Thiazolidinedione analogues
a technology of thiazolidinedione and analogues, applied in the field of pharmaceutical compositions, can solve the problems of sodium reabsorption and other unpleasant side effects, and achieve the effects of stimulating transcription, and reducing binding and activation of the nuclear transcription factor ppar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Formulation of Pharmaceutical Compositions
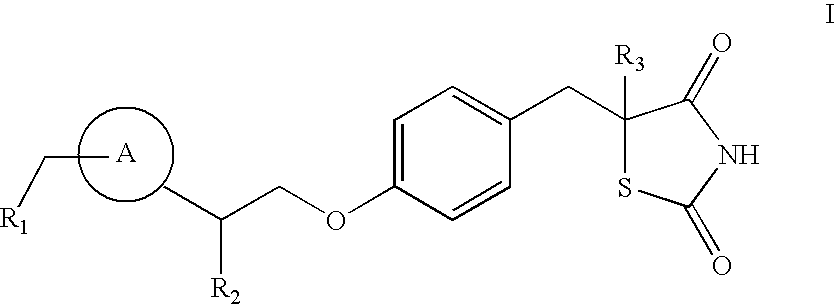
[0149]A pharmaceutical composition including a compound of formulae I, Ia, II, III, IV, V, or VI can be produced, for example, by tableting[0150]a. between about 1 mg to about 200 mg of a compound of formulae I, Ia, II, III, IV, V, or VI, e.g., between about 10 mg to about 100 mg, or between about 15 mg to about 60 mg;[0151]b. carboxymethylcellulose or carmellose;[0152]c. magnesium sterate,[0153]d. hydroxypropyl cellulose; and[0154]e. lactose monohydrate.
example 2a
Assays for Measuring Reduced PPARγ Receptor Activation
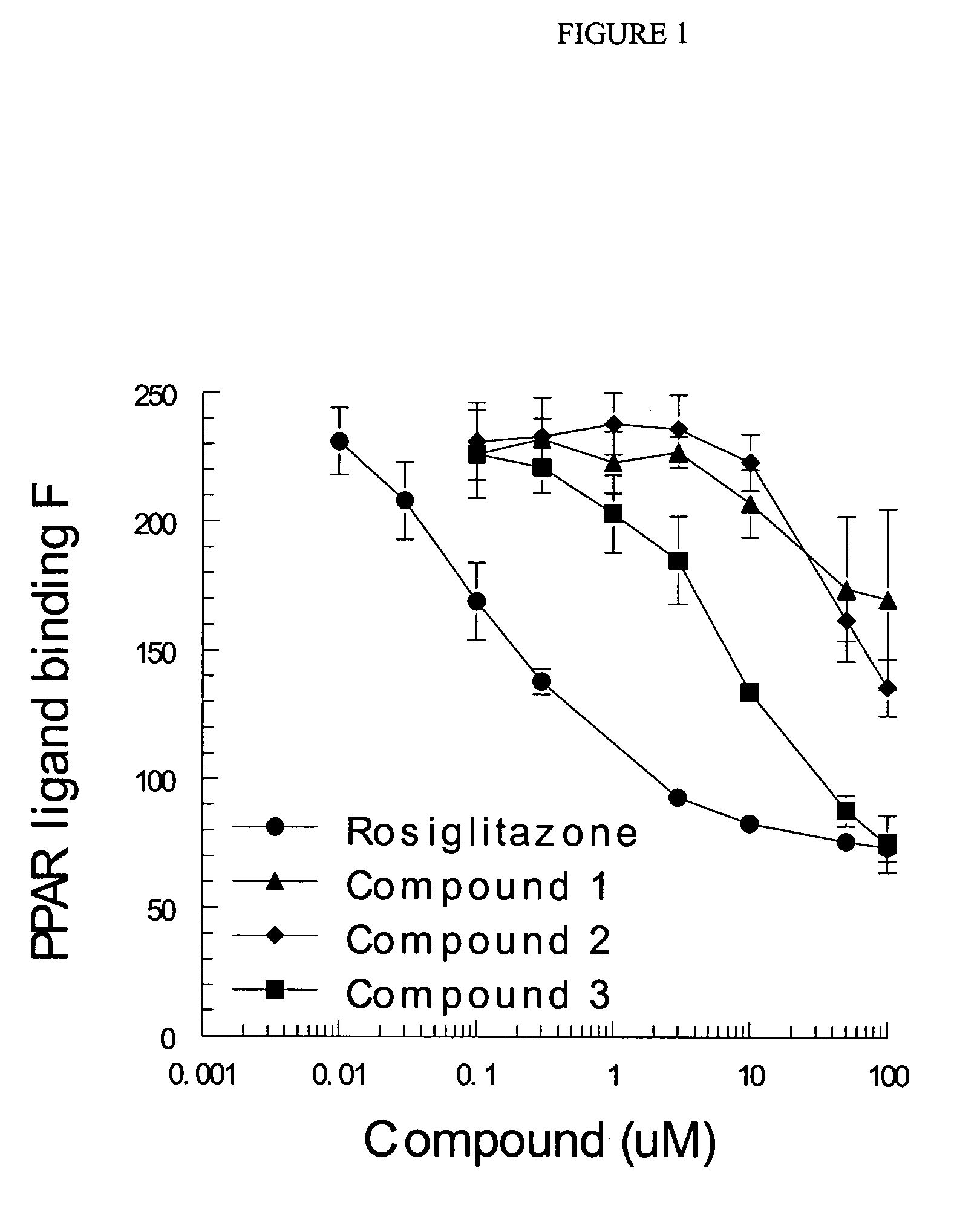
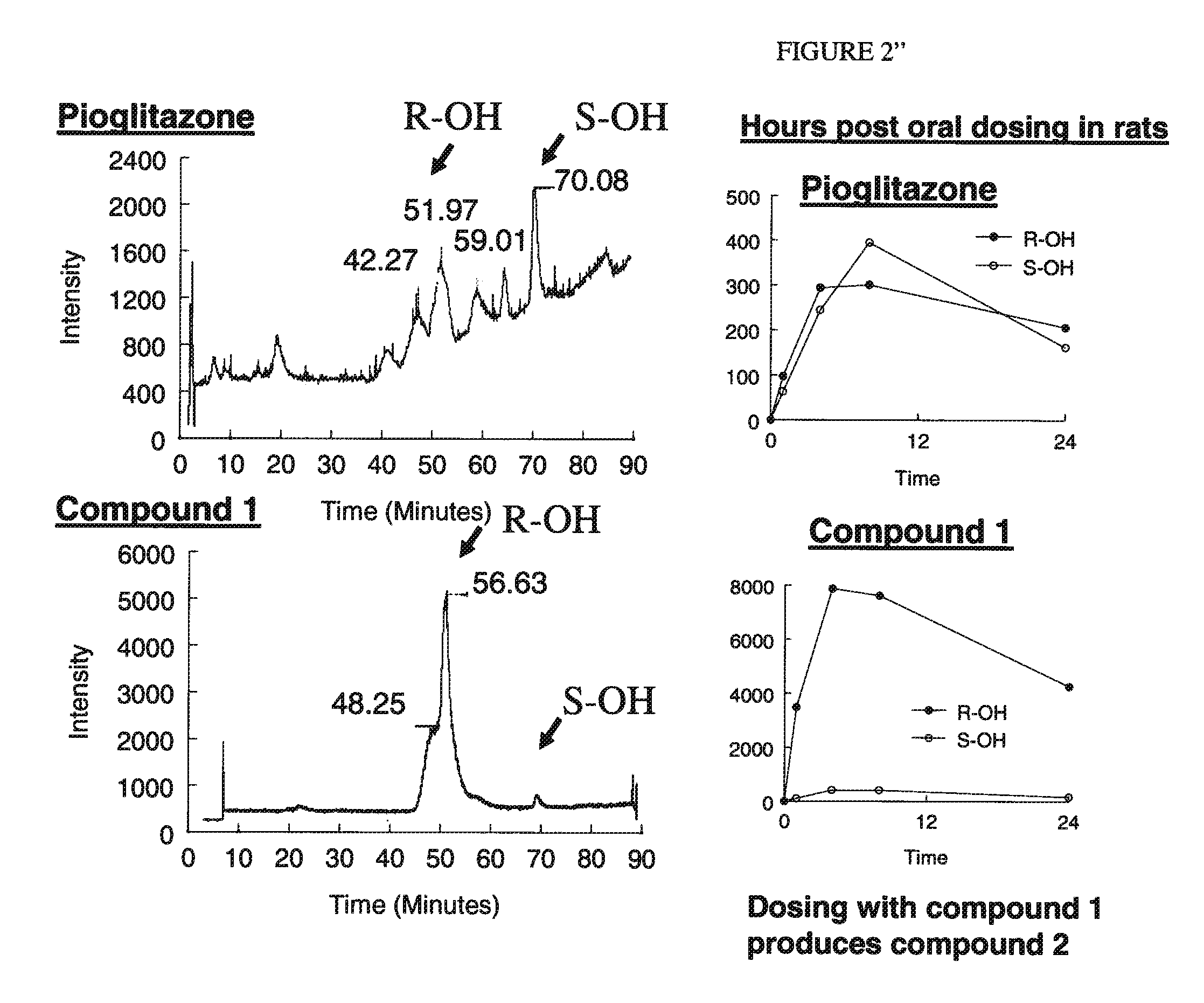
[0155]Whereas activation of the PPARγ receptor is generally believed to be a selection criteria to select for molecules that may have anti-diabetic and insulin sensitizing pharmacology, this invention finds that activation of this receptor should be a negative selection criterion. Molecules will be chosen from this chemical space because they have reduced, not just selective, activation of PPARγ. The optimal compounds will have at least a 10-fold reduced potency as compared to pioglitazone and less