Construction of gliding board and method of production
a technology of gliding boards and construction methods, applied in the field of gliding boards, can solve the problems that the two layers of inner boards are not effective in alleviating impulses, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, reducing production costs, and improving tenacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
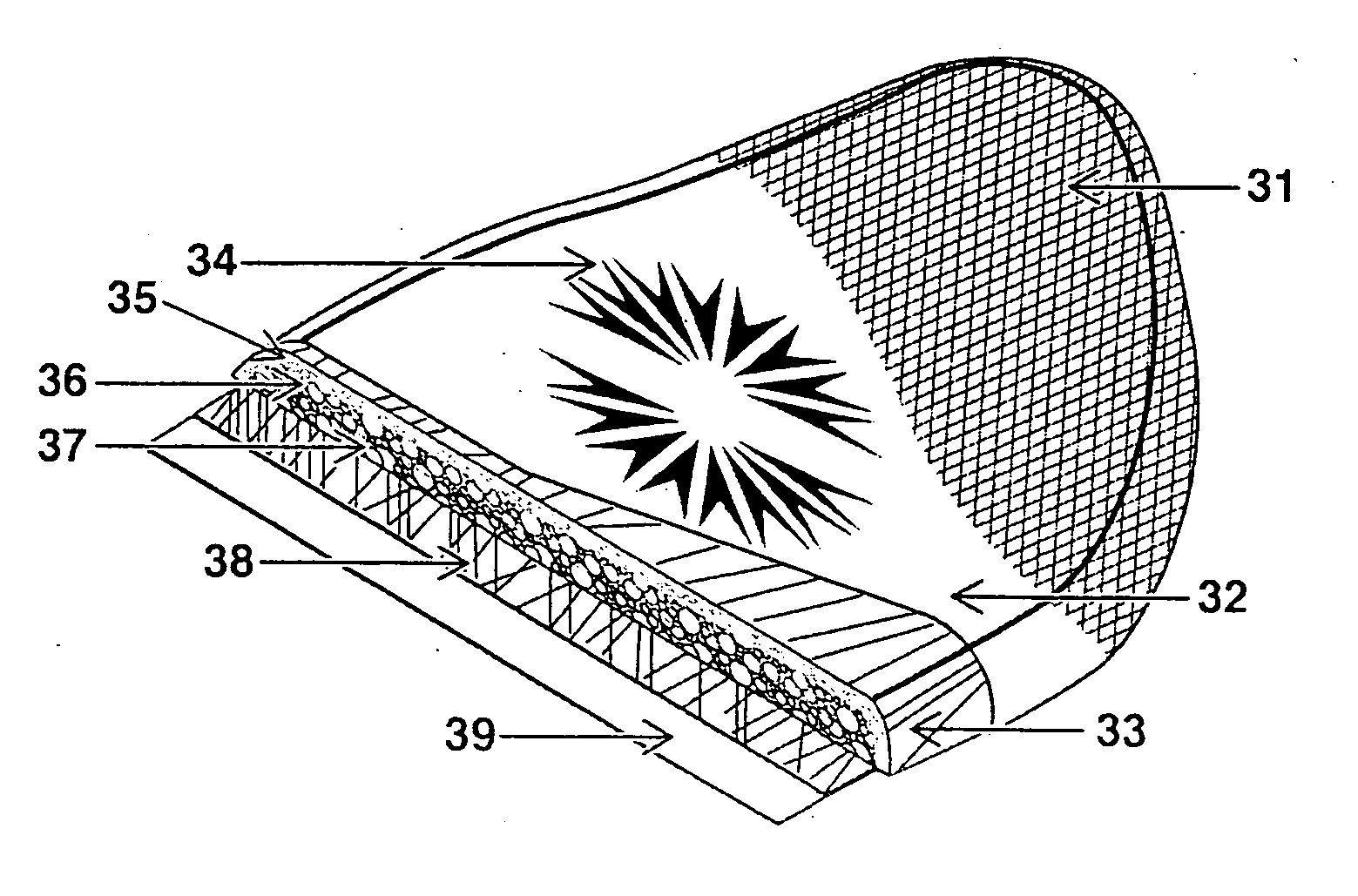
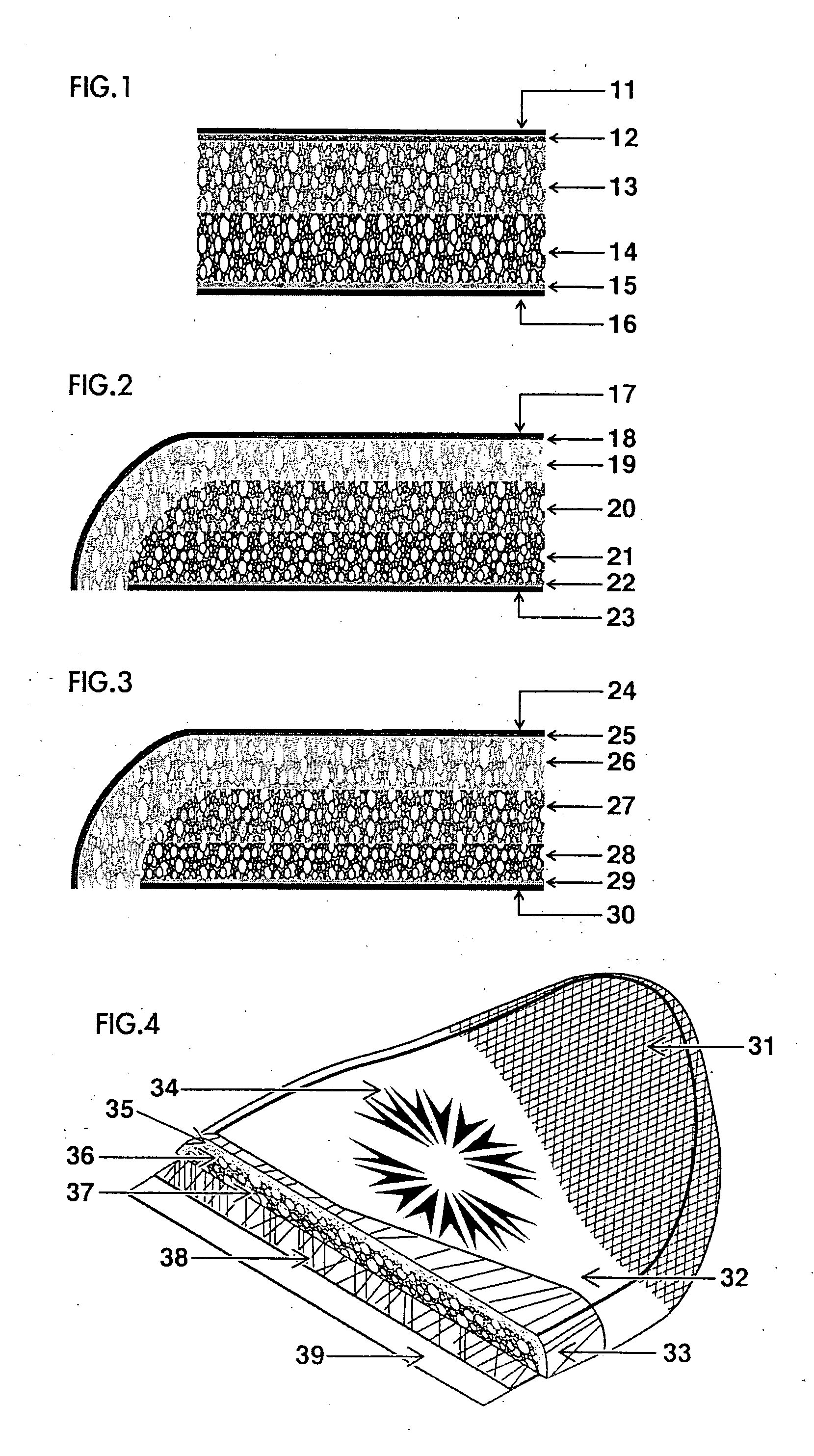
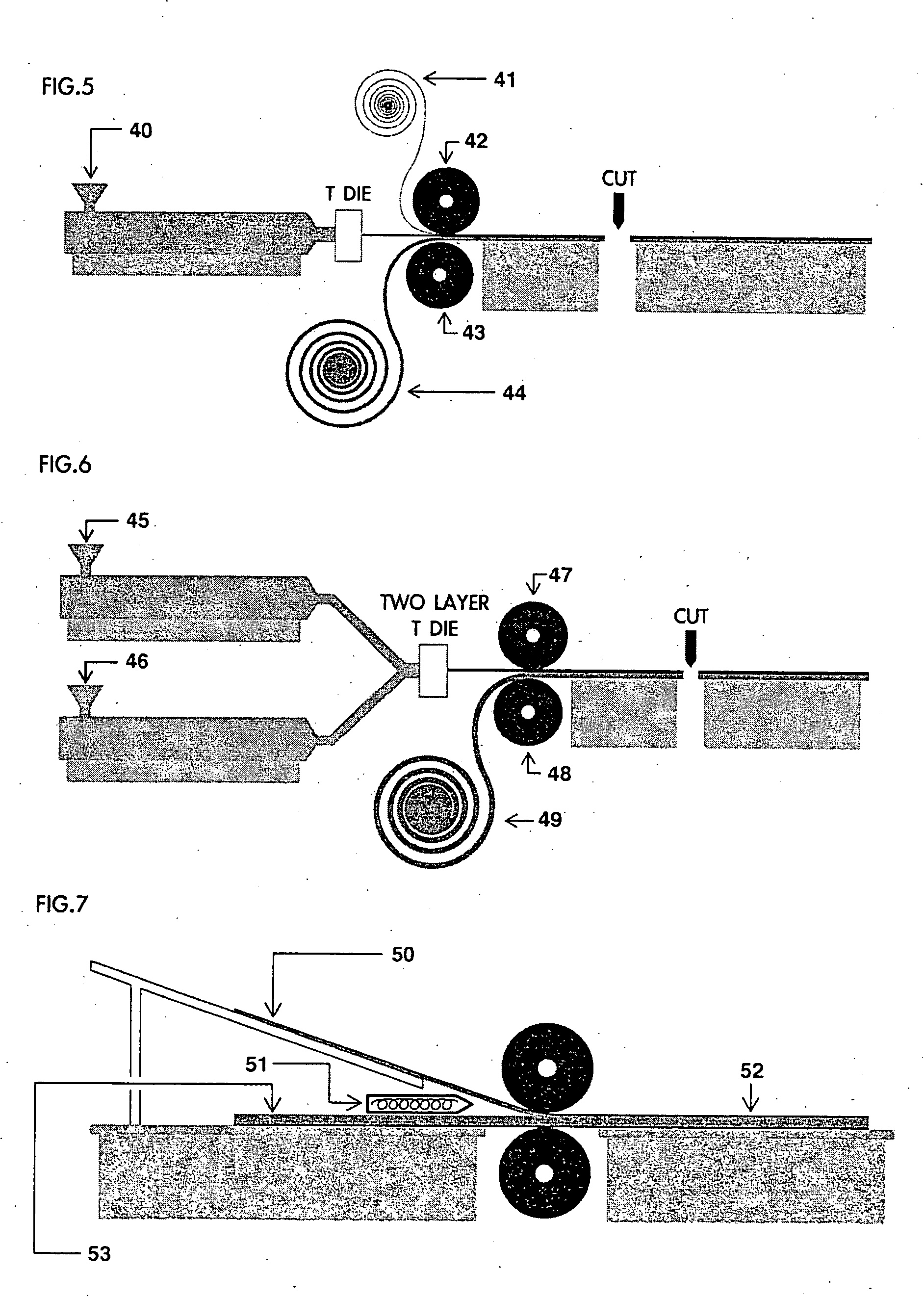
[0017]FIG. 1 shows that a structure of a prior art sports board 13, the inner board core is formed by heat lamination of 13 and 14, a lower density, closed-cell polyethylene foam material, thereon, 12 the outer core of backing foam board sheet, with higher density and closed-cell foam, heat laminated to 13 for further heat lamination of the surfaces to 11, the plastic polymer graphic film 15, a layer of backing foam sheet, by heat lamination to 15 as a media laminate with 16, the plastic polymer protective board
[0018]FIG. 2 shows a cross-sectional view of the structure of the invention in which three layers of polyethylene board core are in same thickness or in same density. Adopting the compound thermoplastic substance 18 for agglutination with 17 the plastic polymer graphic film to 19 first layer board core with high density with closed-cell polyethylene foam material, thereafter, 22 a dual-layer of thermoplastic polymer substance agglutinated with 23 the plastic polymer protecti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com