Method and apparatus for selective filtering of ions
a selective filtering and ion technology, applied in the field of methods and apparatus for selective filtering of ions, can solve the problems of space charge reducing the mass measurement accuracy of various instruments, changing the optimal excitation amplitude, and ion traps suffering from detrimental effects. the effect of lessening the detrimental effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
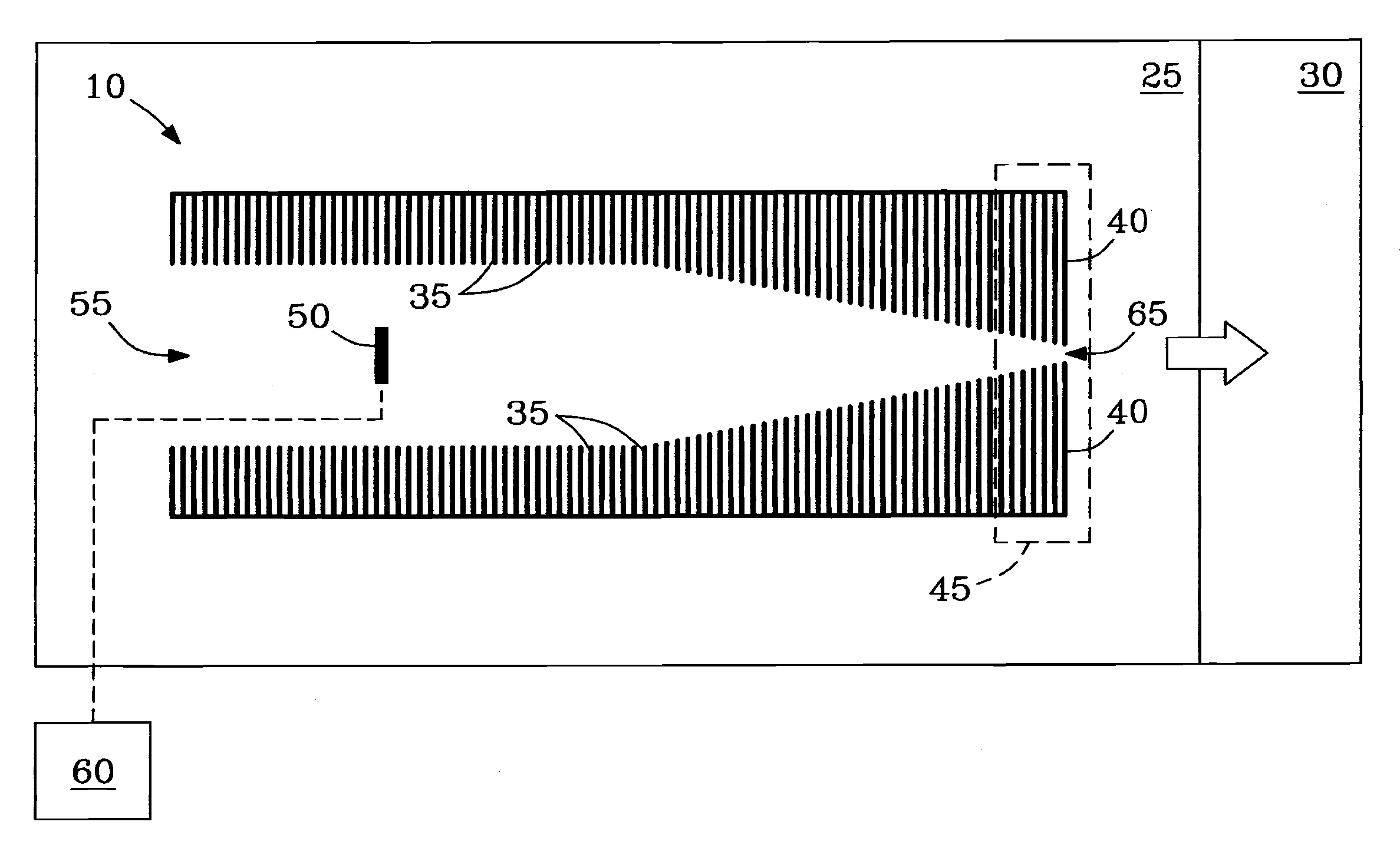
[0042]Example 1 describes tests showing ability of the conductance limiting electrode 40 of ion funnel 10 to perform selective low-mass filtering, e.g., as a low m / z filter 40.
