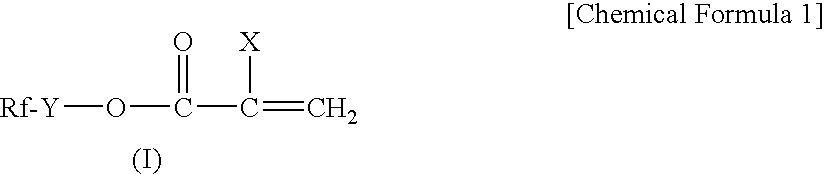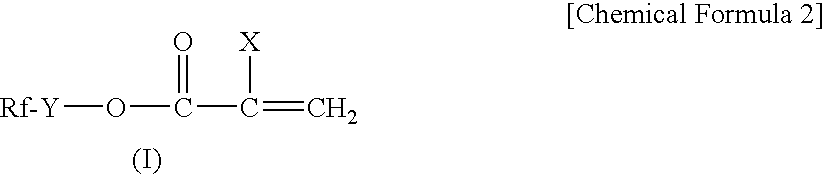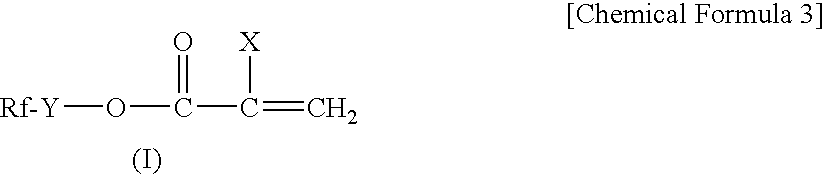Polymer for masonry treatment and treating agent
a technology of masonry treatment and polymer, which is applied in the direction of other chemical processes, coatings, chemistry apparatuses and processes, etc., can solve the problems of not having both and not having sufficient soil resistance for masonry treatment agents, etc., to achieve excellent water repellency and oil repellency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0108] Into a 200 cc four-necked flask equipped with a stirrer, an inert gas inlet, a condenser and a thermometer, 12.0 g of CF3CF2(CF2CF2)3CH2CH2OCOCCH═CH2, 1.0 g of stearyl acrylate, 7.0 g of acrylic acid and 30.0 g of tetrahydrofuran were charged and heated to 60° C. 0.2 g of azobisvaleronitrile was added and the polymerization reaction was conducted with stirring at 60° C. for at least 12 hours. A gas chromatography revealed that a polymerization reaction conversion was at least 97%. An aqueous solution containing 1.7 g of ammonia was added to the resultant polymer solution. Tetrahydrofuran was distilled off under reduced pressure. The mixture was diluted with water to give a treatment liquid having a solid content of 3%.
[0109] A surface of each of polished natural granite (mined in China, and purchased from Nittai Kogyo Kabushiki-Kaisha) and limestone (purchased from Inax Corp.) was coated with the treatment liquid (1 mL of the treatment liquid was applied to an area of 5 cm x...
example 2
[0118] Into the same apparatus as in Example 1, 12.0 g of CF3CF2(CF2CF2)3CH2CH2OCOCCH═CH2, 4.0 g of stearyl acrylate, 4.0 g of acrylic acid and 30.0 g of isopropyl alcohol were charged and heated to 60° C. 0.2 g of azobisvaleronitrile was added and the polymerization reaction was conducted with stirring at 60° C. for at least 12 hours. A gas chromatography revealed that a polymerization reaction conversion was at least 97%.
[0119] An aqueous solution containing 1.0 g of ammonia was added to the resultant polymer solution. Isopropyl alcohol was distilled off under reduced pressure. The mixture was diluted with water to give a treatment liquid having a solid content of 3%. The treatment and the soil resistance test were conducted in the same manner as in Example 1. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
example 3
[0120] Into the same apparatus as in Example 1, 10.0 g of CF3CF2(CF2CF2)3CH2CH2OCOCCH═CH2, 2.0 g of CF3CF2(CF2CF4CH2CH2—OCOCCH═CH2, 3.0 g of stearyl acrylate, 5.0 g of acrylic acid and 30.0 g of acetone were charged and heated to 60° C. 0.2 g of azobisvaleronitrile was added and the polymerization reaction was conducted with stirring at 60° C. for at least 12 hours. A gas chromatography revealed that a polymerization reaction conversion was at least 97%.
[0121] An aqueous solution containing 1.2 g of ammonia was added to the resultant polymer solution. Acetone was distilled off under reduced pressure. The mixture was diluted with water to give a treatment liquid having a solid content of 3%. The treatment and the soil resistance test were conducted in the same manner as in Example 1. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com