Methods of treatment of type 2 diabetes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Methods
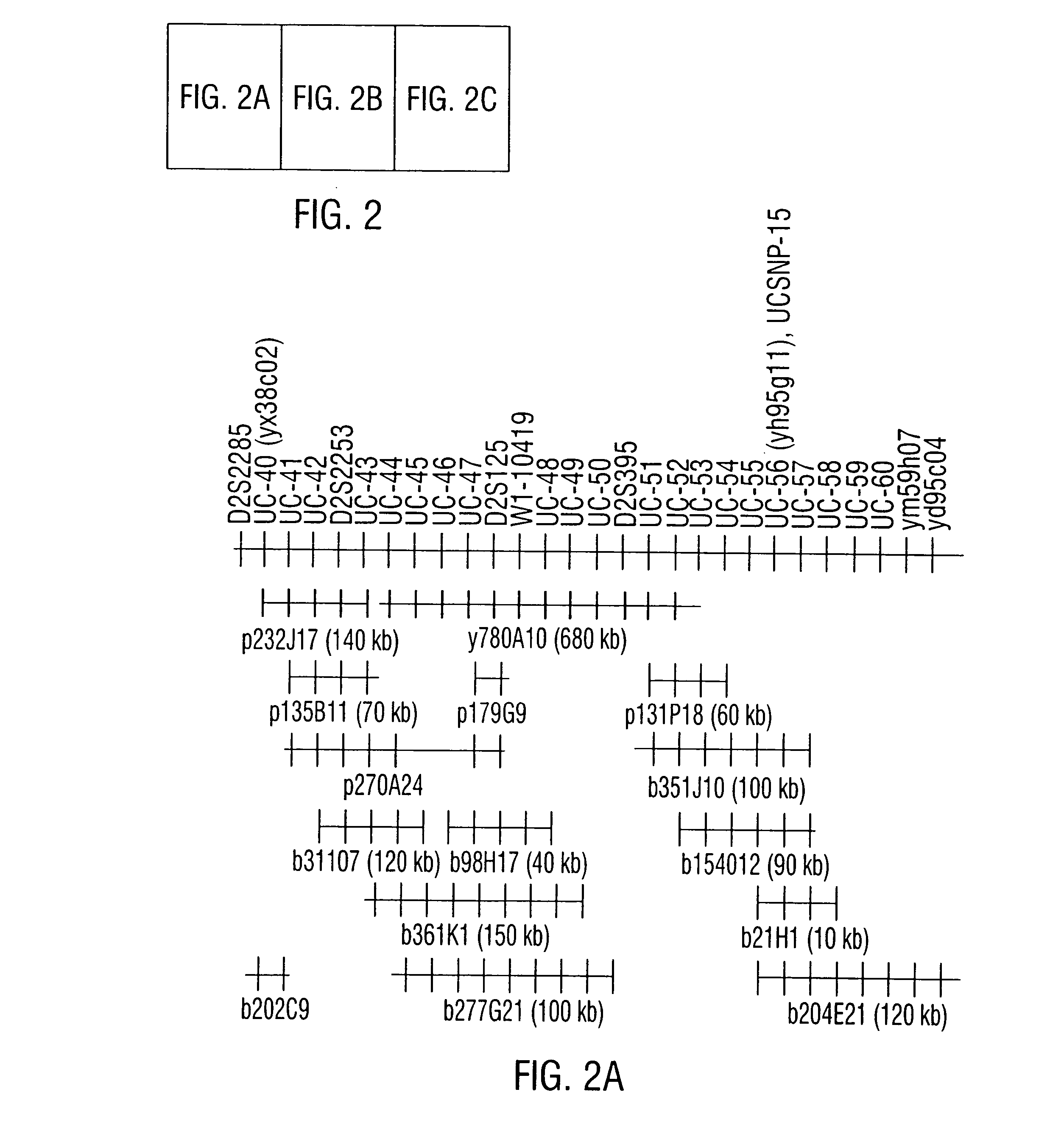
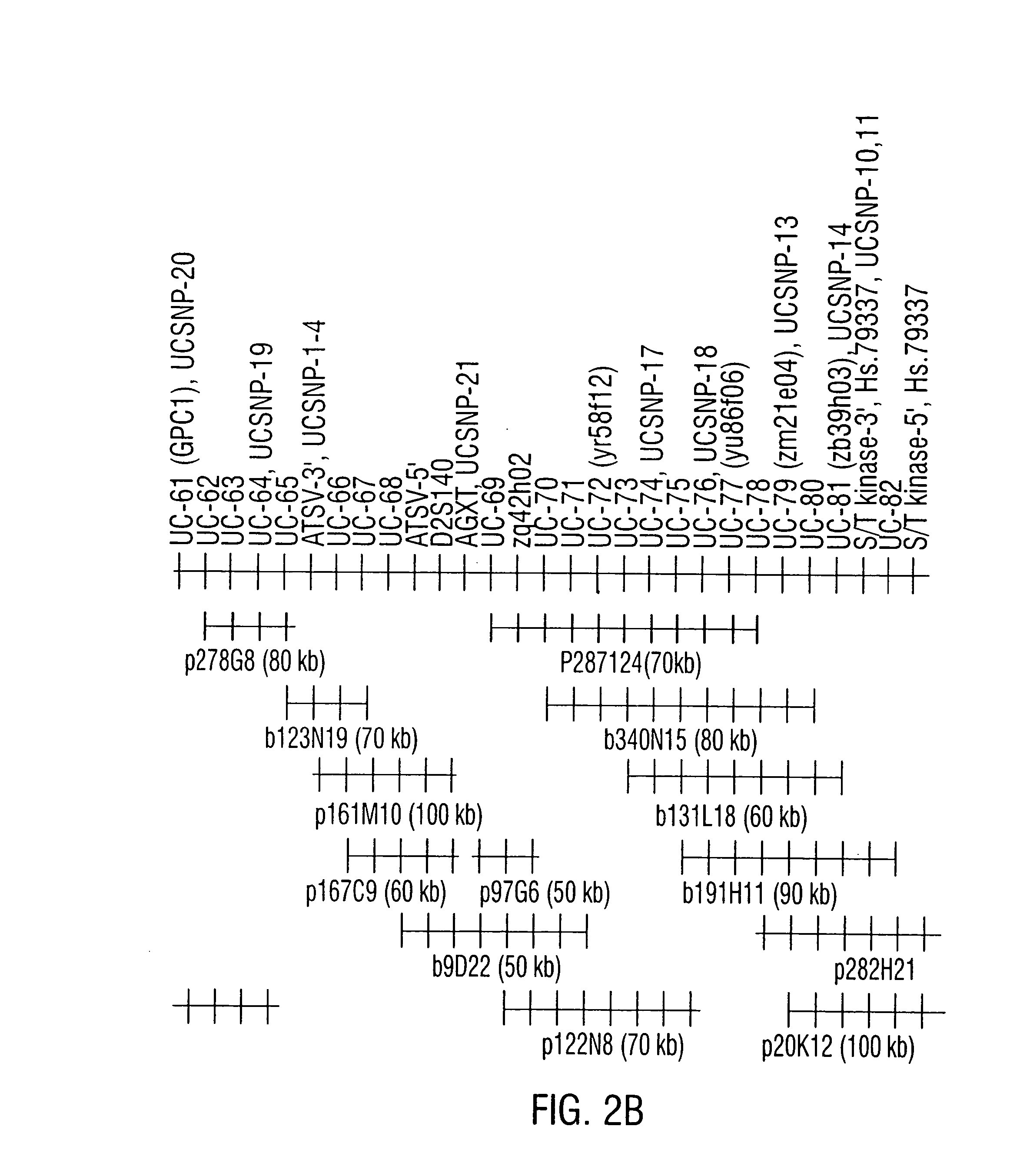
Generation of a Physical Map and Sequence of the NIDDM1 Region
[0433] YAC clones containing sequences of interest were identified by screening the CEPH ‘A’ and ‘B’ Human YAC DNA pools (Research Genetics, Huntsville, Ala.) using PCR™ and standard methods. PAC (PAC-6539; Genome Systems, St. Louis, Mo.) and BAC clones (CITB Human BAC DNA Pools—Release IV, Research Genetics) were identified in a similar manner.
[0434] DNA was prepared from each clone and tested directly for the presence of each STS. STSs were selected from the Généthon human genetic linkage map and the human transcript map in the interval around D2S125-D2S140 (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Additional STSs were generated by sequencing ends of clones and by sequencing random PstI fragments from the PACs and BACs after cloning in pGEM-4Z. The sequences of these clones were compared to those in the nonredundant GenBank database to identify unmapped ESTs from this region.
