Determination of AM-binding proteins and the association of adrenomedullin (AM) therewith
a technology of adrenomedullin and am, which is applied in the field of detection of adrenomedullin (am)binding proteins, can solve the problems of reducing the levels of insulin in the bloodstream, and achieve the effects of inhibiting am/fh activity, affecting am/fh activity, and affecting am/fh activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0123] Non-radioactive labeling of AM was accomplished by conjugating synthetic AM comprising amino acids 1-52 (Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Mountainview, Calif.) with succinimidyl esters linked to biotin (Pierce Chemical Co., Rockford, Ill.), fluorescein (Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, Oreg.), or dinitrophenol (DNP; Molecular Probes, Inc.). Briefly, 100 μg of AM (16 μM) was dissolved in 1 ml of 50 mM sodium bicarbonate, pH 8.5, and the succinimidyl ester was added to yield a final molar concentration of 10:1 (linker:AM). The mixture was incubated with slow agitation for 1 hr at room temperature and the reaction was terminated by the addition of 0.1 M ethanolamine followed by another incubation for 1 hr. Unincorporated ligand was removed by extracting the AM using reverse phase Sep-Pak C-18 cartridges (Waters, Milford, Mass.) and eluting the sample with acidic-isopropanol. The extract was lyophilized and reconstituted in 1 ml of TBS (0.05 M Tris-HCl, 0.15 M NaCl), 0.1% alkali-tre...
example 2
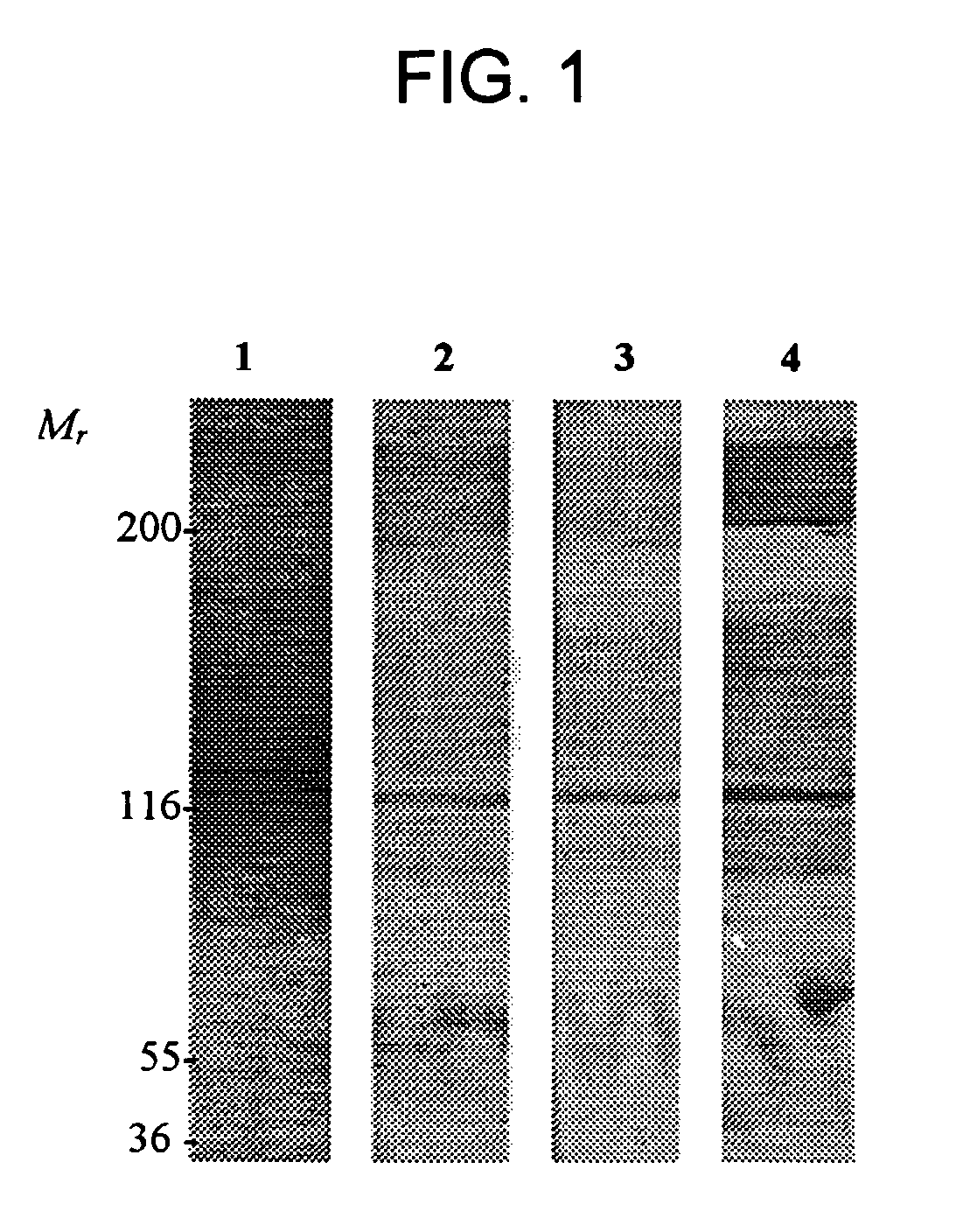
[0124] AM-binding proteins were identified using an in vitro screening method. Total proteins derived from human plasma (2 μl) were electrophoretically fractionated on 3-8% Tris-acetate gel (Novex, San Diego, Calif.) under non-reducing conditions. For the ligand blotting experiment, the proteins were transferred to a 0.2 mm nitrocellulose membrane that was incubated for 15 min with 1% Nonidet P-40 (NP-40). Non-specific binding was further blocked with a 2 hr incubation in TBS containing 0.1% ATC. Incubations with 70 nM AM labeled with biotin, fluorescein, or DNP were carried out overnight at 4° C. in blocking buffer containing 0.1% Tween 20. For biotin detection, the ligand blot was incubated with an avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex and the AEC reagent (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, Calif.). For fluorescein and DNP, the ligand blots were incubated 1 hr at room temperature with rabbit anti-fluorescein or anti-DNP IgG, respectively, (1:1000 in incubation buffer; Molecular Pro...