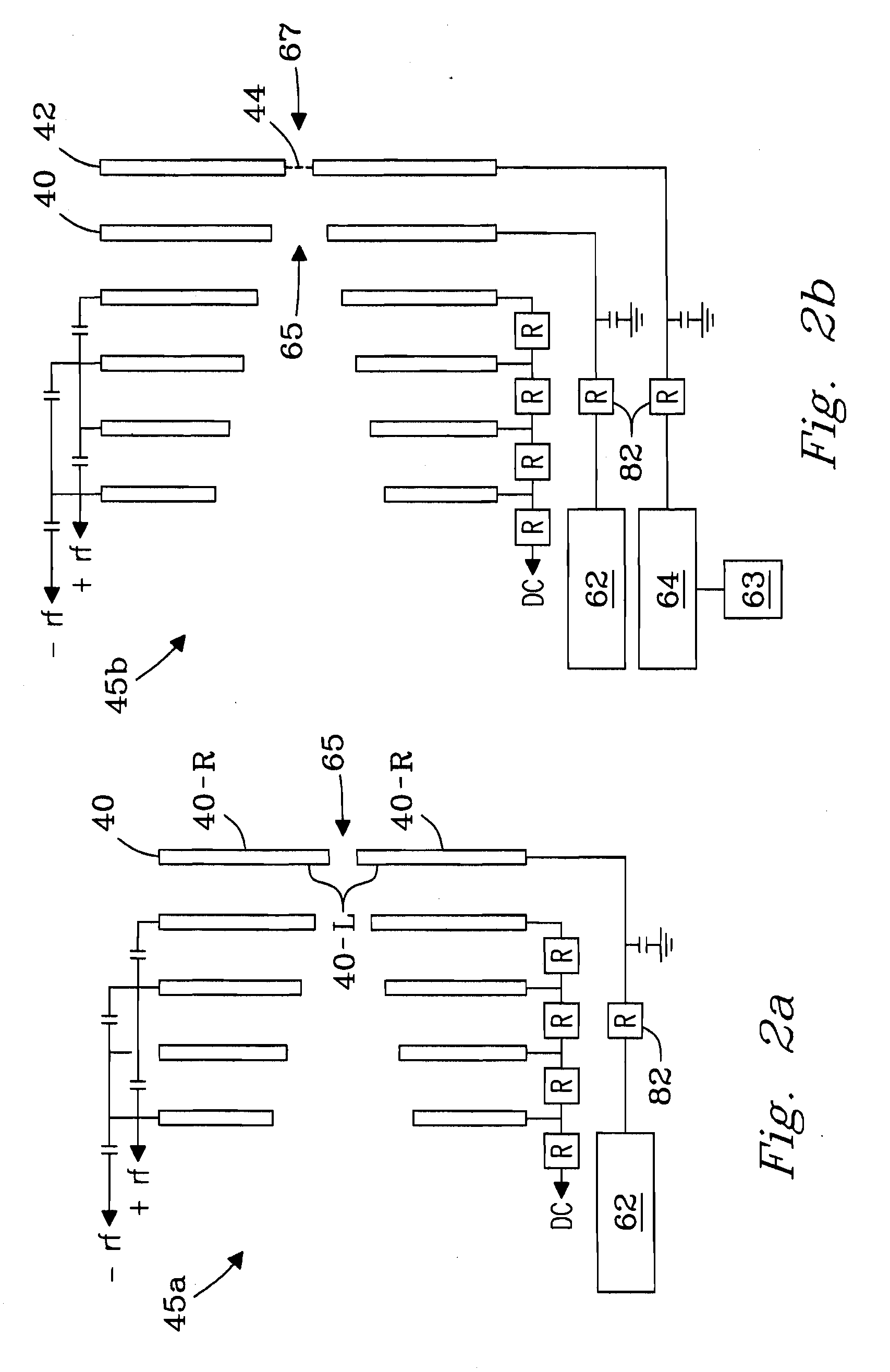
[0043]Ability of conductance limiting electrode 40 of ion funnel 10 to perform selective low-mass filtering was tested on a single quadrupole mass spectrometer (e.g., model 1100 quadrupole MS, Agilent, Palo Alto, Calif., USA) modified with an ESI / ion funnel source. The ESI / ion funnel configuration described in reference to FIG. 2b was employed. Ion funnel 10 was operated by applying an RF voltage of 500 kHz at 90 V peak-to-peak (90 Vp-p), but was not limited thereto. DC voltage applied to funnel plates 35 of ion funnel 10 yielded a constant gradient of 200 V at inlet 55 down to 5 V at exit aperture 65 of ion funnel 10. Pressure in funnel 10 was 1.9 Torr. ESI emitters were made by pulling sections of 100-μm i.d. / 200-μm o.d. fused silica capillary (Polymicro Technologies, Phoenix, Ariz., USA) either by hand with...
example 2
[0045]Example 2 describes tests relating m / z cut-off of filter plate 40 to the potential applied to filter plate 40 necessary to achieve filtering of low m / z ions.
[0046]A solvent mixture was prepared by combining methanol (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, Pa., USA) and water (Nanopure Infinity Purification system, Barnstead, Dubuque, Iowa, USA) in a 50:50 ratio by volume and adding 1% by volume acetic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo., USA). Filtering capacity of filter plate 40 was characterized by infusing and electrospraying (i.e., using an ESI / ion funnel source 25) the solvent mixture and acquiring mass spectra with the instrument described in Example 1. By observing the m / z cut-off at which chemical noise in the acquired mass spectra was eliminated, cut-off threshold could be ascertained as a function of voltage applied to filter plate 40. Filter plate 40 voltages were adjusted in one-volt increments in the range from about 12 V to about 18 V.
