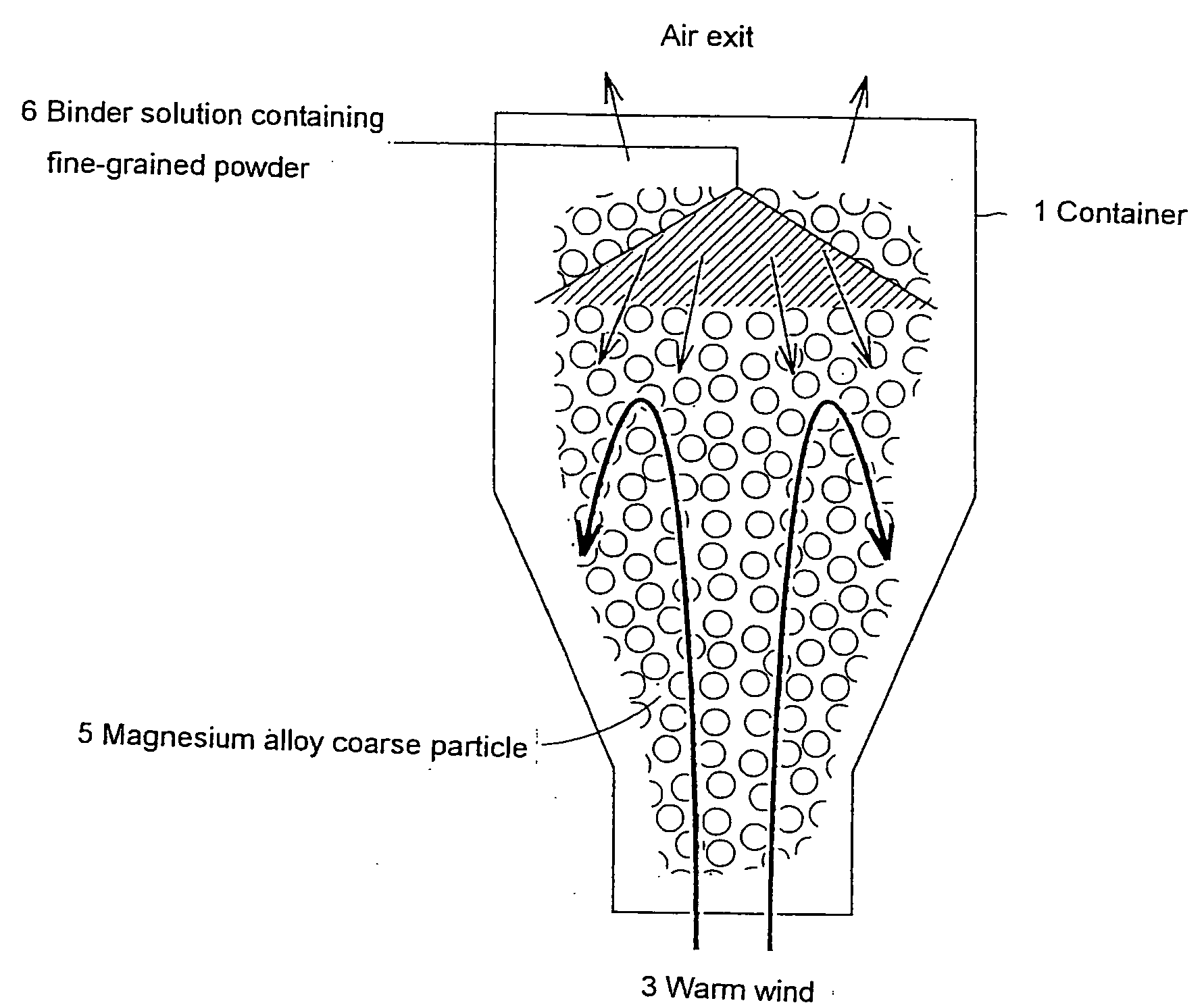
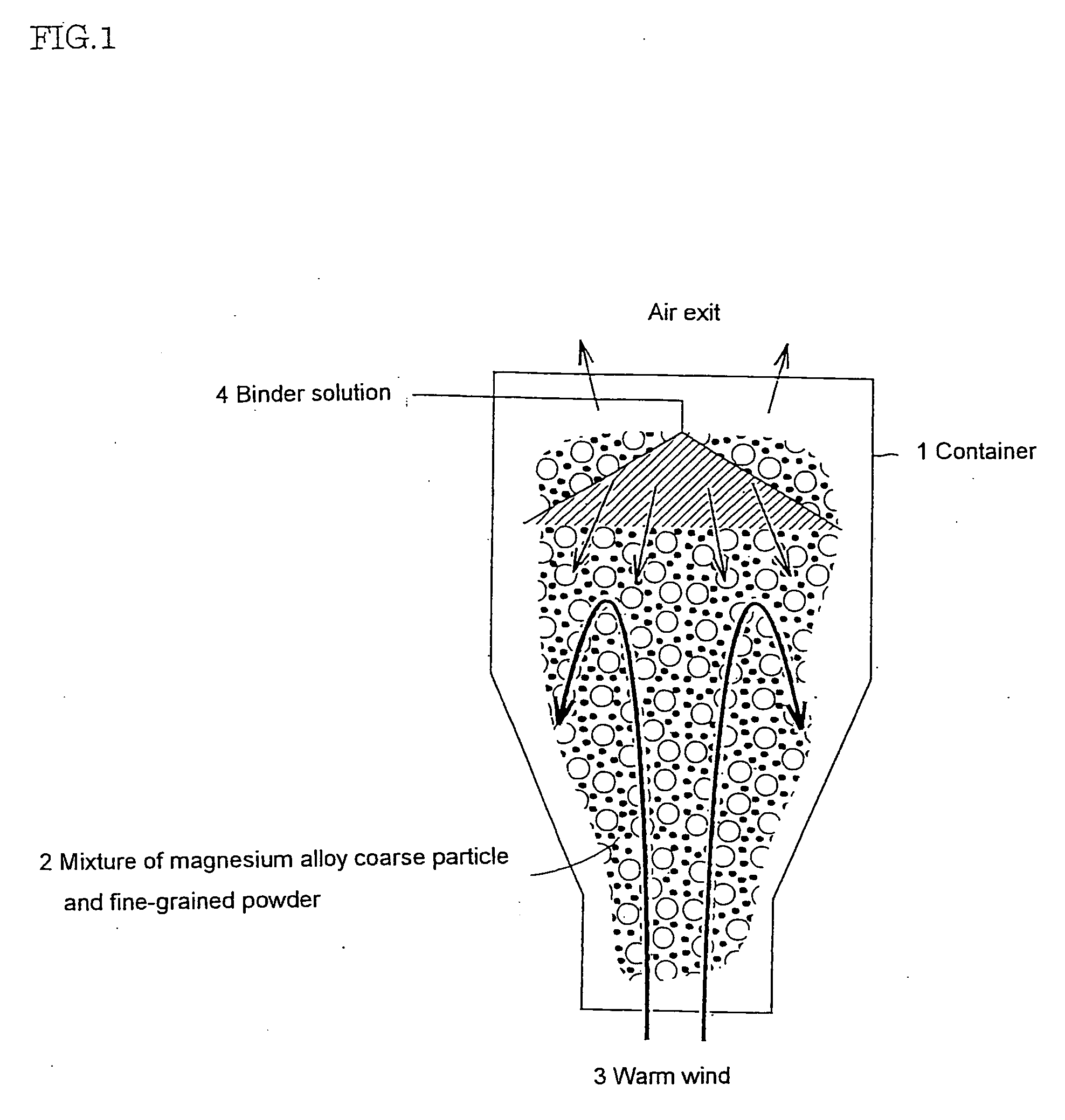
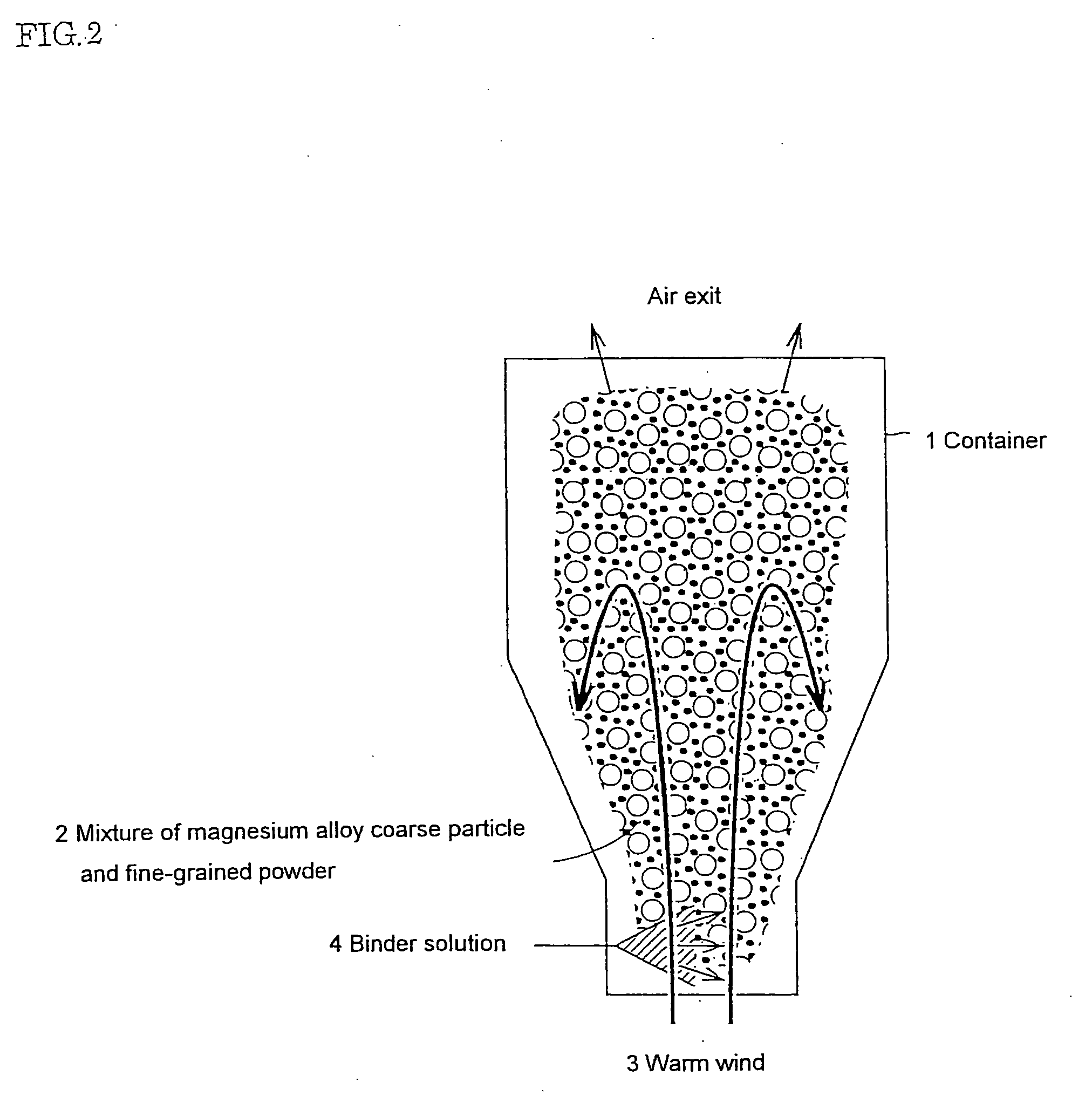
Manufacturing method of a magnesium group composite material
a composite material and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of magnesium composite powder, can solve the problems of demerits of magnesium alloy, low rigidity, low hardness, etc., and achieve the effects of high economic efficiency, high mechanical characteristics, and superior characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working example 1
(1) Working Example 1
[0104]As a starting raw material to constitute a matrix to manufacture the magnesium alloy, AZ31 magnesium alloy coarse particle powder having a maximum particle diameter of 1.5 mm, a minimum particle diameter of 550 μm and an average particle diameter of 870 μm was prepared. Meanwhile, as the added powder, fine-grained powder of silicon (Si), silica (SiO2), γ alumina (Al2O3) and aluminum (Al) were prepared. Particle diameters (maximum, average, minimum) of the above powder measured by laser diffraction and scattering method are shown in a table 1.
TABLE 1SiliconSilicaγaluminaAluminumFine-grained powder(Si)(SiO2)(Al2O3)(Al)Maximum value (μm)55483844Average value (μm)22201423Minimum value (μm)4359
