Methods for using soy peptides to inhibit h3 acetylation, reduce expression of hmg-coa reductase and increase ldl receptor and sp1 expression in a mammal
a technology of soy peptides and h3 acetylation, which is applied in the field of peptides, can solve the problems of no known effective method of safely inhibiting h3 acetylation, and achieve the effects of inhibiting h3 acetylation, increasing ldl receptor and sp1 expression, and reducing expression of hmg-coa reductas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
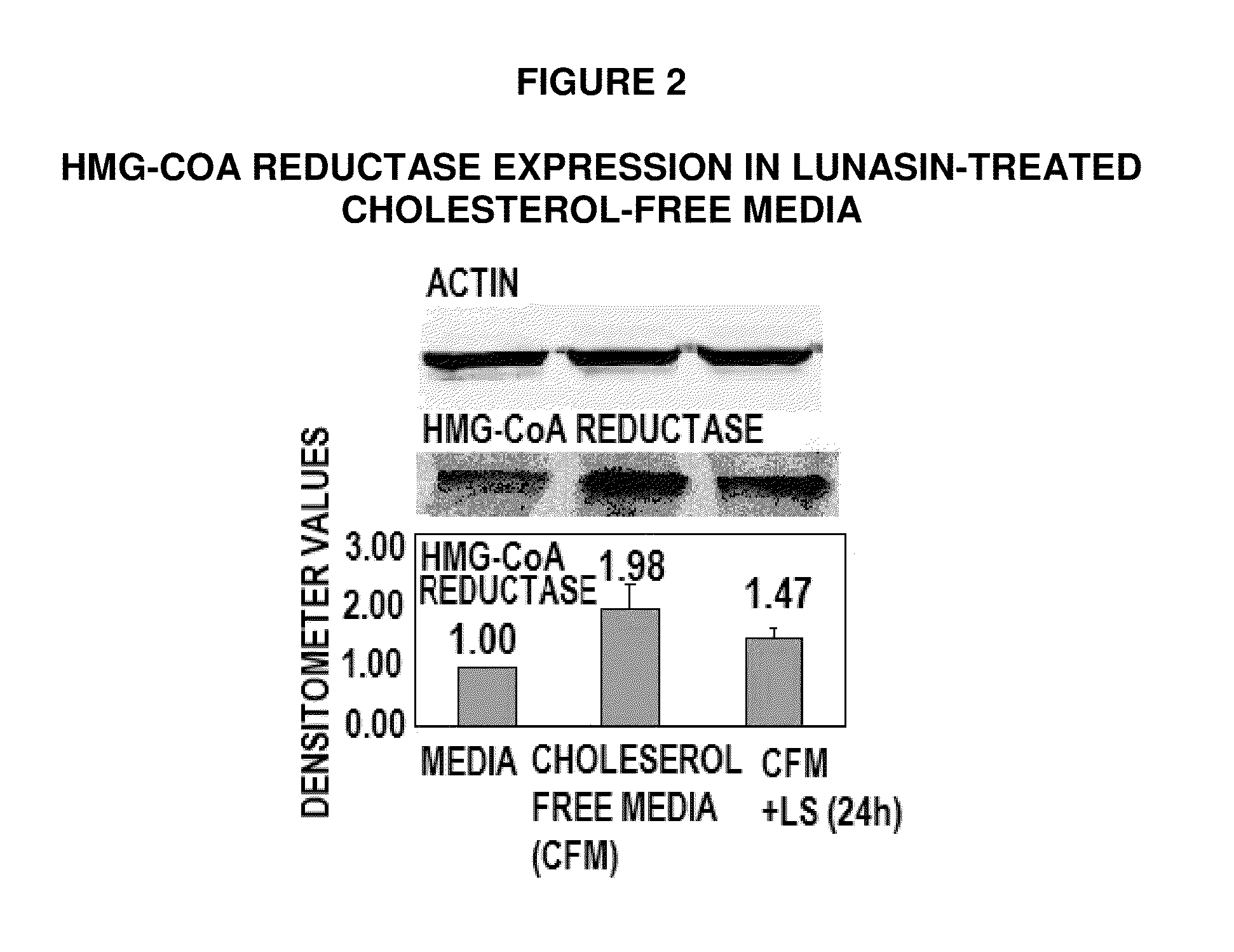
Lunasin Reduces Expression of HMG-CoA Reductase, Increases Expression of LDL Receptor
[0120]The lowering of serum cholesterol by statin drugs is achieved by competitively inhibiting the HMG-CoA reductase, the rate limiting enzyme in the body's metabolic pathway for synthesis of cholesterol. By reducing endogenous cholesterol synthesis, statins also cause liver cells to up regulate expression of the LDL receptor, leading to increased clearance of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from the bloodstream (9). In 1985, Michael Brown and Joseph Goldstein received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for their work in clarifying this LDL-lowering mechanism.
