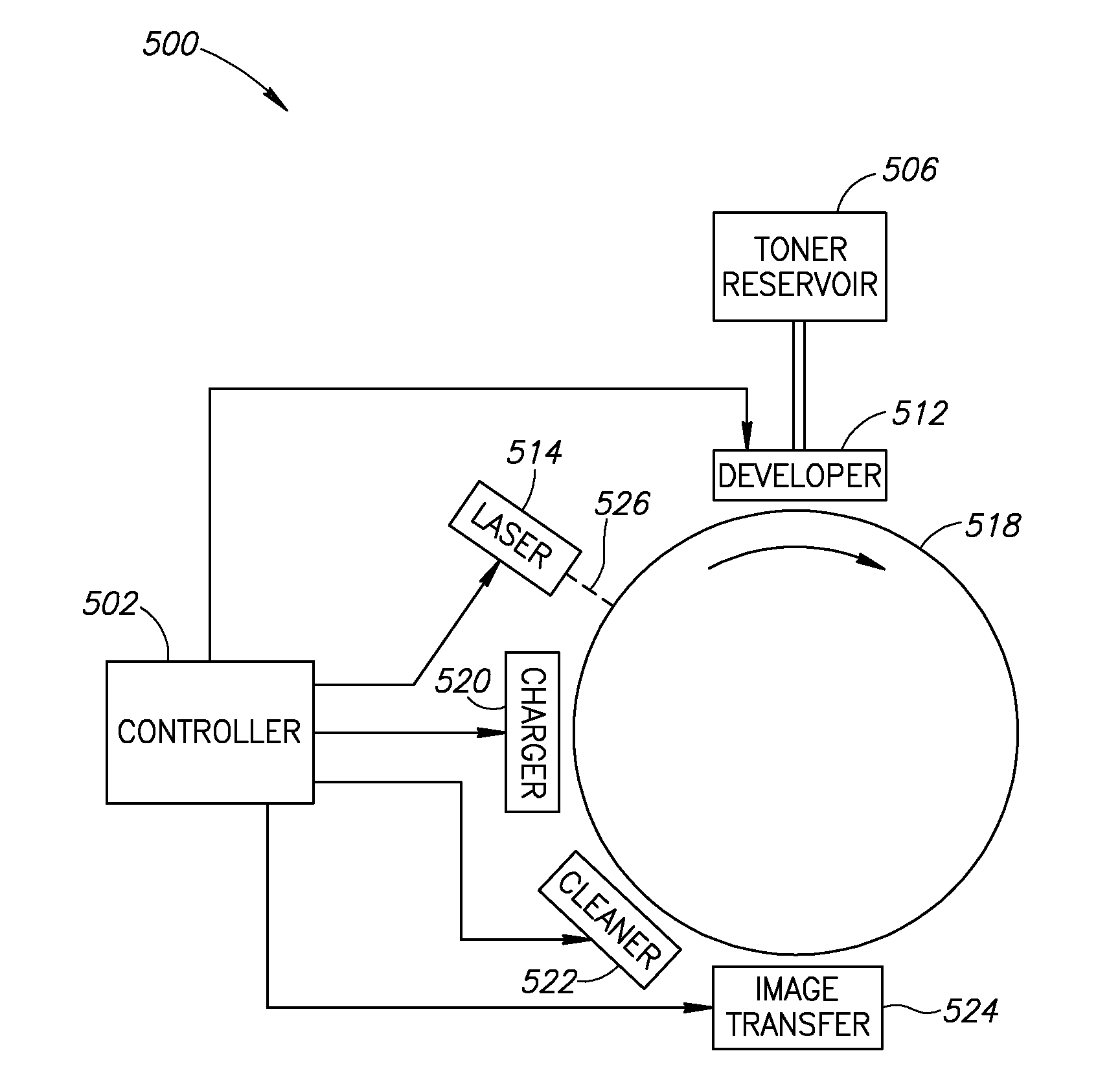
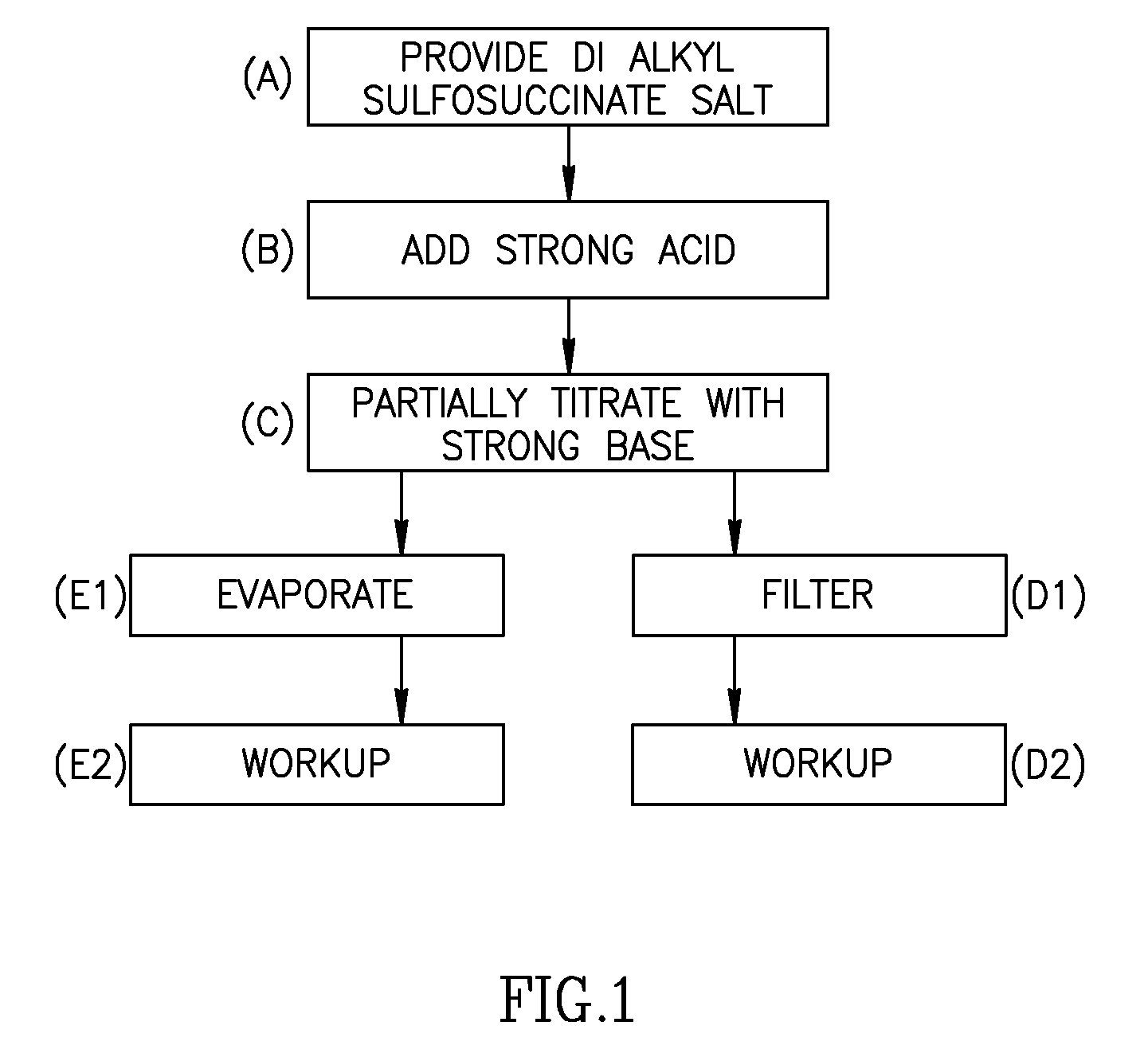
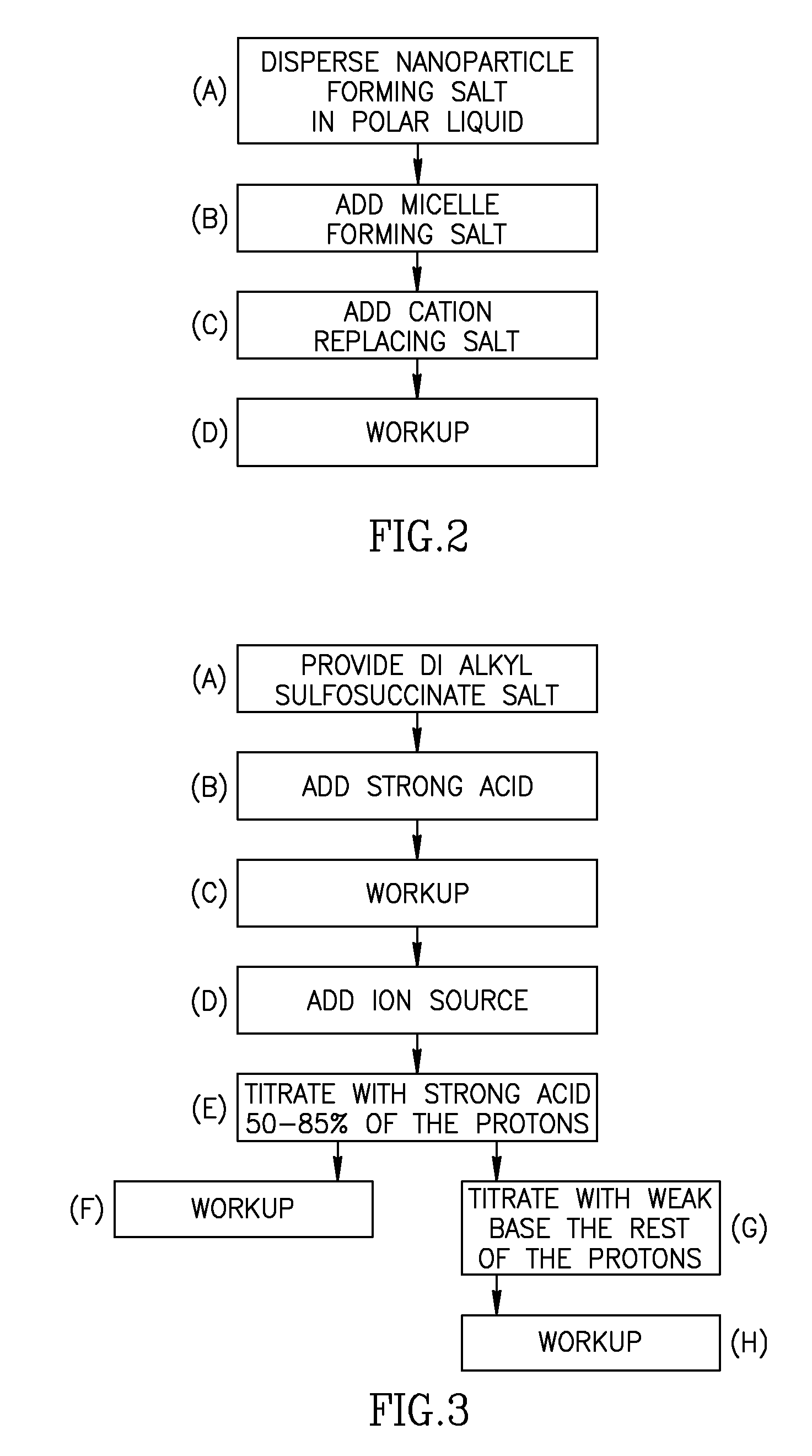
Charge Director for Liquid Toner
a technology of liquid toner and charge director, which is applied in the direction of electrographic process, instruments, cameras, etc., can solve the problems of differential depletion of components, non-controllable change of charge director composition, and inability to selectively adsorb certain charge director components onto the surface of ink particles, etc., to achieve less background printing and less water-sensitive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0107]In order to better understand the invention and to see how it may be carried out in practice, some exemplary embodiments will be described in detail hereinafter, as non-limiting examples only.
[0108]In the following, TR is used to denote di-bistridecylsufosuccinate anion and OT is used to denote dioctylsulfosuccinate anion. The solvent in all the reactions recited below was ISOPAR-L (Exxon), unless otherwise mentioned.
[0109]The term workup refers herein to aqueous workup, as this term is used in the field. It may include, for instance, rinsing of the worked up material with water, adding water immiscible organic solvent, separating the phases, evaporating the organic liquid, adding another organic solvent, and evaporating.
[0110]According to an exemplary embodiment of the invention there is provided a charge director material that includes a micelle forming salt enclosing nanoparticles of a simple salt. In this embodiment, the micelle forming salt is a salt of a dialkylsulfosucc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com