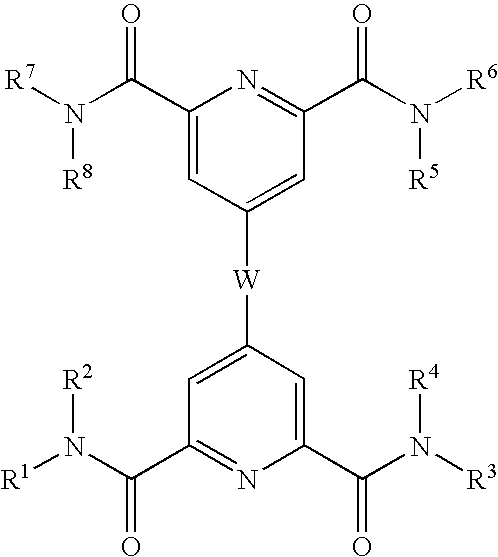
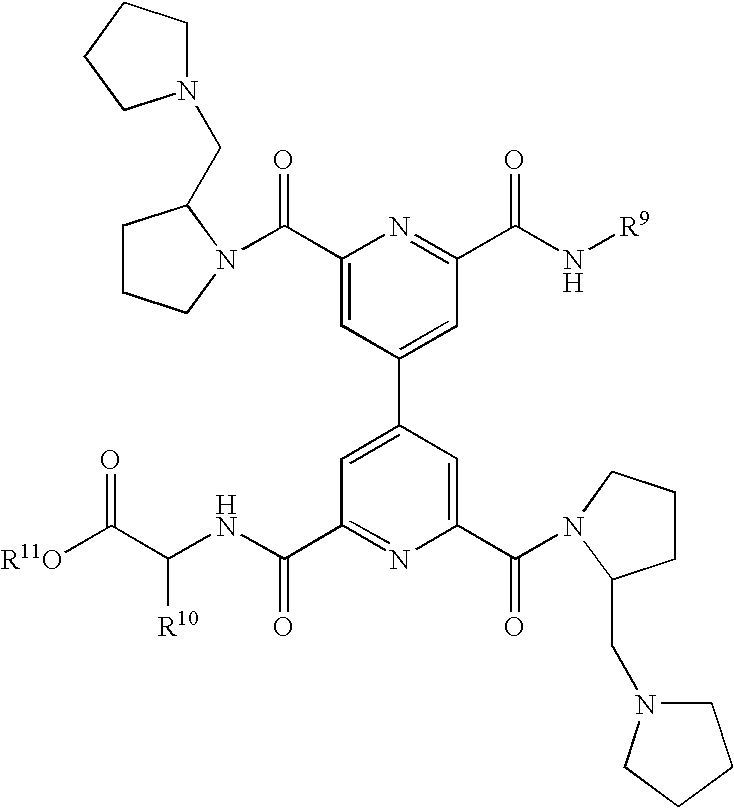
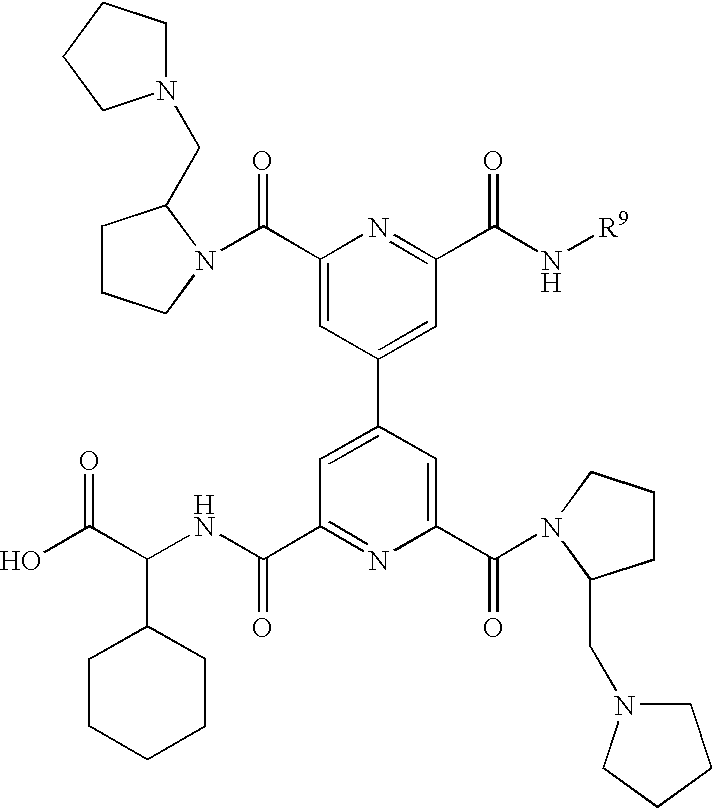
Novel CD40:CD154 binding interruptor compounds and use thereof to treat immunological complications
a technology of interruptor compounds and cd154, which is applied in the field of cd40 : cd154 binding interrupter compounds, can solve the problems of impaired memory b cell development, impaired spleen and lymph node germinal centers, and deficient ability of murine nullizygotes to figh
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Chemical Synthesis of Compound 7
[0112] Step 1: A mixture of chelidamic acid monohydrate (1.00 g, 4.97 mmol) and phosphorus pentabromide (8.45 g, 19.6 mmol) was warmed to 90° C. for 3 hours (h). Chloroform (100 mL) was added to the warm reaction mixture and the resulting slurry was filtered. The filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to give a pink solid. The solid was dissolved in ethanol (vigorous reaction), stirred for 0.5 h and then concentrated in vacuo to give a yellow solid. The solid was dissolved in ether (250 mL), washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (50 mL×2), dried (MgSO4) and concentrated in vacuo to give 1.30 g of a white solid.
[0113] Step 2: A solution of KOH (0.83 g, 3.31 mmol) in anhydrous ethanol (40 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of the compound from step 1 (3.85 g, 12.7 mmol) in anhydrous ethanol (100 mL) over the course of 3 h. A white precipitate formed. The unstirred slurry was allowed to sit at room temperature (RT) for 7 h and then at 0° C. ov...
example 2
Chemical Synthesis of Compound 8
