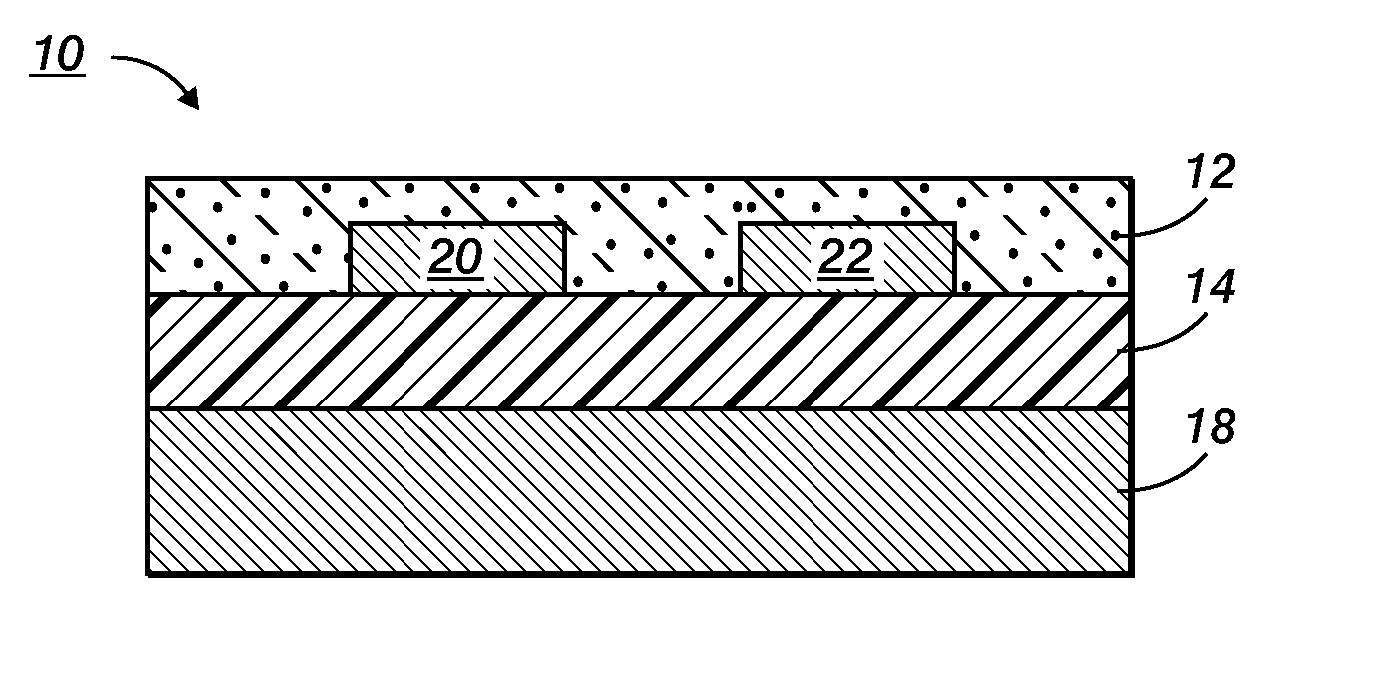
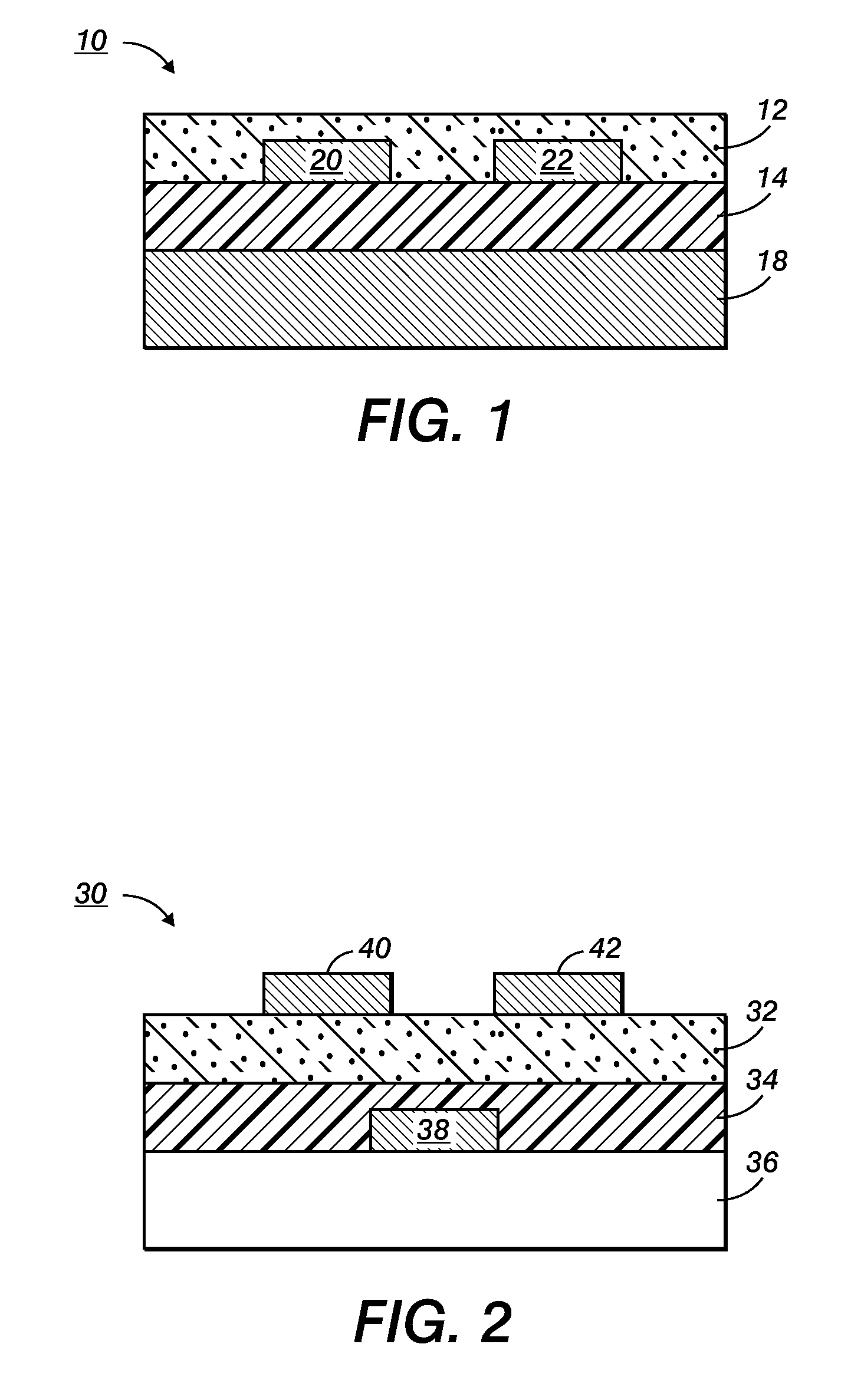
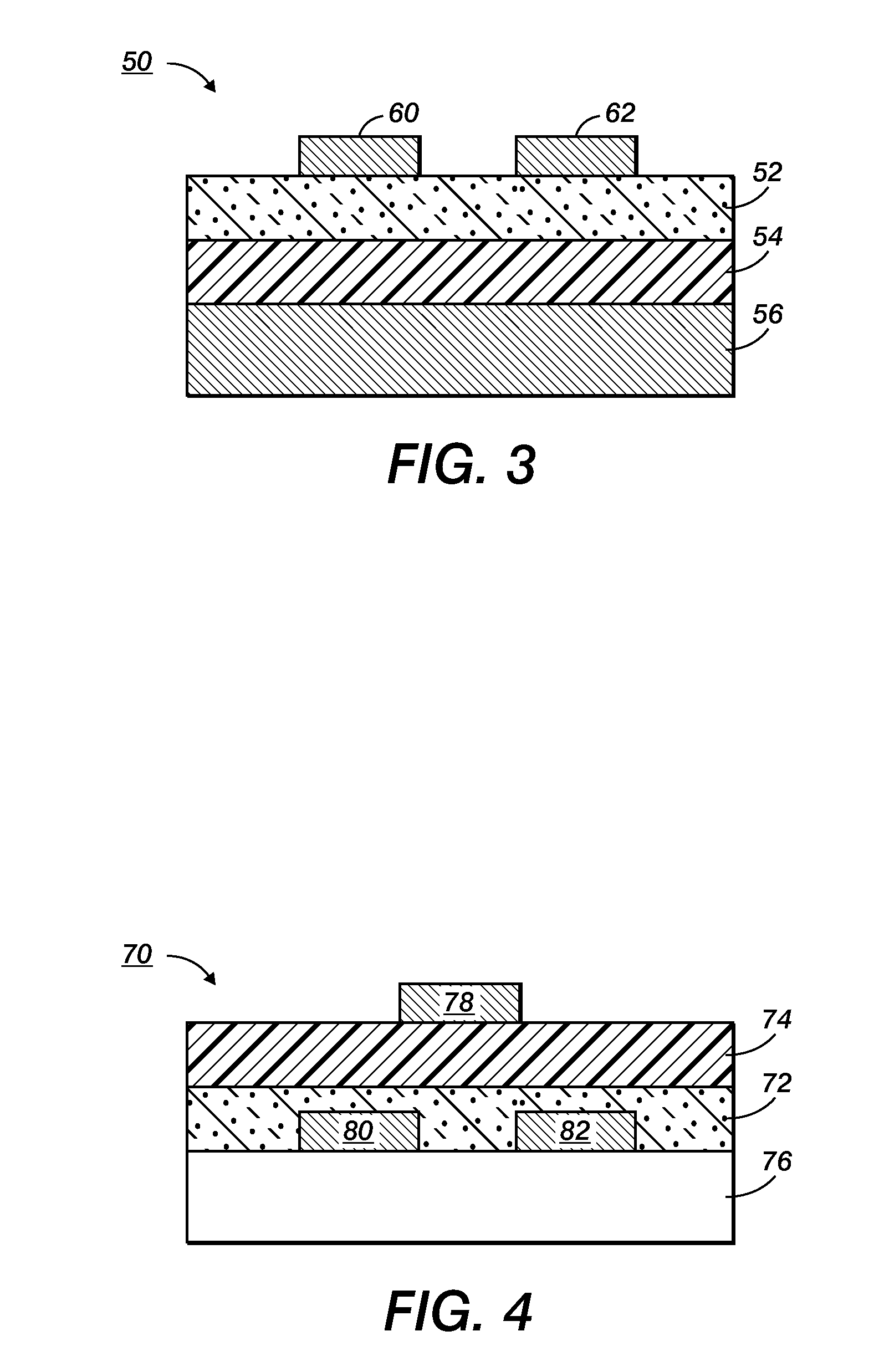
Devices containing annealed stabilized silver nanoparticles
a technology of stabilized silver nanoparticles and devices, which is applied in the direction of solid-state devices, non-conductive materials with dispersed conductive materials, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of pixel pads, conductive traces, lines and tracks which meet the conductivity, processing, and cost requirements for practical applications, and achieve the effect of meeting conductivity, cost and cost requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0099] Silver acetate (0.167 g, 1 mmol) and 1-dodecylamine (3.71 g, 20 mmol) were first dissolved in toluene (100 mL) by heating at 60° C. until silver acetate was dissolved. To this solution was added a solution of phenylhydrazine (0.43 g, 4 mmol) in toluene (50 mL) with vigorous stirring over a period of 10 min. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred at 60° C. for 1 hr before cooling down to room temperature. Subsequently, acetone (10 mL) was added to the reaction mixture to destroy excess phenylhydrazine. Solvent removal from the reaction mixture gave a residue