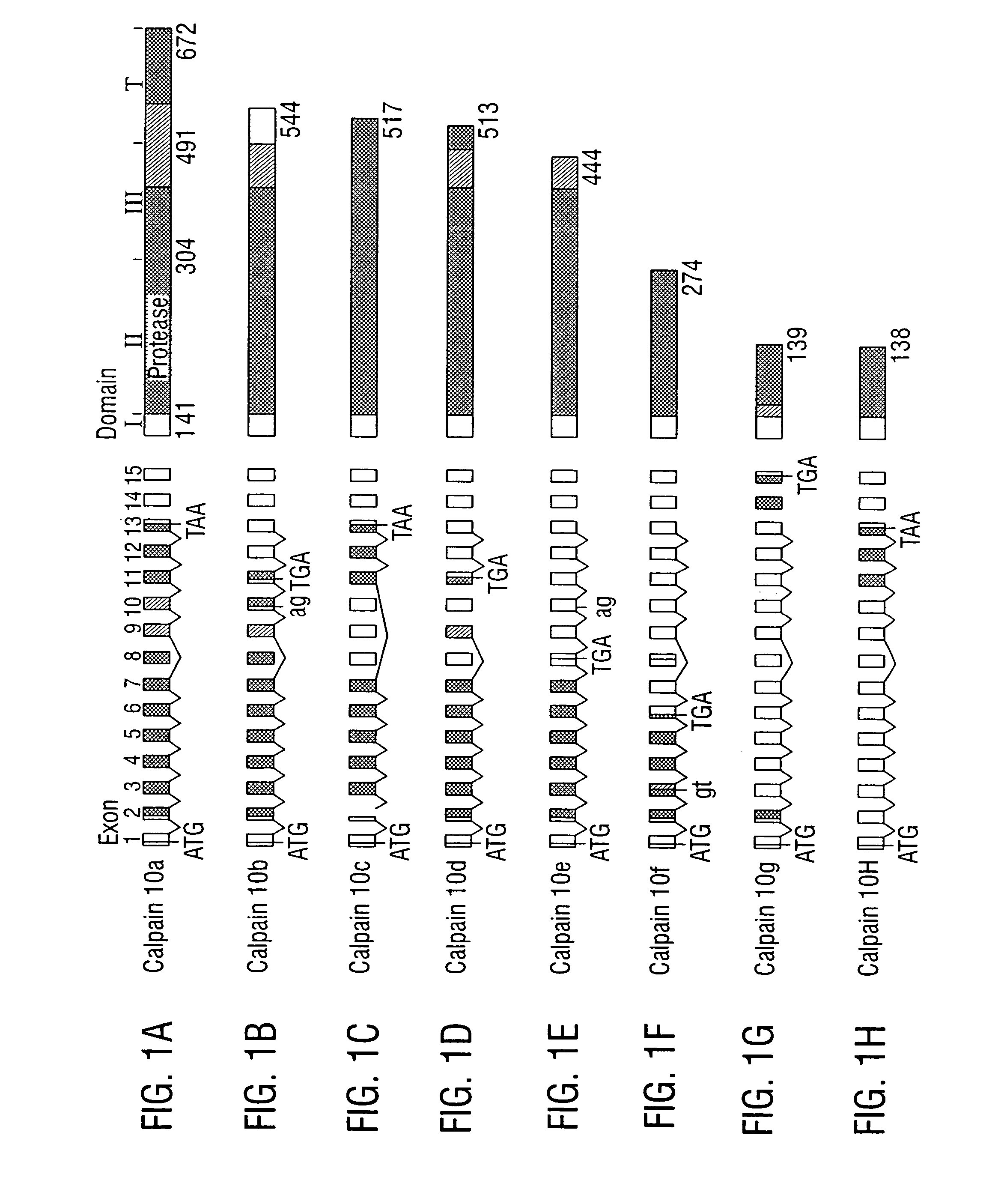
[0435] The sequence of a 50 kb region includ...
example 2
Physical Mapping of NIDDM1
[0448] Initial linkage studies localized NIDDM1 to the distal long arm of chromosome 2 near D2S125. Further genotyping and refinement of the genetic map placed NIDDM1 near D25140 at 263.56 cM in the genetic map (Broman et al., 1998) with a 1-lod confidence interval from 257-269 cM, a 12 cM interval which included D25125 (260.63 cM). Although the 1-lod confidence interval for NIDDM1 was quite large and thus made the identification of NIDDM1 a rather formidable task, subsequent genetic studies identified a region on chromosome 15 near CYP19 which interacts with NIDDM1 to affect susceptibility to type 2 diabetes.
[0449] Taking the evidence for linkage at chromosome 15 into account in linkage analyses on the NIDDM1 region of chromosome 2 increased the lod score from 4.0 to 7.3 and decreased the 1-lod confidence interval from 12 to 7 cM (i.e. from 259-266 cM). The inventors focused the inventors' search for NIDDM1 in the 7 cM interval from 259-266 cM, knowing t...
example 3
Identification of NIDDM1
[0453] Allele and haplotype frequencies were compared among controls (n=112), patients (patients all, n=110), the subgroup of patients from families most likely to have susceptibility at NIDDM1 (patients NIDDM1, n=37) and subsequently with a smaller subgroup from families most likely to have susceptibility at NIDDM1 and the interacting locus near CYP19 on chromosome 15 (patients NIDDM1 / CYP19, n=20), once this interaction became evident. The expectation was that the degree of association would increase as the inventors examined those patients with type 2 diabetes due to variation at NIDDM1 or to the interaction between NIDDM1 and the unknown diabetes susceptibility locus on chromosome 15. The inventors began the search for NIDDM1 by first typing SNPs that the inventors had identified in known genes and ESTs and comparing the frequencies of alleles and estimated haplotypes formed between adjacent markers (most haplotypes were between two adjacent markers altho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com