[0122] Step 1: steps 1-9 of EXAMPLE 1 were carried out.
[0123] Step 2: Catalytic 10% Pd / C was added to a solution of the compound from step 1 (0.100 g) in ethyl acetate. The reaction was stirred under a hydrogen atmosphere (1 atm) overnight. The reaction was then centrifuged and the supernatant decanted and concentrated in vacuo.
[0124] Step 3: A solution of the compound from step 2 (0.020 g) in 2:1 TFA / methylene chloride (6 mL) was stirred at RT for 2 h. The reaction was then concentrated in vacuo and purified via reverse phase HPLC (acetonitrile / water) to give an off-white solid.
example 3
Chemical Synthesis of Compound 4
[0125] Step 1: steps 1 and 2 of EXAMPLE 1 were carried out.
[0126] Step 2: Catalytic DMF and 2.0 M oxalyl chloride / dichloromethane (3.0 mL, 6.0 mmol) were added to a solution of the compound from step 1 (2.72 g, 2.64 mmol) in dichloromethane (20 mL) at RT. The reaction solution was stirred until bubbling ceased, diluted with toluene (40 mL) and reduced in volume in vacuo. A solution of 3-phenyl-1-propylamine (1.7 mL, 11.9 mmol) in pyridine (8 mL) was added and the resulting solution was stirred at RT overnight. The reaction solution was diluted with ethyl acetate (300 mL), washed with water (150 mL), 1N HCl (150 mL×3) and water (150 mL), dried (MgSO4) and concentrated in vacuo to give an oil. The oil was dissolved in 1:1 saturated aqueous lithium hydroxide / THF and stirred overnight at RT. The reaction was then acidified with 1N HCl, extracted with ethyl acetate, dried (MgSO4) and concentrated in vacuo to give 3.456 g of an oil.
[0127] Step 3: A solut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com