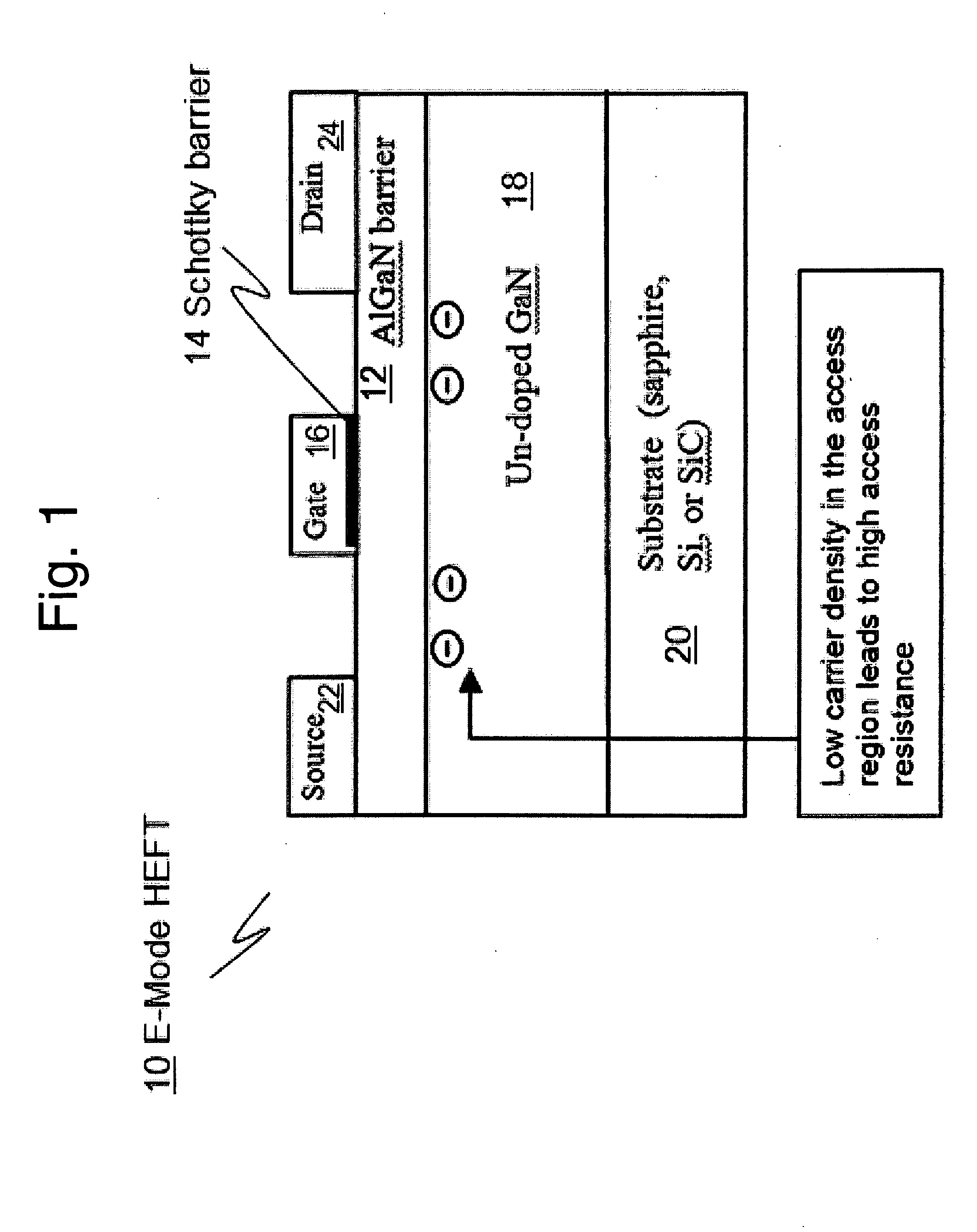
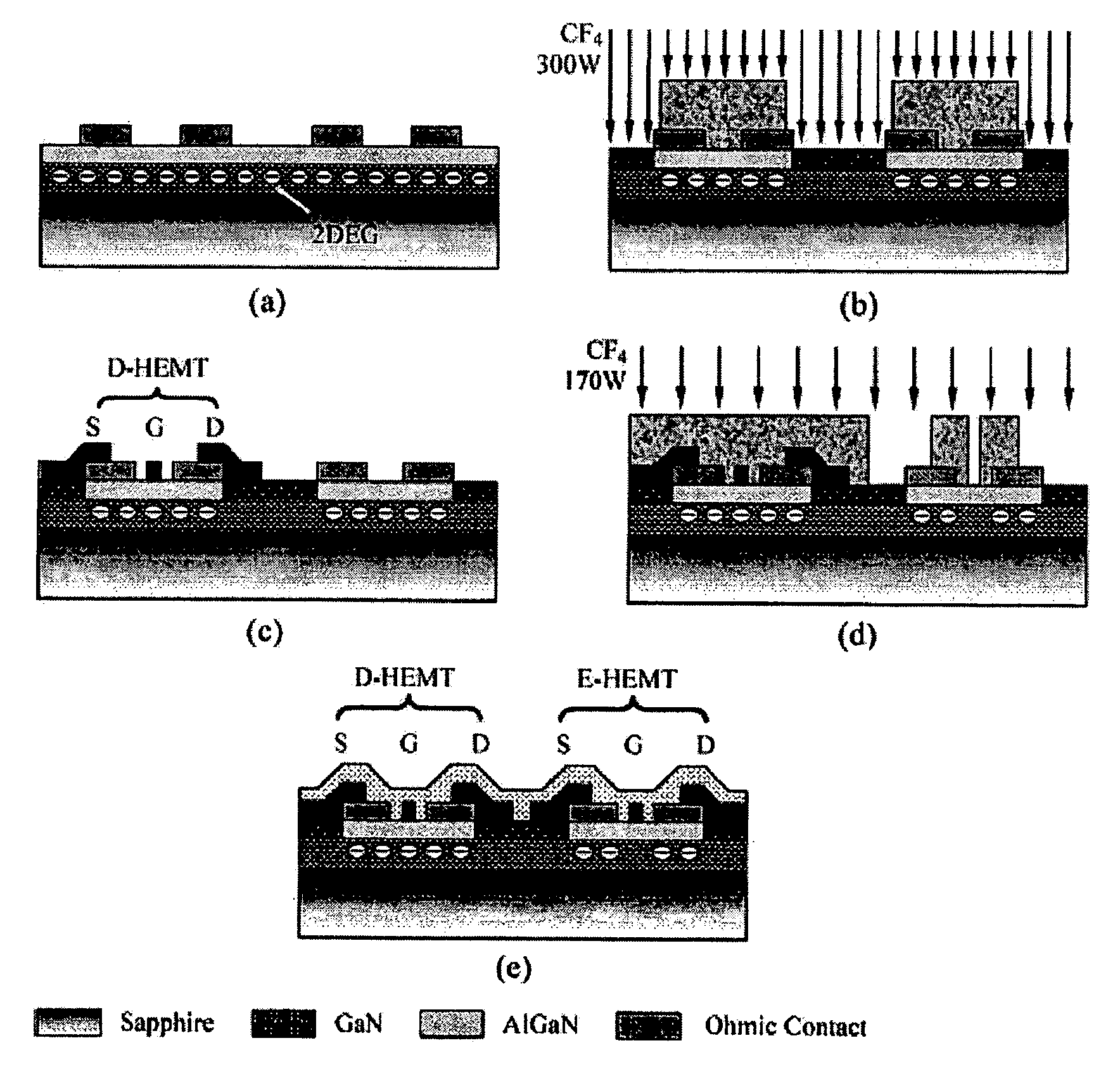
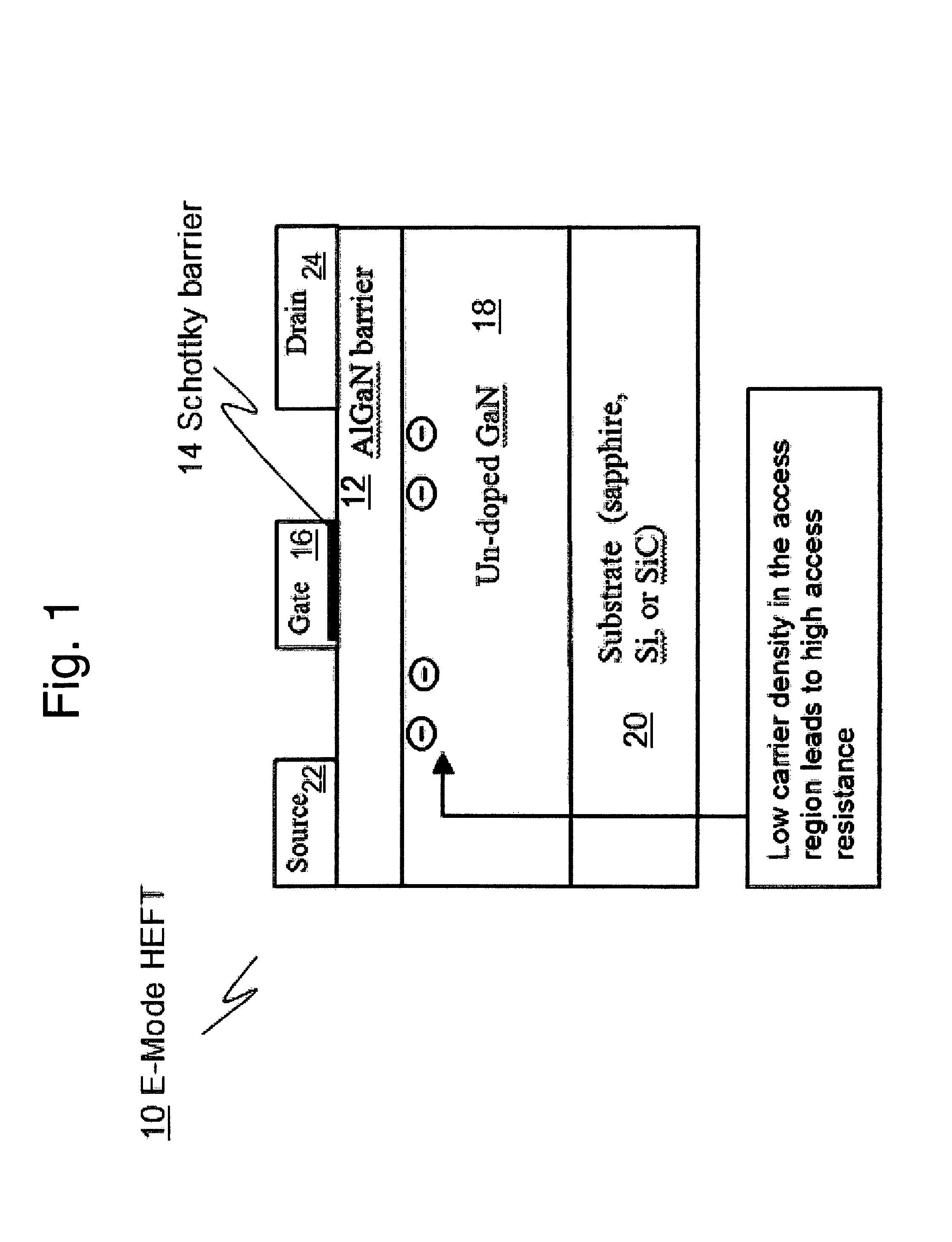
Monolithic Integration of Enhancement- and Depletion-mode AlGaN/GaN HFETs
ActiveUS20070228416A1Wide bandgapHigh breakdown fieldTransistorSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionEtching
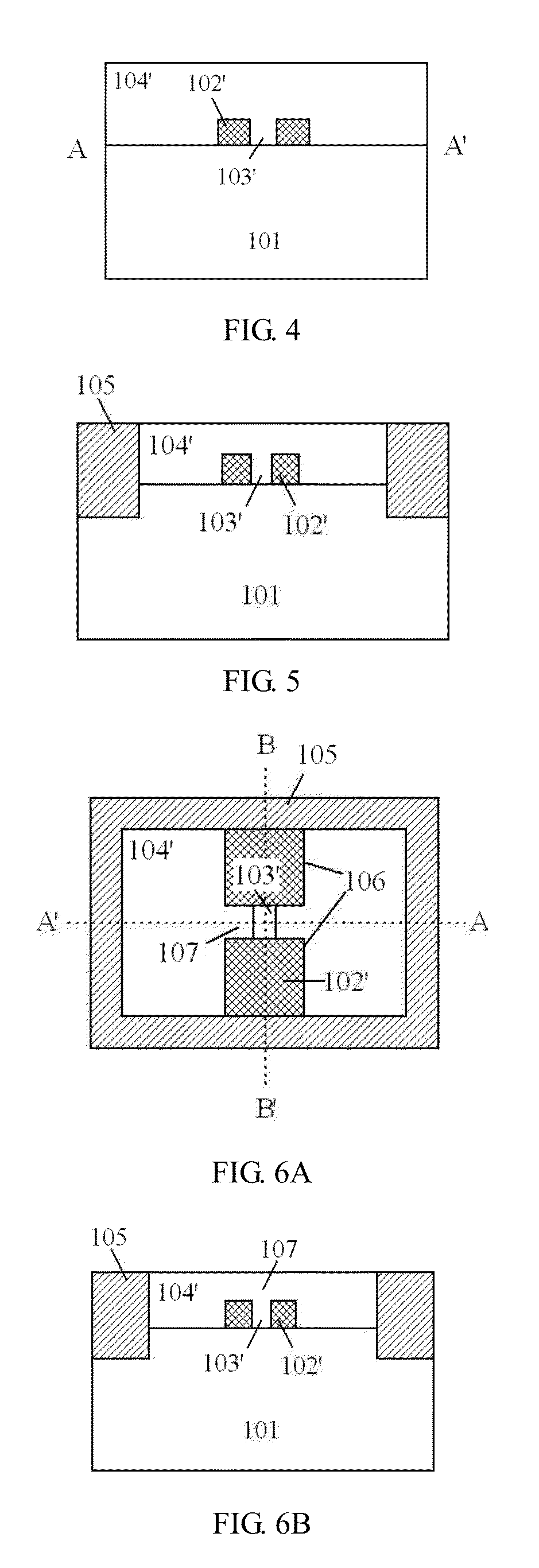
A method for and devices utilizing monolithic integration of enhancement-mode and depletion-mode AlGaN / GaN heterojunction field-effect transistors (HFETs) is disclosed. Source and drain ohmic contacts of HFETs are first defined. Gate electrodes of the depletion-mode HFETs are then defined. Gate electrodes of the enhancement-mode HFETs are then defined using fluoride-based plasma treatment and high temperature post-gate annealing of the sample. Device isolation is achieved by either mesa etching or fluoride-based plasma treatment. This method provides a complete planar process for GaN-based integrated circuits favored in high-density and high-speed applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
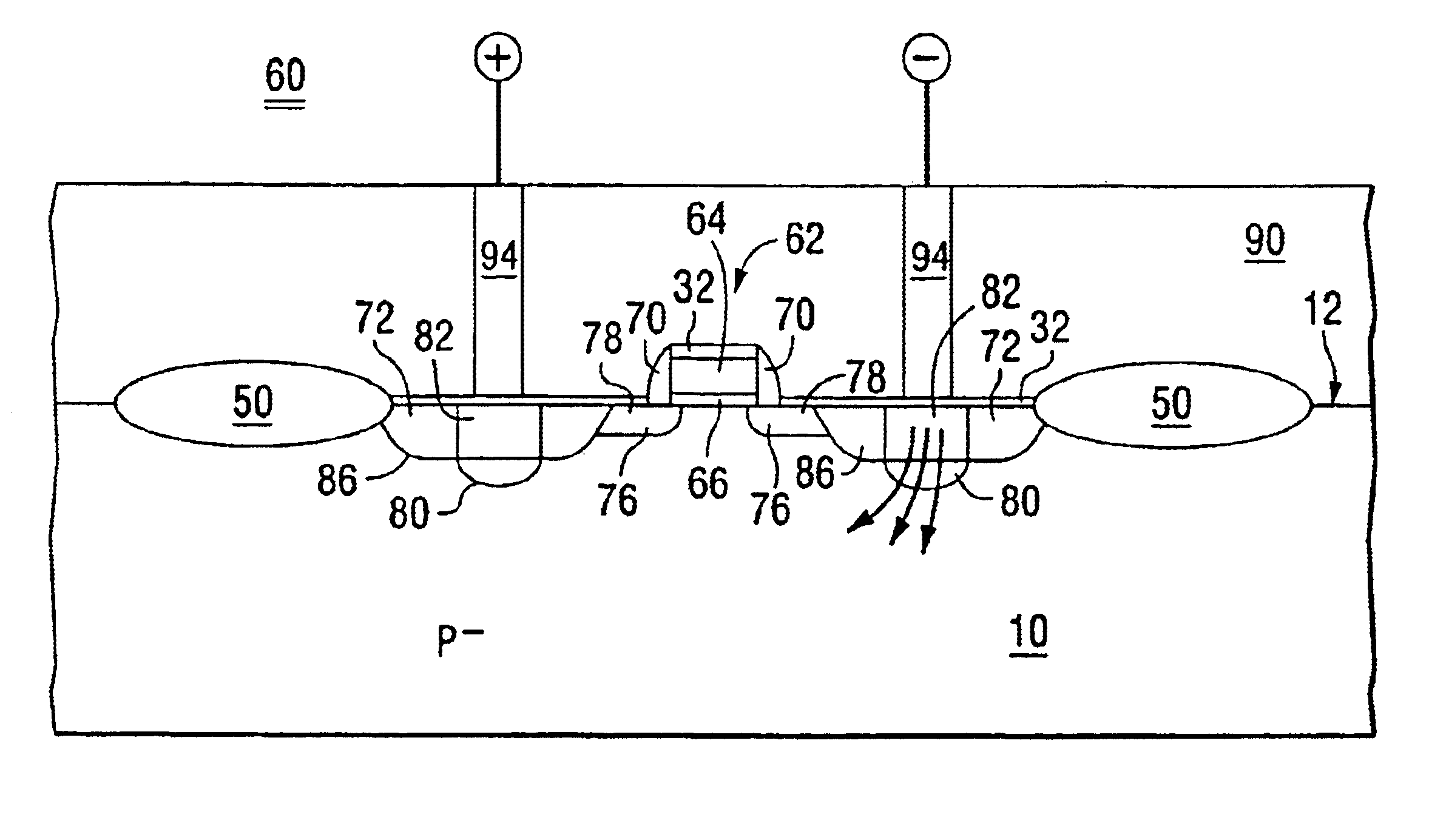
ESD protection for semiconductor products
InactiveUS6873017B2Reduces lateral currentCurrent densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
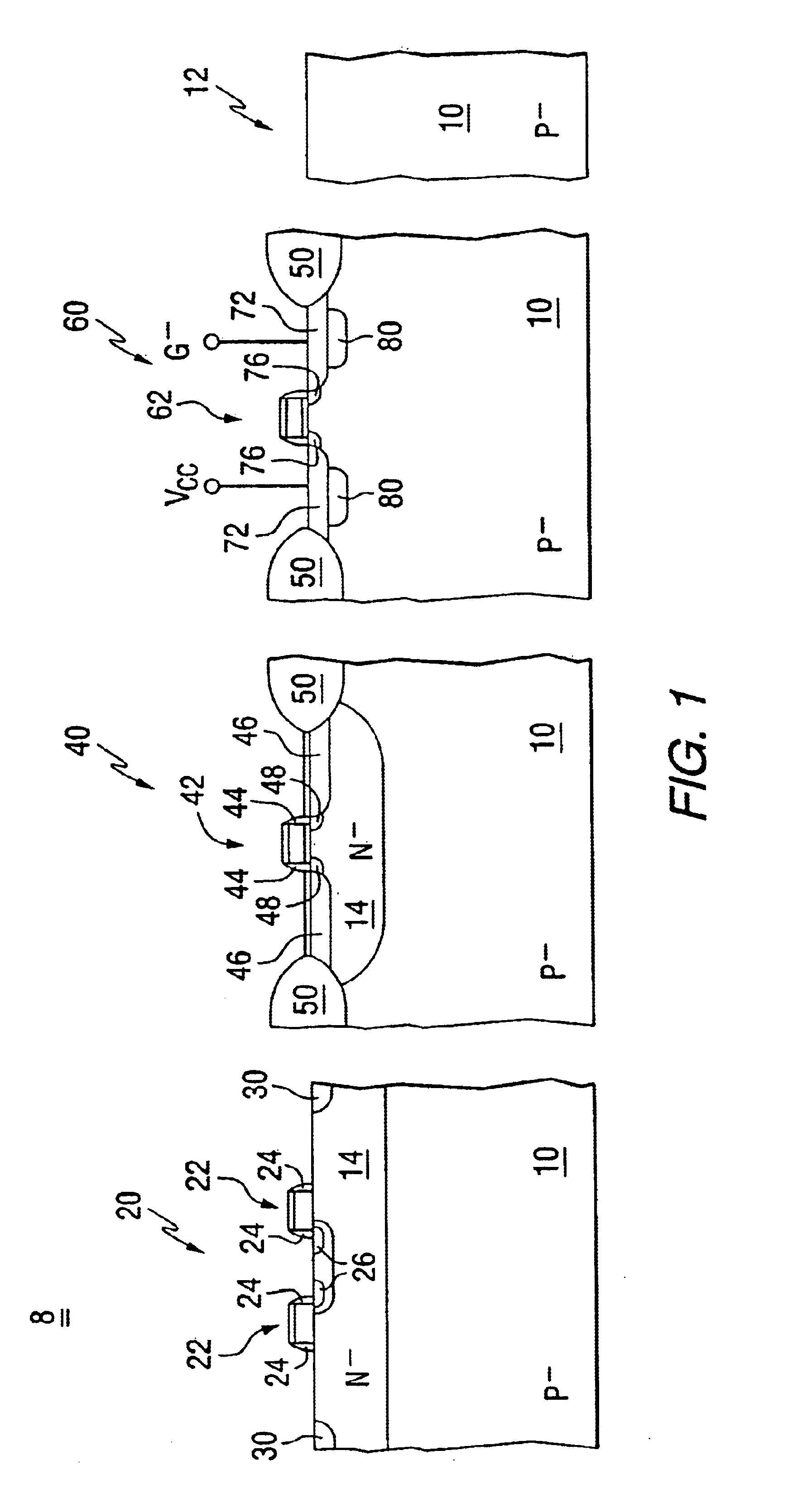
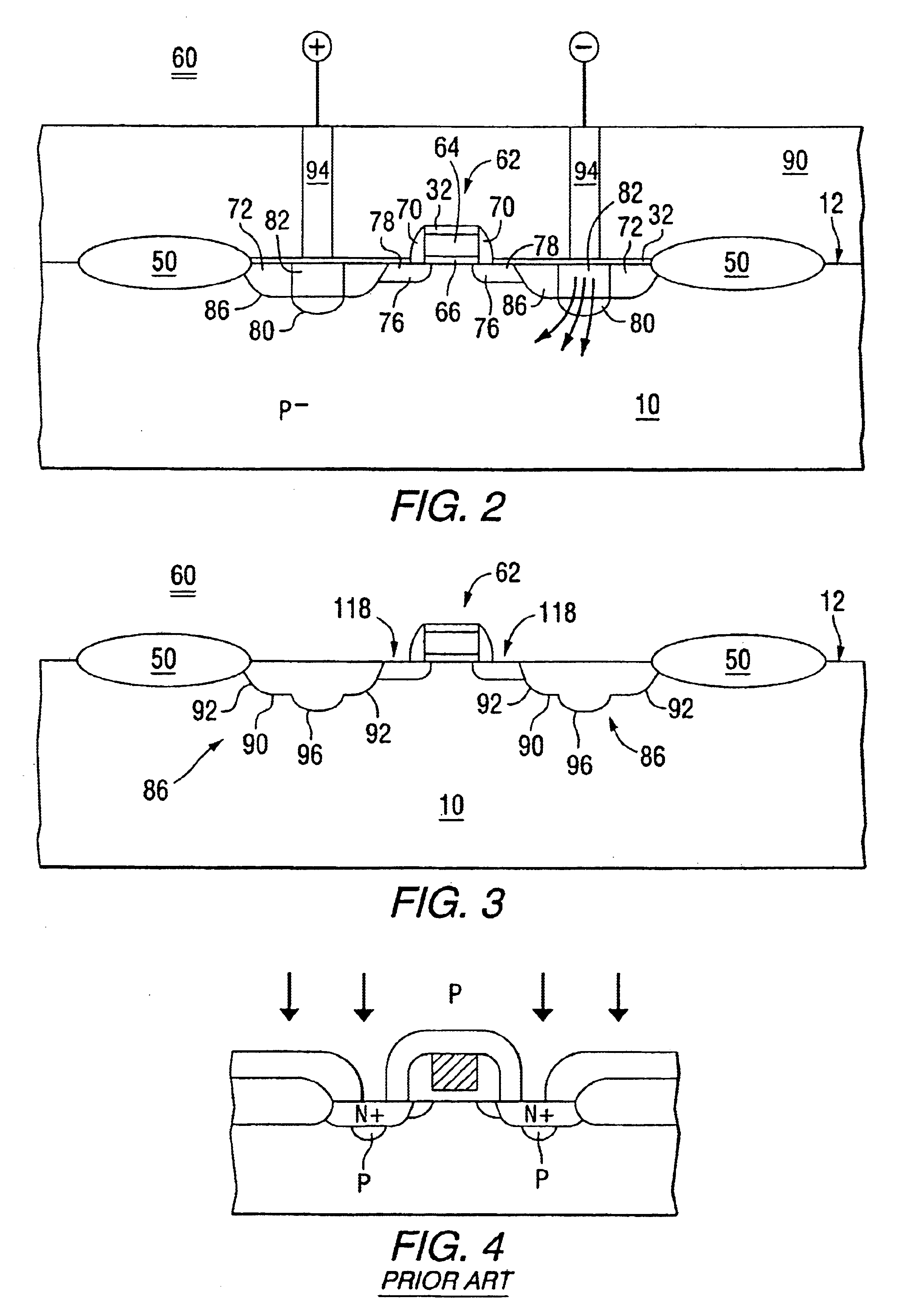
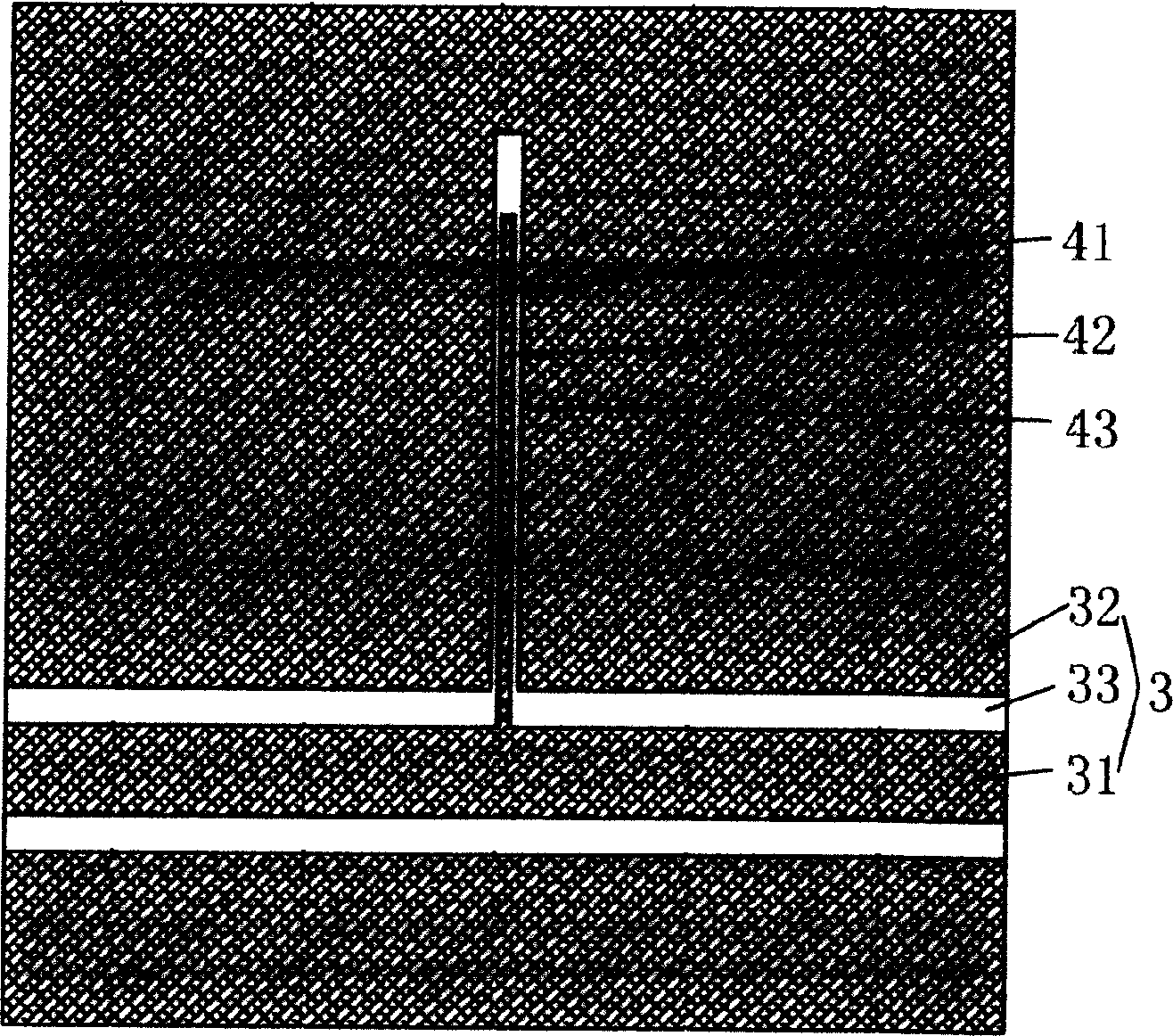
Device 60 in FIG. 3 has junctions 86 each with a lateral portion 90 and a second portion 92 extending upward toward the surface 12 from the lateral portion 90. The lateral portions 90, as illustrated in FIG. 3, are more or less formed along a plane parallel with the surface 12. The upwardly extending portions 92 include characteristic curved edges of the diffusion fronts which are associated with the planar process. With the regions 80 and 82 each having relatively high net dopant concentrations of different conductivity types, each lateral junction portion 90 includes a relatively large sub region 96 which extends more deeply into the layer 10. When compared to other portions of the junctions 86, the subregions 96 are characterized by a relatively low breakdown voltage so that ESD current is initially directed vertically rather than laterally.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
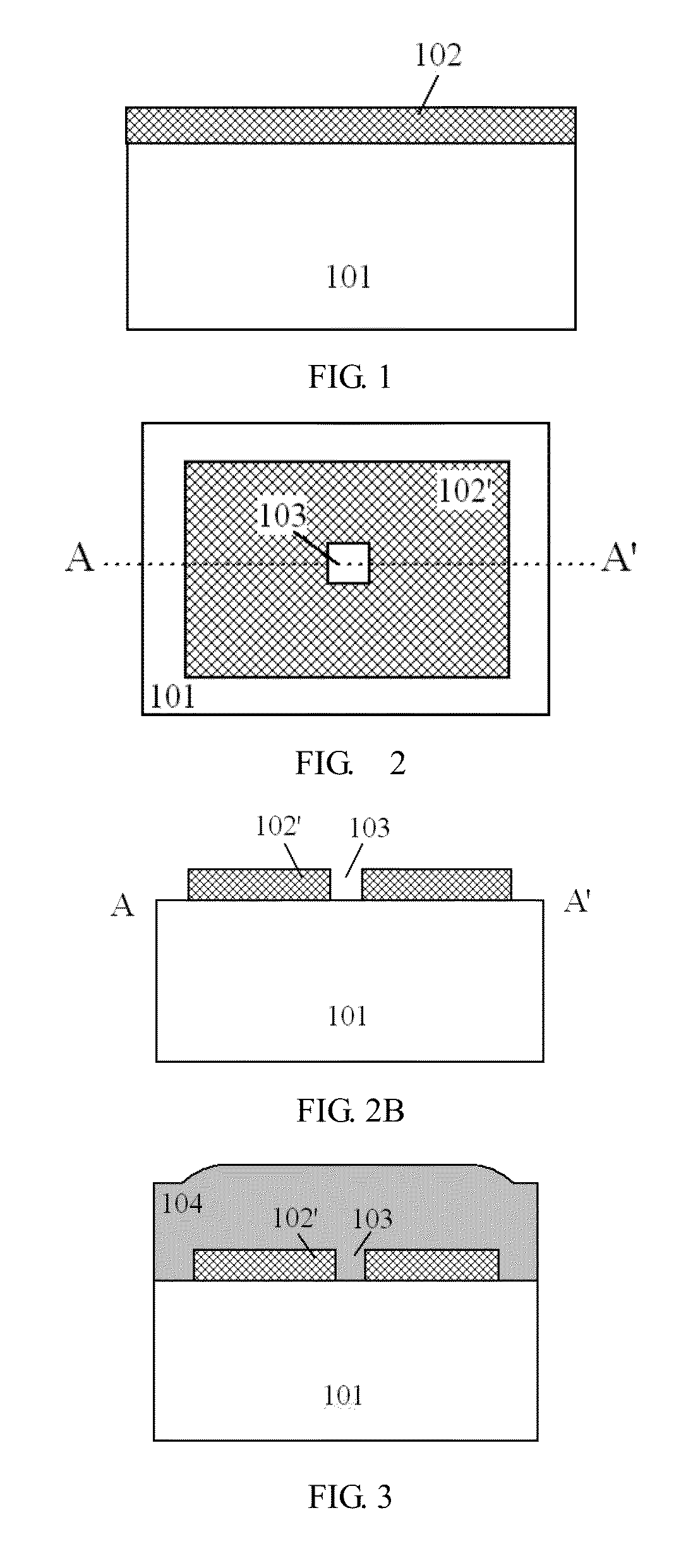
