Inkjet recording head and inkjet recording apparatus having the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
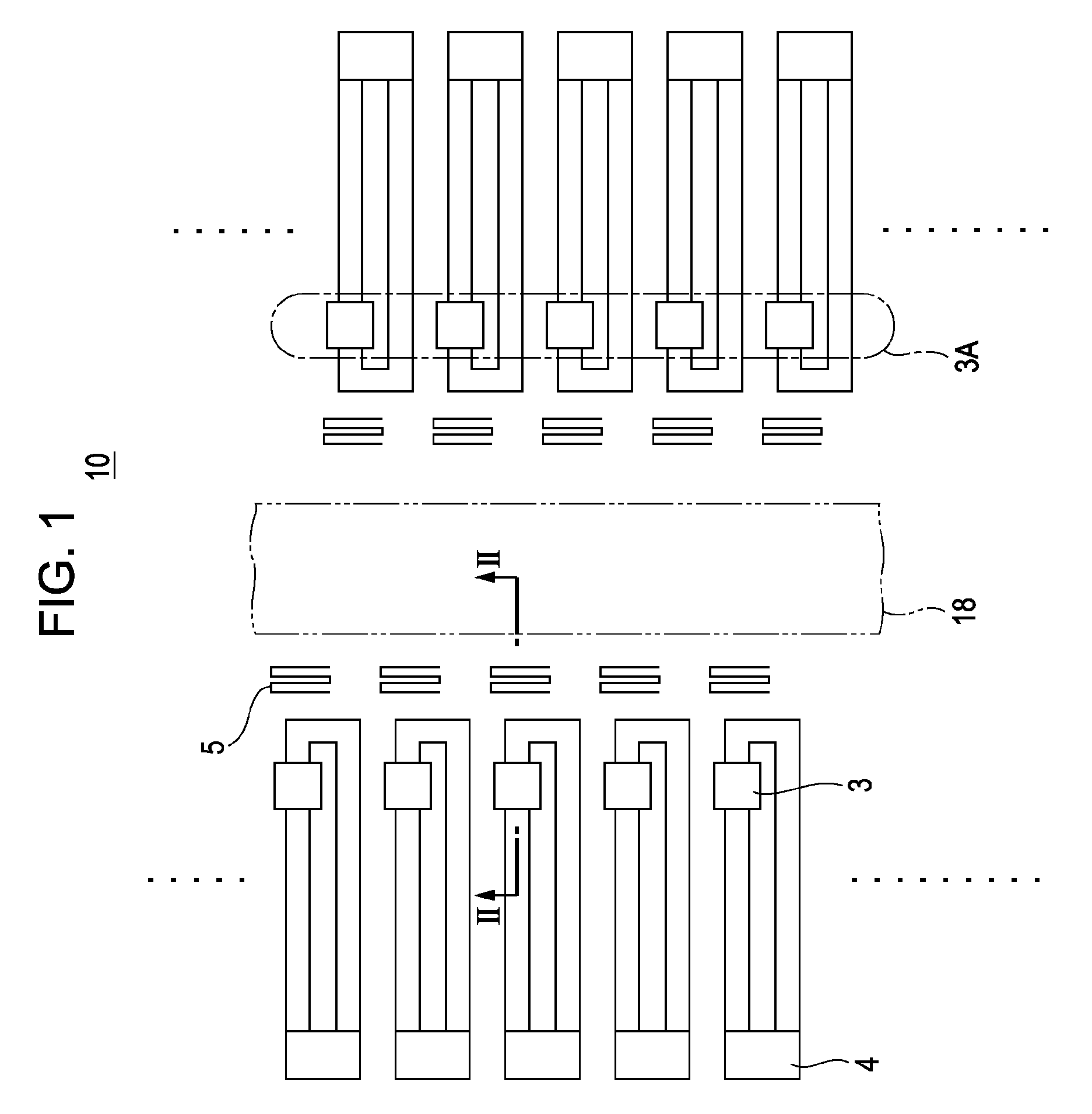
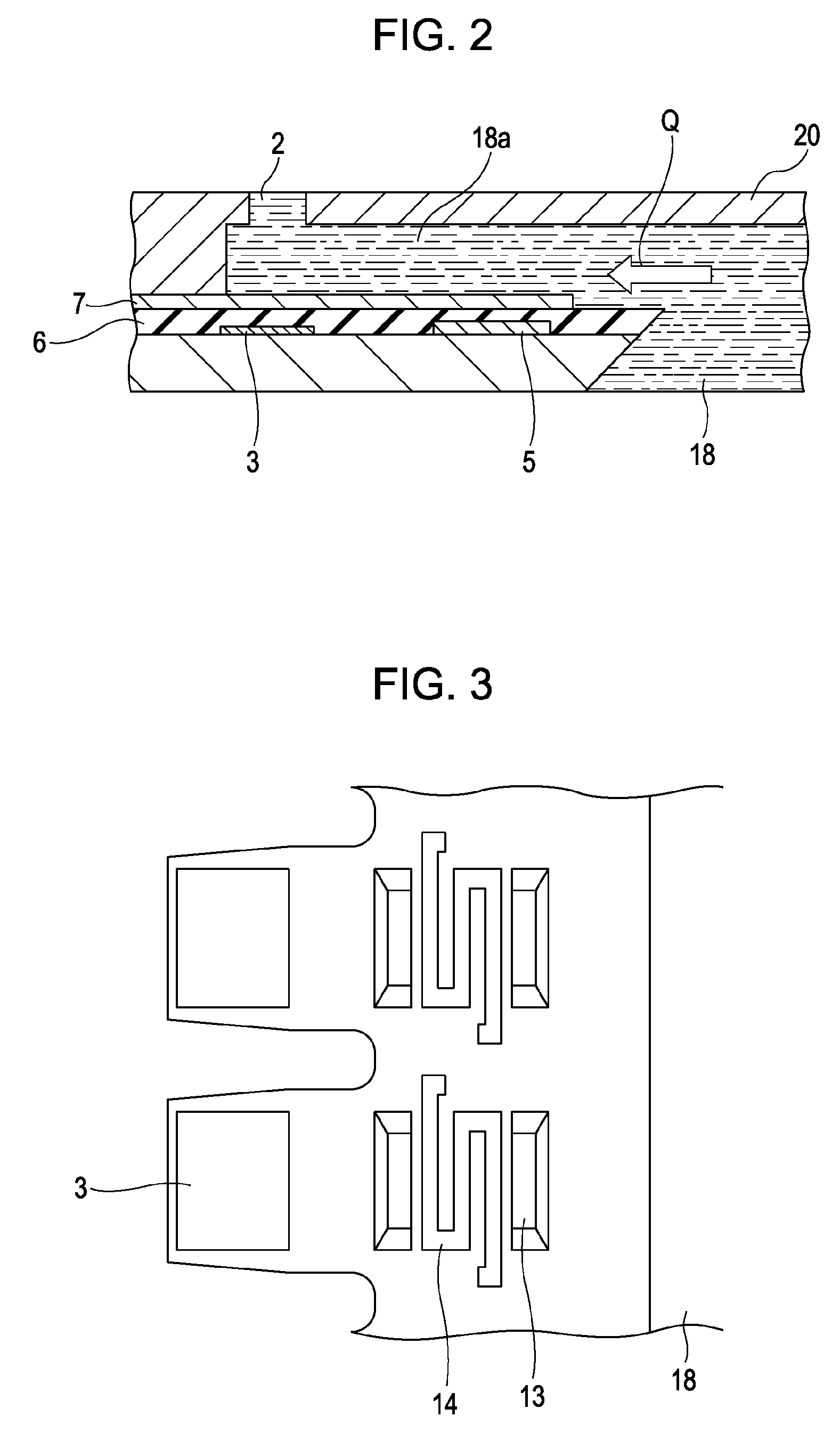
[0054]FIG. 1 is a schematic view showing a part of a substrate in an inkjet recording head according to a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of the substrate, taken along line II-II in FIG. 1.
[0055]Referring to FIG. 1, a heater board 10 has a structure in which a common liquid chamber 18 is provided at the center thereof, as viewed in a direction perpendicular to the board surface. On each side of the common liquid chamber 18 in the heater board 10, a heater unit 3A including a plurality of discharging heaters 3 arranged in line is provided.
[0056]Dummy resistors (not shown) are provided near the heater units 3A. The dummy resistors are not used for discharging of ink droplets. The discharging heaters 3 are electrothermal transducers (discharging-energy generating elements) that generate heat energy in accordance with the applied voltage, and are connected to terminals 4 to which a driving signal is applied. The terminals 4 are connected to ex...
second embodiment
[0112]An inkjet recording head according to a second embodiment has a basic configuration similar to that of the recording head of the first embodiment except in an operation of detecting defective discharging with a flow sensor. The inkjet recording head of the second embodiment also includes an ink-flow detector (ink-flow detecting unit) similar to that shown in FIG. 5.