[0105]The AZ31 coarse particle powder and each fine-grained powder were weighed and mixed so that 5% by weight of the fine-grained powder might be contained. As a binder solution, PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) water solution having a concentration of 2% was prepared.
[0106]Each ...
working example 2
(2) Working Example 2
[0109]As a starting raw material to constitute a matrix to manufacture the magnesium alloy, AZ91 magnesium alloy coarse particle chip having a maximum particle diameter of 4.6 mm, a minimum particle diameter of 680 μm and an average particle diameter of 3.8 mm and manufactured by cutting processing was prepared. Meanwhile, as the added powder, the silicon (Si) powder shown in the working example 1 was prepared.
[0110]The AZ91 coarse particle chip and the Si fine-grained powder were weighed so that 95% by weight of the AZ91 coarse particle chip and 5% by weight of the Si fine-grained powder might be provided. As a binder solution, the PVP (polyvinyl pyrrolidone) water solutions having concentrations shown in a table 3 were prepared to which the weighed Si fine-grained powder was mixed. In addition, 20% by weight of the PVP water solution was provided in the whole mixed powder.
TABLE 3PVP water solutionPVA solidAttached state of SiNo.concentration (%)quantity (%)fin...
working example 3
(3) Working Example 3
[0114]The AZ91 magnesium alloy coarse particle chip used in the working example 2 and the silica (SiO2) fine-grained powder shown in the working example 1 were prepared. The AZ91 coarse particle chip and the silica fine-grained powder were weighed and mixed so that 70% by weight of the coarse particle chip and 30% by weight of the silica fine-grained powder might be provided. The mixture was mechanically granulated using a vertical type of roller compactor. In addition, a roller had a configuration of a toothed wheel here. A speed of the roller at a peripheral part was set at 10 mm / sec and a load between the toothed wheels was set at about 10 Kgf. Result of appearance of provided granulated object observed by a scanning electronic microscope is shown in FIG. 13.
[0115]As shown in FIG. 13, the granules provided by the roller compactor were the magnesium composite powder in which the silica fine-grained powder was mechanically and uniformly attached on the AZ91 chi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com