which was added to stirring methanol (100 mL) to precipitate the crude silver nanoparticle products. The crude silver nanoparticle product was isolated by centrifugation, washed with acetone twice, and air-dried. It was then dispersed in cyclohexane (2 mL) to form a dispersion of silver nanoparticles in cyclohexane (with molecules of the 1-dodecylamine stabilizer on the surface of the silver nanoparticles). This disper...
example 2
[0101] Silver acetate (0.167 g, 1 mmol) and 1-hexadecylamine (4.83 g, 20 mmol) were first dissolved in toluene (100 mL) by heating at 60° C. until silver acetate was dissolved. To this solution was added a solution of phenylhydrazine (0.43 g, 4 mmol) in toluene (50 mL) with vigorous stirring over a period of 10 min. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred at 60° C. for 1 hr before cooling down to room temperature. Subsequently, acetone (10 mL) was added to the reaction mixture to destroy excess phenylhydrazine. Solvent removal from the reaction mixture gave a residue which was added to stirring methanol (100 mL) to precipitate the crude silver nanoparticle product. The crude silver nanoparticle product was isolated by centrifugation, washed with acetone twice, and air-dried. It was the dispersed in cyclohexane (2 mL) to form a dispersion of silver nanoparticles in cyclohexane (with molecules of the 1-hexadecylamine stabilizer on the surface of the silver nanoparticles). This disp...
example 3
[0103] Silver acetate (0.167 g, 1 mmol) and 1-dodecylamine (3.71 g, 20 mmol) were first dissolved in toluene (100 mL) by heating at 60° C. until silver acetate was dissolved. To this solution was added a solution of benzoic hydrazide (benzoylhydrazine) (0.54 g, 4 mmol) in toluene (50 mL) with vigorous stirring over a period of 10 min. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred at 60° C. for 1 hr before cooling down to room temperature. Subsequently, acetone (10 mL) was added to the reaction mixture to destroy excess benzoic hydrazide. Solvent removal from the reaction mixture gave a residue which was added to methanol (100 mL) with stirring to precipitate crude silver nanoparticle product. The crude silver nanoparticle product was isolated by centrifugation, washed with acetone twice, and air-dried. It was dispersed in cyclohexane (2 mL) to form a dispersion of silver nanoparticles in cyclohexane (with molecules of the 1-dodecylamine stabilizer on the surface of the silver nanoparti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com