Process for recovering used lubricating oils using clay and centrifugation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
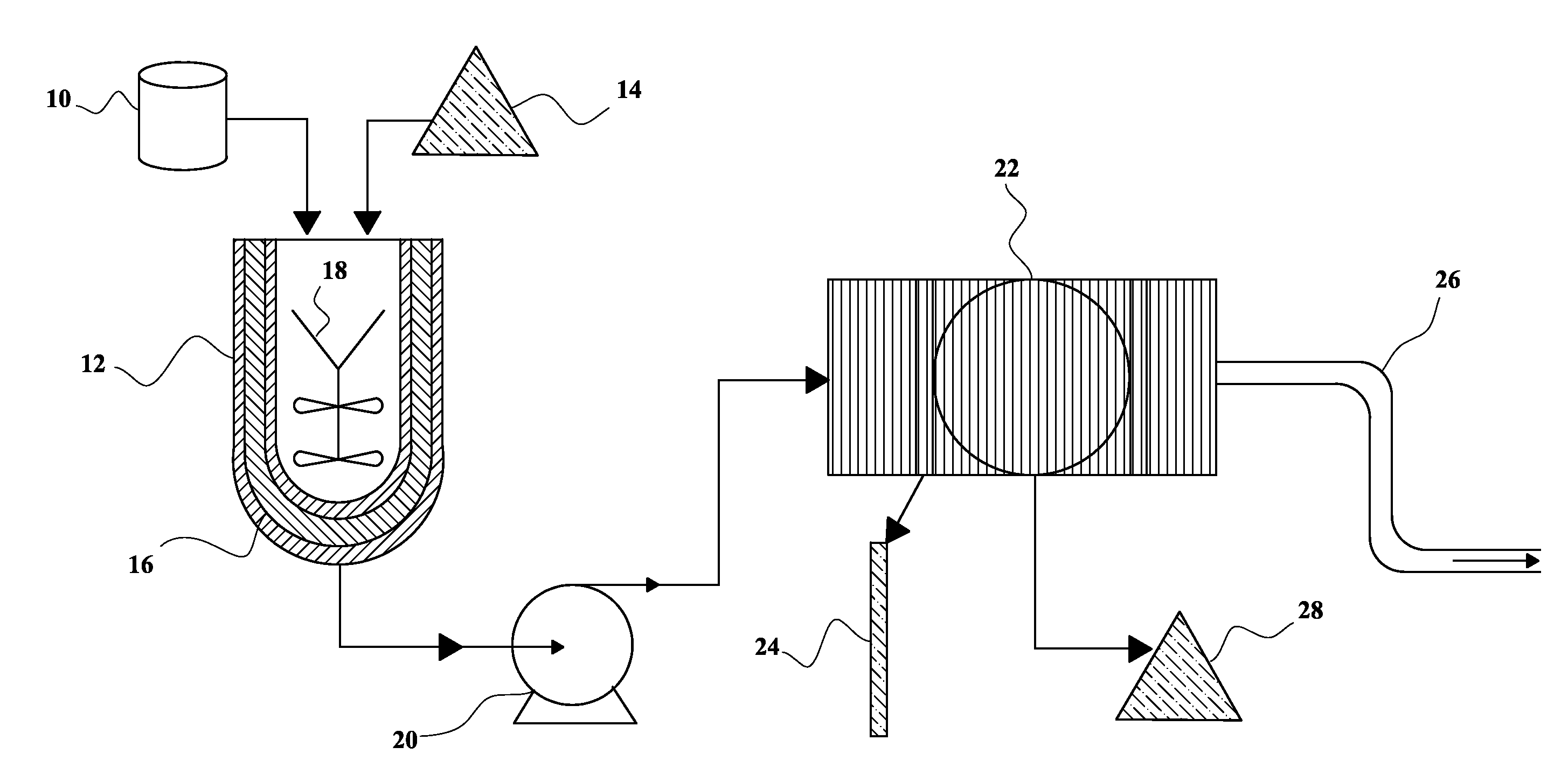
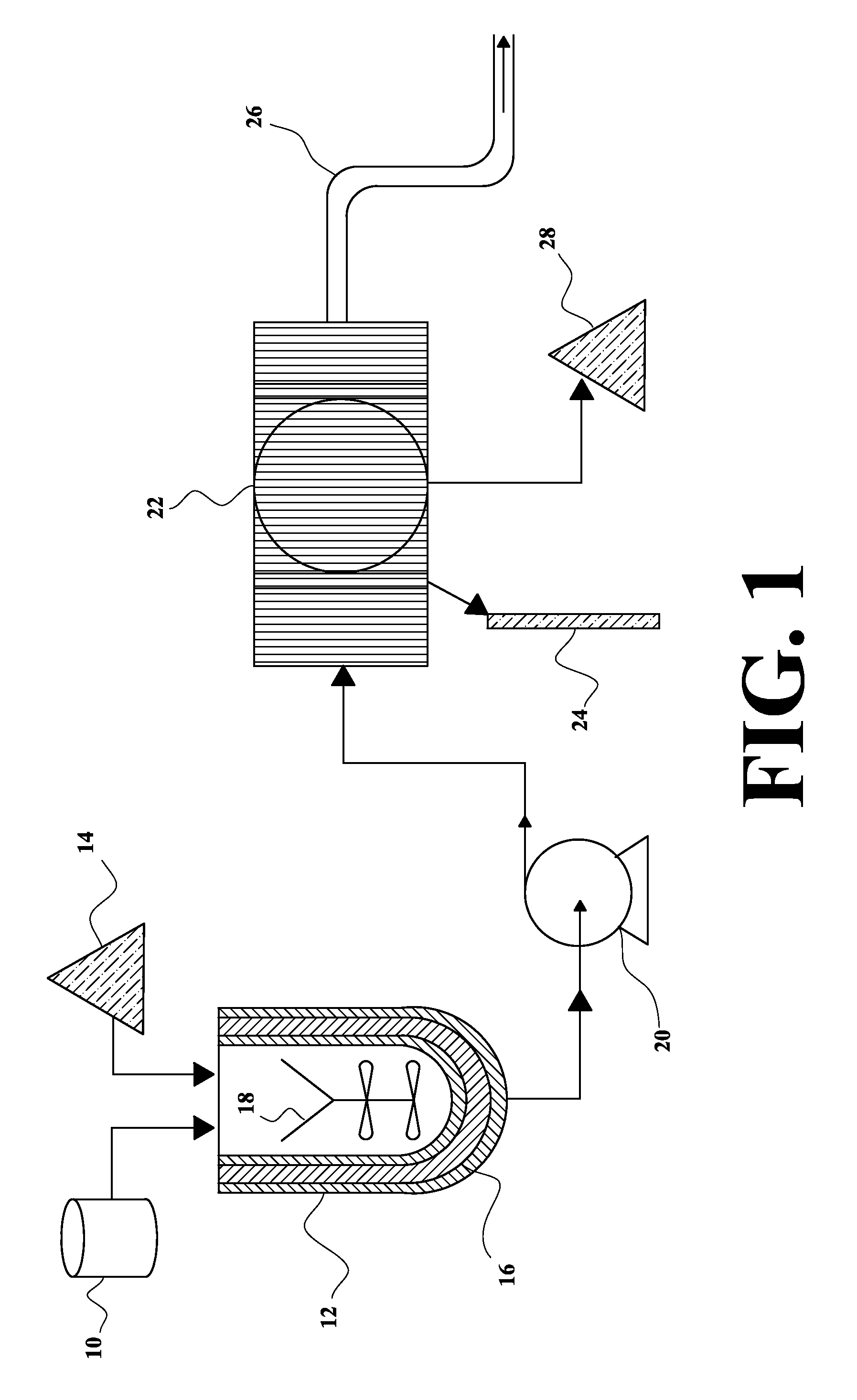
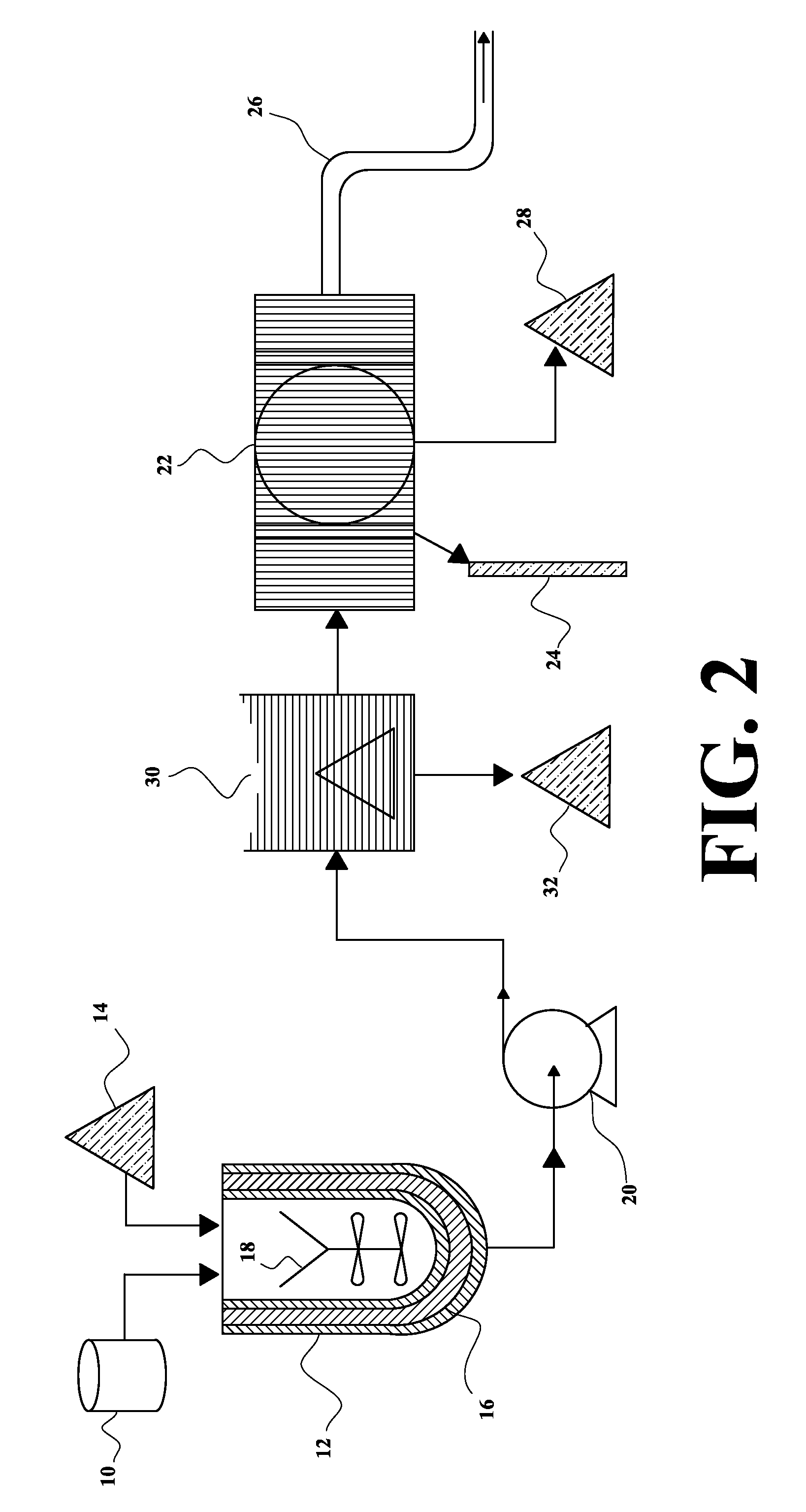
Image
Examples
example 1
A treatment of 1,800 liters of used oil of industrial origin was performed, to show the effectiveness of the present invention.
Process of Recovery of Used Industrial Oils (Example Industrial Plant)
Materials.—
[0045]1,800 liters of lubricating oils for industrial gears coming from Carbonorca Enterprise C.A.
Initial Characteristics of the used Oils.—
1. Color: Opaque brown, non-translucent.
[0046]2. Presence of free water and / or in emulsion: (10-50% v / v).
3. Presence of solid suspended particles (>1000 mg / Kg, 0-30% v / v)