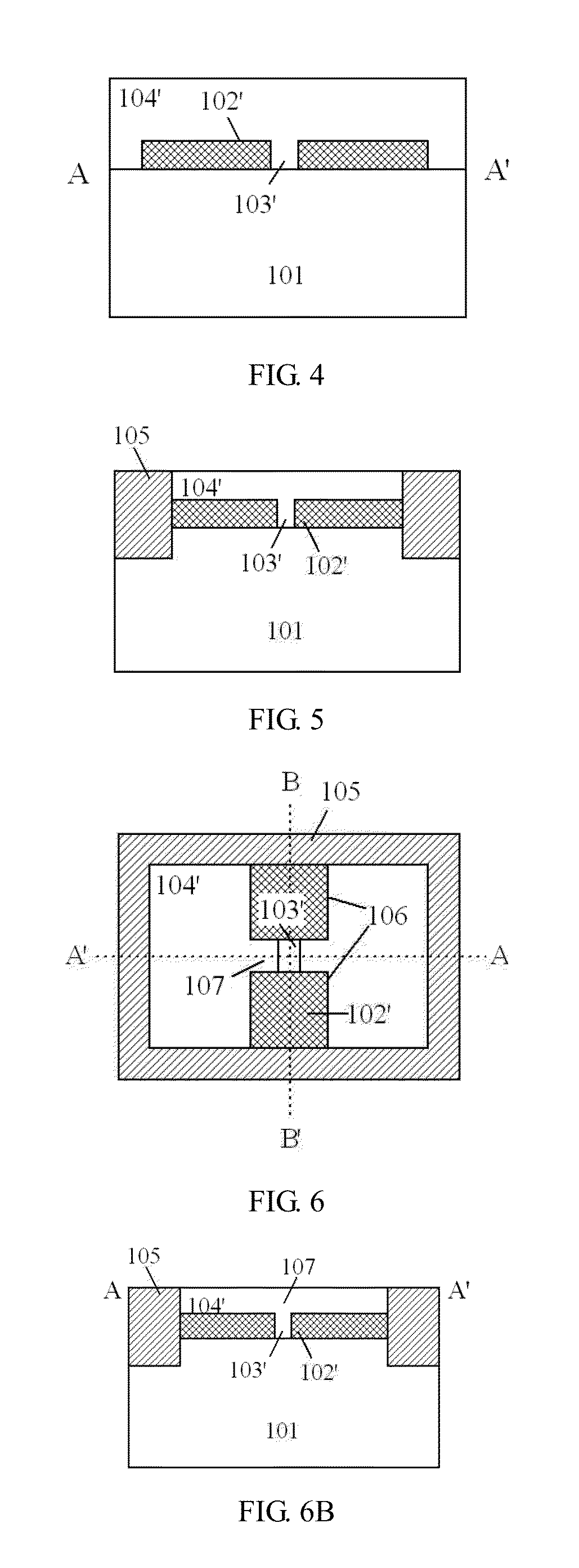
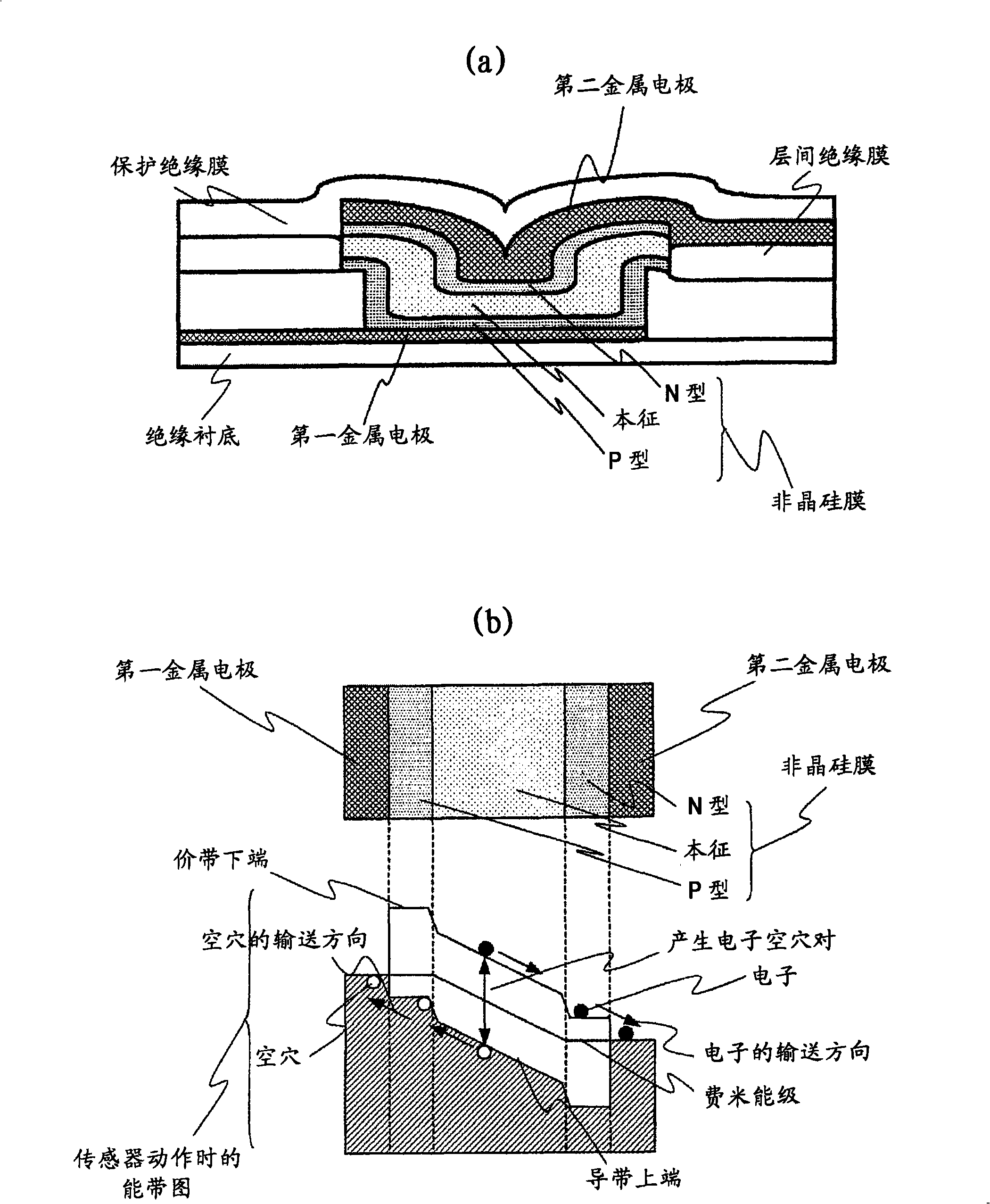
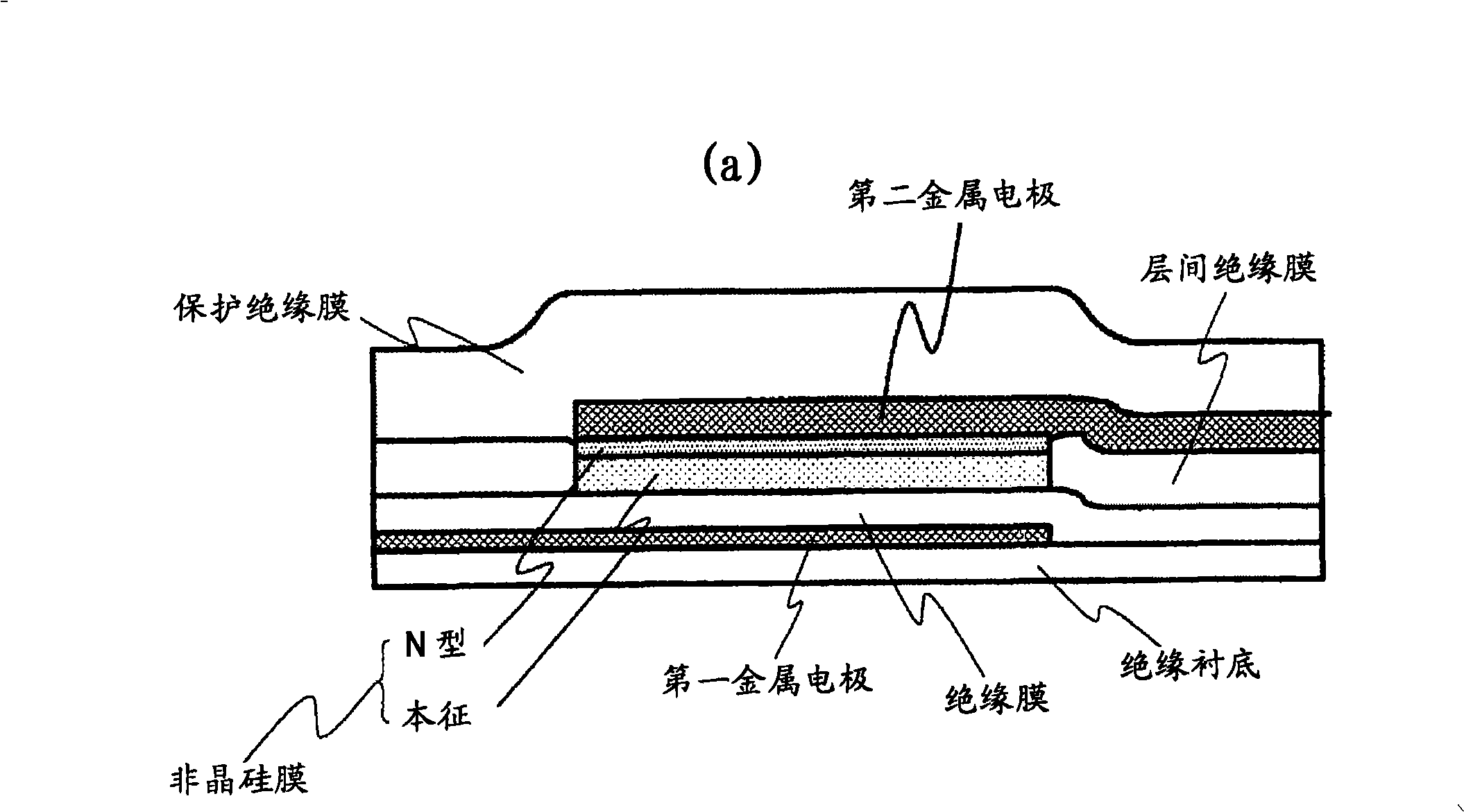
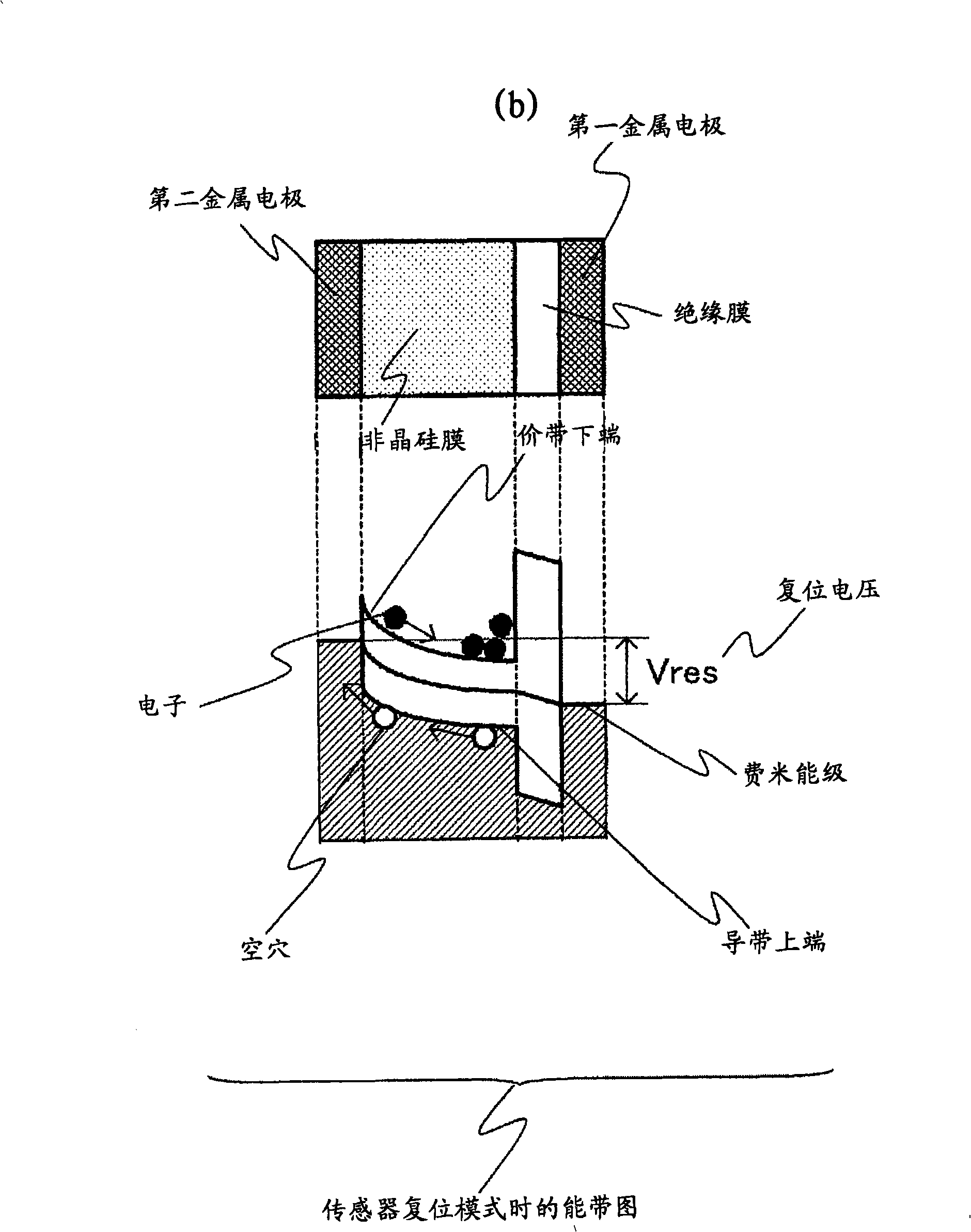
Optical sensor element, optical sensor device and image display device using optical sensor element
InactiveUS20080303022A1High sensitivityLow noise characteristicsSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationDriver circuitDisplay device
A highly sensitive optical sensor element, and a switch element such as a sensor driver circuit are formed on the same insulating substrate by using an LTPS planar process to provide a low cost area sensor (optical sensor device) incorporating the sensor driver circuit and the like or an image display device incorporating the optical sensor element. As an optical sensor element structure, one electrode of the sensor element is manufactured with the same film of the polycrystalline silicon film that is an active layer of the switch element constituting a circuit. A photoelectric conversion unit for performing photoelectric conversion is made of an amorphous silicon or a polycrystalline silicon film of an intrinsic layer. A structure in which the amorphous silicon of the photoelectric conversion unit and the insulating layer are sandwiched between two electrodes of the sensor element is adopted.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
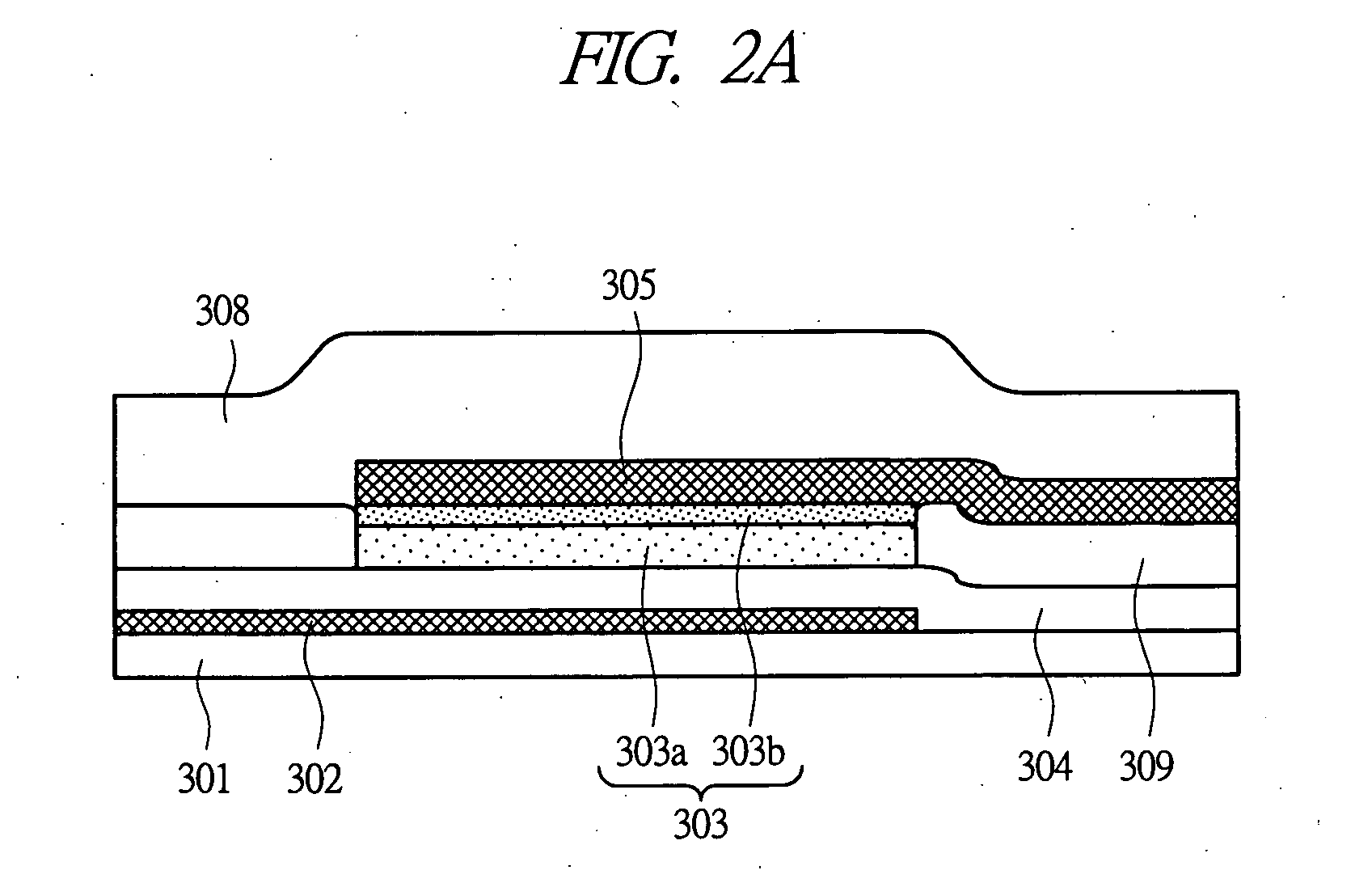
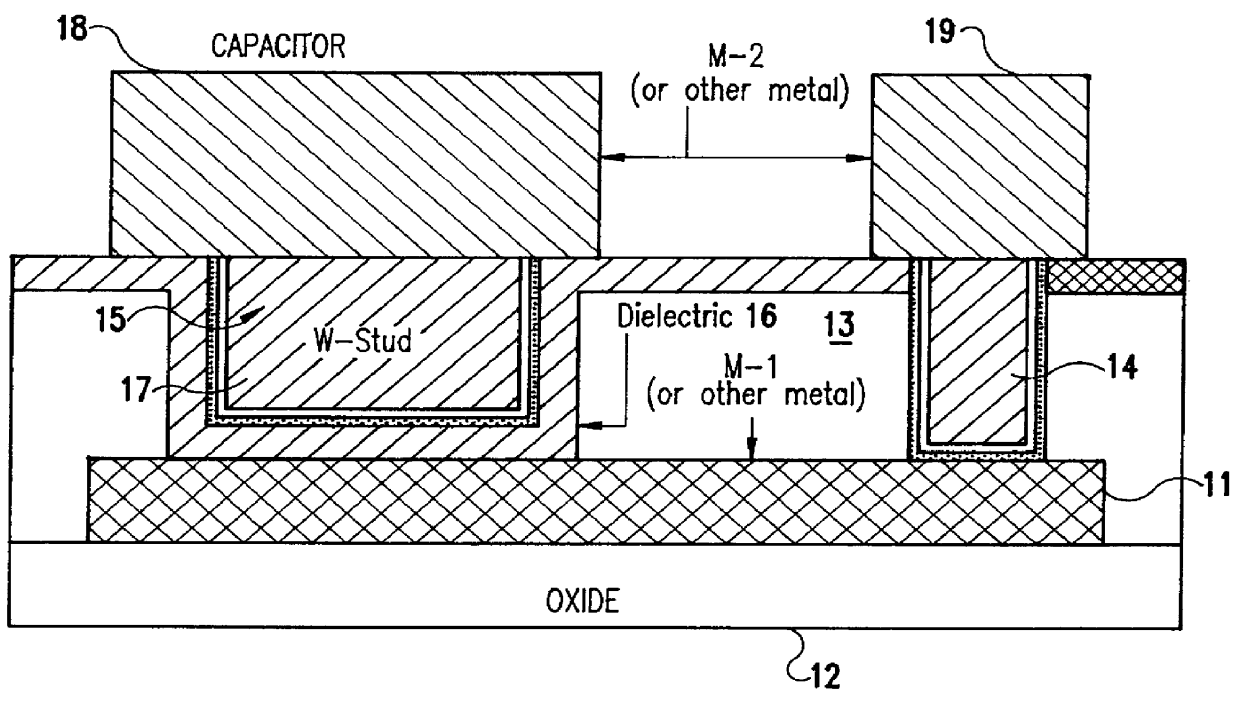
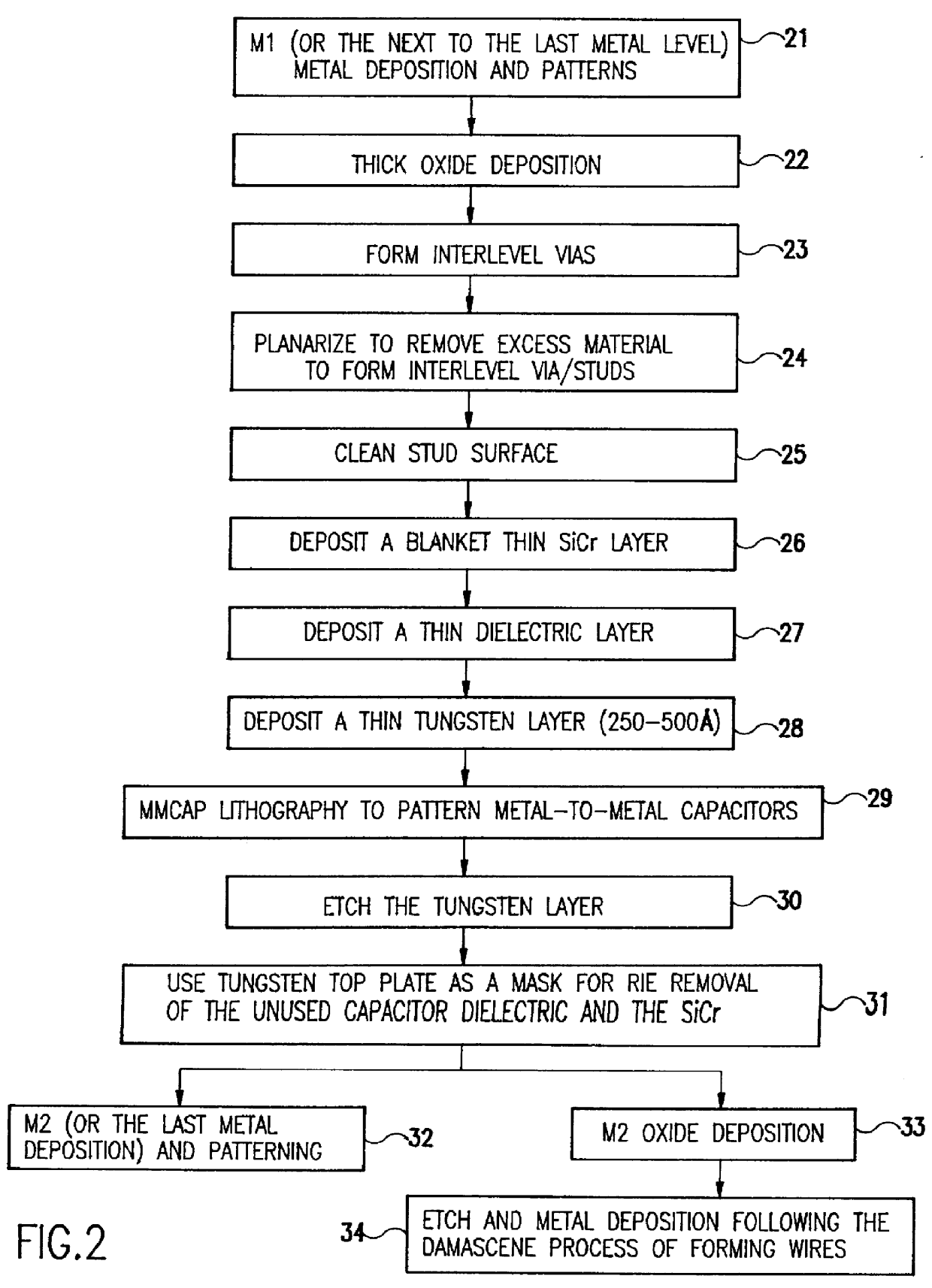
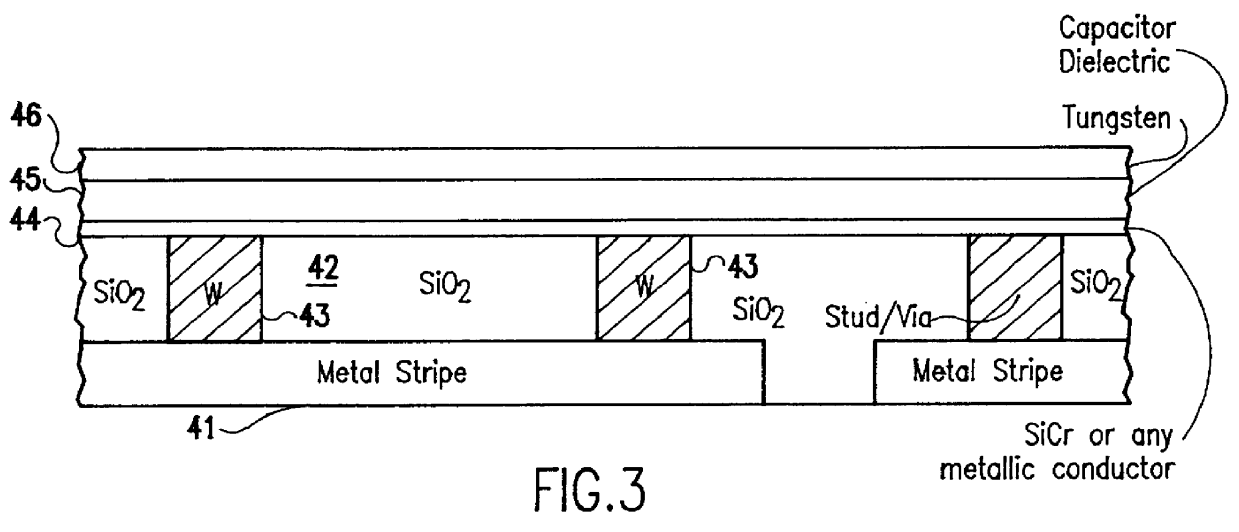
Method of producing planar metal-to-metal capacitor for use in integrated circuits
InactiveUS6069051ASimple processHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsEdge effectsEngineering
A method of fabricating on chip metal-to-metal capacitors (MMCAP) uses planar processing with a flexible choice of dielectric, thickness and capacitor shape. The method provides a simpler process which has a better yield and more reliable structure by creating a metal-to-metal capacitor on a planar surface, not in deep trenches. In addition to the process simplicity, the method also allows the use of any dielectric materials which are needed by the product designer; e.g., higher or lower dielectric constant and also not limited by high etch rate difference. Because the inventive process is a planar process, there are no corners in the bottom of deep trenches to cause yield and reliability problems. The capacitor area can be adjusted to any shape because there are no edge effects.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Monolithic integration of enhancement- and depletion-mode AlGaN/GaN HFETs
