Methods and compositions for identifying morphogen analogs
a technology of morphogen analogs and compositions, applied in the field of screening and identifying substances, can solve the problems of affecting the effectiveness of drug effects, and presently encountered complications,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Effect of OP-1 on the Proliferation and Differentiation of C5.18 Cells
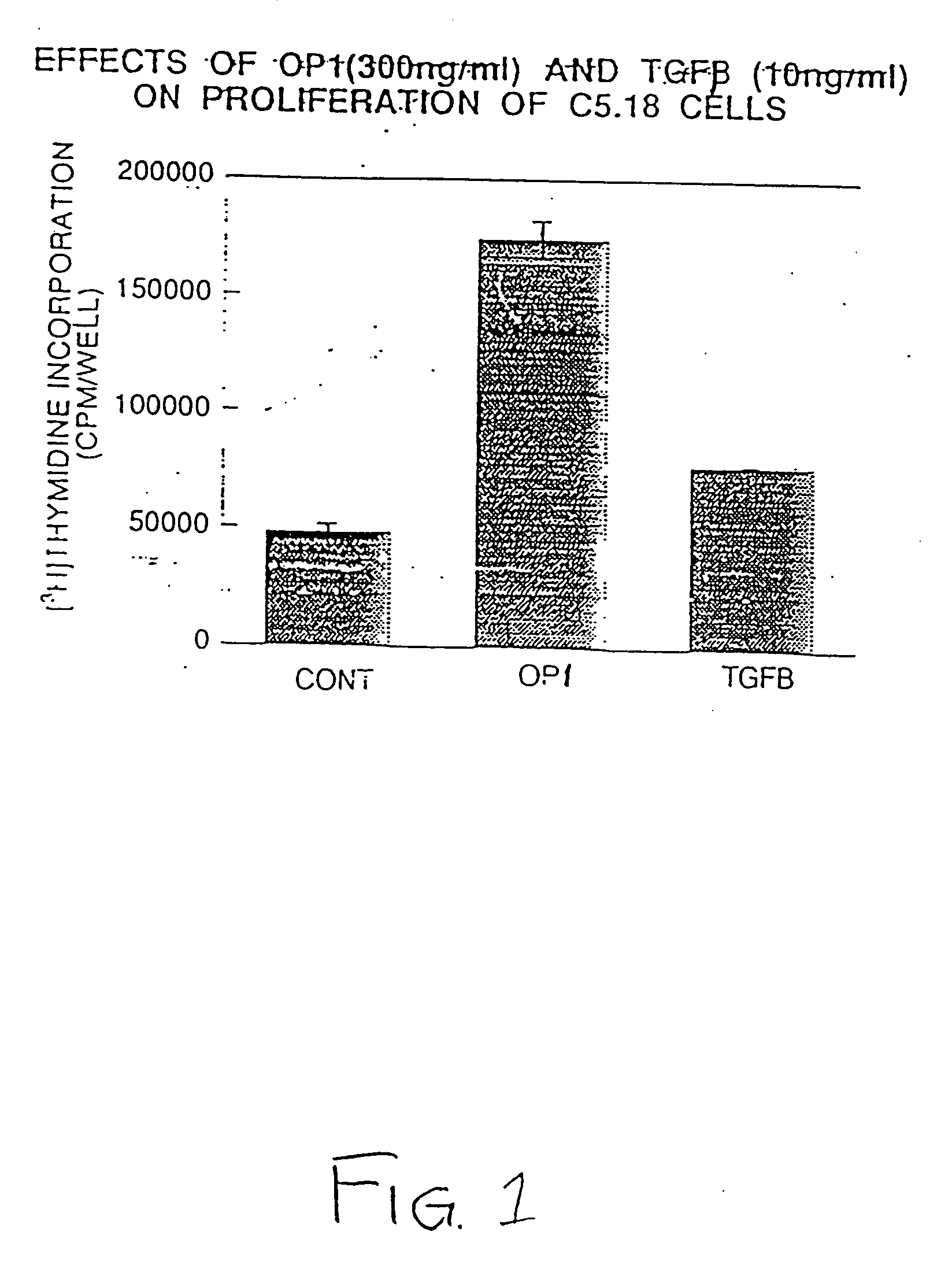
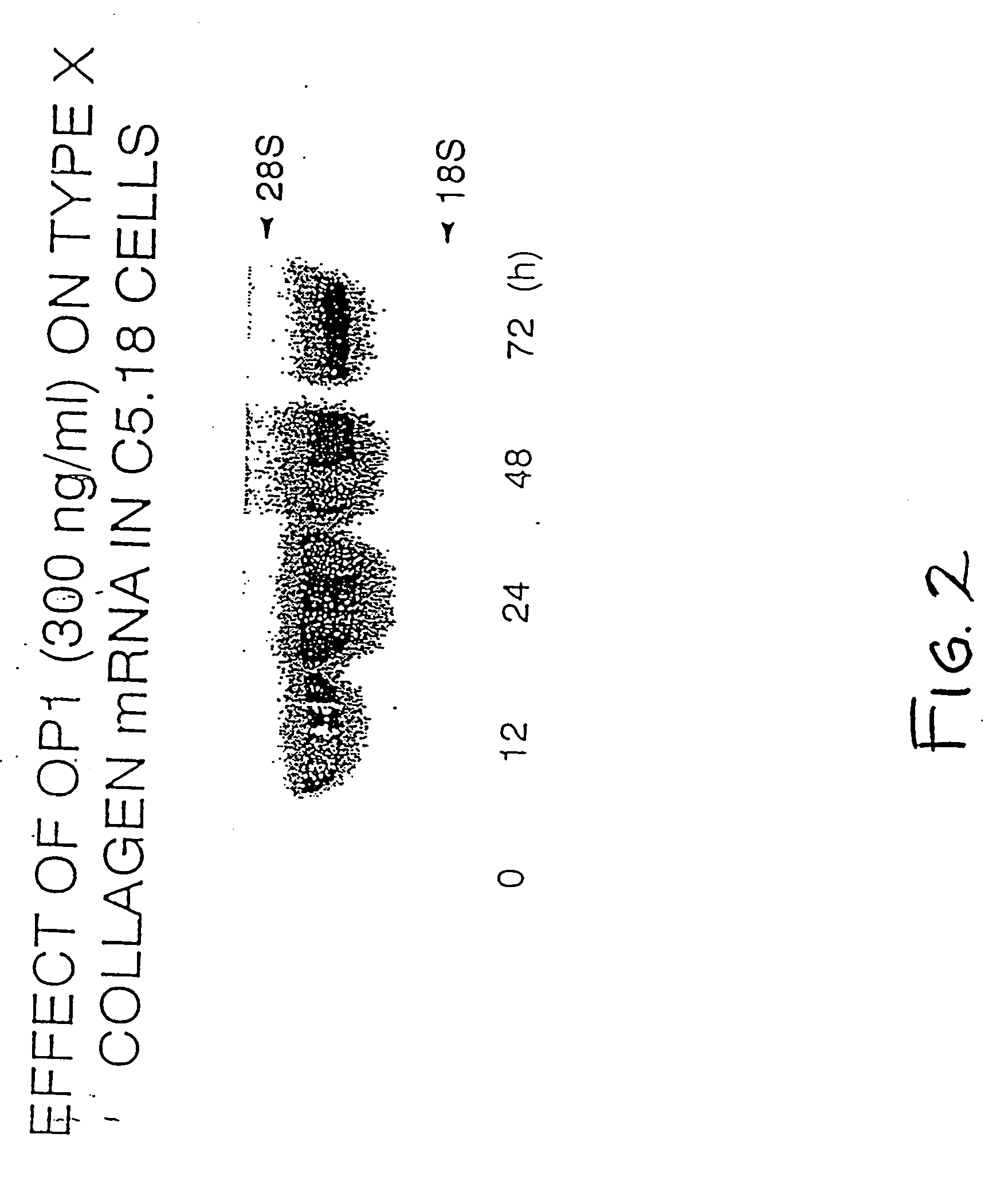
[0075] To characterize the biological effects of OP-1 on bone derived cell lines, OP-1 responsiveness was examined in C5.18 cells, spontaneously immortalized fetal rat calvaria cells well-known in the art and described, for example, in Grigoriadis et al. (1990) Developmental Biology 142:313-318 and in Von Schroeder et al. (1994) Teratology 50:54-62, the disclosures of which are herein incorporated by reference. C5.18 cells were plated in 12-well culture dishes (1×105 cell / well) in αMEM containing 15% fetal bovine serum. As described below, varying amounts of recombinant human OP-1 (Creative BioMolecules, Inc., Hopkinton, Mass.) were added to the culture media and the calvaria cells were incubated with the OP-1 containing medium for varying lengths of time as indicated below. OP-1 was prepared and formulated generally as earlier described in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,258,494; 5,266,683; and 5,354,557, the disclosures of wh...