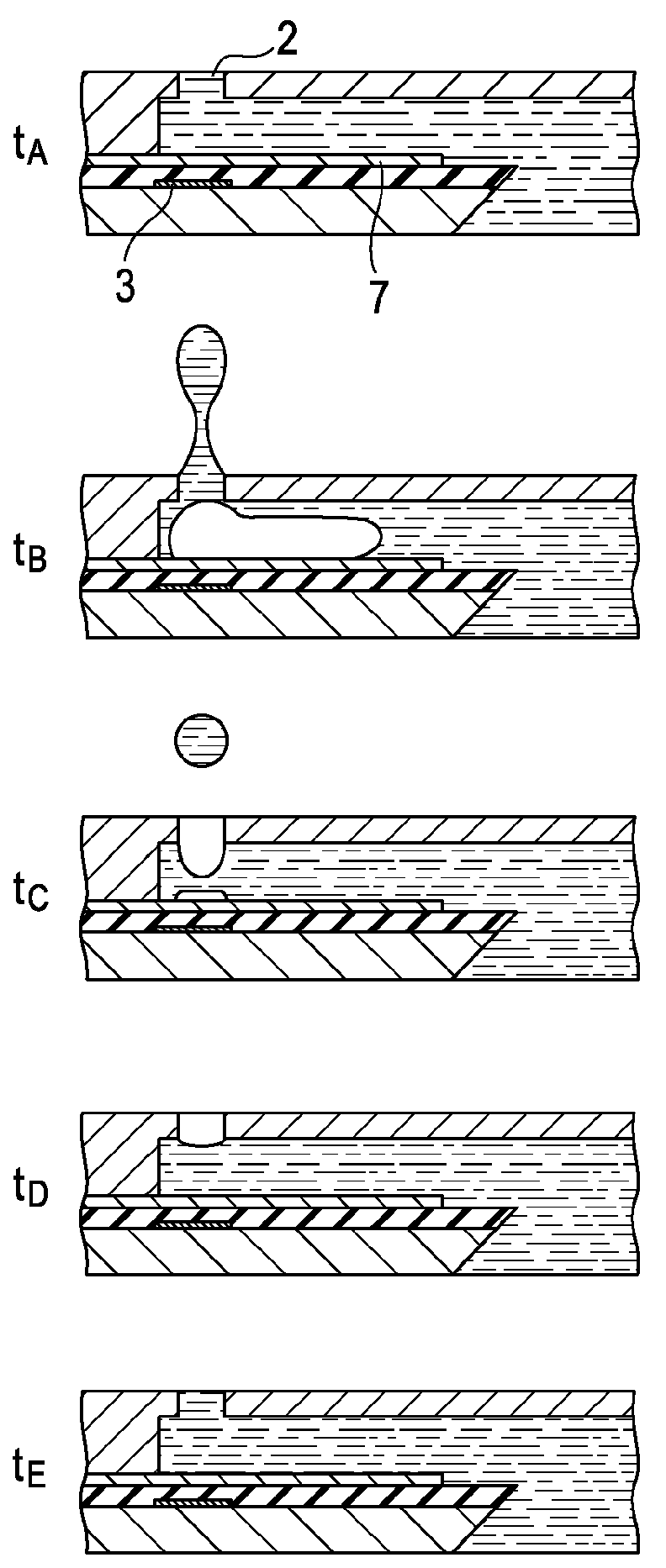
[0113]FIGS. 9A to 9E explain the principle of operation of the ink-flow detector. FIG. 9A is a waveform chart of the voltage applied to the electrothermal transducer 15. FIG. 9B shows the change in ink flow rate on the time axis when the direction from the common liquid chamber 18 to the discharge port 2 shown in FIG. 1 is a positive direction. FIG. 9C is a waveform chart of the current applied to the detecting element 17. FIG. 9D shows the change in temperature on the time axis of ink on the detecting element 17. FIG. 9E is a waveform chart of the detected output voltage in accordance with the changes in ink flow r...
third embodiment
[0119]FIG. 10 is a partial sectional view of an inkjet recording head according to a third embodiment of the present invention. In this recording head, a nozzle forming member 20 that defines a passage by being combined with a heater board (head substrate) is not formed of an organic material, but of silicon (Si). In this nozzle forming member 20, a flow sensor 5 serving as an ink flow-rate detecting element is formed by a film deposition process similar to the process for a semiconductor. Other structures are similar to those adopted in the first embodiment.
[0120]The flow sensor 5 may have a meandering shape in order to increase the resistance, or may have a square shape.
[0121]The inkjet recording head of the third embodiment also includes an ink-flow detector having a configuration similar to that shown in FIG. 5. The ink-flow detector operates in a manner similar to that adopted in the first embodiment.
[0122]Since the flow sensor 5 is provided apart from a discharging heater 3 in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com