A method for and devices utilizing monolithic integration of enhancement-mode and depletion-mode AlGaN / GaN heterojunction field-effect transistors (HFETs) is disclosed. Source and drain ohmic contacts of HFETs are first defined. Gate electrodes of the depletion-mode HFETs are then defined. Gate electrodes of the enhancement-mode HFETs are then defined using fluoride-based plasma treatment and high temperature post-gate annealing of the sample. Device isolation is achieved by either mesa etching or fluoride-based plasma treatment. This method provides a complete planar process for GaN-based integrated circuits favored in high-density and high-speed applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-contrast-grating coupled-cavity narrow-spectral-line-width surface-emitting laser
ActiveCN106058642AReduce processing technologyImprove yieldLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserResonant cavity
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of the photoelectron, discloses a high-contrast-grating coupled-cavity narrow-spectral-line-width surface-emitting laser. A high-contrast grating having high reflectivity and large reflecting width is used as a reflector and is integrated to the top of a transverse-mode-based vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser; and on the basis of the high reflectivity of the high-contrast grating, emergent light of a device is fed back and photoinjection is carried out on the device, thereby obtaining a novel coupled-cavity integrated surface-emitting laser. Therefore, extension of an effective resonant cavity of the device is realized; and the spectral line width of the transverse-mode-based vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser is reduced to obtain a narrow-spectral-line-width surface-emitting laser. Because of utilization of the high-contrast-grating structure with support of the low refractive index, the integrated outer cavity preparation difficulty is reduced and the device processing process is simplified; the preparation process is a pure planar process, so that the yield and reliability of the device are improved effectively. The laser has advantages of large spectral line width adjusting range, obvious narrowing effect, and simple design and preparation process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
