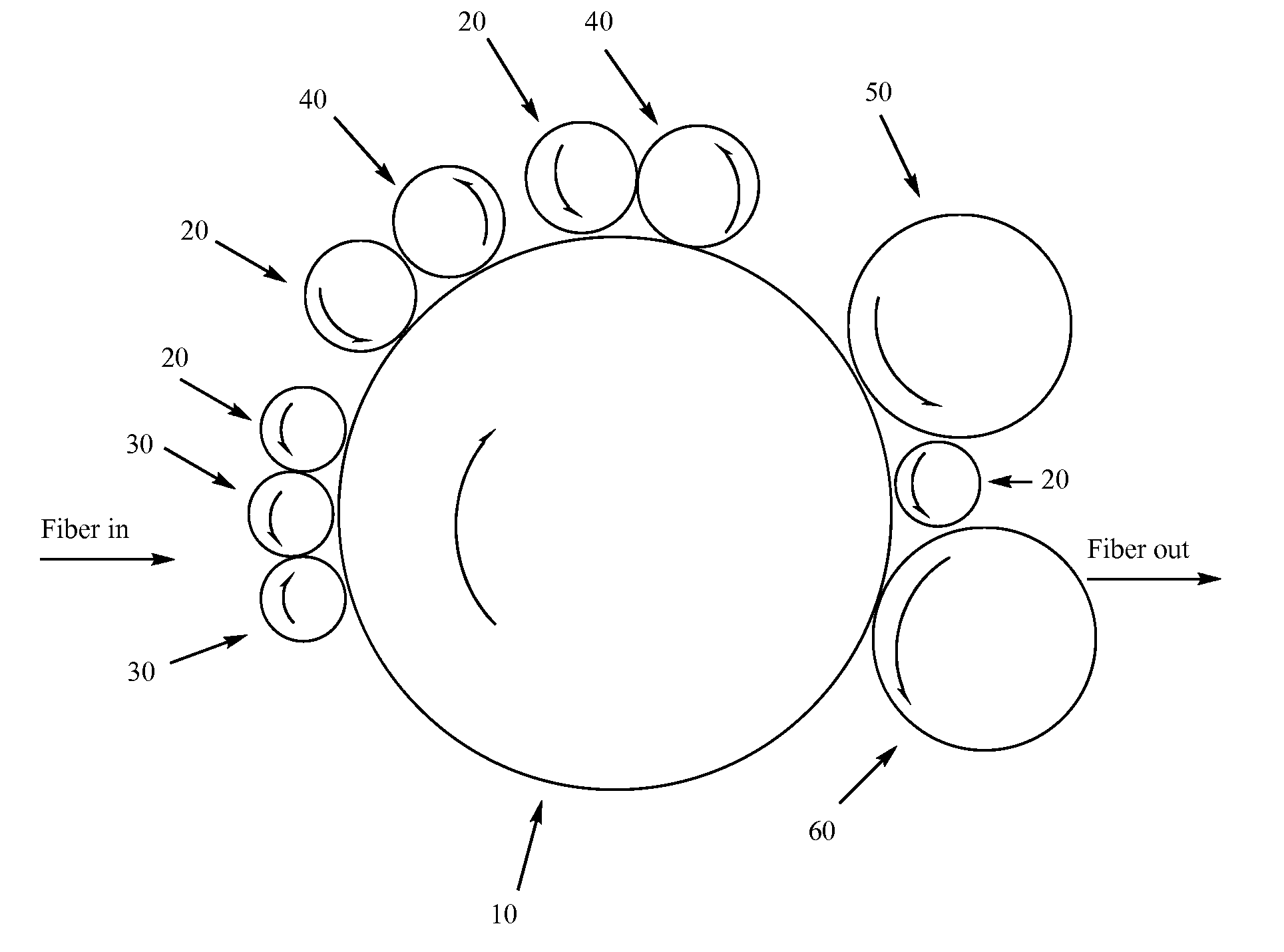
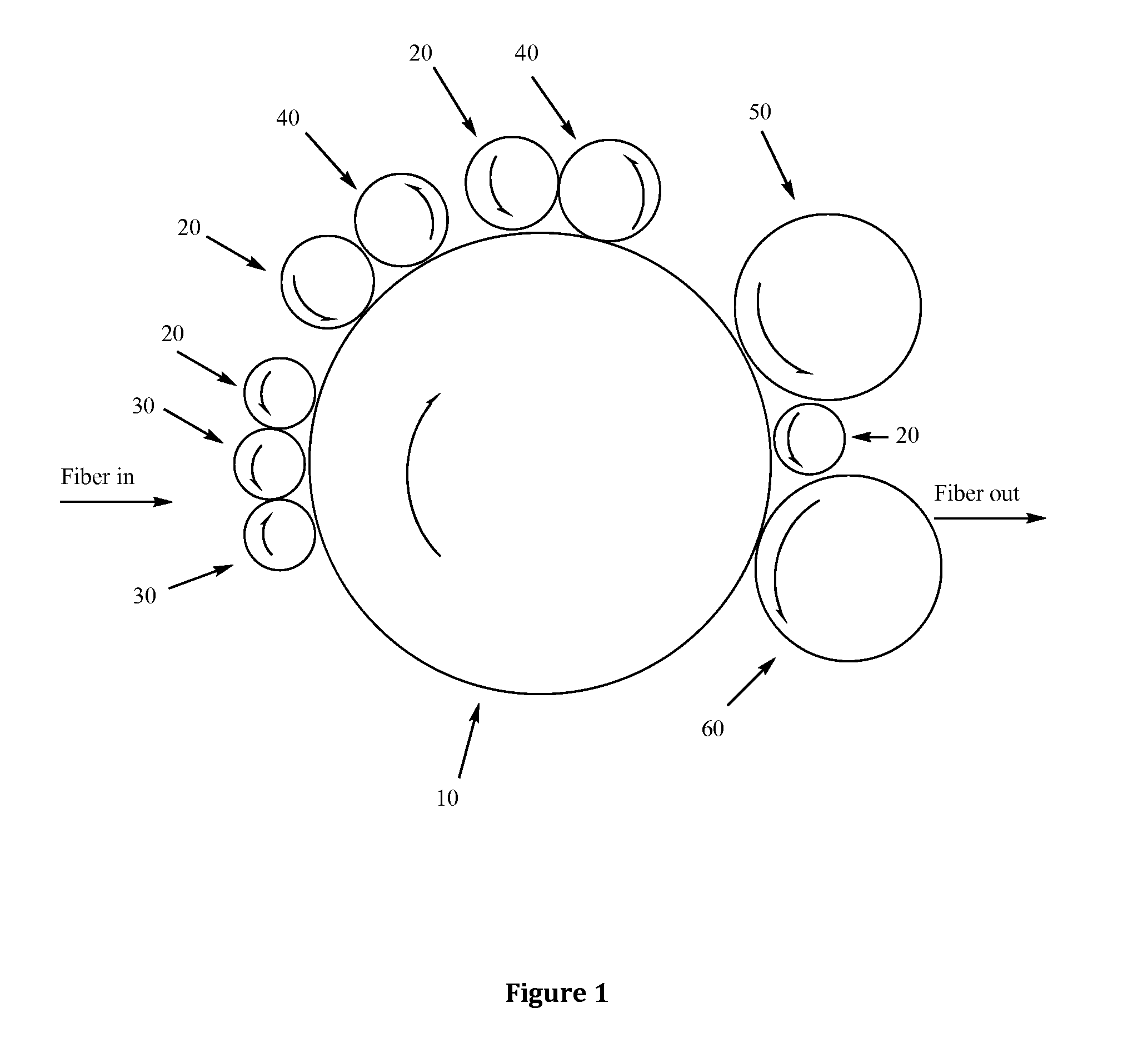
Process for regenerating post-consumer and post-industrial fibers
a post-consumer and post-industrial fiber technology, applied in the direction of fiber disintegration, glass making apparatus, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of shortening the service life of fibers, weakening and damage, and achieve the effect of reducing neps, reducing dust particles, and improving product performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Process for Creating Regenerated Cotton Fiber
[0128]The following process was used to create regenerated cotton fiber, and covers the process from raw material to finished roll goods produced from the fiber:[0129]1. + / −40,000 lbs sorted cotton clips were gathered and collected at textile cutting room locations, packaged and shipped to regenerator location.[0130]2. After complete inspection and receipt to regeneration facility's warehouse, the cotton clippings were placed into a robot loader for automatic bale opening and conveyed to specialty cutters.[0131]3. They were cut to targeted size of 2-4 in×2-4 in. These cut pieces were transported by belt to the storage box where the first blending of materials began.[0132]4. The cut clips were transported via spike apron to a rotary pin cylinder where they are pulled to untwist the fibers into threads that comprised the fabric.[0133]5. They were transported via air duct to another large storage box where it was treated with a solution of a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com