Asthma associated factors as targets for treating atopic allergies including asthma and related disorders
a technology of asthma and associated factors, applied in the field of methods for treating atopic allergies and related disorders, can solve the problems of allergic inflammation, huge burden on our health-care resources, and damage to surrounding tissues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
RNA Isolations, RT-PCR, Cloning and Sequencing of RT-PCR Products
[0065] Total cellular RNA was extracted after 24 hours from cultured PBMC, murine spleen cells and M07e cells using RNA PCR corekit (Perkin-Elmer, Foster City Calif.) according to manufacturer's instructions. One microgram of RNA from each source was denatured for five minutes at 65° C. and then reverse transcribed into cDNA using a 20 μl reaction mixture containing 50 units of MLV Reverse Transcriptase, one unit per μl RNAse inhibitor, 2.5 mM oligo d(T)16 primer, 1 mM each dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP, 50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0, 25 mM MgCl2. The reaction mixture was pipetted into thermocycler tubes, placed in a PCR thermal cycler and subjected to one cycle (fifteen minutes at 42° C., five minutes at 99° C. and five minutes at 4° C.). A mock reverse transcription reaction was used as a negative control.
[0066] This mixture was then added to a second tube containing 2 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0, 65.5...
example 2
IL-9 Biological Assay in M07e Cells
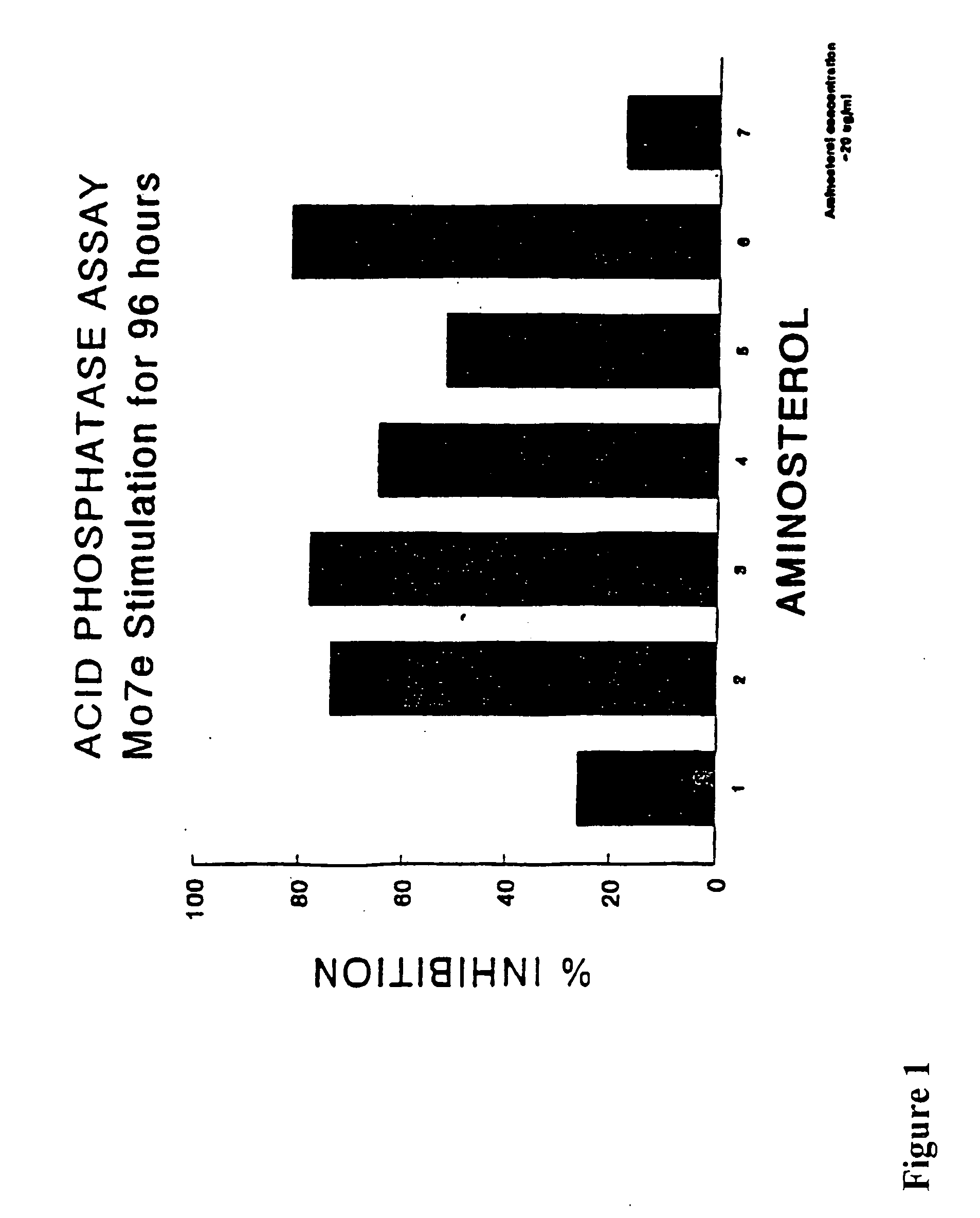
[0068] The M07e line is a human megakaryoblastic cell line, cultured in RPMI-1640, 20% fetal bovine serum and 10 ng / ml IL-3 (R&D Systems). The cell line responds to cytokines including IL-9. The cells were fed and split at 2×105 cells per milliliter every 72 hours.
