Heart assist device
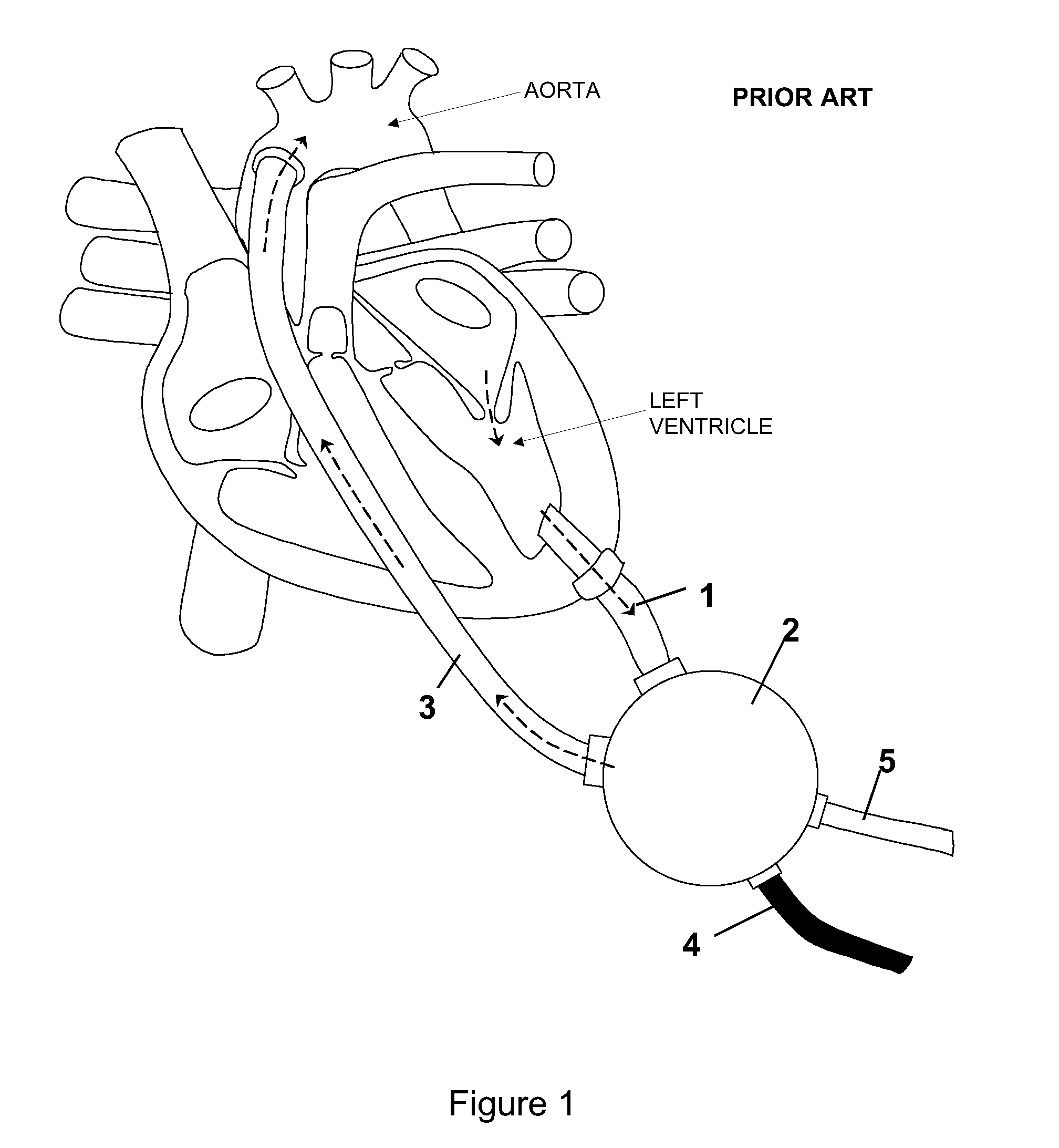
a heart assist device and heart tube technology, applied in the field of heart assist devices, can solve the problems of affecting the ability of the heart tube to fully unload the ventricle, the risk of bleeding and/or thromboembolic complications, and the vads may also present a risk of complications, so as to reduce the size of the device, prevent the backflow into the ventricle, and enhance the natural flow of blood
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