[0047]4. pH: >7
5. Aromatics: <1 mg / Kg.
6. Solvents: 0-10% v / v.
System of Absorbent / Adsorbent.—
[0048]Activated clays, hybrid type of hormite and smectite, with acid characteristic, with pH (5% solids diluted in H2O) equal to 2.5-3.0, density of 336-416 g / l, and particle size, by sieve analysis (Tyler Standard), particles with sizes less than 150 μm: 100%, and particles with sizes less than 45 μm: of 73-76%.
Procedure Description.—
[0049]1) Pre-filtration: The used industrial oil ...
example 2
[0057]A laboratory experiment was performed, with a sample of used motor oil. The following is a description of the details of the experiment:
Materials:
[0058]800 ml of used oil, coming from a Fiat “Ritmo” car, 1987 model, 1600 ml motor, with 45 days of running, and a total of 55,000 km passed over. The original oil was PDV (Petroleum of Venezuela) brand, 20W-50W multigrade (Experiment No. 1). There was also used 800 ml of a mixture of used oils coming from an workshop for oil change, located in Maracay, Aragua State-Venezuela (Experiment No. 2).
System of Absorbent:
[0059]Activated clays, hybrid type of hormite and smectite, with acid characteristic.
Experimental Process and Preparation of Samples for Analysis:
[0060]A sample of 800 grams of used motor oil was put in a glass beaker, with a magnetic stirrer inside, and was placed on an electric heating plate with continuous magnetic stirring.
[0061]The heating of the sample was between 100-120° C. during 30 minutes, in order to eliminate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com