than 50% of the full activation produced by rosiglitazone in assays conducted in vitro for transactivation of the PPARγ receptor. These assays will be conducted by first evaluation of the direct interactions of the molecules with the ligand binding domain of PPARγ. This will be performed with a commercial interaction kit that measures the direct interaction by florescence using rosiglitazone as a positive control. Further assays will b...
example 2b
Measuring PPARγ Receptor Activation
[0158]The ability of several exemplary compounds of the present invention, shown in Table A, to bind to PPARγ was measured using a commercial binding assay (Invitrogen Corporation, Carlsbad, Calif.) that measures the test compounds ability to bind with PPAR-LBD / Fluormone PPAR Green complex. These assays were performed on three occasions with each assay using four separate wells (quadruplicate) at each concentration of tested compound. The data are mean and SEM of the values obtained from the three experiments. Rosiglitazone was used as the positive control in each experiment. Compounds were added at the concentrations shown, which range from 0.1-100 micromolar. In Table B, “—” indicates that no data is available.
TABLE BActivation of PPARγ.Compound(μM).01 μM.03 μM.1 μM.3 μM1 μM3 μM10 μM50 μM100 μMRosiglitazone230208169138— 93 83 76 74 (13) (15) (15) (5) (2) (2) (4) (5)Compound 1——227232223228207174170 (1) (8) (12) (6) (13) (28) (35)Compound 2——23123...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pharmaceutical composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com