[0121]Transcriptional regulation of HMG-CoA reductase and LDL receptor is controlled by the Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-1 and -2 (SREBP). This protein binds to the sterol regulatory element (SRE) located on the 5′ end of the reductase and the LDL receptor genes. When SREBP is inactive, it is bound to the ER or nuclear membrane. When chole...
example 2
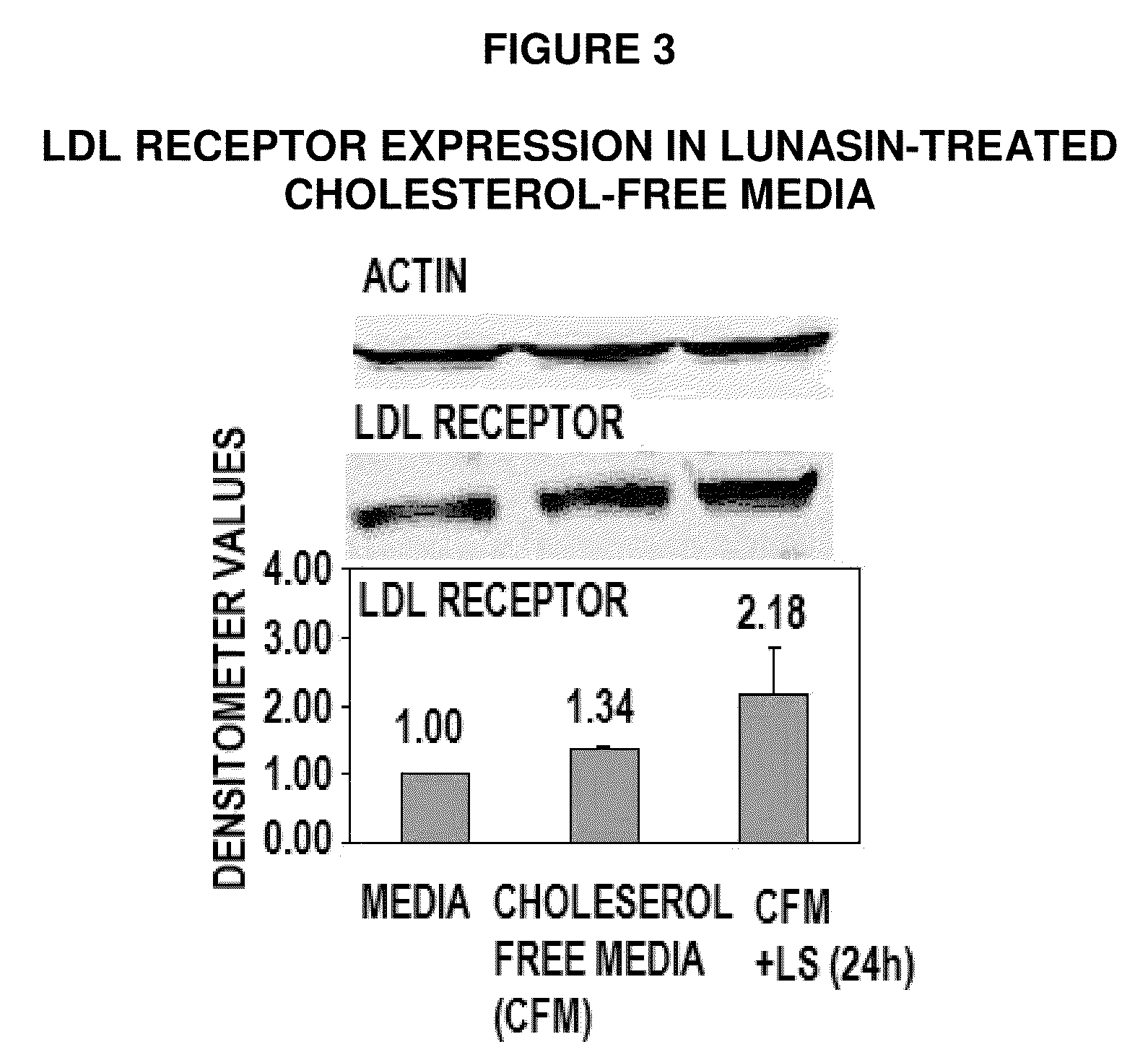
Lunasin's Effect on Expression of Sp1 Coactivator
[0128]Unlike HMG-CoA reductase, SREBP activation of LDL-receptor by sterol depletion requires increased recruitment of Sp1 co-activator to a site adjacent to SREBP in the promoter / regulatory sequence of LDL-receptor gene (25). As shown in FIG. 3, the up regulation of LDL-receptor by lunasin (LS) in cholesterol-free media may be due to increased availability and recruitment of the Sp1 coactivator to the LDL-receptor promoter / regulatory sequence. To test this hypothesis, the level of Sp1 was determined in lunasin-treated growth media and cholesterol-free media by Western analysis using Sp1 antibody, as follows: HepG2 cells (1×106) were grown from confluence in DMEM with 10% FBS for 24 hours before growth media was replaced with fresh growth media or cholesterol-free media (to activate SREBP) and treated with, or without 10 uM synthetic lunasin. After 24 hours, total protein was extracted from each treatment and 10 ug protein loaded onto...
example 3
[0133]Lunasin can be extracted from commercial sources of soy protein. Lunasin has been found in significant amounts from commercial sources of soy protein and its homologues from other seed sources such as barley and wheat. To identify preferred sources for the starting raw material that can be used for lunasin extraction, several commercially available soy protein products were screened for the presence of lunasin.
[0134]The procedure used was as follows: approximately 500 mg of soy protein samples obtained from different commercial sources (Solae, St. Louis, Mo.) were dissolved in 50 mL of aqueous phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) by shaking for 1 hour at room temperature. Samples were centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 30 minutes and the aqueous fraction separated and put in separate tubes. Protein concentrations were measured by Bradford assay and around 20 ug of total protein were loaded onto two Bio-Rad Laboratories (Hercules, Calif.) 16% Tris-Tricine gels. One of the SDS-PAGE gels (I) was s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com