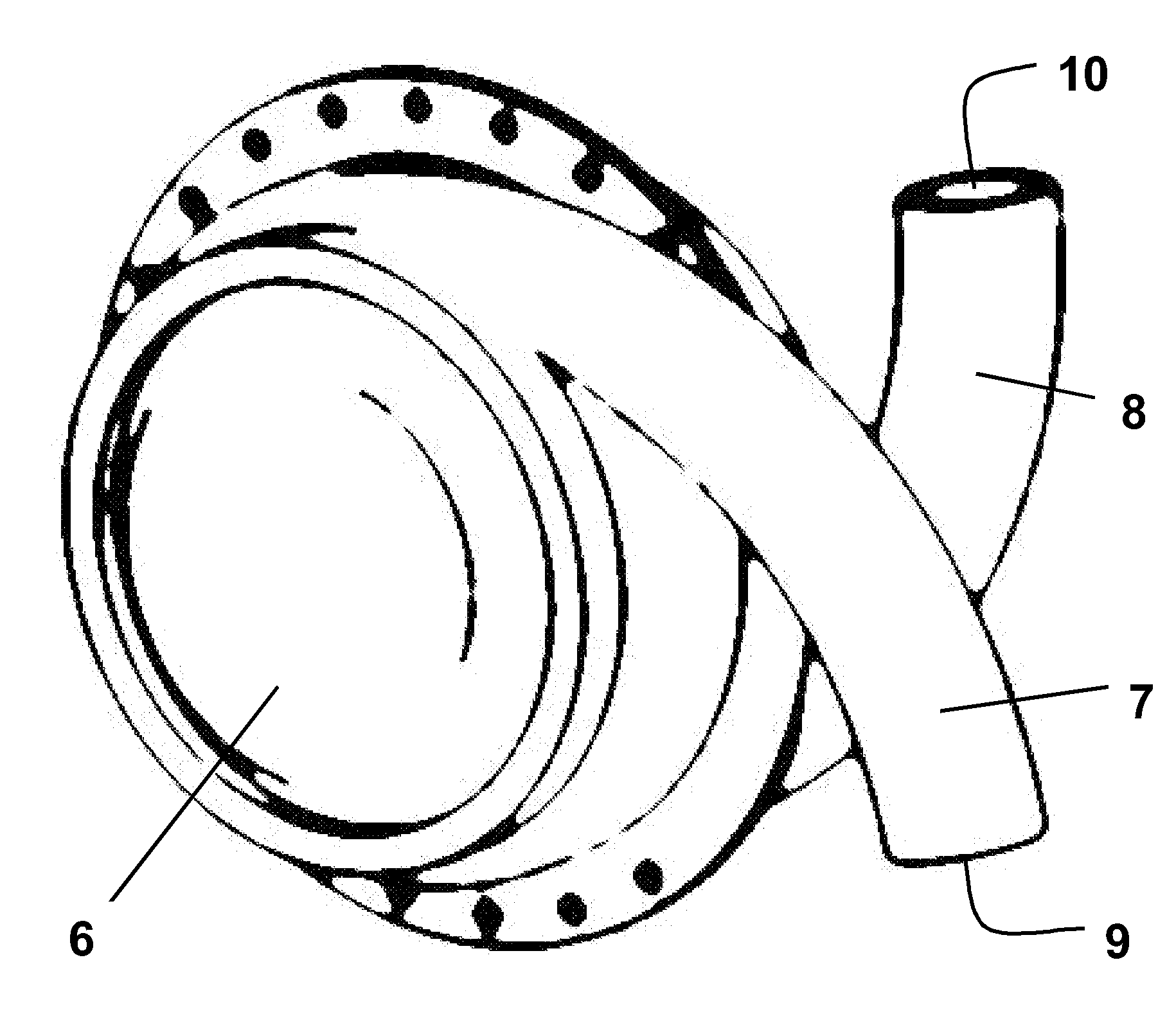
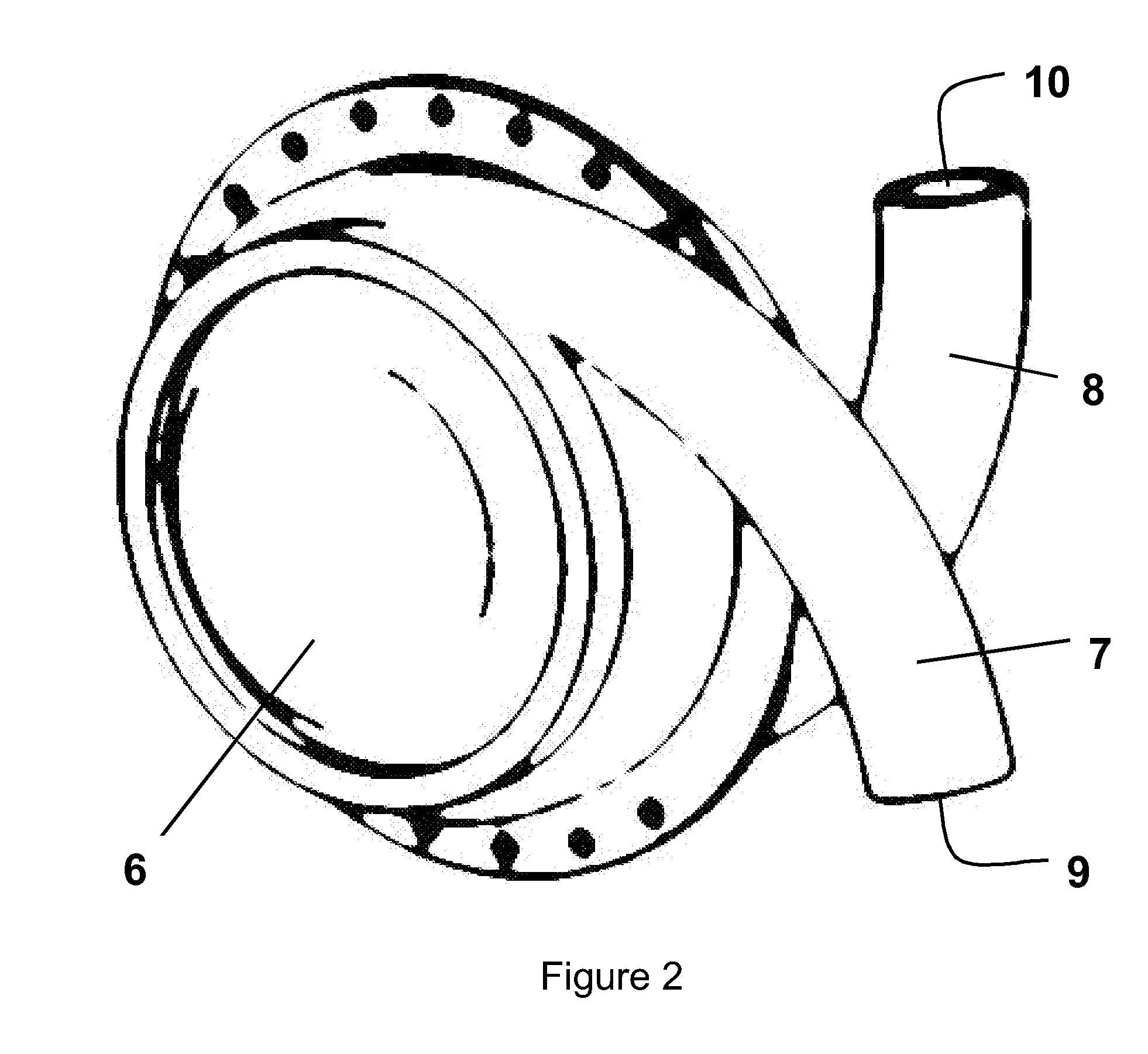
[0037]FIG. 2 shows a LVAD comprising left and right side plates secured together with an airtight seal to form a generally hollow cylindrical housing 6. Each of the side plates is connected to or formed integrally with a curved hollow tube 7, 8. When the side plates are secured together the tubes 7, 8 open into the hollow interior of the housing at substantially diametrically opposed locations, entering the housing with a curvature that follows that of the curved interior surface of the housing. The ends of the tubes remote from the housing, referred to hereinafter as the “descending port”9 and “ascending port”10, face in substantially opposite directions. Neither the tubes 7,8 nor the housing 6 are provided with valves.
[0038]The side plates forming the housing, and the tubes, are made from a durable, biocompatible material such as titanium or moulded polyurethane. The hollow interior of the housing can have a volume in the region of 60 cc to 80 cc and the internal diameter of the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com