example 2
Effects of OP-1 on Type X Collagen Promoter Reporter Constructs
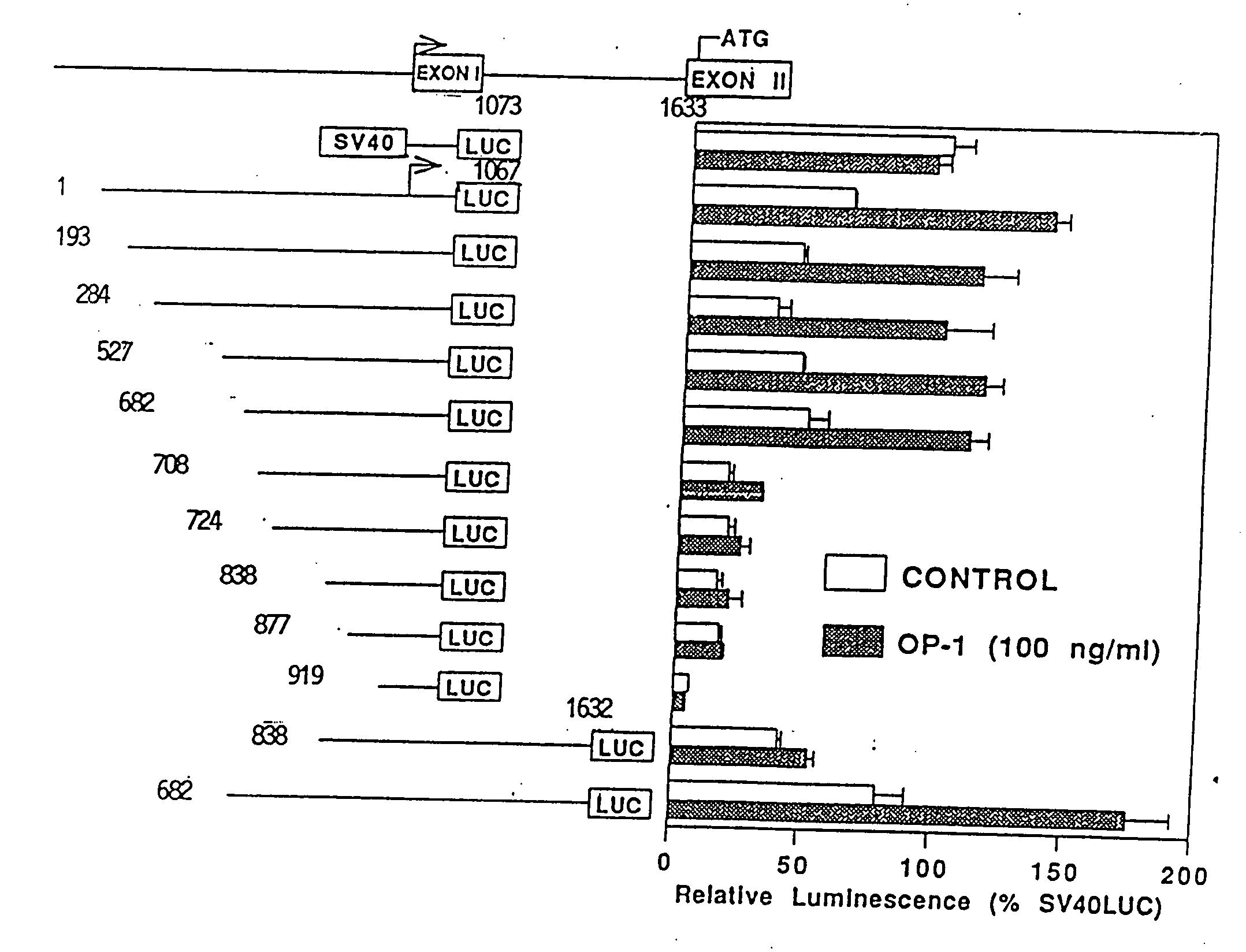
[0082] The above-described effect of OP-1 on the expression of type X collagen was of particular interest, as this phenotypic marker is generally understood to be specific for hypertrophic chondrocytes and thus of endochondral bone formation. The mouse type X collagen gene promoter was therefore employed as a model in order to examine the molecular mechanisms for OP-1 induction of chondrocyte phenotypic markers. The responsiveness of the type mouse X collagen gene promoter to OP-1 was therefore studied using the below described luciferase reporter gene deletion analyses:
[0083] The promoter region of the mouse type X collagen gene (nucleotides 1 to 1067, as designated by Elima et al. (1993) Biochem. J. 289:247-253, and by GenBank EMBL Data Bank: Accession #X67348; COLI0A1 gene; collagen alpha I type X) (also designated herein as nucleotides 1-1067 of SEQ. ID No. 1) was cloned according to well-known PCR (polymerase chai...
example 3
Mutation Analysis of the Transcription Activating Element
[0092] To characterize the respective roles of the AP-1 like (nucleotides 715-724 of SEQ. ID No. 1) and the A / T rich sequences (nucleotides 699-711 of SEQ. ID No. 1) (both of which are depicted within sequence “w” in FIG. 12) in the OP-1 driven induction of the collagen X promoter, mutations of the nucleotides 699-731 (SEQ. ID No. 1) upstream of the heterologous RSV promoter were analyzed (FIG. 12). Mutation of a portion of the AP-1 like sequence (nucleotides 715-724 of SEQ. ID No. 3) which changes the sequence (GAAT) to (TCCG) (depicted as sequence “M1” in FIG. 12) strongly suppressed the enhancer activity of this region and abolished the stimulatory effects of OP-1 (100 ng / ml) on this region. The above mutation also abolished the stimulatory effects of bFGF (10 ng / ml), which is capable of inducing the expression of the (699-731)x3-RSV construct in the presence of 1% serum (FIG. 12). In contrast, mutation of a portion of the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| apparent molecular weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| apparent molecular weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| apparent molecular weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com