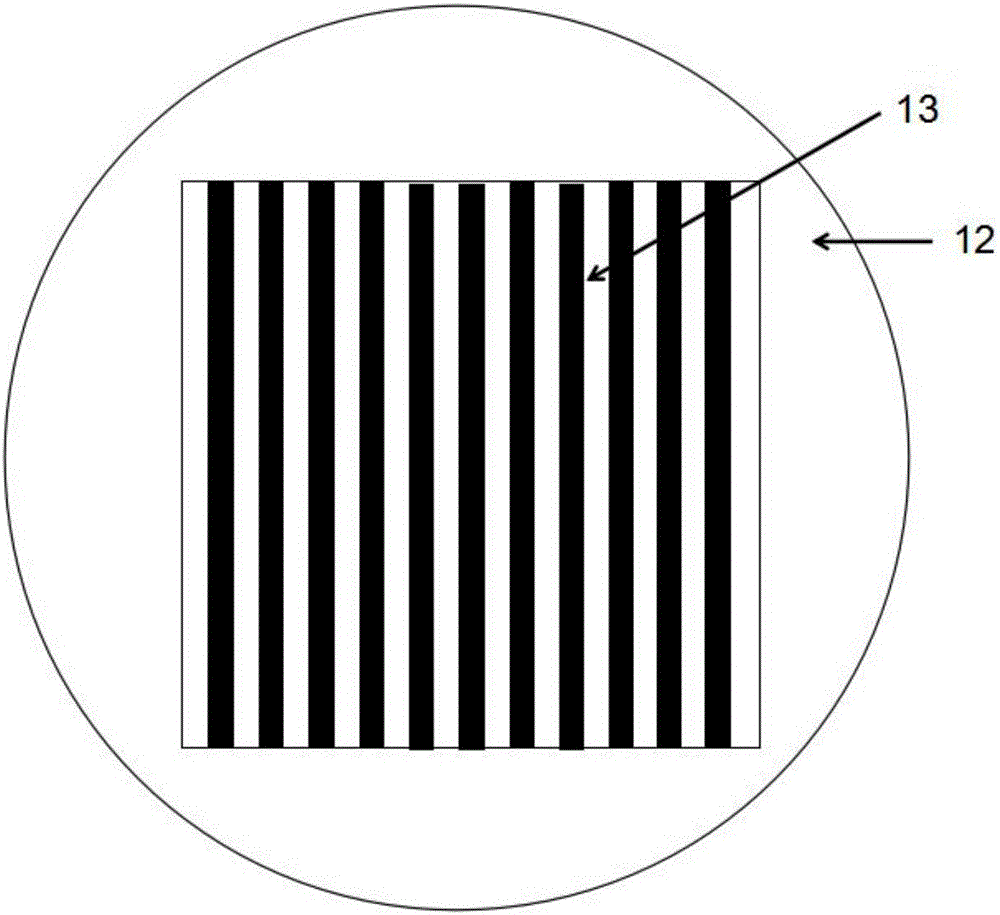
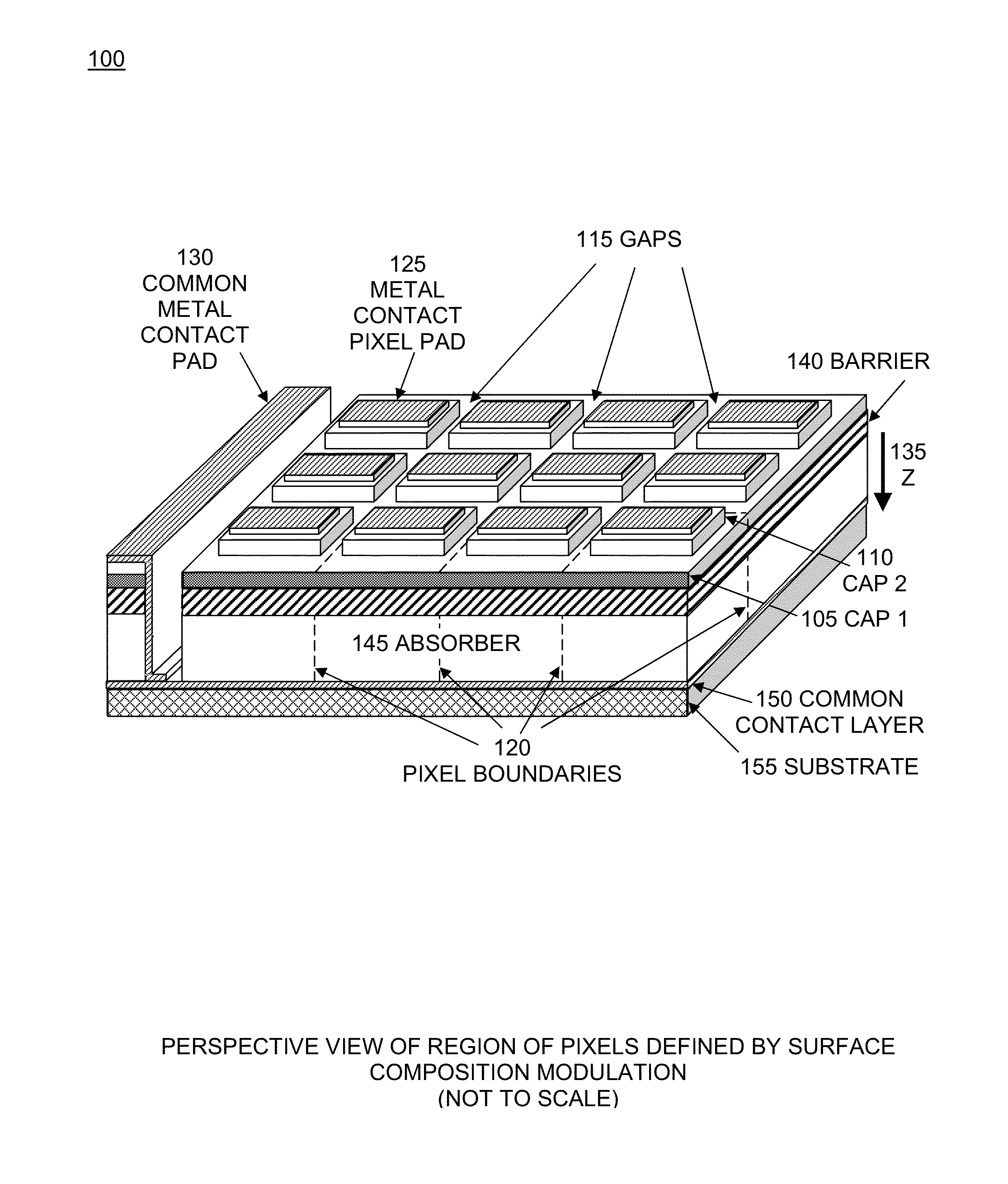
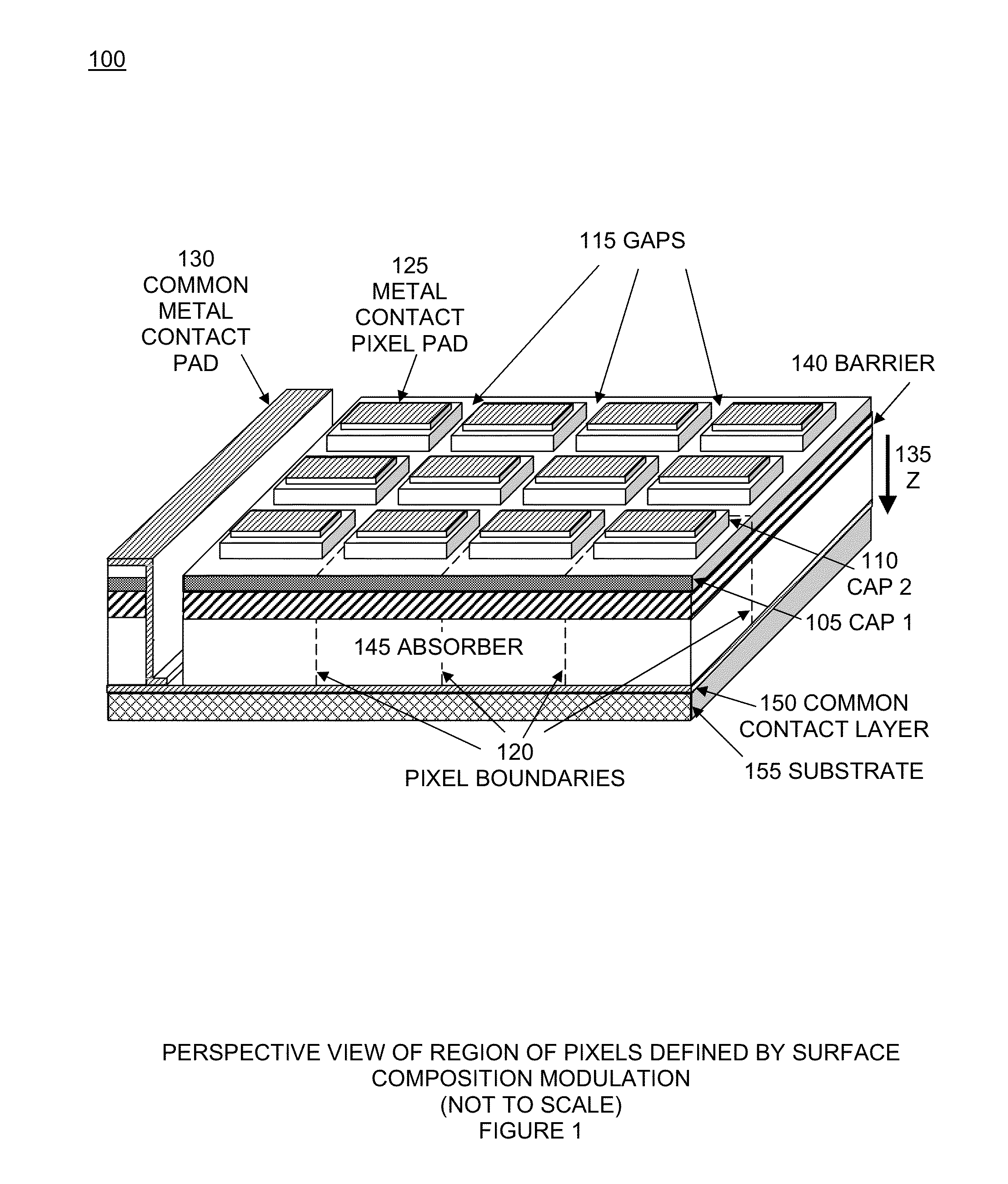
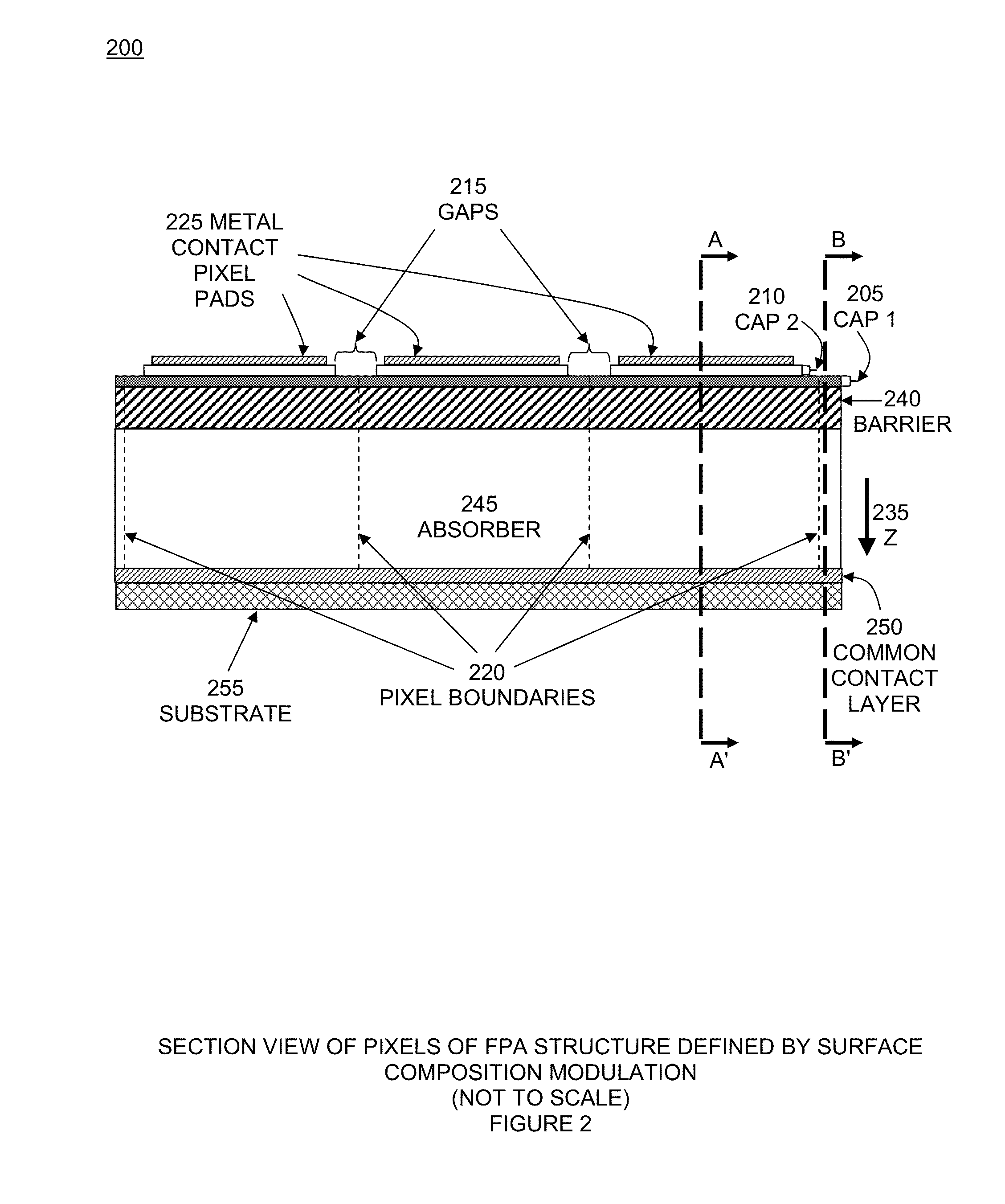
Focal plane array with pixels defined by modulation of surface fermi energy
ActiveUS20140191195A1Minimize the possibilitySimplify the manufacturing processSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesDetector arrayFocal Plane Arrays
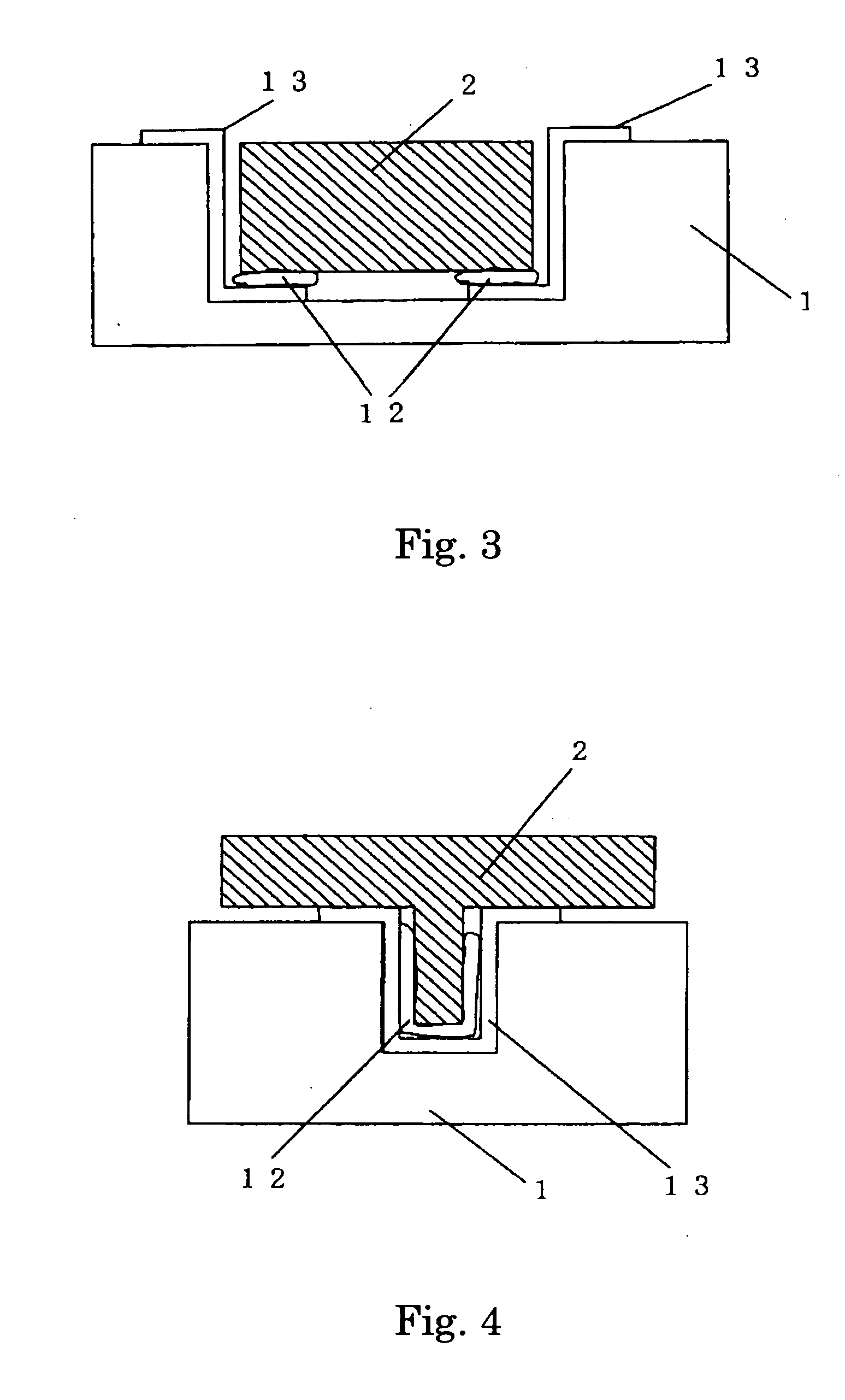
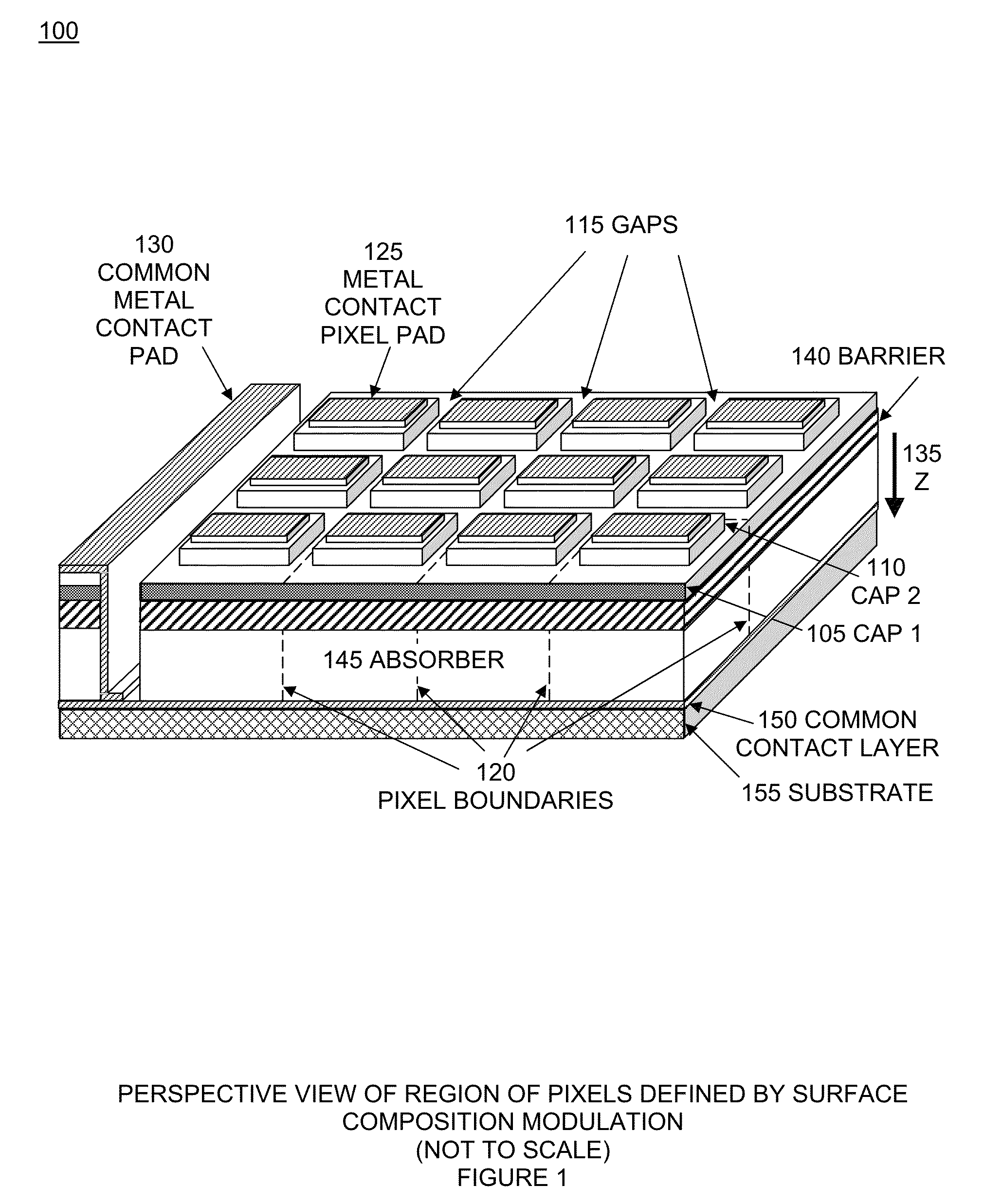
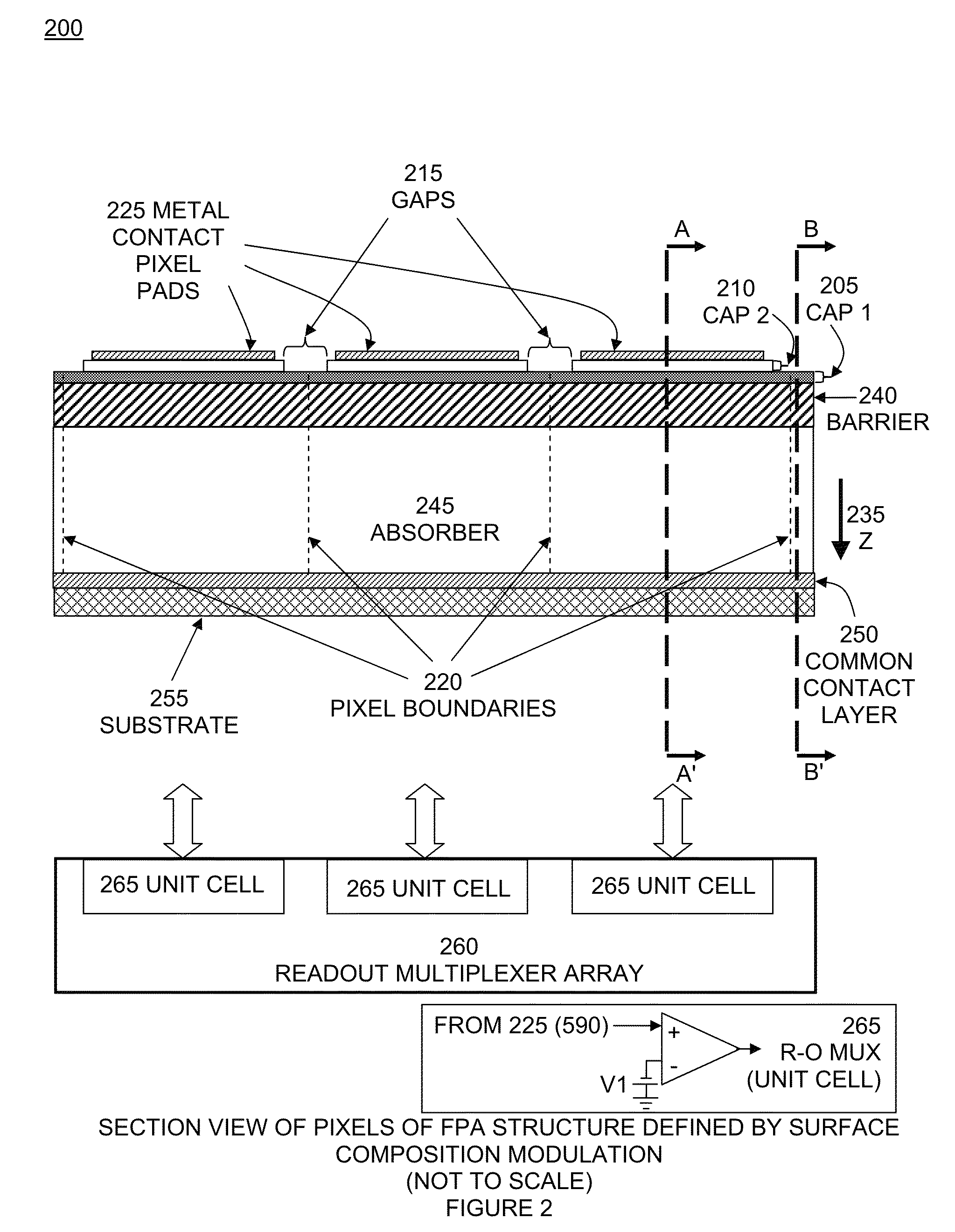
Pixels in a focal plane array are defined by controlled variation of the Fermi energy at the surface of the detector array. Varying the chemical composition of the semiconductor at the detector surface produces a corresponding variation in the surface Fermi energy which produces a corresponding variation in the electric field and electrostatic potential in the bulk semiconductor below the surface. This defines pixels by having one Fermi energy at the surface of each pixel and a different Fermi energy at the surface between pixels. Fermi energy modulation can also be controlled by applying an electrostatic potential voltage V1 to the metal pad defining each pixel, and applying a different electrostatic potential voltage V2 to an interconnected metal grid covering the gaps between all the pixel metal pads. Methods obviate the need to etch deep trenches between pixels, resulting in a more manufacturable quasi-planar process without sacrificing performance.
Owner:SUNDARAM MANI +1
Bidirectional transient voltage suppression device
ActiveCN105374815AIncrease holding voltageImprove electrostatic discharge capacity per unit areaThyristorSolid-state devicesOvervoltageTransient voltage suppressor
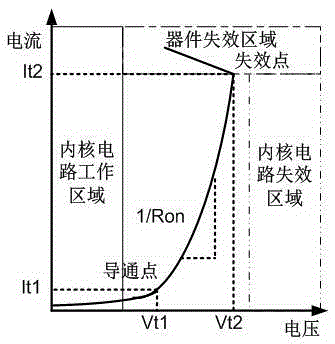
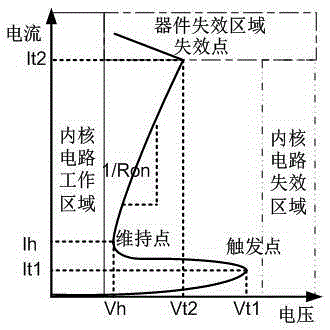
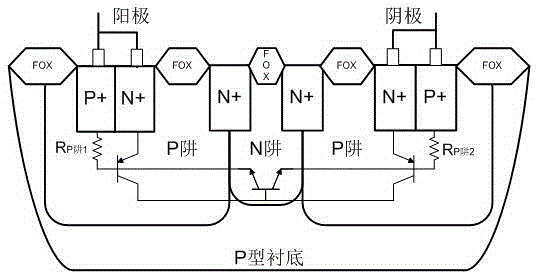