example 3
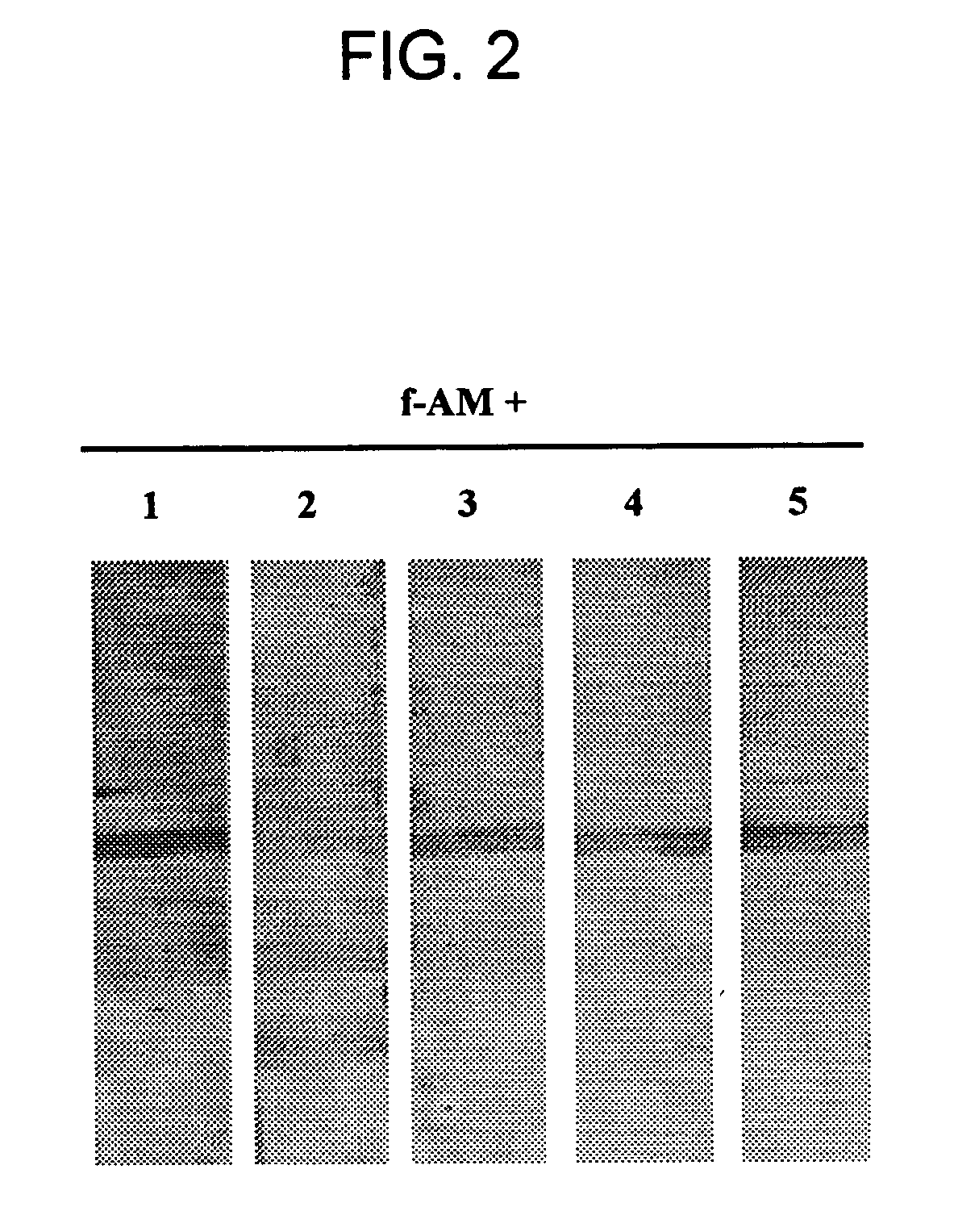
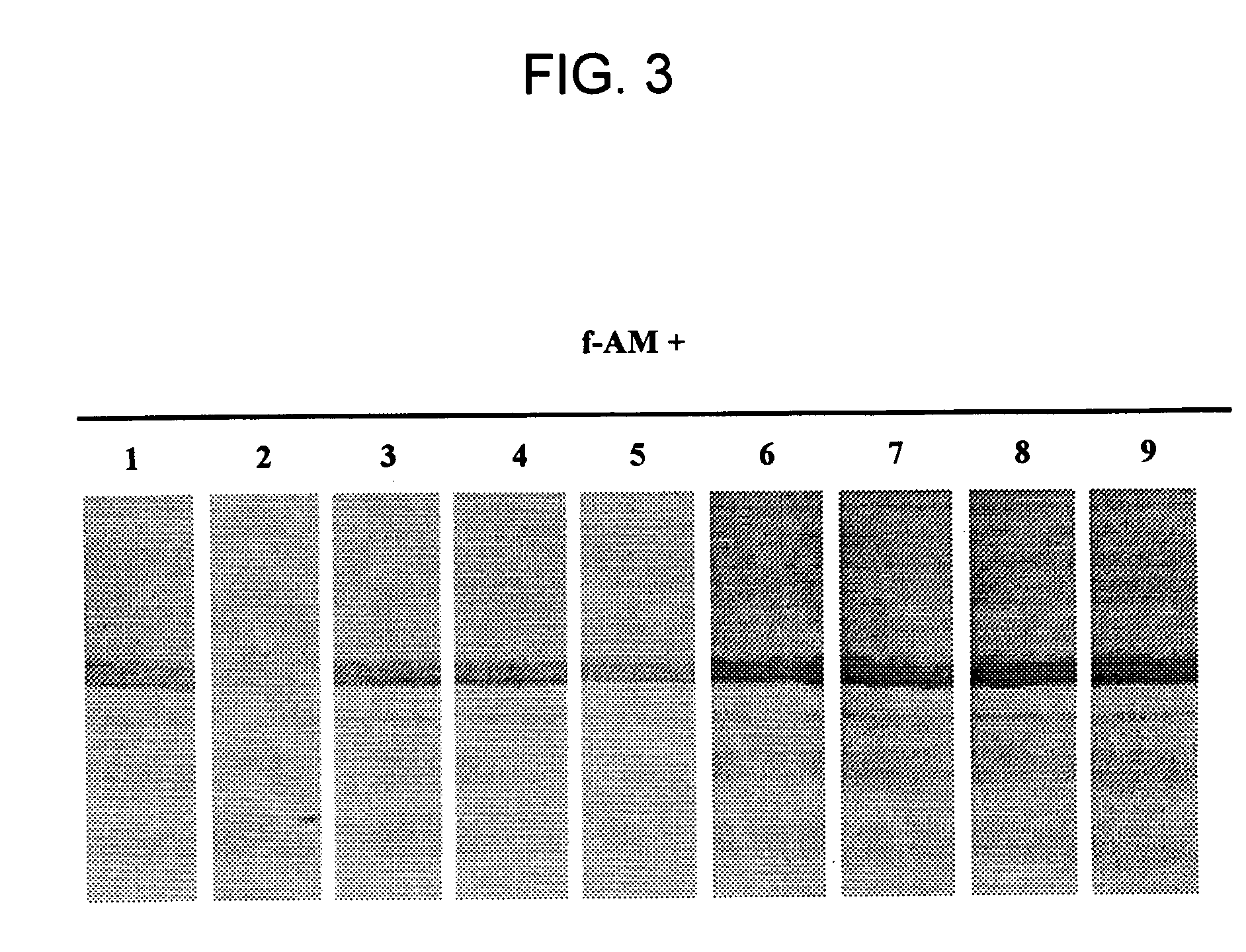
[0125] Competition of full-length AM binding to AM-binding proteins was tested by pre-incubating a membrane having plasma derived proteins bound thereto with 7 μM of unlabeled peptides; e.g., CGRP, amylin, insulin, IGF-1, PAMP, or AM truncated polypeptides (AM1-12, AM16-21, AM22-52, AM13-52, AM34-52) for 6 hr at 4° C. Following this preincubation, labeled full-length AM was introduced and incubated overnight at 4° C. Competition studies indicated that only full-length AM was able to dissociate the AM / AMBP-1 (AM / fH) complex. FIGS. 2 and 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com