[0069] The cells were centrifuged for ten minutes at 2000 rpm and resuspended in RPMI-1640 with 0.5% bovine serum albumin and insulin-transferrin-selenium (ITS) cofactors (Gibco-BRL). Cells were counted using a hemocytometer and diluted to a concentration of 1×105 cells / ml and plated in a 96-well microtiter plate. Each well contained 2×104 cells per well. The cells were stimulated with 50 ng / ml Stem Cell Factor (SCF) alone, 50 ng / ml SCF plus 50 ng / ml IL-3 (R&D Systems) or 50 ng / ml SCF plus 50 ng / ml IL-9. A control was included which contained cells and basal media only. Serial dilutions of test compounds were added to each test condition in triplicate. Cultures were incubated for 72-96 ...
example 3
Identification of Immunomodulatory 3-Aminosteroids in vitro
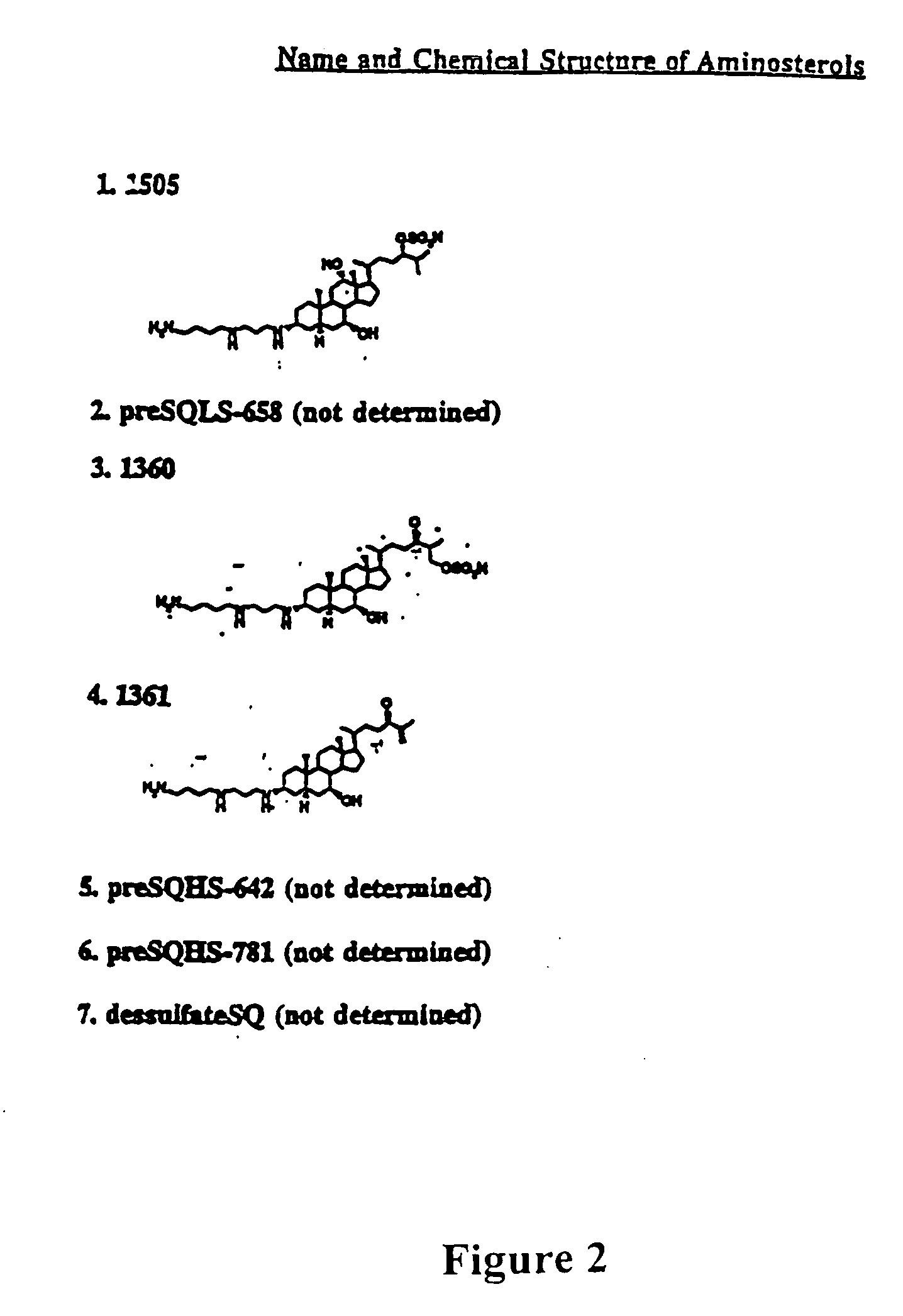
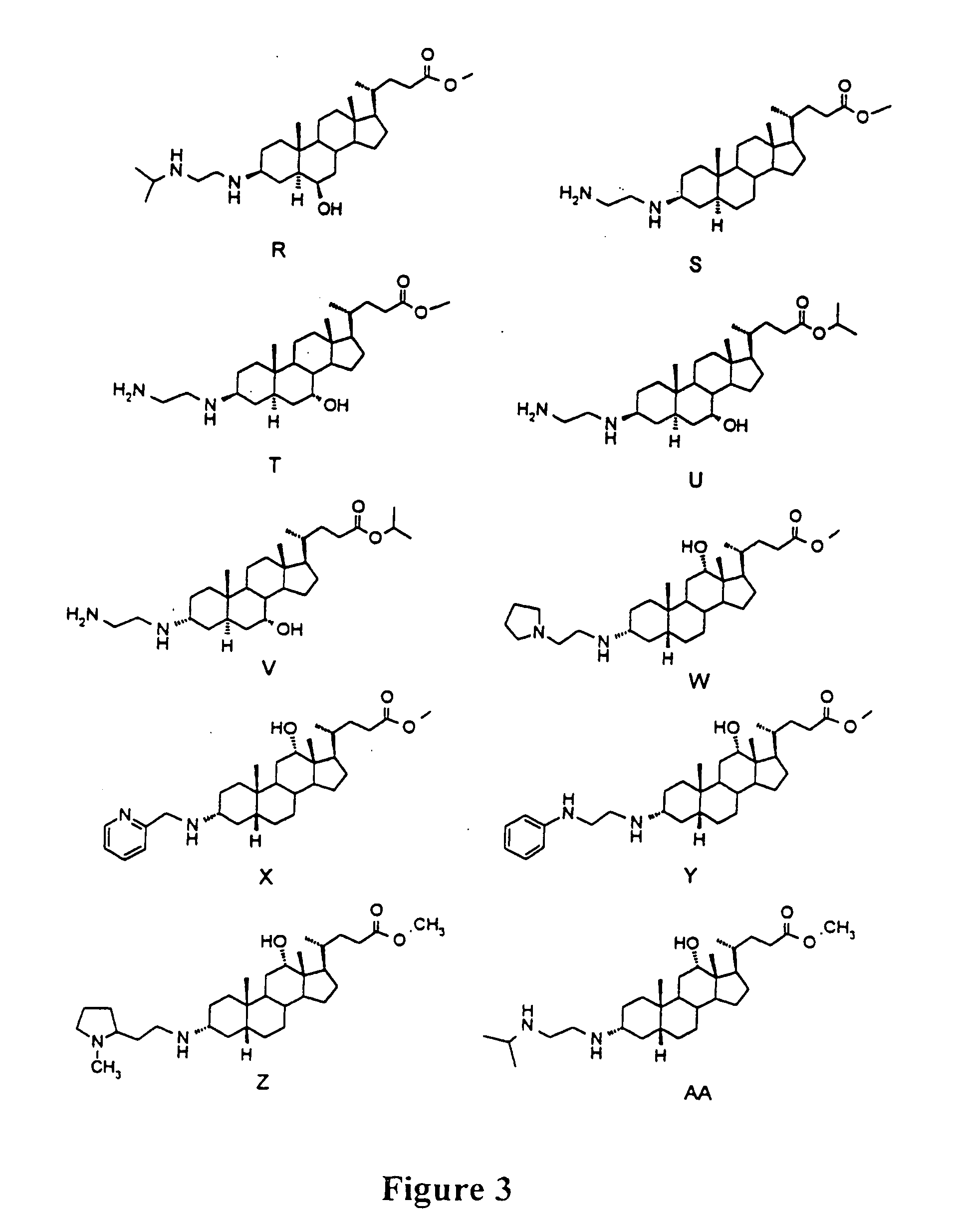
[0072] Immunomodulatory 3-aminosteroids (FIGS. 3-7 and Table I) were identified in vitro based on their ability to inhibit homo- or hetero-typic aggregation and subsequent proliferation of mitogen or antigen stimulated murine or human lymphocytes. Human or mouse lymphocytes were isolated from peripheral blood by Ficoll-Hypaque as described (Stoeckert et al., (1990) Exp. Hematol. 18, 1164-1170). For mitogen stimulation, 1×105 cells per well were plated in varying amounts of 3-aminosteroid compounds and assayed for aggregation and proliferation after twelve hours of stimulation by PHA-PMA mitogens. Wells were microscopically counted for aggregates of greater than 100 cells to assess aggregation and proliferation was determined using tritiated thymidine incorporation and analysis on a Packard Top Count as suggested by the manufacture. For antigen stimulation, lymphocytes were isolated from BALBc mice which had been sensitized ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com