The invention discloses an NPNPN-type bidirectional transient voltage suppression device which is based on a silicon planar process, has high maintaining voltage and high peak current, and is capable of bidirectionally clamping transient overvoltage. The NPNPN-type bidirectional transient voltage suppression device comprises a P-type substrate, wherein an N-type deep pit is arranged on the P-type substrate, a first P pit, a first N pit and a second P pit are arranged in the N-type deep pit, a first P+ injection region, a first N+ injection region, a second N pit and a second N+ injection region are sequentially arranged in the P pit from left to right, the second N+ injection region bridges the first P pit and the first N pit, a third N+ injection region, a third N pit, a fourth N+ injection region and a fifth P+ injection are sequentially arranged in the second P pit from left to right, the third N+ injection region bridges the second P pit and the first N pit, the first P+ injection region and the first N+ injection region are connected with a positive electrode, and the fourth N+ injection region and the second P+ injection region are connected to a negative electrode. The device can be used for transient overvoltage suppression on a chip pin with a signal level of (-5)V to (+5)V.
Owner:SUPERESD MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Method for forming 3D NAND flash memory
ActiveCN106129010AReduce areaReduce sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGraphicsEngineering
The invention relates to the manufacturing technical field of a semiconductor, and particularly to a method for forming a 3D NAND flash memory. By optimization of structures of channel holes and gate lines, nine rows of perpendicular hole patterns can be placed in one gate line; then after the processing of the channel holes is finished, the separation of the channel holes in the upper and lower rows can be realized through etching of a first trench so as to reduce the required area of a second trench and overlap; finally, the separate line connection of each CH BL in the same layer of GL SL is realized through a back section dual-pattern etching process so as to effectively reduce the size of an effective storage cell; and therefore, under the premise of not increasing the technological difficulty, the equivalent storage area is improved by about 35-40% by optimization of the planar process structure and the back section line connecting process.