[0047]FIG. 4a presents a mass spect...
example 3
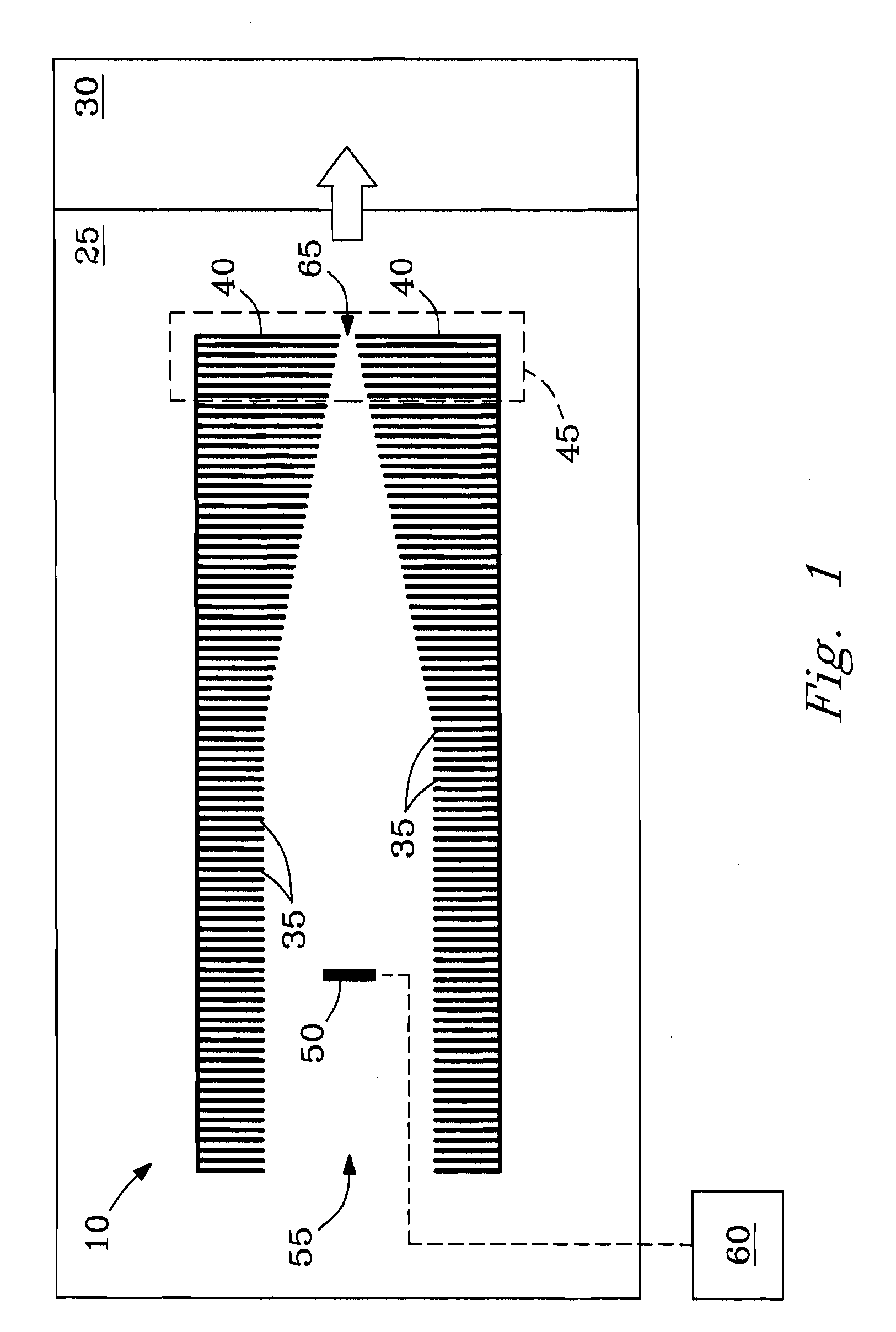
[0050]Example 3 describes the distribution of DC voltages and electric fields generated in the region near exit aperture 65 of filter plate 40 at an applied voltage of 15 V to filter plate 40. The DC electric field E was estimated using calculations based on the geometry shown in FIG. 1. As illustrated, e.g., in FIG. 2a, filter plate 40 can be considered a 3-dimensional plate having left and right surface planes (surfaces) 40-L and 40-R, respectively, and any suitable thickness (e.g., 0.5 mm), the left surface plane 40-L facing into the interior of ion funnel 10.
[0051]FIG. 5a shows the distribution of DC potentials observed for radial distances (r) of 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1 mm, respectively from the center of exit aperture 65 of filter plate 40 toward the radial edge of aperture 65 of filtering plate 40 as a function of axial coordinate “z” for rear section 45 of funnel 10. The origin of axial coordinate “z” is positioned at left-most surface plane 40-L (left surface) of filter pl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com