Owner:WUHAN XINXIN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
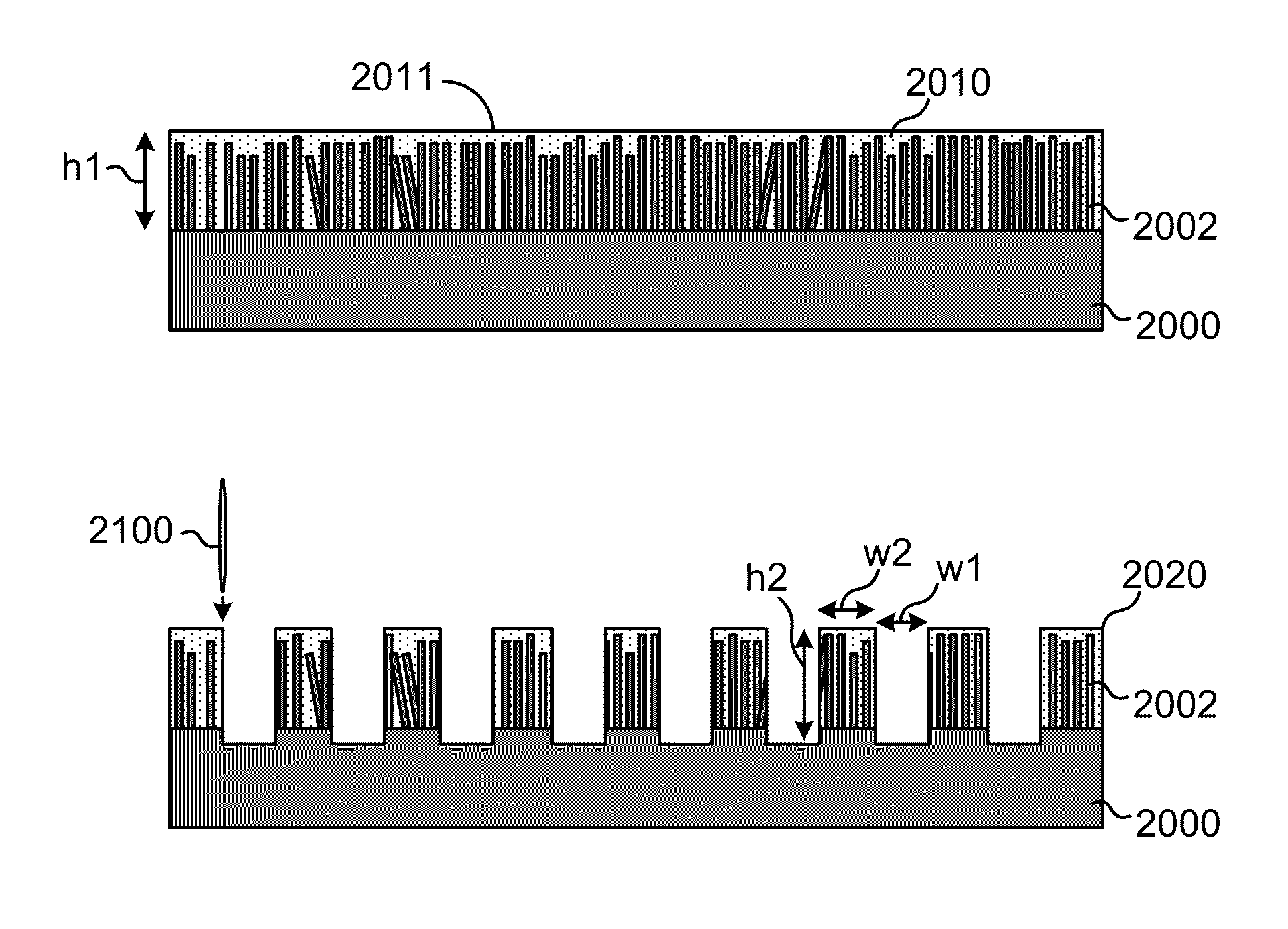
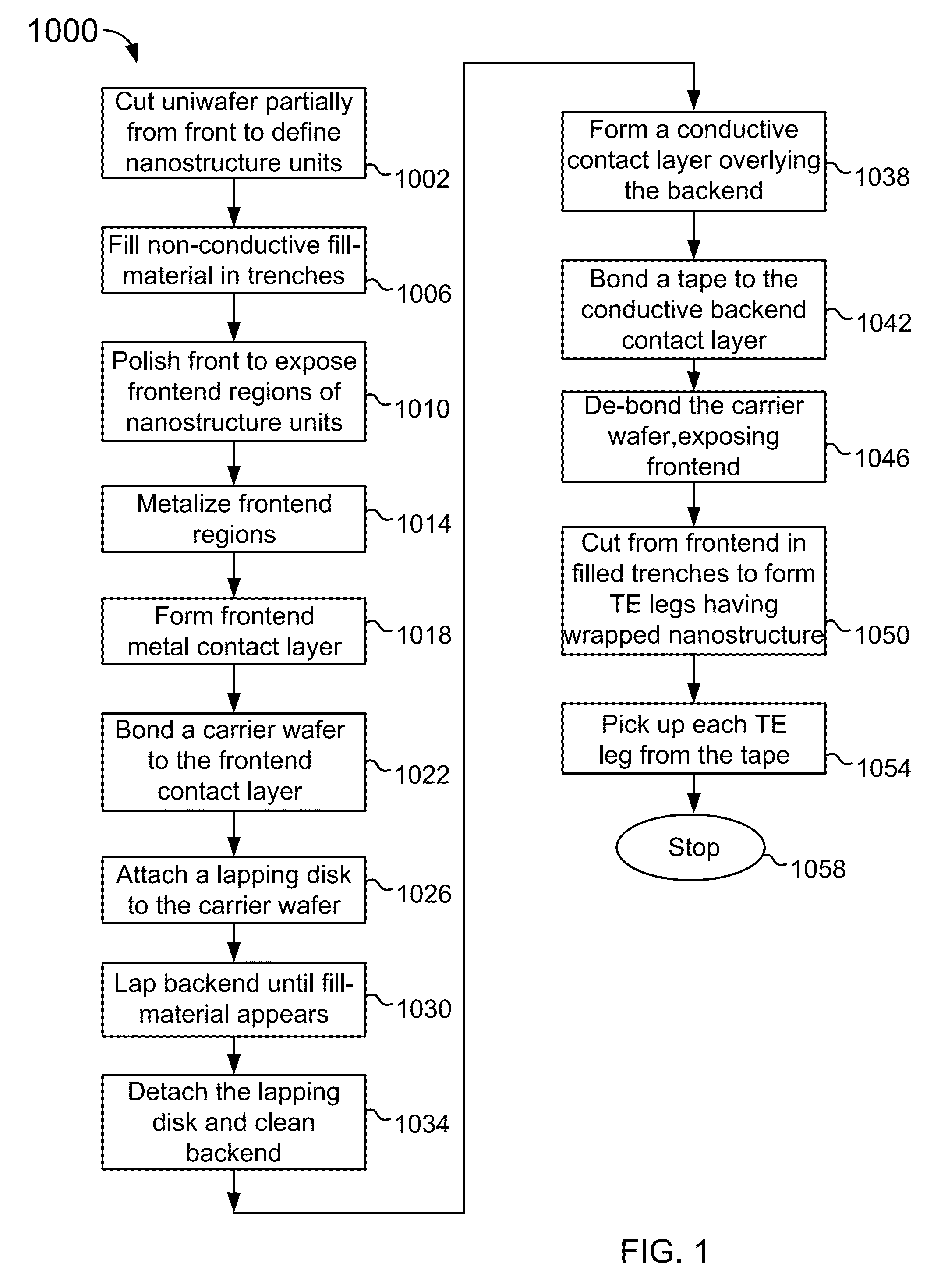
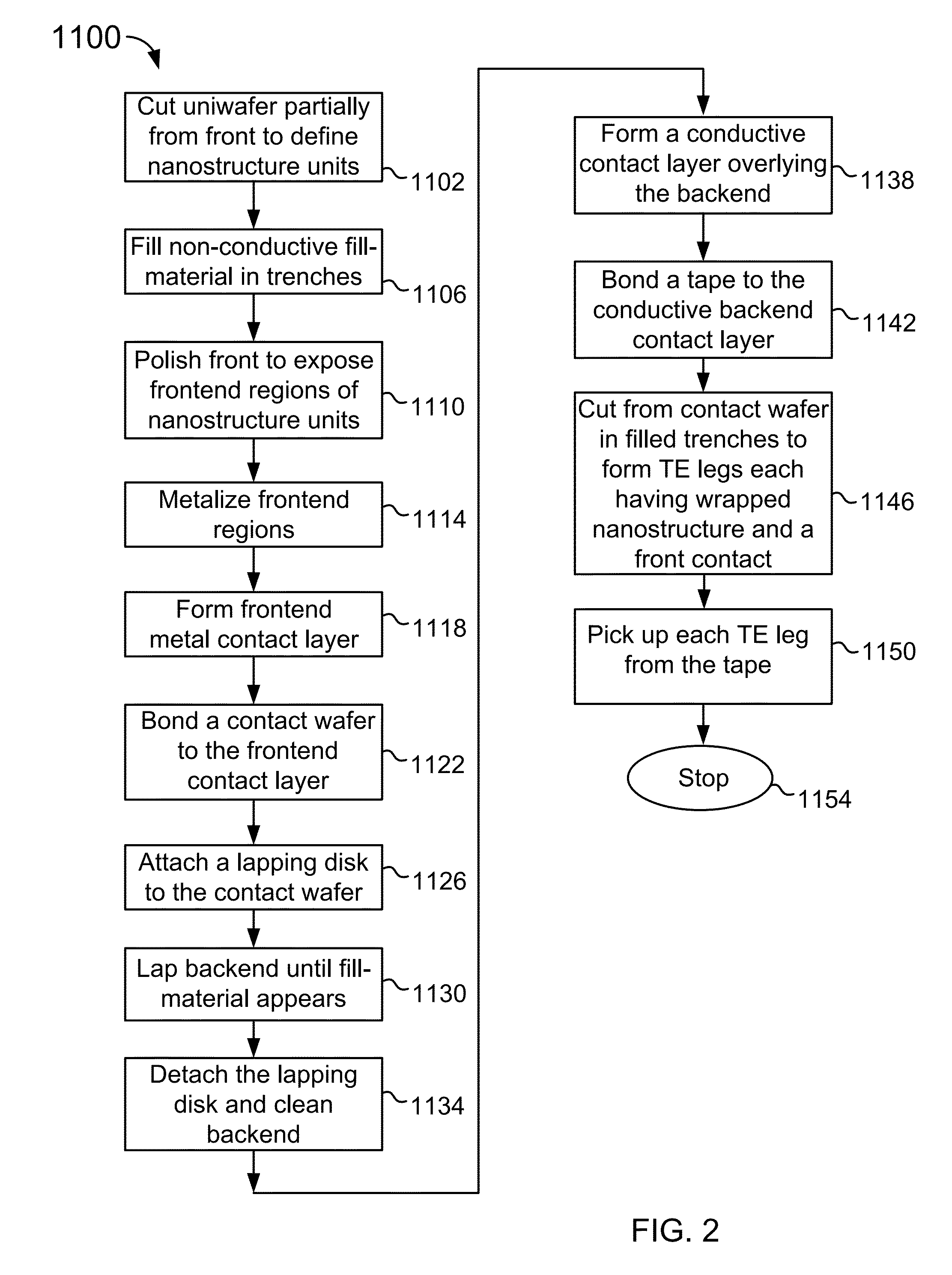
Nanostructured thermolectric elements and methods of making the same
InactiveUS9082930B1Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFilling materialsContact layer
Nanostructured thermoelectric elements are made from planar uniwafer processing methods. The method includes producing either n-type or p-type thermoelectric uniwafer structure bearing nanostructure material embedded in a low thermal conductivity fill material. The method further includes partially cutting the uniwafer structure to form a plurality of chip structures separated by trenches. The method includes filling the trenches with the fill material to surround the nanostructure material within each chip structure. The method further includes additionally planar processing to form both frontend and backend conductive contact layers respectively coupled to frontend regions and backend regions of the chip structures. Additionally, the modified thermoelectric uniwafer structure is cut to turn the chip structures to bulk-sized nanostructured thermoelectric legs, each bulk-sized nanostructured thermoelectric leg being wrapped around by the fill material and ready for assembling thermoelectric modules.
Owner:SYNERGY THERMOGEN INC +1
Method for realizing silicon based silicon dioxde waveguide polarization irrelevancy by employing non-planar process
InactiveCN1670550AAchieving polarization insensitivityAchieving polarization independenceOptical waveguide light guideCompound (substance)Silicon dioxide
This invention relates to a silicon base dioxide silicon wave polarization switch method by use of non-plane process and is characterized by the following steps: a, etching the ion on the silicon underlay for wave guide core area space; b, forming down cover layer and side cover layer with thickness of 15 mu m; c, growing core area by use of ion strengthening chemical gas deposition method and flame solution in wave guide core area; d, growing upper cover layer of 15 mu m by use of ion strengthening chemical gas deposition method or flame solution; f, polishing and removing the core layer of the oxidation layer, upper cover of materials; whole silicon dioxide silicon polarization wave guide process.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for detecting ferro-electric film microwave dielectric property
The present invention is method and device for detecting the microwave dielectric characteristic of ferroelectric film. The device includes substrate, measured ferroelectric film on the substrate, coplanar waveguide line including main transmission line and earthing areas separated on two sides on the film, and coplanar quarter-wave open-circuited line on the film and including transmission line connected to the main transmission line and earthing areas separated on two sides. Owing to the coplanar quarter-wave open-circuited line to form the resonant peak, the dielectric characteristic of the measured film may be obtained easily. The pattern for detection of the ferroelectric film may be formed in once forming process. Therefore, compared with available technology, the present invention has simple principle and easy device making and assembling, and is convenient and practical.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bionic hair-type silicon micro-gyroscope for angular velocity sensing
ActiveCN106289210AQuality improvementChange the capacitance valueSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeSquare waveform
The invention discloses a bionic hair-type silicon micro-gyroscope for angular velocity sensing. The bionic hair-type silicon micro-gyroscope is composed of upper polymer hair, a middle silicon micro-sensor and a bottom glass substrate equipped with a circuit, wherein the middle silicon micro-sensor comprises a circular mass block and an annular mass block with a same circle center as the circular mass block; two torsion beams are arranged between the circular mass block and the annular mass block; the upper polymer hair is adhered onto the center of the circular mass block; and the circumferential lateral part of the annular mass block are uniformly provided with a plurality of comb groups and square wave supporting beams which are arranged in a staggered way. The bionic hair-type silicon micro-gyroscope is novel in structure, has high sensitivity and is compatible with conventional planar process; and compared with a simple conventional planar structure, the arrangement of the upper polymer hair is favorable for enlarging the Coriolis effect and improving structure sensitivity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Bio-sample tomography micro-imaging system
ActiveCN104833659AFast cutting speedShorten the timeWithdrawing sample devicesAnalysis by material excitationCamera lensMicro imaging
The invention discloses a bio-sample tomography micro-imaging system which includes a low-light imaging sub system and a sample planar processing sub system. The low-light imaging sub system is used for performing integral imaging during planar processing on the sample, and the sample planar processing sub system is used for processing the surface of the sample to form a tomography for imaging by the low-light imaging sub system. The low-light imaging sub system comprises a linear scanning module and a light spot shaping module, wherein the linear scanning module comprises a linear detector and an imaging lens. The light spot shaping module, in the direction of light path, successively comprises a beam expansion unit and a beam shrinkage unit. In the invention, by means of separation of a cutting module from the imaging system, the low-light imaging sub system is designed, so that the bio-sample tomography micro-imaging system is suitable for various resin-embedded samples. By means of separation of cutting speed from imaging speed, longitudinal low-sampling quick imaging acquisition can be carried out. In addition, the bio-sample tomography micro-imaging system can perform quick 3D information acquisition on low-light objects, such as fluorescent biological organs and the like.
Owner:WUHAN OE BIO CO LTD
Semiconductor structure and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8932927B2Reduce manufacturing costReduce difficultySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor structure
The present application discloses a semiconductor device structure and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein the method comprises: forming a semiconductor substrate comprising a local SOI structure having a local buried isolation dielectric layer; forming a fin on the silicon substrate on top of the local buried isolation dielectric layer; forming a gate stack structure on the top and side faces of the fin; forming source / drain structures in the fin on both sides of the gate stack structure; and performing metallization. The present invention makes use of traditional quasi-planar based top-down processes, thus the manufacturing process thereof is simple to implement; the present invention exhibits good compatibility with CMOS planar process and can be easily integrated, therefore, short channel effects are suppressed desirably, and MOSFETs are boosted to develop towards a trend of downscaling size.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120220093A1Reduce manufacturing costLarge leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceElectricity
The present application discloses a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising: forming a local buried isolation dielectric layer in a semiconductor substrate; forming a fin in the semiconductor substrate and on top of the local buried isolation dielectric layer; forming a gate stack structure on a top surface and side surfaces of the fin; forming source / drain structures in portions of the fin which are on opposite sides of the gate stack structure; and performing metallization. A conventional quasi-planar top-down process is utilized in the present invention to achieve a good compatibility with the CMOS planar processes, easy integration, and suppression of short channel effects, which promotes the development of MOSFETs having reduced sizes.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An electronic emitter on silicon-based surface and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101286430AHigh energySolve complexityImage/pattern display tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactDisplay device
The invention discloses a silica-based surface electronic emitter and a preparation method thereof. The emitter deposits a SiO2 or Al2O3 thin film layer at the front of an 'n' type silicon substrate, a gate electrode is deposited on the SiO2 or Al2O3 thin film layer and an ohmic contact electrode is deposited at the back of the silicon substrate; the producing method comprises the following steps: an 'n' type silicon chip is washed firstly; a SiO2 or Al2O3 thin film is deposited on the silicon chip by a thermal oxidation method or a chemical vaporous deposition method or an evaporation method or a sputtering method or a sol-gel method; the gate electrode is sputtered on the SiO2 or Al2O3 thin film, and the ohmic contact electrode is sputtered at the back of the silicon substrate. The silica-based surface electronic emitter of the invention has higher electronic emission energy and good performance for high field emission, can be used for producing a field emission display, has simple producing technique and is compatible with the existing mature silicon device planar technique.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Out-plane piezoelectric type hemispheric micro-gyroscope and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104897146AEasy to detectLarge effective vibration displacementDecorative surface effectsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeParasitic capacitance
The invention provides an out-plane piezoelectric type hemispheric micro-gyroscope and a preparation method thereof. The out-plane piezoelectric type hemispheric micro-gyroscope comprises a monocrystalline silicon substrate, a miniature hemispheric harmonic oscillator, a central fixed support pillar, a common electrode, a uniformly distributed film piezoelectric body and a uniformly distributed signal electrode. According to the invention, the hemispheric structure is adopted as a harmonic oscillator, so that great effective vibration displacement is obtained, and detection effect for Coriolis effect can be enhanced; the common electrode, the film piezoelectric body and the signal electrode are manufactured by adopting an MEMS planar process, so that the manufacturing precision is high, and the structural degree of symmetry of the micro-gyroscope can be improved; the out-plane driving and the detection method are adopted, so that interconversion between out-plane force and in-plane can be realized, and Coriolis effect vertical to the direction of the substrate can be detected; the piezoelectric type driving and the detection method are adopted, miniature capacitance space needed by electrostatic micro-gyroscope is not needed, and meanwhile, the problems of stray capacitance, electrostatic adherence and the like are avoided; the technology is simple, the integrated degree is high, and batch production can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Semiconductor structure and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130134516A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce difficultySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor structure
The present application discloses a semiconductor device structure and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein the method comprises: forming a semiconductor substrate comprising a local SOI structure having a local buried isolation dielectric layer; forming a fin on the silicon substrate on top of the local buried isolation dielectric layer; forming a gate stack structure on the top and side faces of the fin; forming source / drain structures in the fin on both sides of the gate stack structure; and performing metallization. The present invention makes use of traditional quasi-planar based top-down processes, thus the manufacturing process thereof is simple to implement; the present invention exhibits good compatibility with CMOS planar process and can be easily integrated, therefore, short channel effects are suppressed desirably, and MOSFETs are boosted to develop towards a trend of downscaling size.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of producing group iii nitride substrate wafers and group iii nitride substrate wafers
InactiveCN101106081APromote crystallizationEasy to shapeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaxWafering
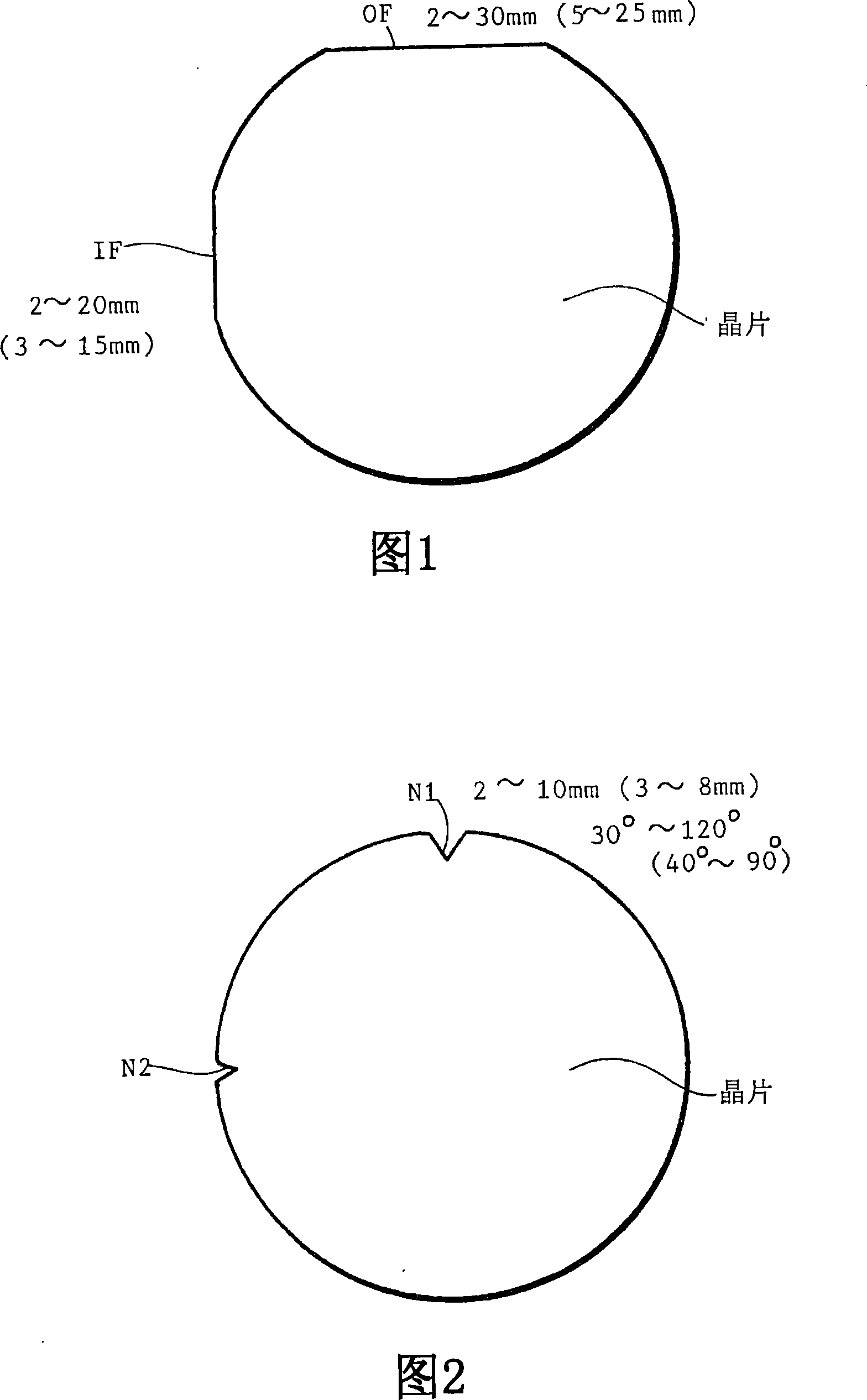
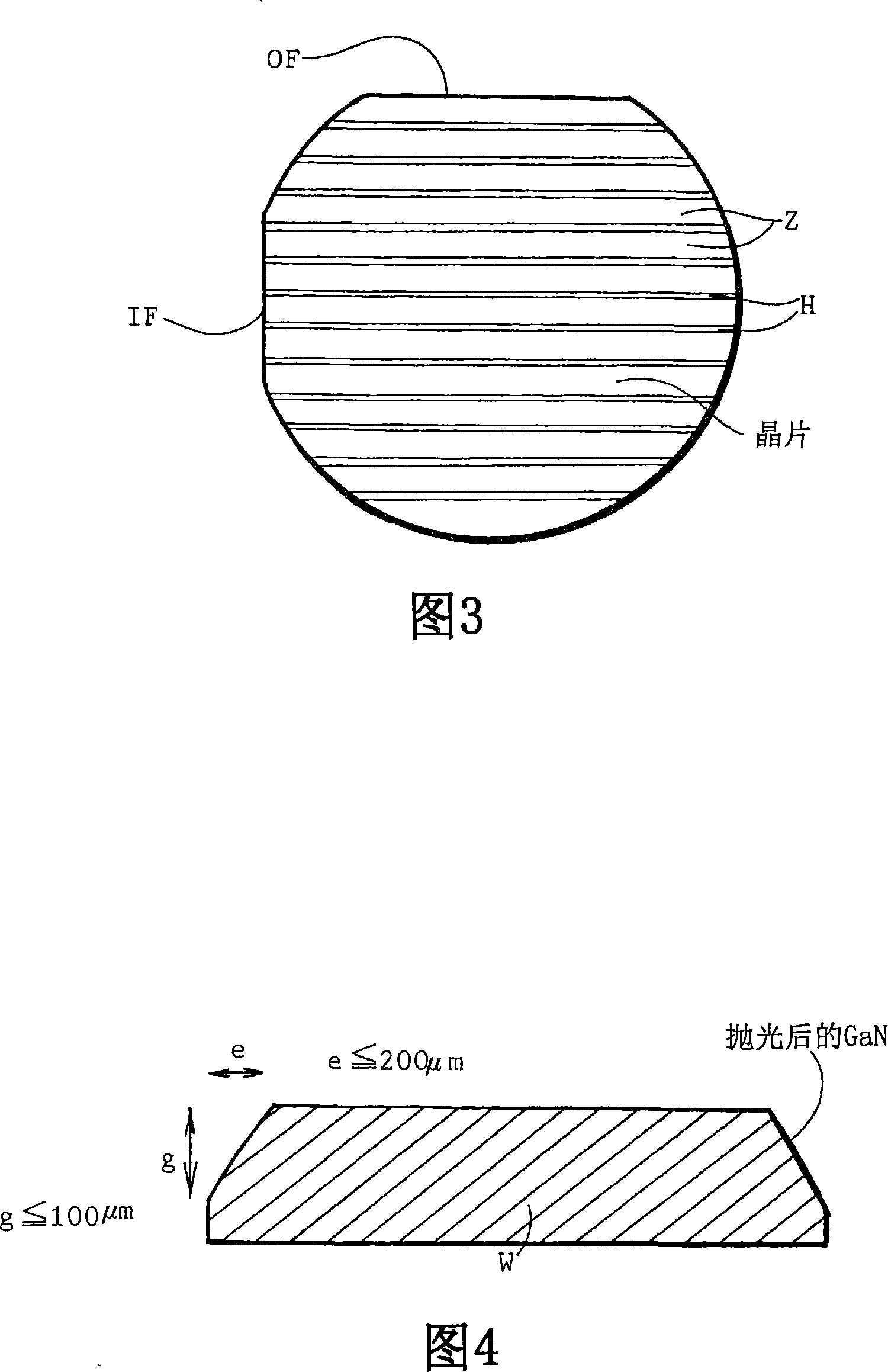
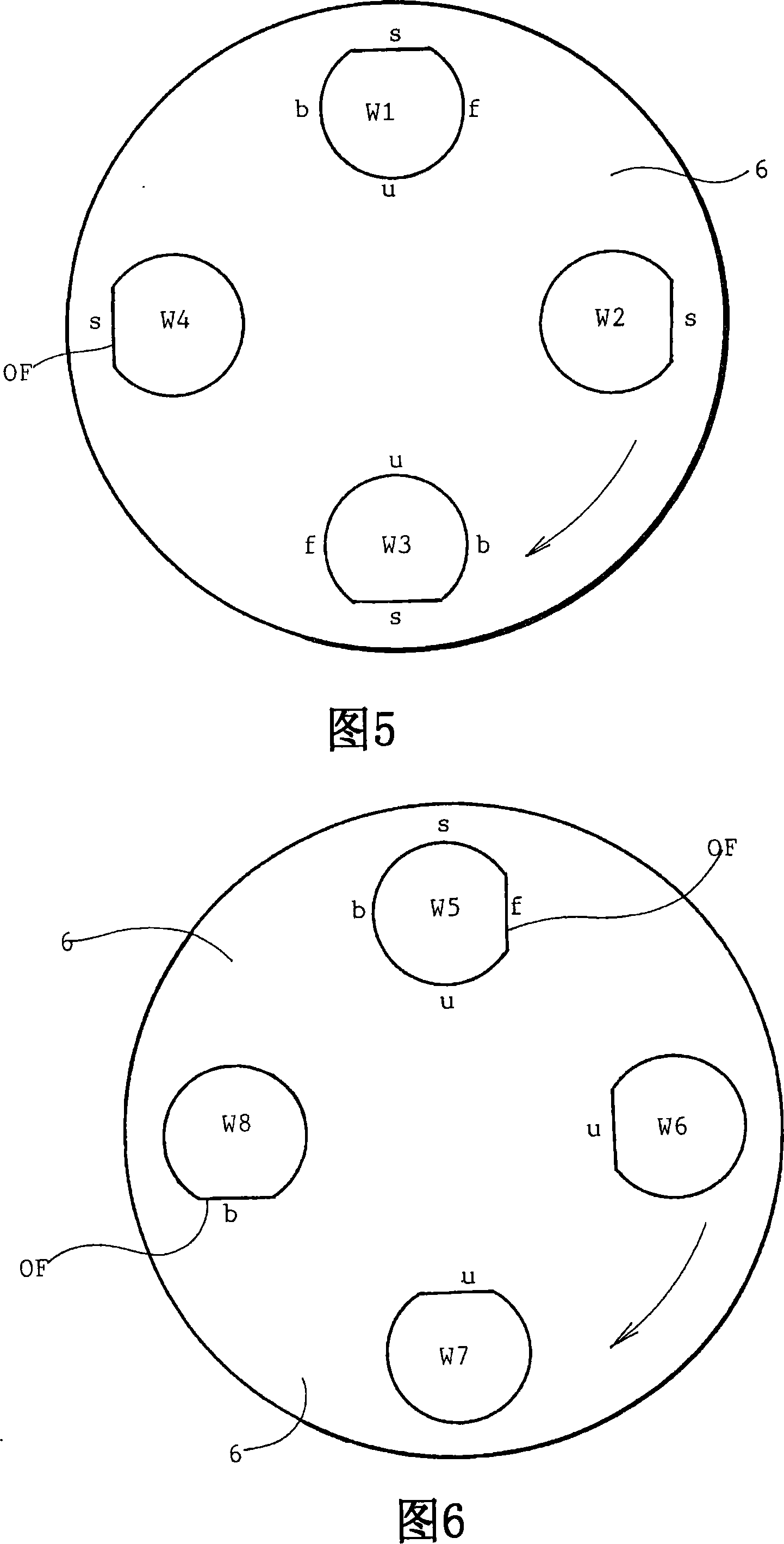
Quality of one-surface planar processed group 3 nitride wafers depends upon a direction of pasting of wafers on a polishing plate. Low surface roughness and high yield are obtained by pasting a plurality of group 3 nitride as-grown wafers on a polishing plate with OFs or notches facing forward (f), backward (b) or inward (u) with thermoplastic wax having a thickness of 10[mu]m or less, grinding the as-grown wafers, lapping the ground wafers, polishing the lapped wafers into mirror wafers with a bevel of a horizontal width of 200[mu]m or less and a vertical depth of 100[mu]m or less.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
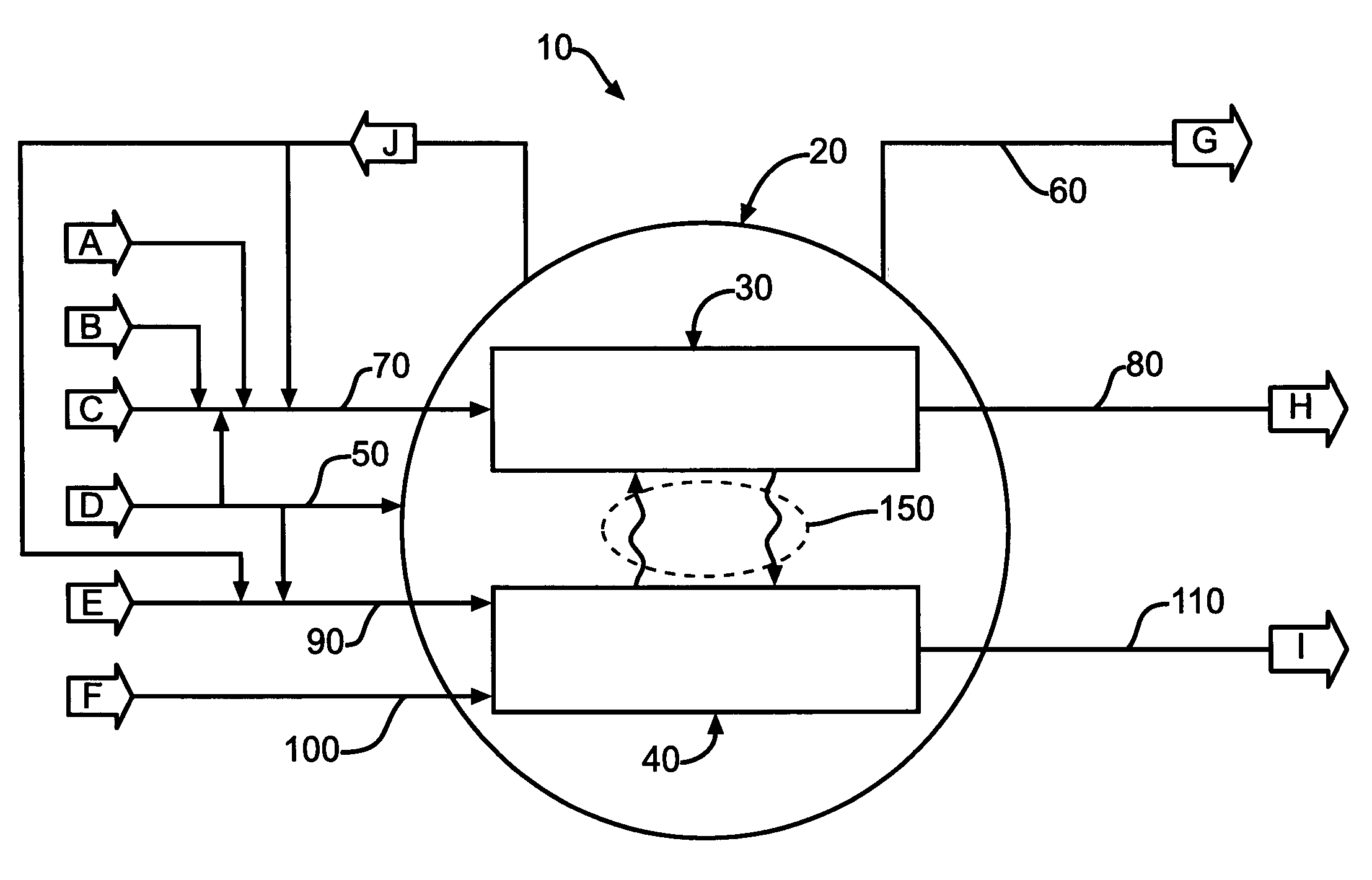
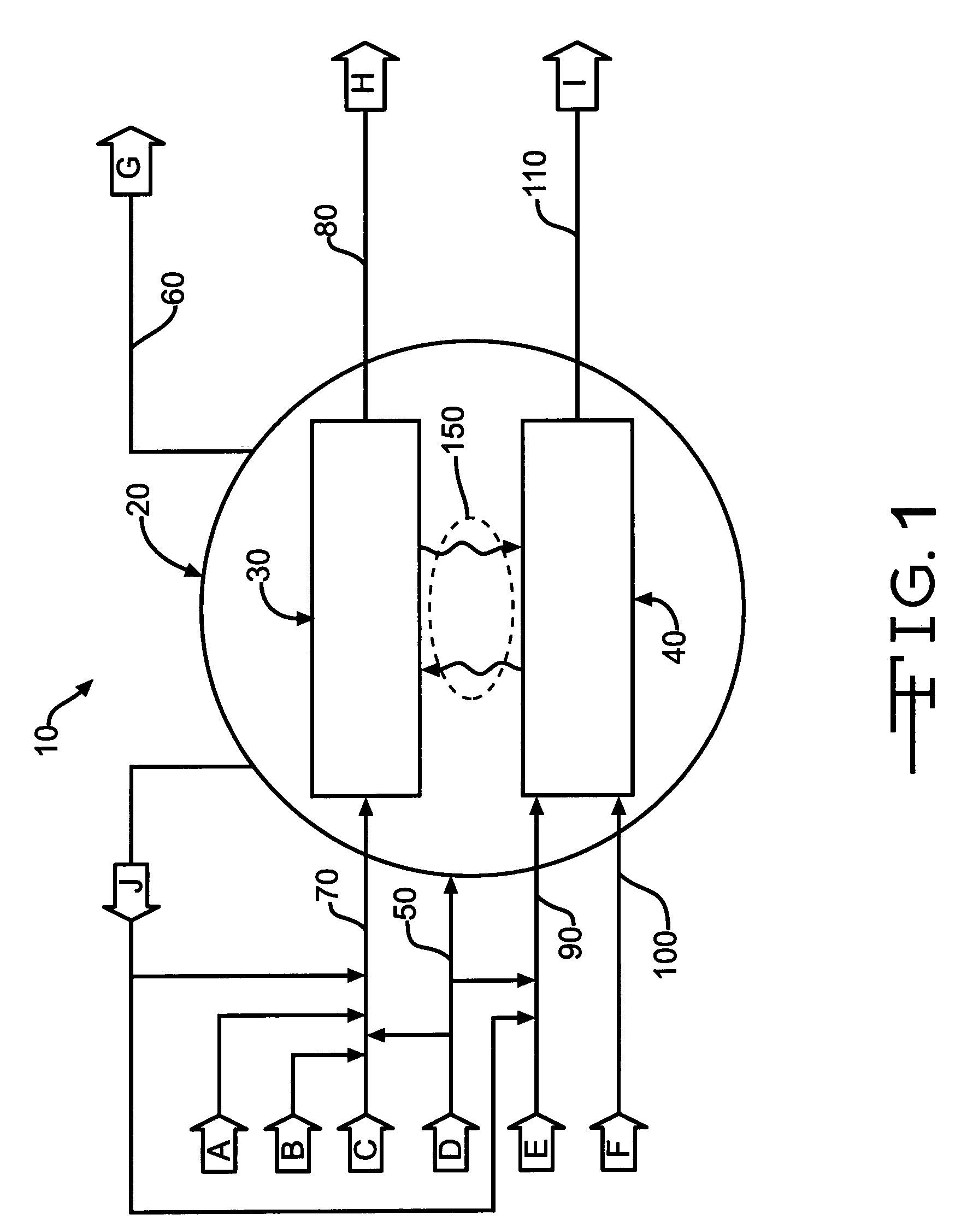
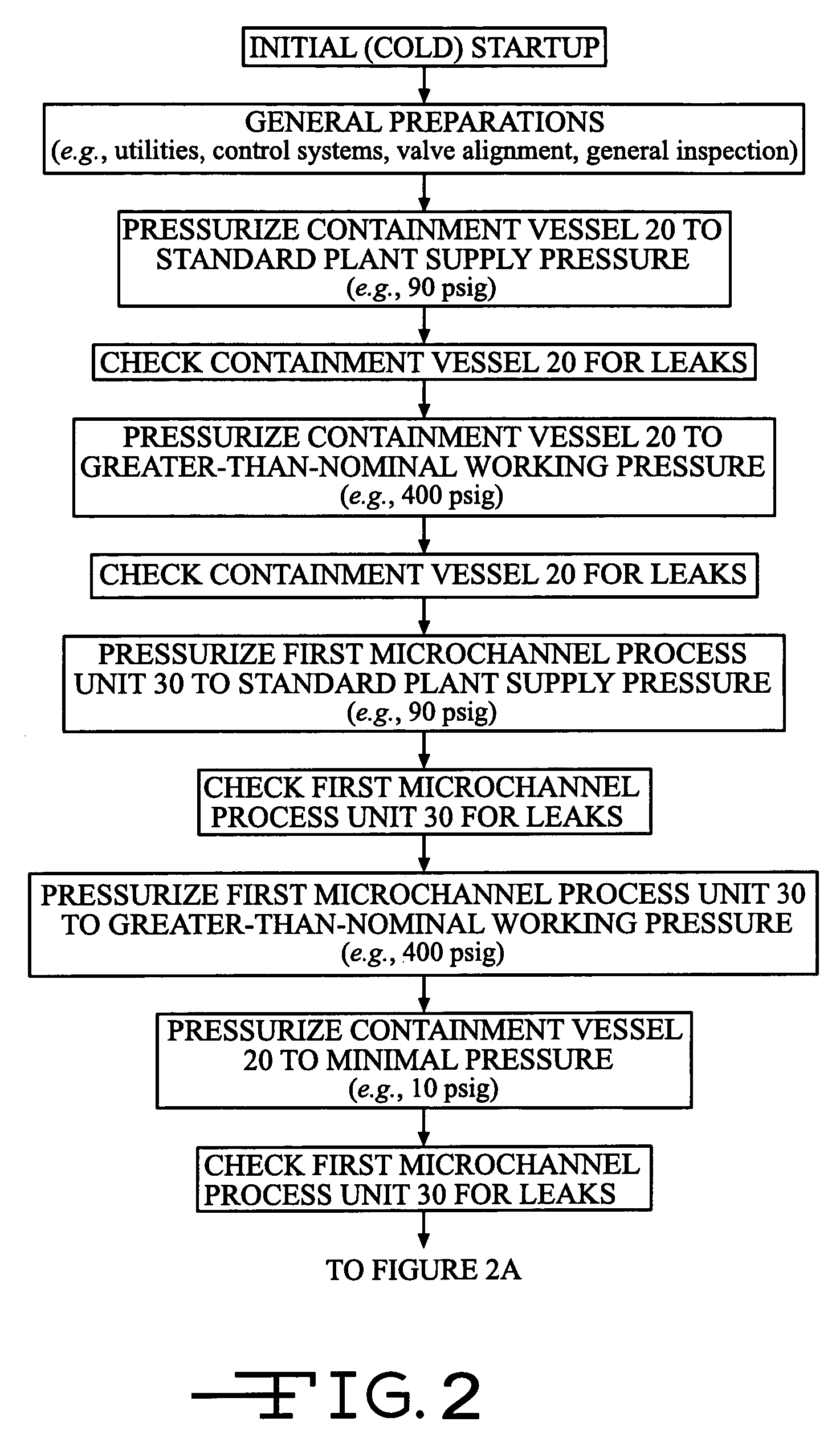
Control of pressurized microchannel processes
InactiveUS7445650B2Good thermal controlIncrease flexibilityOxygen-containing compound preparationPressurized chemical processThermal energyVolumetric Mass Density
A method of starting up and shutting down a microchannel process is provided. Included are the steps of providing a first multi-planar process unit, preferably adapted to process an endothermic reaction, a second multi-planar process unit, preferably adapted to process an exothermic reaction, providing a containment vessel, the containment vessel containing at least a portion of the first, and preferably the second, process unit. In startup, the microchannel process is first checked for pressure integrity by pressurizing and checking the important components of the process for leaks. Subsequently, the process units are heated by introducing a dilute low-thermal energy density material, preferably to the second process unit, followed by the introduction of a dilute high-thermal energy density material, and adjusting the proportion of high-thermal energy density material as required. In shutdown, a purge material from the containment vessel is introduced into the first, and preferably the second, process unit.
Owner:VELOCYS INC
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
ActiveUS8389367B2Easy to mergeImprove compatibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSGate stack
The present application discloses a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising: forming a local buried isolation dielectric layer in a semiconductor substrate; forming a fin in the semiconductor substrate and on top of the local buried isolation dielectric layer; forming a gate stack structure on a top surface and side surfaces of the fin; forming source / drain structures in portions of the fin which are on opposite sides of the gate stack structure; and performing metallization. A conventional quasi-planar top-down process is utilized in the present invention to achieve a good compatibility with the CMOS planar processes, easy integration, and suppression of short channel effects, which promotes the development of MOSFETs having reduced sizes.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for forming totally-enclosed gate structure
ActiveCN104392917AMaintain propertiesAddress process complexitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesState of artGate dielectric
The invention discloses a method for forming a totally-enclosed gate structure. The method is used for manufacturing FinFET devices, and comprises forming a gate dielectric, Fin and a gate in steps by use of a planar process and connecting the lower end of the gate surrounding the Fin with a substrate to form the totally-enclosed gate structure. As the gate dielectric is quite thin and the lower end of the gate is connected with the substrate, the gate is enabled to effectively control channels from all sides still in a totally enclosing form. As a result, the method for forming the totally-enclosed gate structure succeeds in solving the problems of complex process and high cost in the prior art while guaranteeing the desired device characteristics. The method is simple and convenient, and compatible with the existing integrated circuit planar process, and has the advantages of low cost, easy implementation and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor Structure and Method for Manufacturing the Same
ActiveUS20130134515A1Reduce manufacturing costWell formedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSBody contact
The present application discloses a semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (FET) structure and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein the method comprises: forming a semiconductor substrate comprising an SOI structure having a body-contact hole; forming a fin on the SOI structure of the semiconductor substrate; forming a gate stack structure on top and side faces of the fin; forming source / drain structures in the fin on both sides of the gate stack structure; and performing metallization. The present invention makes use of traditional quasi-planar based top-down processes, thus the manufacturing process thereof becomes simple to implement; the present invention exhibits good compatibility with CMOS planar process and can be easily integrated; the present invention also is favorable for suppressing short channel effects desirably, and boosts MOSFETs to develop towards a trend of downscaling size.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical sensor element, optical sensor device and image display device using optical sensor element
InactiveCN101325226ALow costImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesDriver circuitAmorphous silicon
A highly sensitive optical sensor element, and a switch element such as a sensor driver circuit are formed on the same insulating substrate by using an LTPS planar process to provide a low cost area sensor (optical sensor device) incorporating the sensor driver circuit and the like or an image display device incorporating the optical sensor element. As an optical sensor element structure, one electrode of the sensor element is manufactured with the same film of the polycrystalline silicon film that is an active layer of the switch element constituting a circuit. A photoelectric conversion unit for performing photoelectric conversion is made of an amorphous silicon or a polycrystalline silicon film of an intrinsic layer. A structure in which the amorphous silicon of the photoelectric conversion unit and the insulating layer are sandwiched between two electrodes of the sensor element is adopted.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
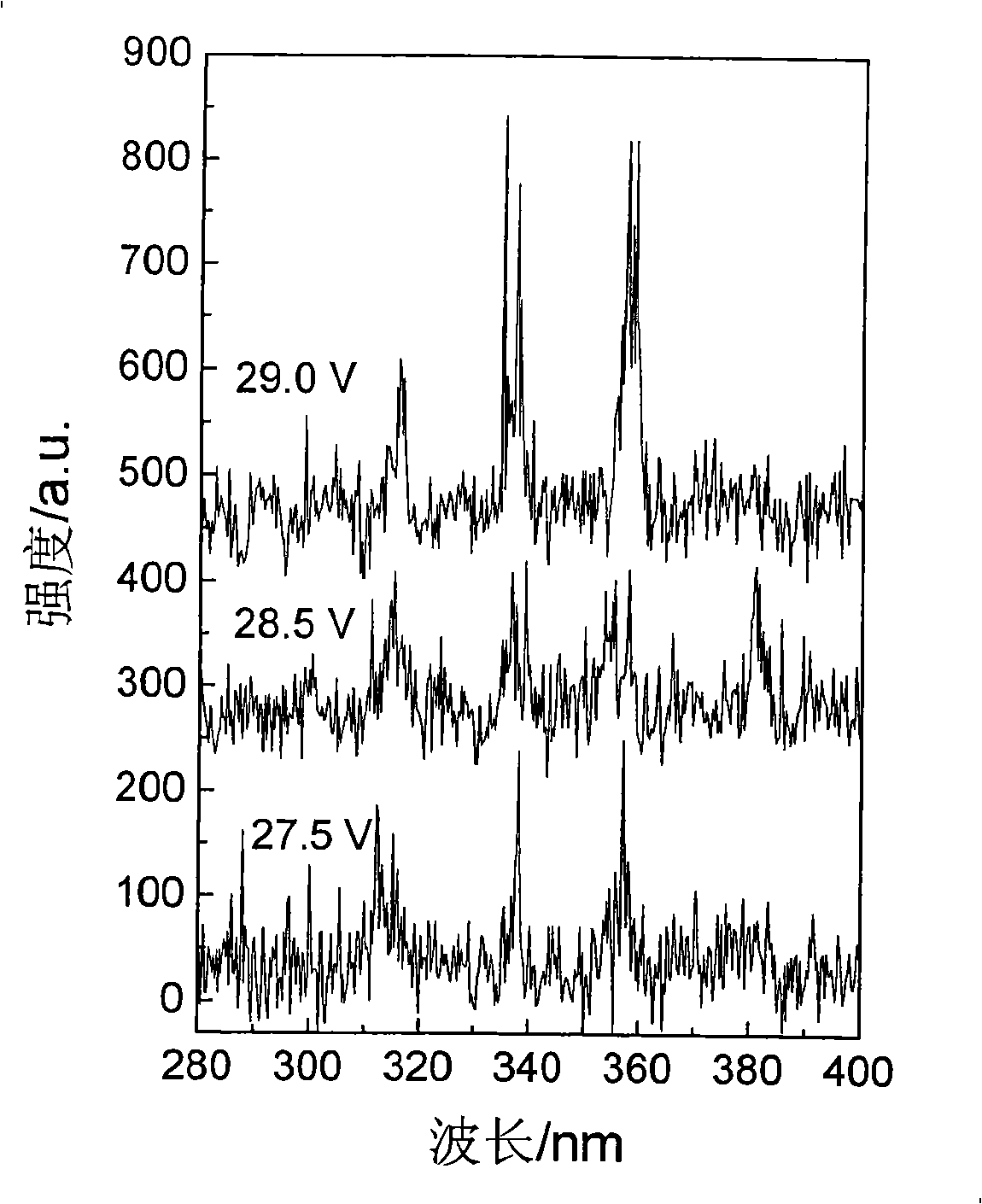
Electric pumping silicon base MgxZn1-xO film ultraviolet accidental laser and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101510664ASimple structure and implementationSimple structureExcitation process/apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingSilicon nitrideResonator
The invention discloses an electric pumping silica-based MgxZn1-xO film ultraviolet random laser and a manufacturing method thereof. The random laser has a structure as follows: the MgxZn1-xO (x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.35) film, a dielectric film and an electrode are deposited on the front face of a silica substrate from bottom to top in sequence and an ohmic contact electrode is deposited on the back face of the silica substrate, wherein the dielectric is silicon oxide, aluminum oxide or silicon nitride. The silica-based random laser does not need a traditional laser cavity resonator and has simple preparation technique. In addition, equipment used is compatible with the prior mature planar technology of silica devices. Therefore, the silica-based random laser has potential application in respect of phoelectron integration and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bistable electromagnetic micro-mechanical relay
InactiveCN1604260AOvercoming the drawbacks of full planar process structuresEasy to manufactureNon-polarised relaysPermalloyElectromagnetic pulse
It is a bistable electromagnetic micro machinery relay, which combines the separate process of moving electrode system, plane coil, contact electrode system and magnetic core. The moving electrode system comprises moving electrode, wring beam, contact and frame; the plane coil and contact electrode system are made on the silicon underlay; the moving electrode system is fixed through the frame on the silicon underlay of plane coil and contact electrode; the constant magnetic metal sticks tightly to the surface of the permalloy magnetic core. This relay uses electromagnetic metal to change the magnetic direction of the moving electrode and to turn in the stable on or off status.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Electronic circuit device having silicon substrate
InactiveUS20050233518A1Small sizeReduce weightSewerage structuresSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSiliconPlanar process
An electronic circuit device having a silicon substrate is provided comprising: a silicon substrate having a semiconductor element and a recess; and at least one passive element which is formed by a process different from a silicon planar process by which the semiconductor element is formed. In the electronic circuit device, the passive element is entrenched in the recess of the silicon substrate, and the semiconductor element formed on the silicon substrate is electrically connected to the passive element.
Owner:ISHIDA MAKOTO +1
Focal plane array with pixels defined by modulation of surface Fermi energy
ActiveUS9024296B2Minimize the possibilitySimplify the manufacturing processSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesDetector arrayFocal Plane Arrays
Pixels in a focal plane array are defined by controlled variation of the Fermi energy at the surface of the detector array. Varying the chemical composition of the semiconductor at the detector surface produces a corresponding variation in the surface Fermi energy which produces a corresponding variation in the electric field and electrostatic potential in the bulk semiconductor below the surface. This defines pixels by having one Fermi energy at the surface of each pixel and a different Fermi energy at the surface between pixels. Fermi energy modulation can also be controlled by applying an electrostatic potential voltage V1 to the metal pad defining each pixel, and applying a different electrostatic potential voltage V2 to an interconnected metal grid covering the gaps between all the pixel metal pads. Methods obviate the need to etch deep trenches between pixels, resulting in a more manufacturable quasi-planar process without sacrificing performance.
Owner:SUNDARAM MANI +1
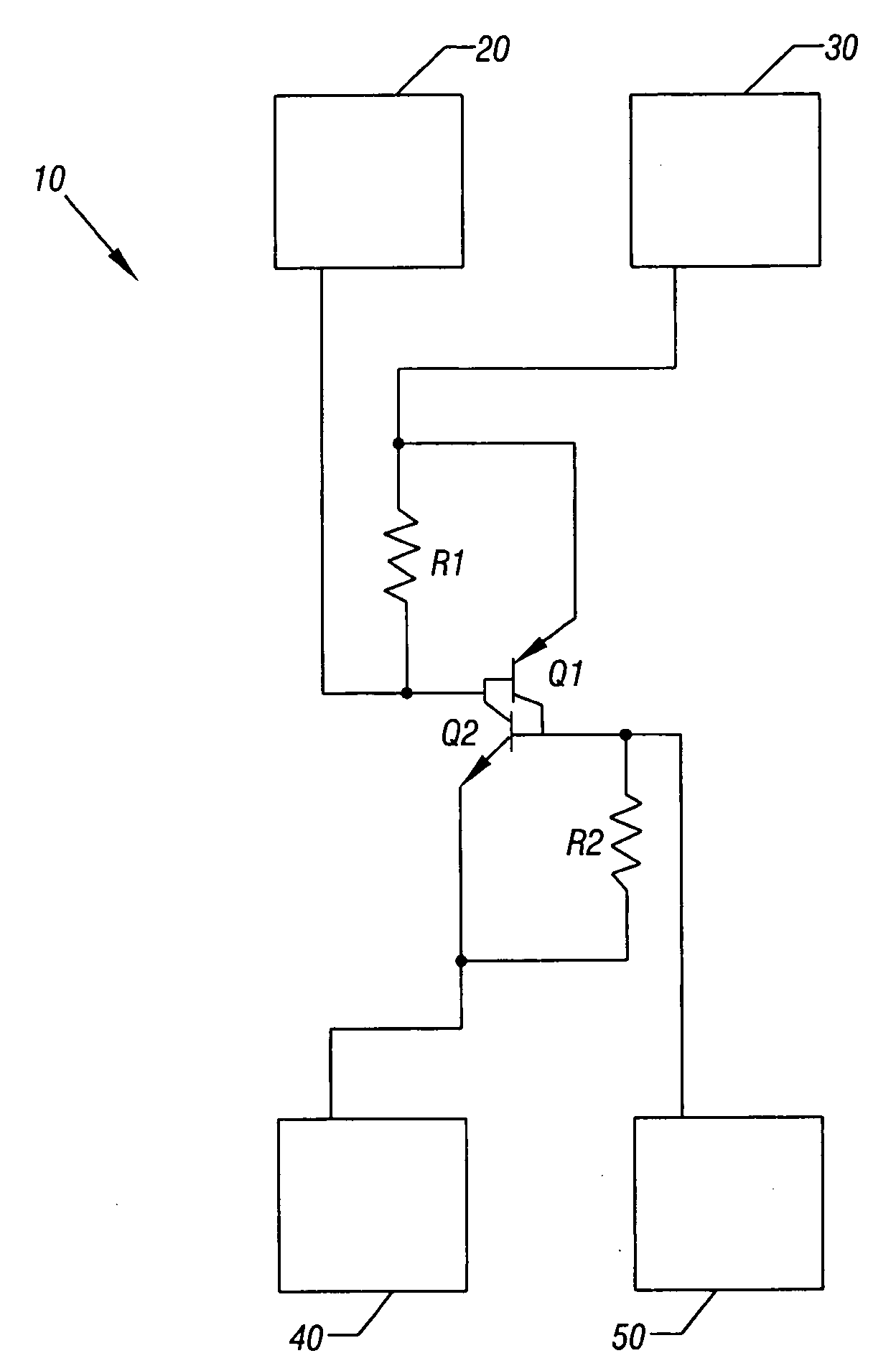
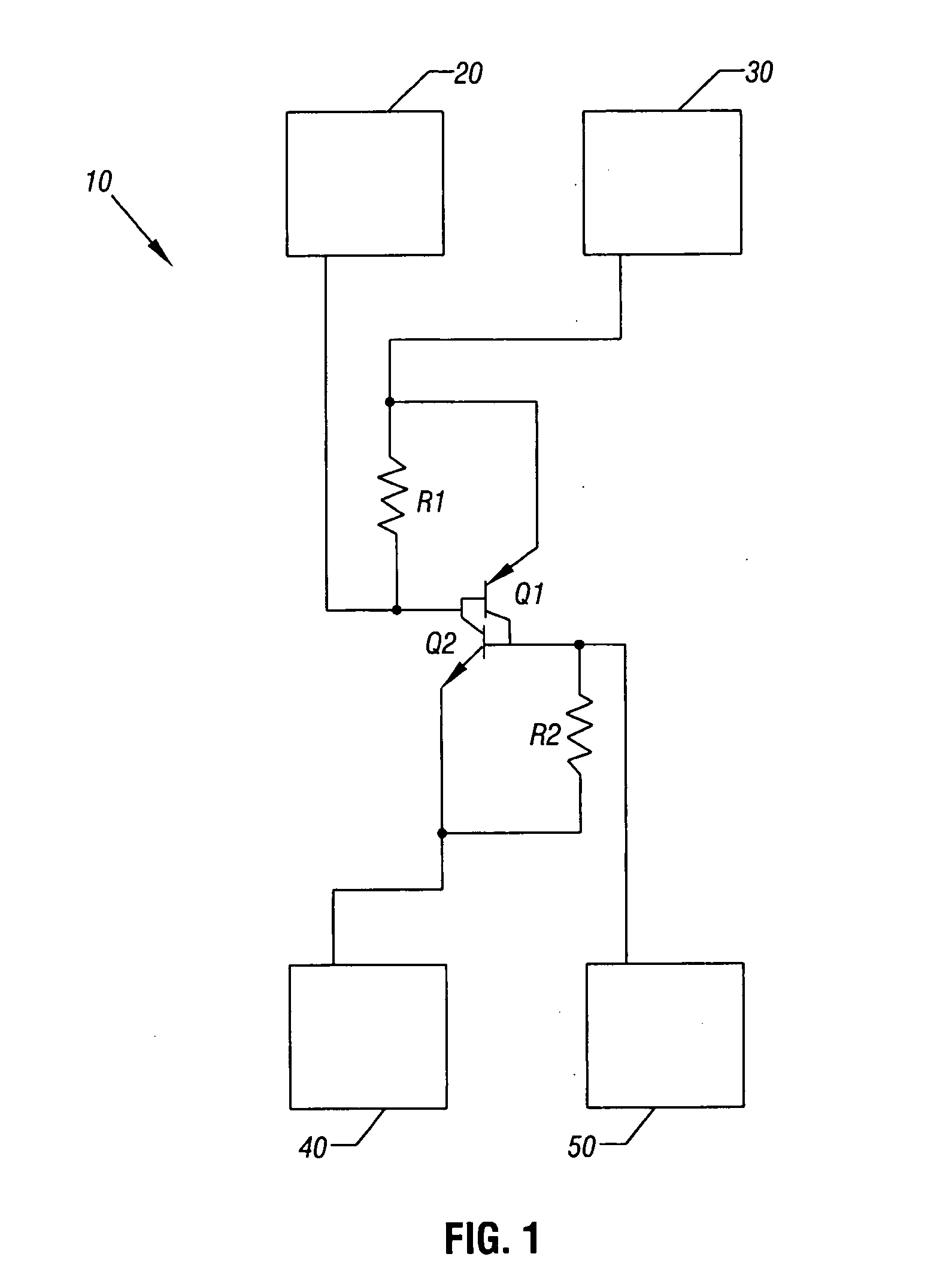
Silicon controlled rectifier protection circuit
In one embodiment, the present invention includes an apparatus having a protection circuit to provide protection from transient surges. The protection circuit may include a silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) that is formed on a substrate via a planar process, along with one or more circuits to be protected by the protection circuit.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com